42 Acl Mcl Pcl Lcl Diagram
Last modified: Aug 27, 2020. Mnemonic: Cross your long fingers over the index finger and superimpose this hand over your ipsilateral knee. This will help us to remember the orientation of the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) and posterior cruciate ligament (PCL) of knee. Also remember the mnemonic “LAMP” which means Lateral ACL and Medial PCL. Dec 12, 2017 · The posterior cruciate ligament (PCL) is the other ligament inside the knee joint. It also runs diagonally across the knee, connecting the back (posterior) of the tibia to the front (anterior) of the femur. The ACL and PCL cross each other inside the knee joint and some people call them the cross ligaments (cruciate means cross-shaped).
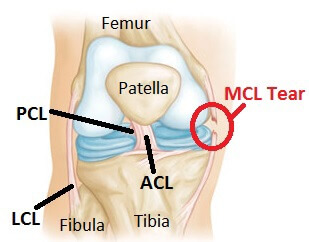
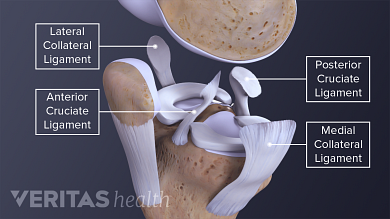
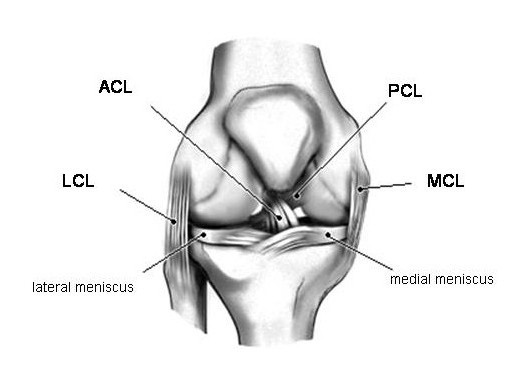
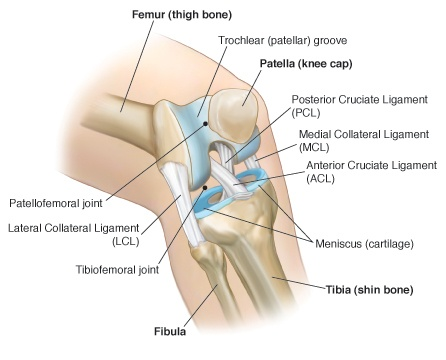
The cruciate ligaments are the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) and posterior cruciate ligament (PCL). The collateral ligaments are the medial collateral ligament (MCL) and the lateral collateral ligament (LCL). The four ligaments work together to stabilize and allow controlled mobility in the knee. Each ligament is like a taut rope that.

Acl mcl pcl lcl diagram
Aug 05, 2021 · This diagram illustrates some areas covered by the main branches, any of which can produce RSI symptoms. RSI can be complicated. Because you have so many nerve fibres that exit from your neck and travel through your arm, the symptoms of this problem can vary wildly. You may experience pain almost anywhere. Nerve-related pain misdiagnosis can occur. ACL vs. MCL tear. The ACL is located inside of the knee joint and connects the top front of the tibia (shinbone) to the bottom back of the femur (thighbone). Together, the ACL and PCL cross each other to form an "X" inside of your knee. The ACL prevents the tibia from sliding too far forward relative to the femur and is important for. The medial collateral ligament (MCL) is on the inner side of your knee. It attaches the thigh bone (femur) to the shin bone (tibia). The lateral collateral ligament (LCL) is on the outer side of your knee.. The posterior cruciate ligament (PCL) is behind the ACL. The cruciate ligaments control the way your knee moves front to back.
