39 Orbital Diagram For Neon
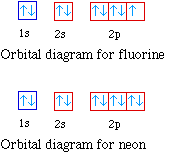
Fluorine electron configuration is 1s 2 2s 2 2p 5.The symbol for fluorine is F. The period of fluorine is 2 and it is a p-block element. The electron configuration of fluorine(F) and the orbital diagram is the main topic of this article. Neon Bohr Diagram. To confirm the third electron of neon enters the orbit of two According to the Bohr hydrogen-like model, the radius. Two electron shells surrounding the nucleus, containing 2 electrons in the n=1 shell and 8 electrons in the n=2 shell. Bohr's model of the atom. Bohr model Neon atomic orbits.
Exam 4 Review: Ch.8-9. Electromagnetic radiation with a wavelength of 745 nm appears as red light to the human eye. The energy of one photon of this light is ________ J. Calculate the wavelength (in nm) of the blue light emitted by a mercury lamp with a frequency of 6.19 × 10^14 Hz. Nice work!

Orbital diagram for neon
[2,8] or 1s^2 2s^2 2p^6 Neon has atomic number 10, so a neon atom has 10 protons in its nucleus and therefore 10 electrons. The n=1 shell can only hold 2 electrons, so the remaining 8 electrons fill the n=2 shell. The more detailed version of the electronic configuration reflects the sub-shells in the n=1 and n=2 shells, where the n=1 shell just has a single s-sub shell containing a single s. orbital diagram (orbital box diagram) : Pairs of electrons occupy the 1s, 2s, 2p x, 2p y, 2p z, 3s, 3p x, 3p y, 3p z and 4s orbital, and only 1 electron occupies each of the 3d orbitals and these electrons have parallel spin (arrows pointing in the same direction) in accordance with Hund's Rule. Sep 16, 2021 · Neon, the last element in the main second energy level, has 10 electrons. How are these electrons distributed and located? The first 2 electrons go in the 1s-orbital, or the s-orbital in the first main energy level. Then, the next 2 electrons occupy in the 2s-orbital, or the s-orbital in the second main energy level.
Orbital diagram for neon. The 1s orbital at the bottom of the diagram is the orbital with electrons of lowest energy. The energy increases as we move up to the 2 s and then 2 p , 3 s , and 3 p orbitals, showing that the increasing n value has more influence on energy than the increasing l value for small atoms. Oxygen electron configuration is 1s 2 2s 2 2p 4.The period of oxygen is 2 and it is a p-block element. This article gives an idea about the electron configuration of oxygen(O) and orbital diagram, period and groups, valency and valence electrons of oxygen, bond formation, compound formation, application of different principles. The eighth element in the periodic table is oxygen. Write the full electron configuration, noble gas electron configuration, and fill in the orbital diagrams, for the following elements. 1. Nitro en 3s B 2. Chlorine Is 3. Sodium a øan a as ap 4. Neon Is 23 5. Nickel 6 Vanadium Is 7 Cop er orbital diagram (orbital box diagram) : Pairs of electrons occupy the 1s, 2s, 2p x, 2p y, 2p z, 3s, 3p x, 3p y, 3p z and 4s orbital, and only 1 electron occupies each of the 3d orbitals and these electrons have parallel spin (arrows pointing in the same direction) in accordance with Hund's Rule.
