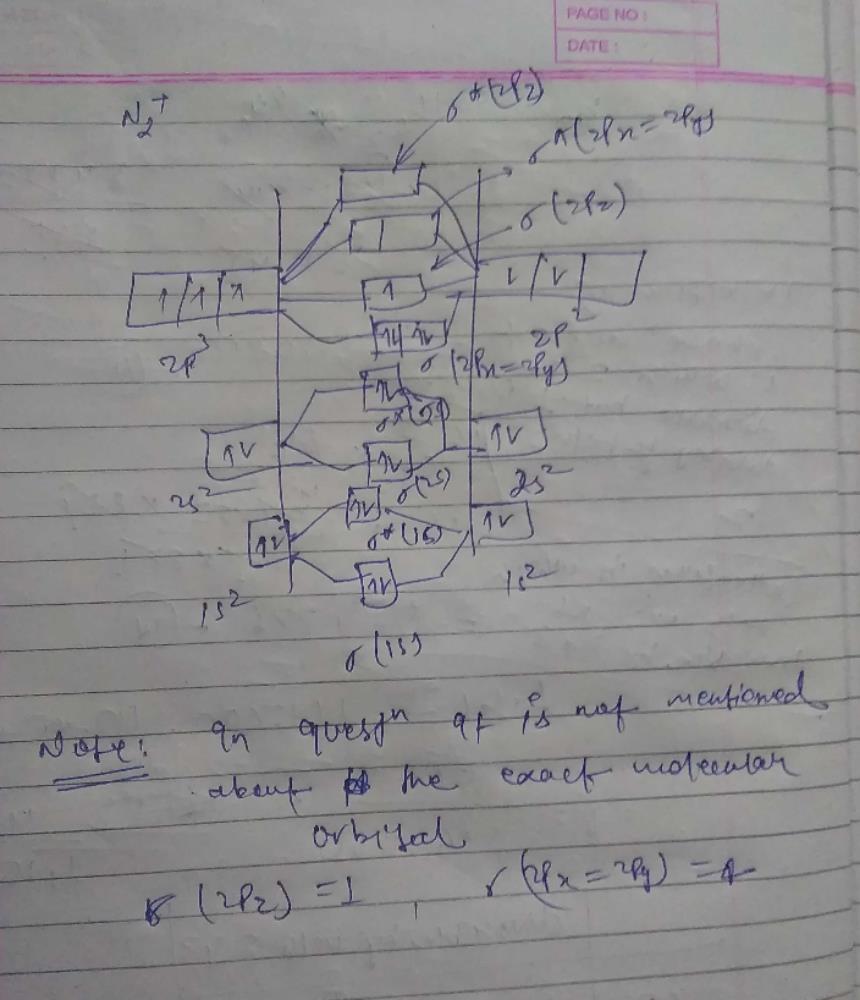
42 N2+ Mo Diagram
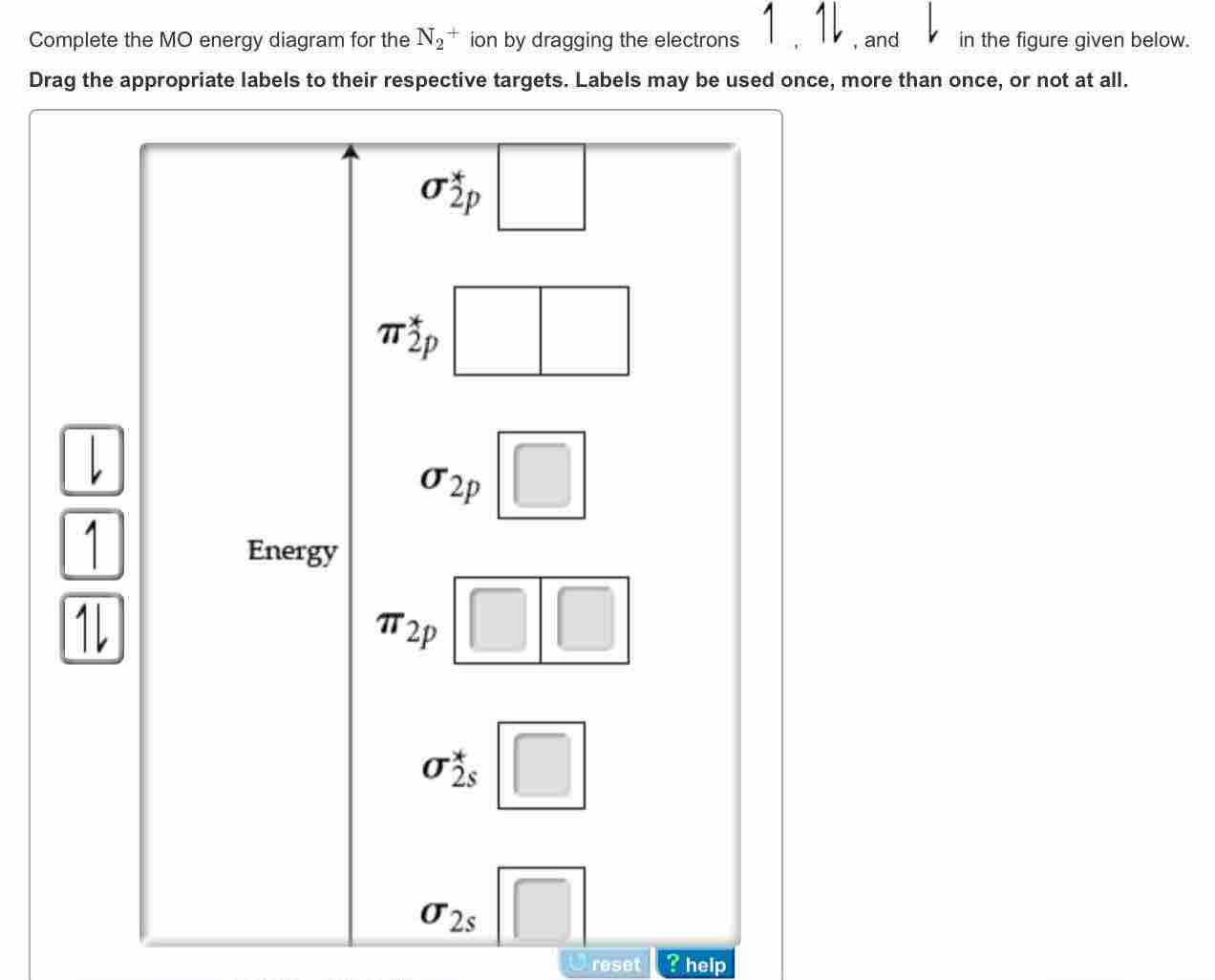
Molecular orbital diagrams of diatomic molecules. Then we rank them in order of increasing energy. This video shows the mo diagrams of the c2 n2 o2 and f2 molecules. For o2f2 and n2 the sigma bond comes first then the pi bo. In the mo approach each carbon atom has four valence orbitals namely a 2s and three 2p. Molecular Orbital Theory – Walsh diagram The Walsh diagram shows what happens to the molecular orbitals for a set of molecules which are related in structure. In this case, the difference is the H-X-H bond angle which decreases from o to 90 o Molecular Orbital Theory –. Item 2: Part A Complete the MO energy diagram for the N2+ ion by.