Acl mcl pcl lcl diagram. Anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) is the most commonly injured knee ligament.It connects the thigh bone to the shin bone. Posterior cruciate ligament (PCL) also links the thigh bone to the shin. Posterior cruciate ligament or PCL - located at the back of the knee, controls backward movement of the shin bone; Medial collateral ligament or MCL - connects the thigh bone to the shin bone on the inside of the knee—MCL stabilizes the inner knee Aug 26, 2021 · The ACL combines with the posterior cruciate ligament, or PCL, as well as the medial and lateral collateral ligaments (MCL and LCL) to connect your femur to. Where is ACL and LCL? The LCL (side security tendon) is a tendon situated on the beyond the knee and adds to side knee security. It is unusual for an LCL injury to be alone. Normally, an LCL tear is related to injuries to the ACL, PCL, or a full knee misplacement.
The lateral collateral ligament is much shorter than the medial collateral ligament making it much less common to injure the LCL than the MCL. Cruciate Knee Ligaments. The cruciates are the most important knee ligaments in providing stability of the knee. There are two cruciate ligaments, anterior (ACL) and posterior (PCL). Jan 23, 2018 · Anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) Medial collateral ligament (MCL) Lateral collateral ligament (LCL) Posterior cruciate ligament (PCL) Damage to the ACL, such as a tear, is a common knee injury. Surgery (ACL, PCL, MCL) Depending on the severity and type of ligament injury, surgery may be recommended. For ACL injuries, arthroscopic or open surgery is done using a graft to replace the damaged ligament. For certain PCL cases where the ligament is no longer attached properly to the shinbone, surgery is considered. Anterior Cruciate Ligament Repair (ACL, MCL, MPFL, PCL, LCL) The ACL, or anterior cruciate ligament, is one of the ligaments in the knee. Athletes who play sports that require sudden stops and turns are more likely to experience injuries or tears to their ACLs, and tears usually have to be reconstructed surgically.
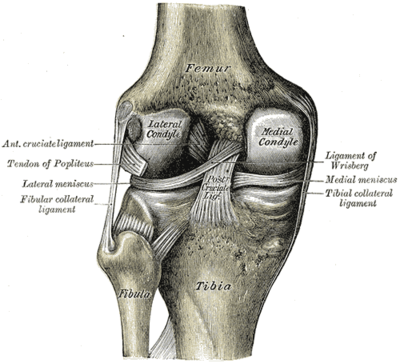
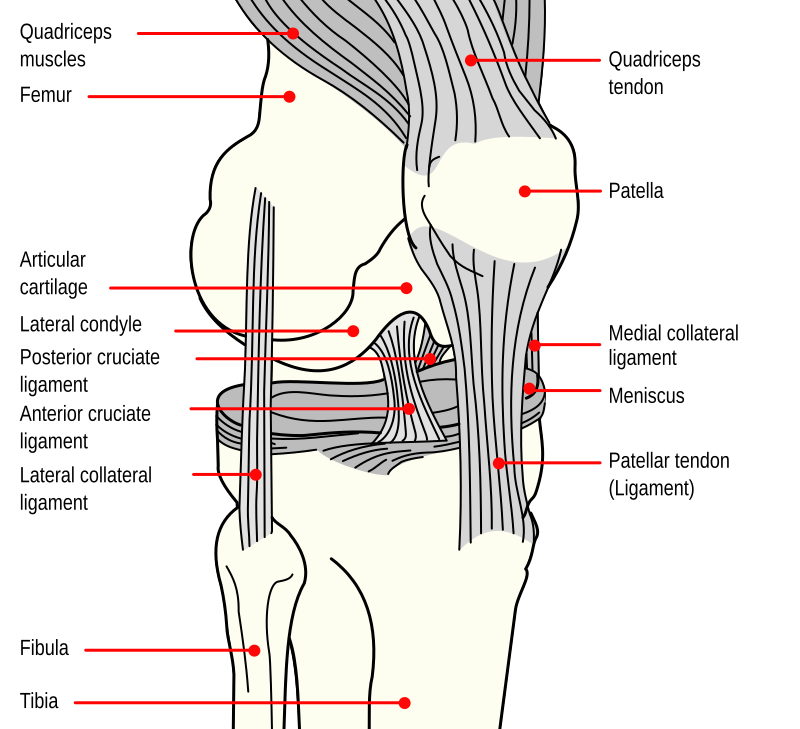
the medial collateral ligament (MCL) (Figure 1a), lateral collateral ligament (LCL) (Figure 1b), anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) (Figure 2a) and posterior cruciate ligament (PCL) (Figure 2b). The MCL connects the femur and tibia medially (on the inside) and resists valgus (knee buckling in) knee motion. A common mechanism of injury Oct 13, 2021 · The knee is made up of 4 very important ligaments, these include the ACL (Anterior cruciate ligament, PCL (posterior cruciate ligament), LCL (lateral collateral Ligament, and finally the MCL. We are pleased to provide you with the picture named Pcl Acl Lcl Mcl Meniscus Anatomy.We hope this picture Pcl Acl Lcl Mcl Meniscus Anatomy can help you study and research. for more anatomy content please follow us and visit our website: www.anatomynote . Anatomynote found Pcl Acl Lcl Mcl Meniscus Anatomy from plenty of anatomical pictures on the internet. A knee ligament injury a sprain of one or more of the four ligaments in the knee, either the Medial Collateral Ligament (MCL), Lateral Collateral Ligament (LCL), Posterior Cruciate Ligament (PCL), or the Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL). ACL, PCL, MCL, and LCL injuries are caused by overstretching or tearing of a ligament by twisting or wrenching the knee.
Anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) Posterior cruciate ligament (PCL) Medial Collateral ligament (MCL) Lateral collateral ligament/Posterolateral Corner (LCL/PLC) This specific rehabilitation protocol should be used when both the ACL and PCL are reconstructed, along with one or more of the other ligaments.
Medical Library: Knee - ACL, PCL, MCL, LCL Tear There are four main ligaments in the knee: Anterior Cruciate Ligament, Posterior Cruciate Ligament, Medial Collateral Ligament, and Lateral Collateral Ligament. Tears to any of these ligaments are serious conditions, and may require surgery, or rest and rehabilitation. ACL An anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) tear is an injury to the knee.
The lateral collateral ligament runs along the outside of your knee and prevents it from moving too far out. Without the MCL or LCL your knee will feel wobbly, especially if you do a side-to-side cutting motion. Thankfully, neither the MCL nor the LCL are removed during a total knee replacement surgery. However, on rare occasions, the MCL can.
The medial collateral ligament (MCL) is one of four ligaments that is responsible for keeping the knee joint stable. (The other three are the anterior and posterior cruciate ligaments [ ACL and PCL] and the lateral collateral ligament [ LCL ].) The MCL connects the inner (medial) surfaces of the thigh bone (femur) and the shin bone (tibia) and.
The medial collateral ligament (MCL) is on the inner side of your knee. It attaches the thigh bone (femur) to the shin bone (tibia). The lateral collateral ligament (LCL) is on the outer side of your knee.. The posterior cruciate ligament (PCL) is behind the ACL. The cruciate ligaments control the way your knee moves front to back.
MCL Tear Symptoms. Just as with an ACL tear, you may hear a popping sound when the injury occurs. Some of the most common symptoms of an MCL tear include: Pain on the inner side of the knee. Feeling the knee "give out". Swelling. The knee feels unstable. Pain when putting weight on the knee. Locked knee.
Anterior and posterior drawer testing for ACL and PCL as well as valgus and varus test for MCL and LCL. http://passionformotion.blogspot /p/knee-assessmen...
ACL, MCL, LCL, and PCL All Present One of the four main ligaments of the knee is the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL). Together with the posterior cruciate ligament (PCL), it forms an 'X' shape inside the knee joint. The ACL runs from the bottom of the femur at the back of the knee, diagonally through the joint and attaches to the top of the.