Sodium electron configuration is 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 1.The symbol for sodium is 'Na'. The period of sodium is 3 and it is a s-block element. This article gives an idea about the electron configuration of sodium(Ne) and orbital diagrams, period and groups, valency and valence electrons of sodium, bond formation, compound formation, application of different principles. The orbital diagrams for fluorine and neon are shown. The next two electrons continue to pair those electrons that are unpaired to fill up the 2p orbitals. With neon the second level is filled with electrons. Completed levels are a characteristic of all noble gases. If we look at the energy level diagram for neon the completed second level. Molecular Orbital Diagram of Neon Molecule Video Lecture from Chapter Nature of Chemical Bond of Subject Chemistry Class 11 for HSC, IIT JEE, CBSE & NEET.Wat... Nov 17, 2021 · Molecular orbital diagram practice worksheet
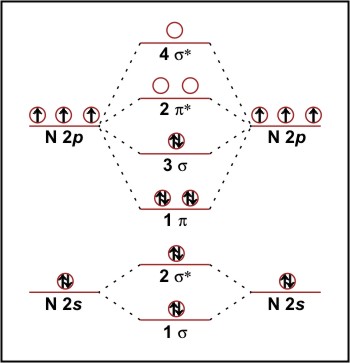
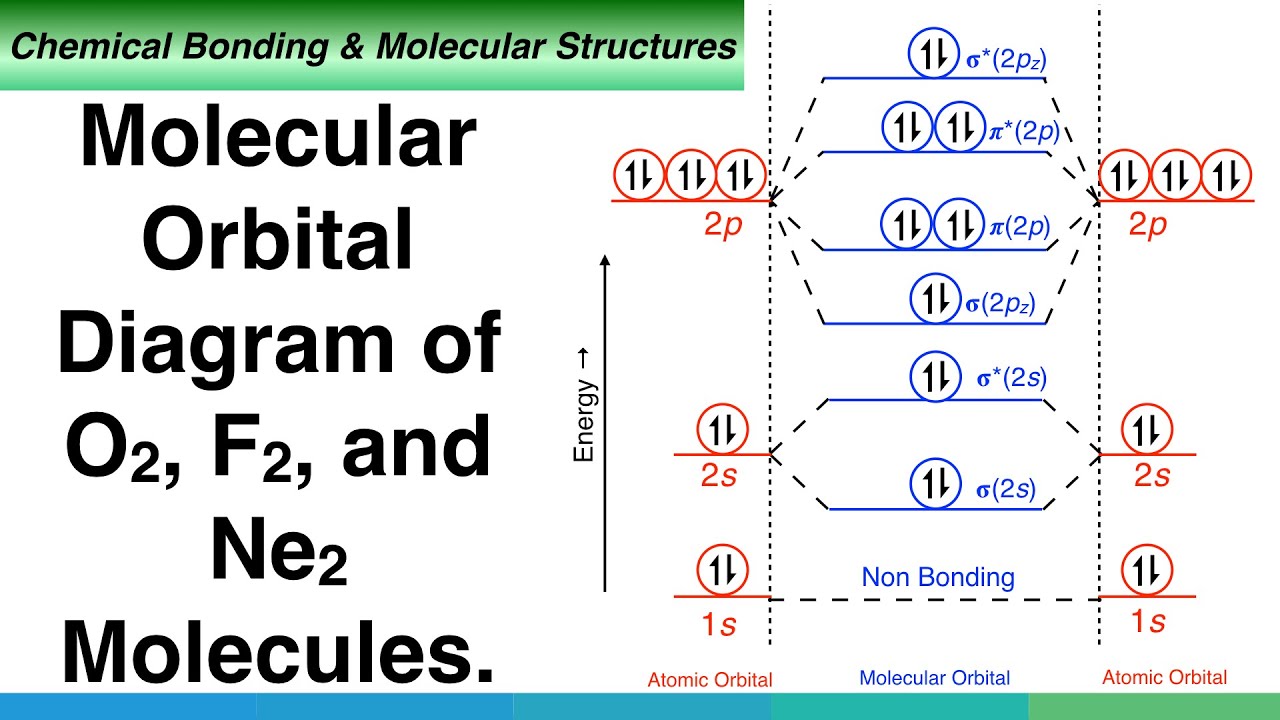
Answer (1 of 4): Neon is denoted by Ne which is noble gas. Noble gases are non-reactive by nature.The outermost shell in Ne element is fully filled with electrons where the electron is 10 in number. This means that will have 20 electrons. This is why it does not need to react with any other atom. Orbital Diagram for Neon. molecular orbital theory home faculty molecular orbital theory the goal of molecular orbital theory is to describe molecules in a similar way to how we describe atoms that is in aufbau principle indiana university northwest the equations of modern atomic theory are difficult to solve fortunately many of the results can be obatined by following some simple rules