Molecular orbital diagram for n2. Then just fill the. One is for the elements up to nitrogen. For the second period elements the 2s and 2p orbitals are important for mo considerations. Since the s h h orbital shows a decrease in bonding between the two nuclei. Perpendicular to these in the yz plane the 2py orbitals on each atom combine to make.

N2+ mo diagram
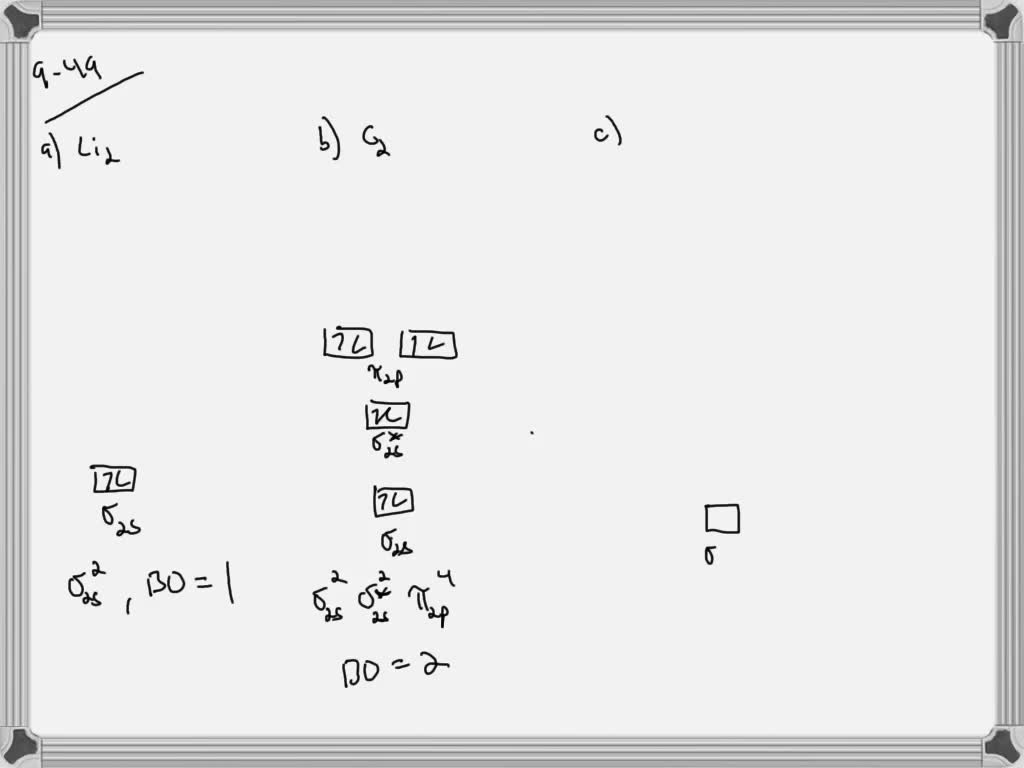
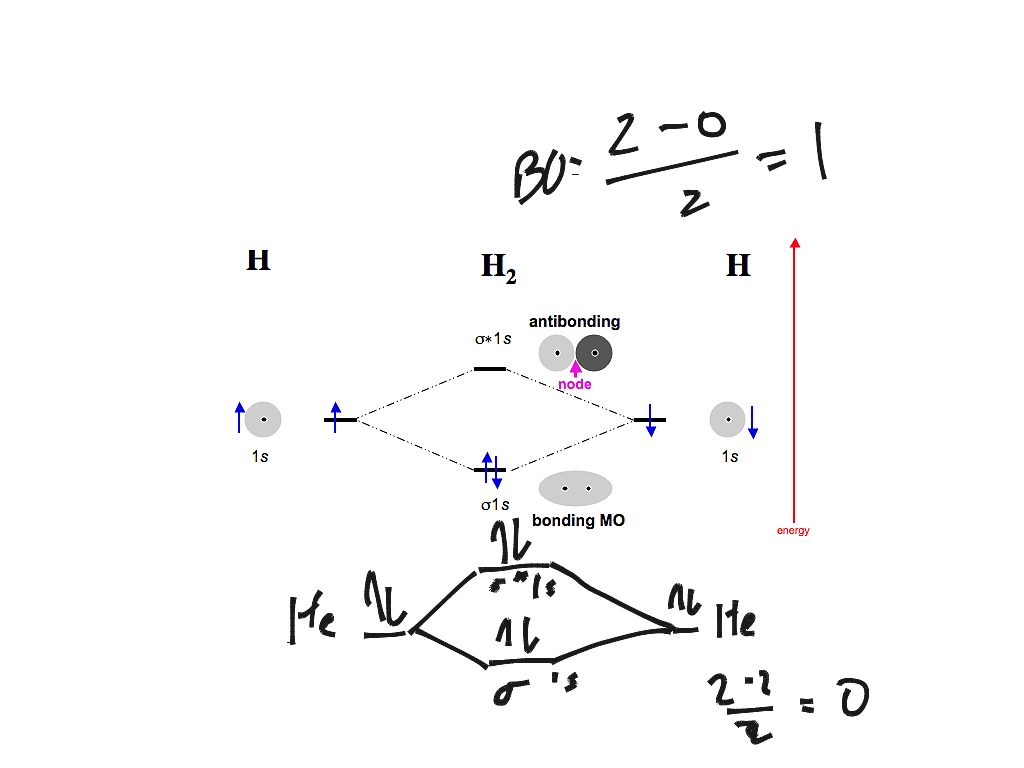
On a very general basis, electrons are not assigned to individual bonds between atoms, but they move under the influence of the nuclei in the whole molecule. Molecular orbital theory is a method for describing the electronic structure of the molecule. Now, let us draw the molecular orbital diagram of ${N_2}$. Molecular orbital (MO) diagram for N2 and N2^- $-$\mathrm{p}$ interaction moving from $\ce{Li2}$ to $\ce{F2}$. The $\mathrm{s}$-$\mathrm{p}$ interaction is the bonding interaction between the $\mathrm{2s}$ orbital of one atom and the $\mathrm{2p_{z}}$ orbital of another atom which (among other things) increases the energy of the $\mathrm. Answer to Create an MO diagram for H2+ H2 and H Post the Lumo, lumo -, homo, homo + near its energy level. Molecular Orbital (MO) Theory of the H2 molecule: Following the MO treatment of H2+, assume the (normalized) ground electronic state wavefunction is. Qualitative MO theory orbital diagram for homonuclear diatomics composed of 1st or.