The overall RTP rate was 64.0%. Athletes with ACL/MCL tears had an RTP rate of 70.8%, whereas athletes with ACL and posterior collateral ligament/lateral collateral ligament (PCL/LCL) tears had an RTP rate of 55.6% ( P = 0.26). Mean time to RTP for all 50 athletes was 388.71 ± 198.52 days.
Different Types Of Knee Injuries - ACL, LCL, MCL and PCL. Our knees are one of the most vital joints in our bodies, shouldering our weight and facilitating movements like walking, running and sitting. Your knee is made up of four distinct ligaments, with one on the front, back and each side. Damage to the knee can result in a partial or.
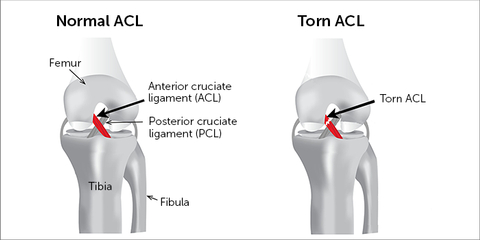
The anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) is one of a pair of cruciate ligaments (the other being the posterior cruciate ligament) in the human knee.The two ligaments are also called "cruciform" ligaments, as they are arranged in a crossed formation. In the quadruped stifle joint (analogous to the knee), based on its anatomical position, it is also referred to as the cranial cruciate ligament.
An ACL tear often leads to the knee “giving out,” and may require surgical repair. PCL (posterior cruciate ligament) strain or tear: PCL tears can cause pain, swelling, and knee instability.
There are four types of ligaments namely Medial Collateral Ligament (MCL), Lateral Collateral Ligament (LCL), Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) and Posterior Cruciate Ligament (PCL). MCL provides stability to the inner knee and LCL provides stability to the outer part. ACL and PCL are present in the center of the knee. ACL helps in limiting the.
Anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) — The ACL and the posterior cruciate ligament (PCL) bridge the inside of the knee joint, forming an "X" pattern that Large Intestine Channel: LI4 – Located on the back side of the hand between the thumb and first finger, this point activates the immune system and helps pain, especially in the face.
Apr 23, 2015 · Medial collateral ligament (MCL): This broad, flat, ligament is on the outside of the knee and connects the head of the femur to the head of the tibia. It is commonly injured in sports involving.
Acl And Mcl Diagram. Signs and symptoms of a medial collateral ligament (MCL) injury include The anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) and posterior cruciate ligament. The MCL is one of four major ligaments that supports the knee. either partial or complete ruptures in the ligament significantly increases the load on the ACL.
ACL vs. MCL tear. The ACL is located inside of the knee joint and connects the top front of the tibia (shinbone) to the bottom back of the femur (thighbone). Together, the ACL and PCL cross each other to form an "X" inside of your knee. The ACL prevents the tibia from sliding too far forward relative to the femur and is important for.
the Posterior Cruciate Ligament (PCL) and Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) control back-and-forth movement; the Medial Collateral Ligament (MLC) helps to brace the inside of the knee; the Lateral Collateral Ligament (LCL) braces the ouside of the knee, controlling sideways motion and protecting the knee from over-extending. While most injuries.