The electron configuration and the orbital diagram are: Following hydrogen is the noble gas helium, which has an atomic number of 2. The helium atom contains two protons and two electrons. The first electron has the same four quantum numbers as the hydrogen atom electron ( n = 1, l = 0, ml = 0, ms = +1 2 m s = + 1 2 ). 3. The molecular orbital diagram for a diatomic oxygen molecule, O 2, is. Bond Order = 1/2(10 - 6) = 2; The bond order is two so the molecule is stable. There are two unpaired electrons, so molecule is paramagnetic. 4.The molecular orbital diagram for a diatomic Neon molecule, Ne 2, is. Bond Order = 1/2(10 - 10) = 0
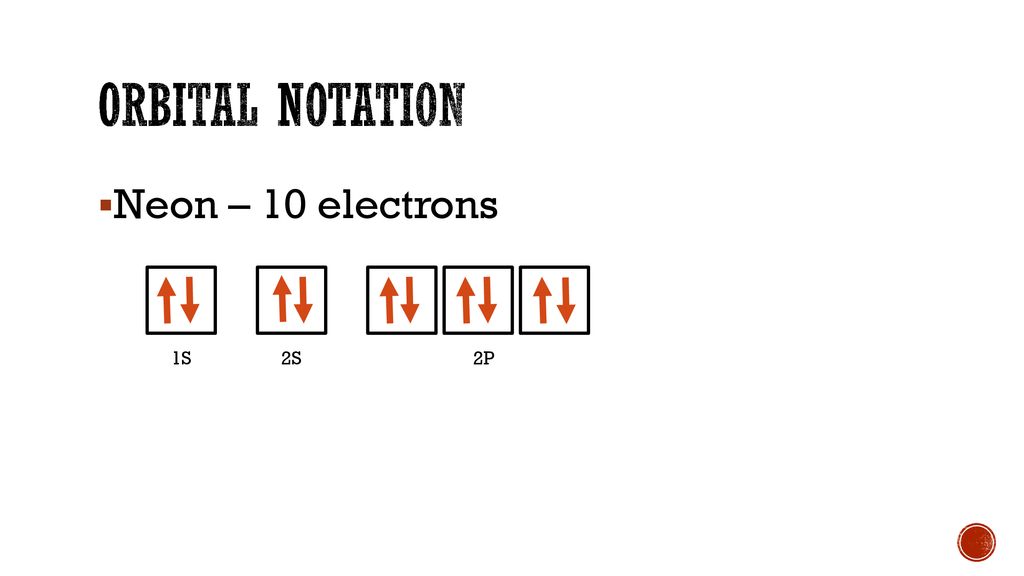
Answer and Explanation: 1. For neon, the atomic number is 10. The electronic configuration for neon is 1s22s22p6 1 s 2 2 s 2 2 p 6. The full orbital diagram for neon is shown below. Orbital diagram.
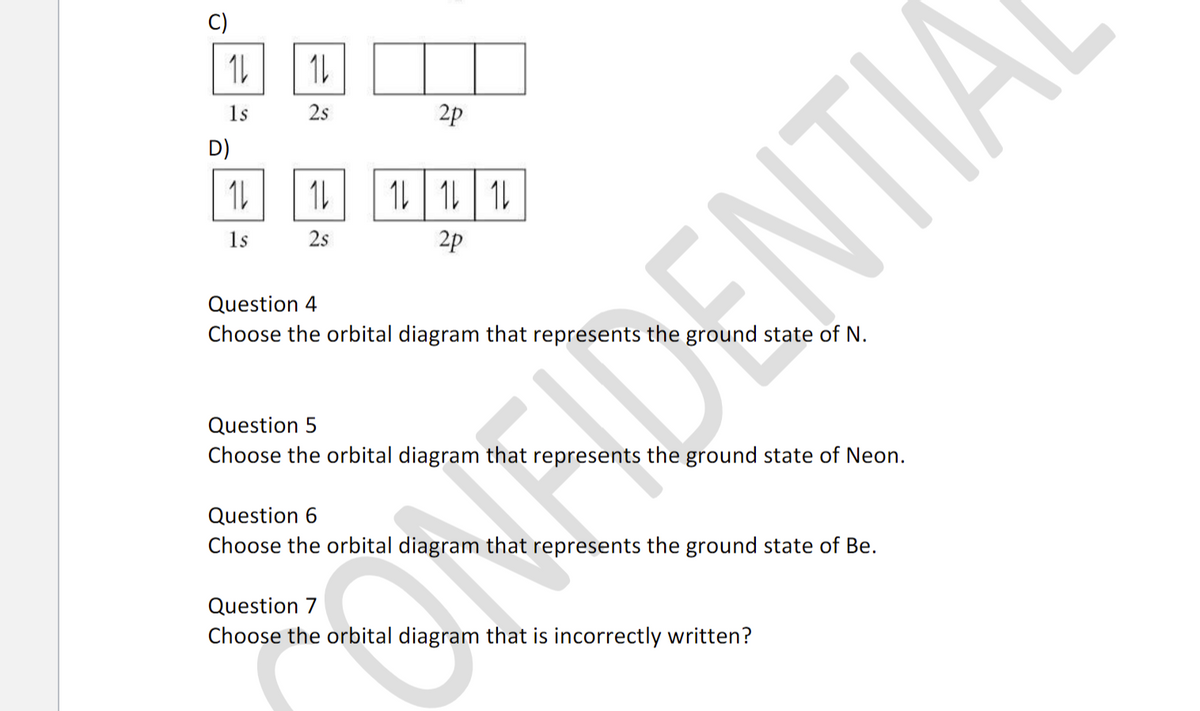
Orbital Filling Diagrams •Each box represents an orbital which can hold a max of 2 e- •Aufbau principal -each electron occupies the lowest energy orbital available; German for "build up" •Electrons are notated with an arrow -Up arrow goes first then, down arrow -Arrows represent the opposing spin of electrons 5.2 Quantum Theory & The Atom
Fill in the orbital energy diagram for the neon atom. 2p El 2s 1s Submit Answer Try Another Version 2 item attempts remaining ; Question: Fill in the orbital energy diagram for the neon atom. 2p El 2s 1s Submit Answer Try Another Version 2 item attempts remaining. This problem has been solved!
It involves placing electrons into orbital diagrams. This provides an arrangement of electrons in a way that is easy to visualize. In an orbital filling diagram, the individual. sodium has one 3s electron in excess of the noble gas neon. The shorthand notation for Na is [Ne]3s1.