N2+ mo diagram. On a very general basis, electrons are not assigned to individual bonds between atoms, but they move under the influence of the nuclei in the whole molecule. Molecular orbital theory is a method for describing the electronic structure of the molecule. Now, let us draw the molecular orbital diagram of ${N_2}$. #3. Draw the MO diagram for `O_2^+` This is a bit of a curveball, but a perfectly valid problem. Recall that a cation indicates a loss of `1` electron. `O_2^+` is just the ionized form of `O_2`; that is, it's `O_2` with `1` missing electron. The MO diagram will be the same as the MO diagram of `O_2`, except with `1` less electron. The MO diagram for "NO" is as follows (Miessler et al., Answer Key): (The original was this; I added the orbital depictions and symmetry labels. For further discussion on the orbital energy ordering being "N"_2-like, see here and comments.) Quick overview of what the labels correspond to what MOs: 1a_1 is the sigma_(2s) bonding MO. 2a_1 is the sigma_(2s)^"*" antibonding MO. 1b_1 is the pi_(2p. Answer (1 of 2): Let me explain the molecular orbital diagram of N2 using its diagram. one atom of nitrogen has 7 electrons so a N2 molecule will have 14 electrons so first 2 electrons go in 1s sigma bond next 2 in 1s sigma anti bond orbital next 2 in 2s sigma bond orbital next 2 in 2s sigma...
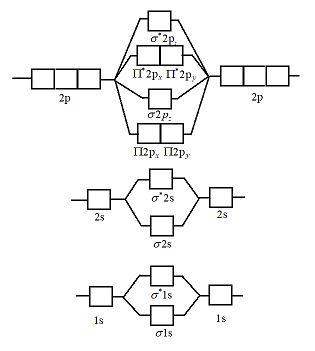
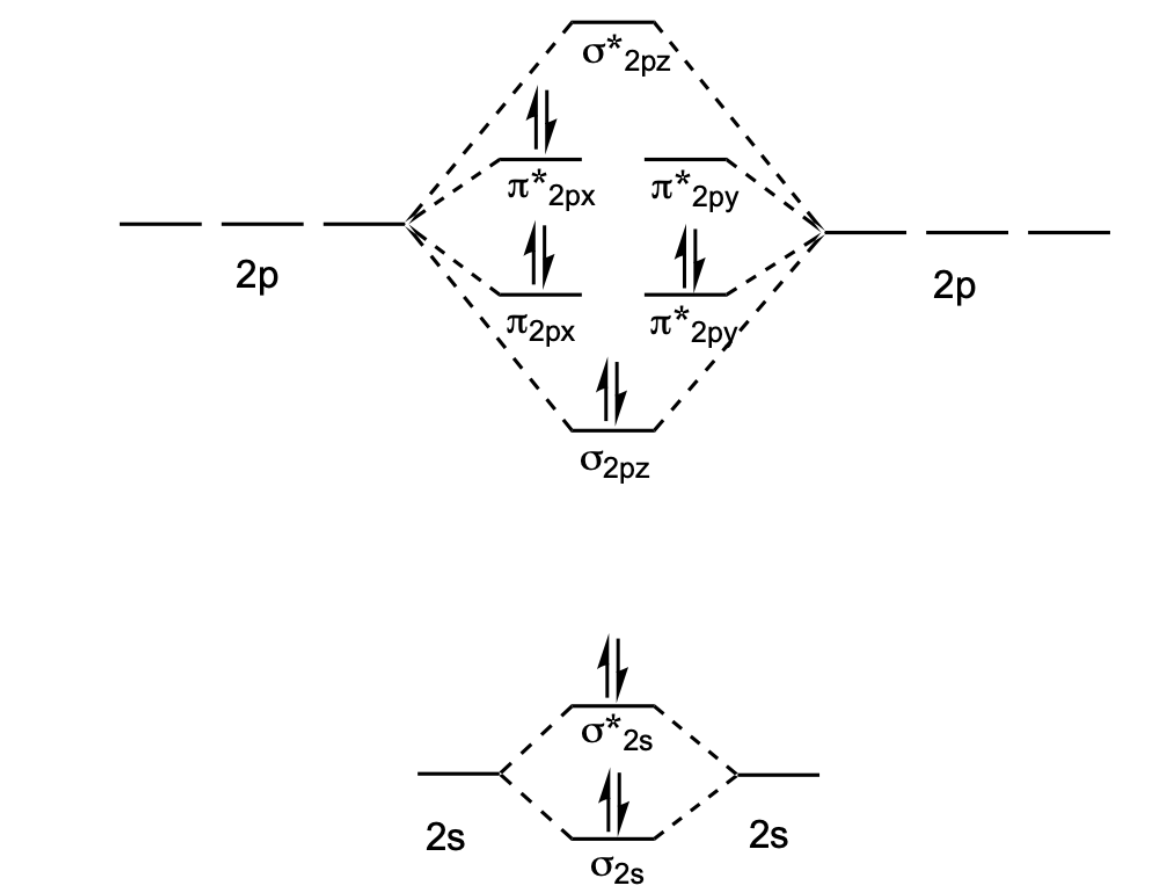
There are two mo diagrams you need to memorize for diatoms n2 o2 ne2 etc. Write molecular orbital configuration of c2 predict magnetic behaviour and calculate its bond order energy levels of molecular orbitals for the second row diatomic molecules a n2 b o2 and c f2 mo diagram for formation of nitrogen molecule from atoms atomic and molecular. N2 2- Molecular orbital Diagram. molecular orbital mo diagram of n2 molecular orbital diagram for nitrogen gas n2 use aufbau and hund to fill with 10 valence electrons you sigma2s 2 sigma2s 2 pi2p 4 mo diagram for n2 molecular orbital there are two mo diagrams you need to memorize for diatoms n2 o2 ne2 etc e is for the elements up to nitrogen the other is for after Molecular orbital (MO) diagram for N2 and N2^- $-$\mathrm{p}$ interaction moving from $\ce{Li2}$ to $\ce{F2}$. The $\mathrm{s}$-$\mathrm{p}$ interaction is the bonding interaction between the $\mathrm{2s}$ orbital of one atom and the $\mathrm{2p_{z}}$ orbital of another atom which (among other things) increases the energy of the $\mathrm. Draw the molecular orbital energy level diagram of N2 molecules. >>. Class 11. >> Chemistry. >> Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure. >> Molecular Orbital Theory. >> Draw the molecular orbital.
Molecular orbital (MO) diagram for N2 and N2^-Ask Question Asked 6 years, 3 months ago. Active 3 years, 10 months ago. Viewed 118k times 24 7 $\begingroup$ I have been taught that the MO diagram is different for molecules with 14 or less electrons than the one used for molecules with 15 or more electrons. For $\ce{N2}$ the orbitals in. A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) method in particular. A fundamental principle of these theories is that as atoms bond to form molecules, a certain number of atomic orbitals combine to form the same number of. Answer to Create an MO diagram for H2+ H2 and H Post the Lumo, lumo -, homo, homo + near its energy level. Molecular Orbital (MO) Theory of the H2 molecule: Following the MO treatment of H2+, assume the (normalized) ground electronic state wavefunction is. Qualitative MO theory orbital diagram for homonuclear diatomics composed of 1st or. A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) N2 Molecular Orbital Diagram. N2 molecular orbital energy level diagram picture, is usually depicted by a diatomic molecules.
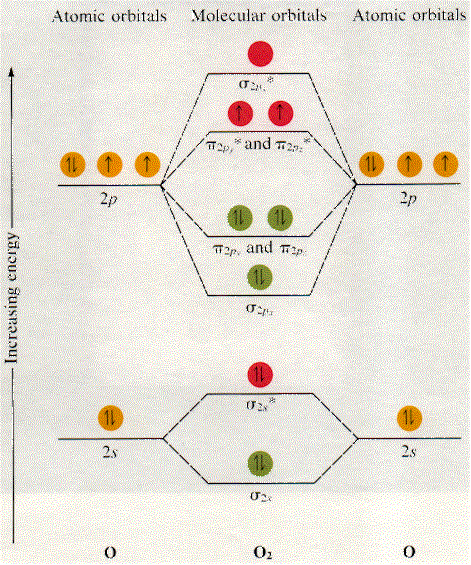
Molecular Orbital Diagram of N2. Molecular orbitals exist in molecules where each molecule has its electron configuration in terms of a sigma bond and pi bond. According to molecular orbital theory, it tells about magnetic nature, stability order, and the number of bonds in a molecule.