The elements from boron to neon in the periodic table are filling the 2p orbital. The three possibilities for 2p orbitals can be associated with spatial directions, say x,y and z. The order of filling will place one electron in each before placing two in any one orbital since the mutually repulsive electrons prefer to be further apart.
Answer: Yes O2 (2+) is diamagnetic. Explanation: We can work this out by looking at the molecular orbital diagram of O2 O2 (2+) has two fewer electrons than O2 which is what it gives it positive charge. And show diamagnetic behavior as have no unpaired electron. Molecular orbital diagram of.
[2,8] or 1s^2 2s^2 2p^6 Neon has atomic number 10, so a neon atom has 10 protons in its nucleus and therefore 10 electrons. The n=1 shell can only hold 2 electrons, so the remaining 8 electrons fill the n=2 shell. The more detailed version of the electronic configuration reflects the sub-shells in the n=1 and n=2 shells, where the n=1 shell just has a single s-sub shell containing a single s.
Boron Through Neon - The 2p Orbitals Draw orbital diagrams and then the electron configurations for the following atoms. The number of electrons in an atom of an element is equal to the at number. the packing of the shell is: 1st (s2) 2nd (s2p6) 3rd (s2p6d10).
Neon is the tenth element with a total of 10 electrons. In writing the electron configuration for neon the first two electrons will go in the 1s orbital. Since 1s can only hold two electrons the next 2 electrons for Ne go in the 2s orbital. The remaining six electrons will go in the 2p orbital. Therefore the Ne electron configuration will be 1s.