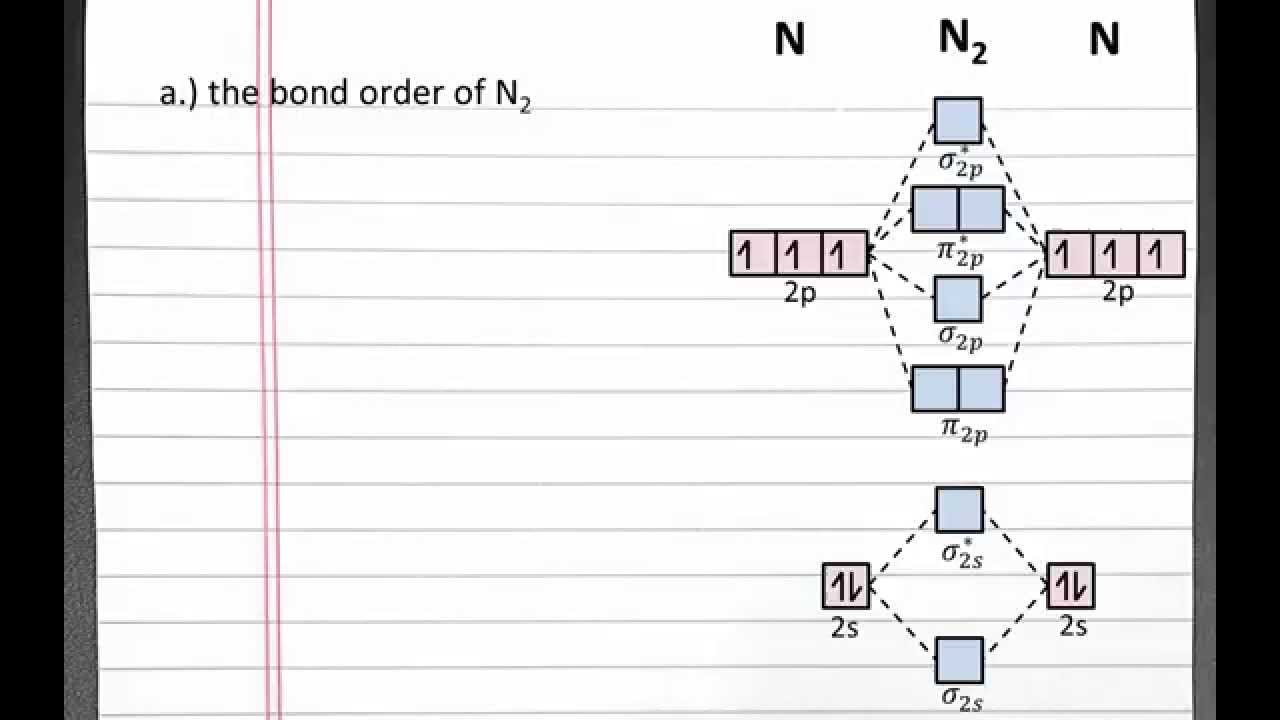
N2 molecular orbital energy level diagram also has the following tags. Three filled bonding orbitals. Mo diagrams for diatomic molecules chapter 5 friday october 9 2015. Here is the full molecular orbital diagram for n2. N2 molecular orbital energy level diagram with description. Now we add the 10 electrons 5 from each nitrogen atom. This image.
There are two MO diagrams you need to memorize for diatoms (N2, O2, Ne2, etc).One is for the elements up to Nitrogen. The other is for AFTER nitrogen (start...
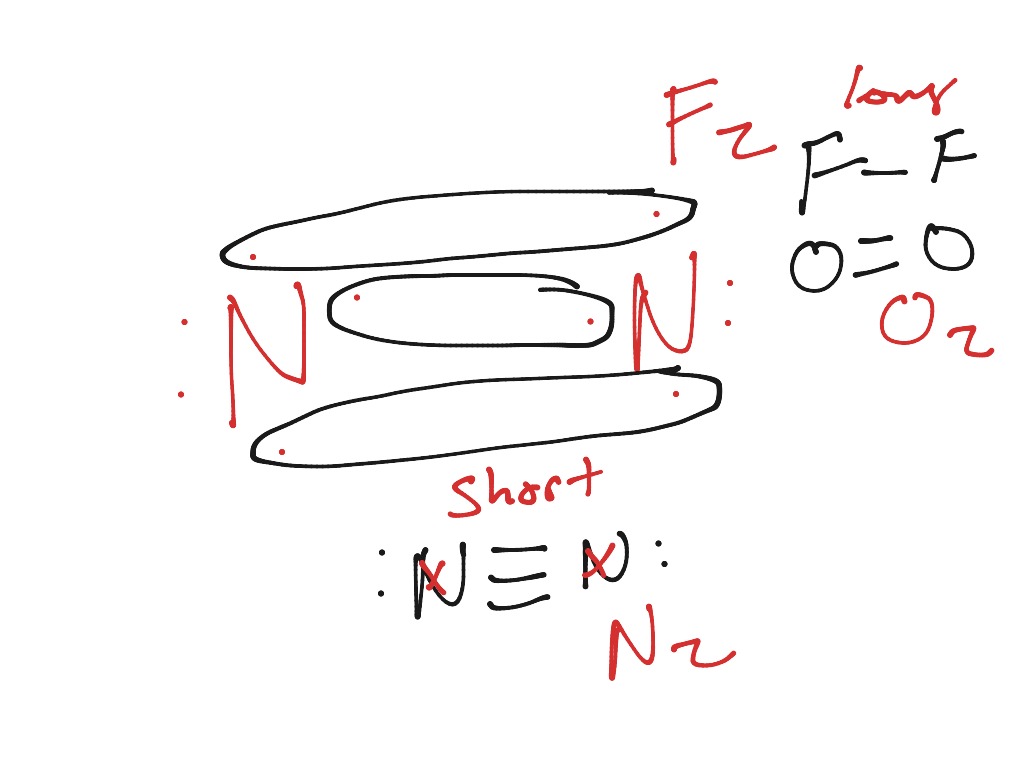
The MO method for N2+ gives the bond order equal to 2.5. But first, we look at the diagram of molecular orbitals for N2 (the bond order for the nitrogen molecule is 3). Let's remember that the.