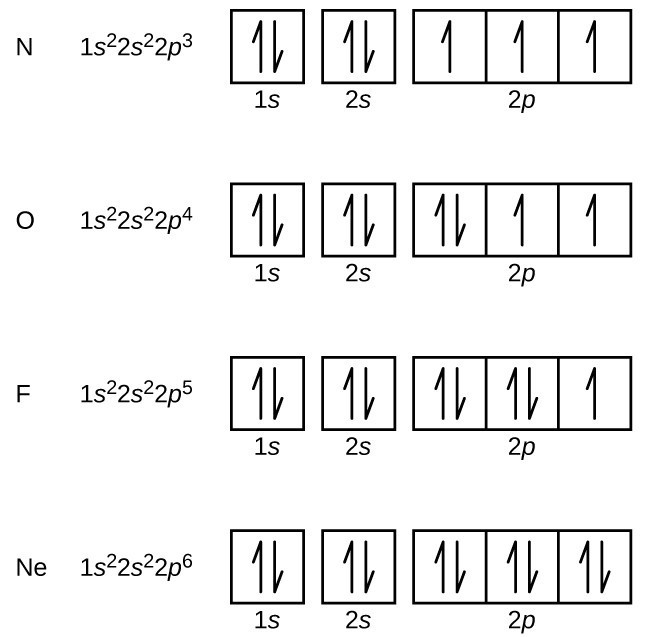
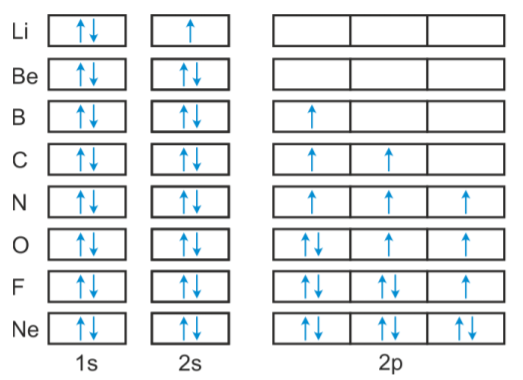
Boron (atomic number 5) has five electrons. Four electrons fill both the 1s and 2s orbitals. The fifth electron is added to a 2p orbital, the sublevel next higher in energy (Figure 5.9). The electron configuration of boron is: B: 1s 2 2s 2 2p 1. Table 5.2 shows the electron configurations of the elements with atomic numbers 1 through 18.
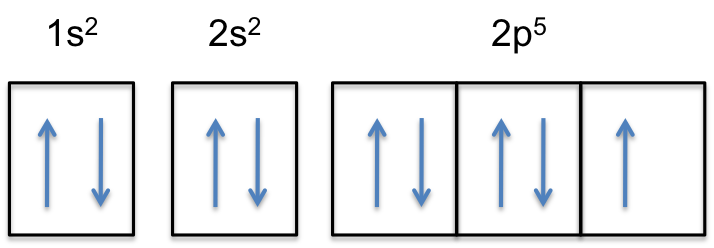
The electron configuration of neon is: 1s22s22p5. An orbital diagram is similar to electron configuration, except that instead of indicating the atoms by total numbers, each orbital is shown with.
Orbital diagram of Hydrogen (H) 2: Orbital diagram of Helium (He) 3: Orbital diagram of Lithium (Li) 4: Orbital diagram of Beryllium (Be) 5: Orbital diagram of Boron (B) 6: Orbital diagram of Carbon (C) 7: Orbital diagram of Nitrogen (N) 8: Orbital diagram of Oxygen (O) 9: Orbital diagram of Fluorine (F) 10: Orbital diagram of Neon (Ne) 11.
Neon has 2 electrons in its first shell and 8 in its secondCheck me out: http://www.chemistnate
Orbital diagram. Tags: Question 12. SURVEY. 300 seconds. Q. The electron configuration of an atom is 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6. The number of electrons in the atom is. answer choices.
In atomic theory and quantum mechanics, an atomic orbital is a mathematical function describing the location and wave-like behavior of an electron in an atom. This function can be used to calculate the probability of finding any electron of an atom in any specific region around the atom's nucleus.The term atomic orbital may also refer to the physical region or space where the electron can be.
Orbital Diagram For Xenon Diagram of the nuclear composition, electron configuration, chemical data, and valence orbitals of an atom of xenon (atomic number: 54), an isotope of this. Sep 8, TL;DR Xenon hexafluoride has a fluxional structure in the gas phase, with. the best explanation is given by qualitative molecular orbital theory.
Neon electron configuration is 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6.The symbol for neon is ‘Ne’ and it is an inert element. This article gives an idea about the electron configuration of neon(Ne) and orbital diagram, period and groups, valency and valence electrons of neon, application of different principles. The tenth element in the periodic table is neon.
The correct orbital diagram, obeying Hund’s Rule, will note the two 2p electrons to be unpaired in two of the three available orbitals, both with “spin-up.” Since electrons always occupy an empty orbital before they fill up, it would be incorrect to draw the two 2p electrons in.
Sep 16, 2021 · Neon, the last element in the main second energy level, has 10 electrons. How are these electrons distributed and located? The first 2 electrons go in the 1s-orbital, or the s-orbital in the first main energy level. Then, the next 2 electrons occupy in the 2s-orbital, or the s-orbital in the second main energy level.
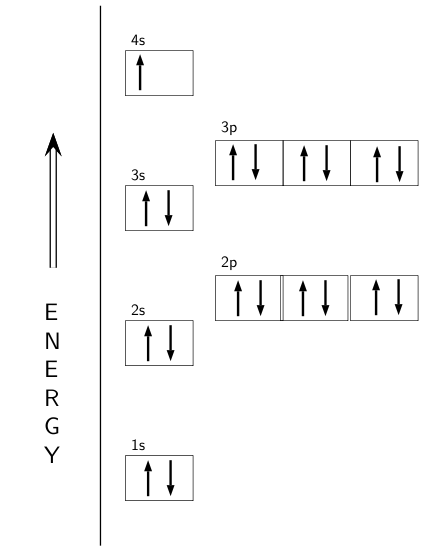
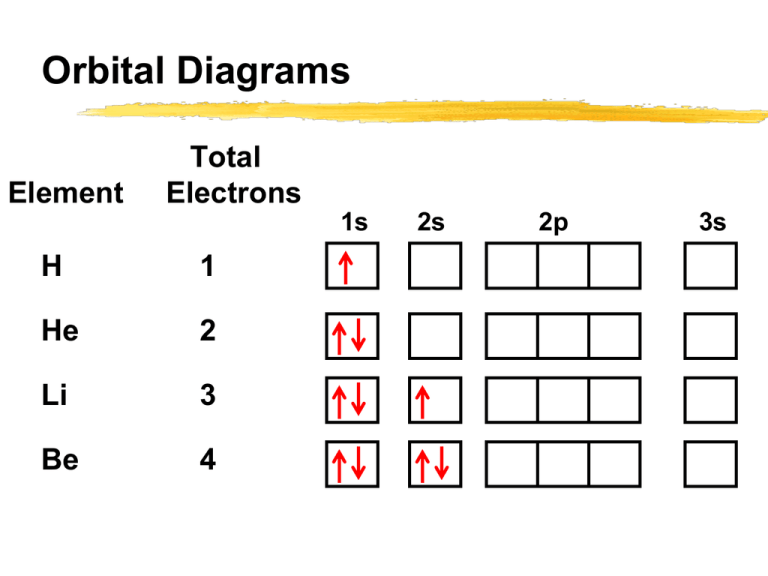
An orbital box diagram can be written as well. Boxes, or horizontal lines represent the orbitals, arrows represent the electrons, and if an orbital is full, the electrons must be of opposite spin-one arrow pointing up and the other one pointing down. The orbital box diagrams are listed for the first 20 elements in the figure below.
Once we reach neon, a noble gas, all of the 2p orbitals will be completely full. Neon has a configuration of 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6. Any further electrons will need to go in the next highest energy orbital, which would be the 3s orbital. Electron configurations and orbital filling diagrams for lithium through neon are provided below.





















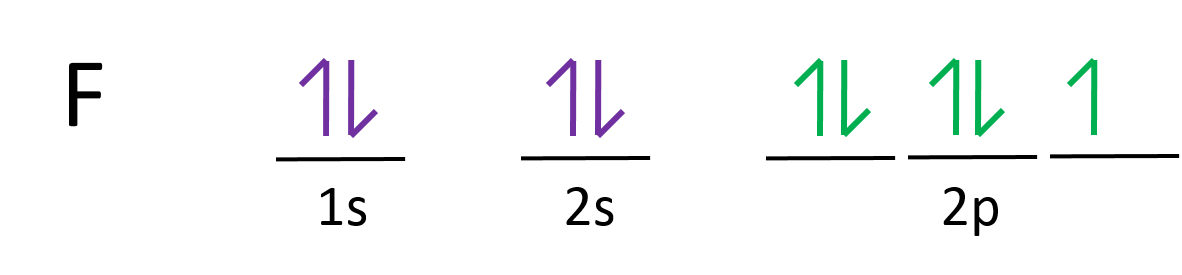




0 Response to "39 Orbital Diagram For Neon"
Post a Comment