If we build the MO diagram for "N"_2, it looks like this: First though, notice that the p orbitals are supposed to be degenerate. They weren't drawn that way on this diagram, but they should be. Anyways, for the electron configurations, you would use a notation like the above. g means "gerade", or even symmetry upon inversion, and u means "ungerade", or odd symmetry upon inversion.
14+ N2 Mo Diagram. With mo diagrams, we can predict the number of bonds in diatomic molecules. Molecular orbital diagram for nitrogen gas (n2) use aufbau and hund to fill with 10 valence electrons you get sigma2s(2),sigma2s*(2),pi2p(4),sigma2p(2). N2 2 Molecular Orbital Diagram — UNTPIKAPPS from www.untpikapps Thus if we know…
energy molecular orbital (σ*) will be empty (recall the Aufbau Principle). While there are only two. There would be four electrons to fill into our molecular orbital diagram and that would force us to fill in the bonding sigma MO and the anti-bonding sigma-star MO. What we gain in the bonding sigma MO, we lose in the anti-bonding sigma-star MO.
An excited state of the N2 molecule has the electron configuration (σ 1s2) (σ*1s2) (σ2s2) (σ*2s2) (π2p4) (σ2p1) (π*2p1)Complete the MO diagram for this excited state and compare the bond length in the excited state to that of ground state N2. For the first part of the problem, we’re being asked to complete the molecular orbital (MO.
What is the MO diagram and bond order for N2 ( in Urdu / Hindi) Nitrogen (N 2 ) molecule: Nitrogen atom has electronic configuration 1s2, 2s2, 2p3.
Molecular orbital diagram for nitrogen gas (N2)Use aufbau and Hund to fill with 10 valence electronsYou get sigma2s(2),sigma2s*(2),pi2p(4),sigma2p(2).Bond Or...
Write the molecular orbital diagram of N2+ and calculate their bond order why nitrogen have different structure of molecular orbital theory An atomic orbital is monocentric while a molecular orbital is polycentric. Explain What is the relationship between bond order and the dissociation energy of a molecule?.
MO Diagram for HF The AO energies suggest that the 1s orbital of hydrogen interacts mostly with a 2p orbital of fluorine. The F 2s is nonbonding. H–F nb σ σ* Energy H –13.6 eV 1s F –18.6 eV –40.2 eV 2s 2p So H–F has one σ bond and three lone electron pairs on fluorine
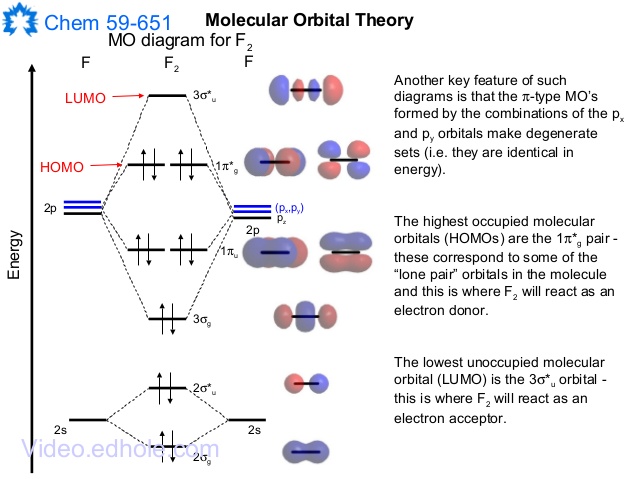
Molecules with Similar Molecular Orbital Diagrams Molecules and ions formed from 2 boron atoms or from 2 carbon atoms have molecular orbitals diagrams of the same sort as N 2. Diatomic molecules made up of two different atoms also have molecular orbital diagrams very similar to that of N 2.When the electronegativity of one atom is lower than the other, the more electronegative atom's orbitals.
The molecular orbital (MO) theory is a powerful and extensive approach which describes electrons as delocalized moieties over adjacent atoms, and you can see the representation of the approach in the MO diagram above. The following orbital diagrams also show you some examples. image via d2gne97vdumgn3.cloudfront .










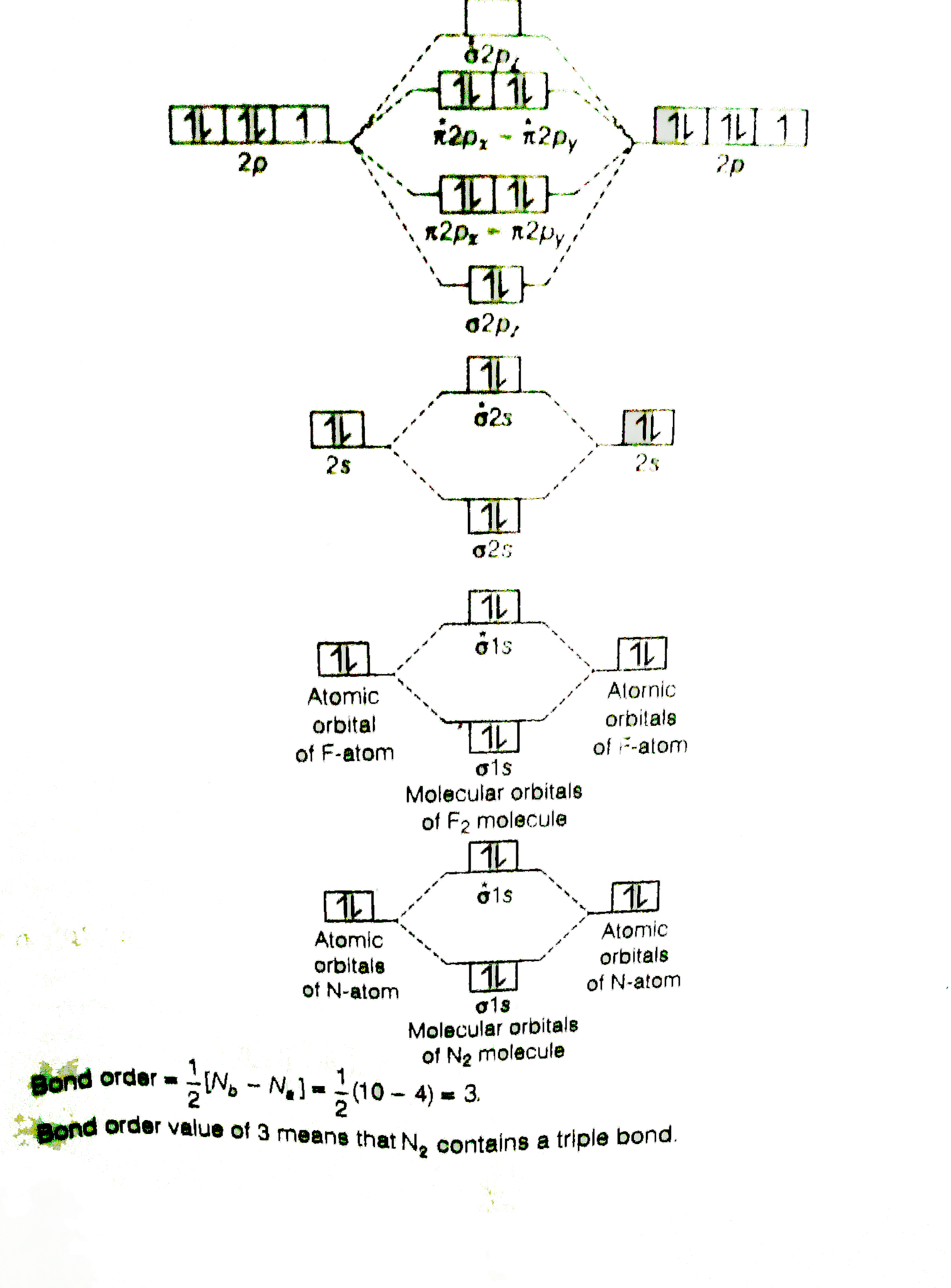












0 Response to "42 N2+ Mo Diagram"
Post a Comment