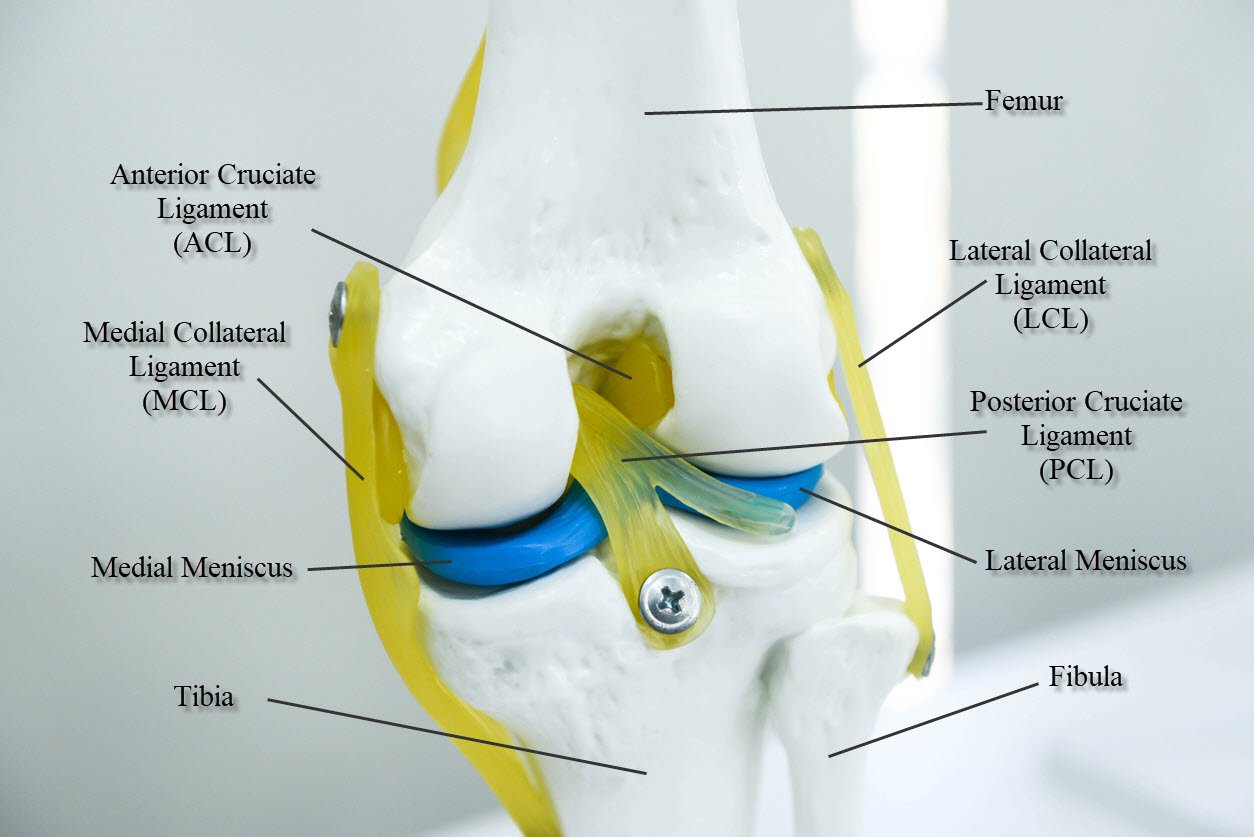
In the model you can see femur, tibia and fibula, with ACL (anterior cruciate ligament), PCL (posterior cruciate ligament), MCL (medial collateral ligament), LCL (lateral collateral ligament) and medial and lateral meniscus. These are the most typical ligament and cartilage structures in the knee to receive an injury.
The posterior cruciate ligament (PCL) is about two inches long and connects the femur to the tibia at the back of the knee. It limits the backward or posterior motion of the tibia (shinbone). Twisting or overextending the knee can cause the PCL to tear, leaving the knee unstable and potentially unable to support a person's full body weight.
PCL = Posterior Cruciate Ligament (this is the good news, it’s OK on me) The stability of the knee largely depends on these four major knee ligaments (the tough, elastic tissues that hold two or more bones together.) The MCL and LCL have sufficient blood flow to heal themselves when torn.
Where are the ACL MCL and LCL located? An injury of this kind is called an ACL tear. You can find braces specifically designed for ACL injuries here. Another of the four main knee ligaments is the medial collateral ligament (MCL). This runs from the bottom of the femur, down the inside of the knee and over the joint to the top of the tibia.
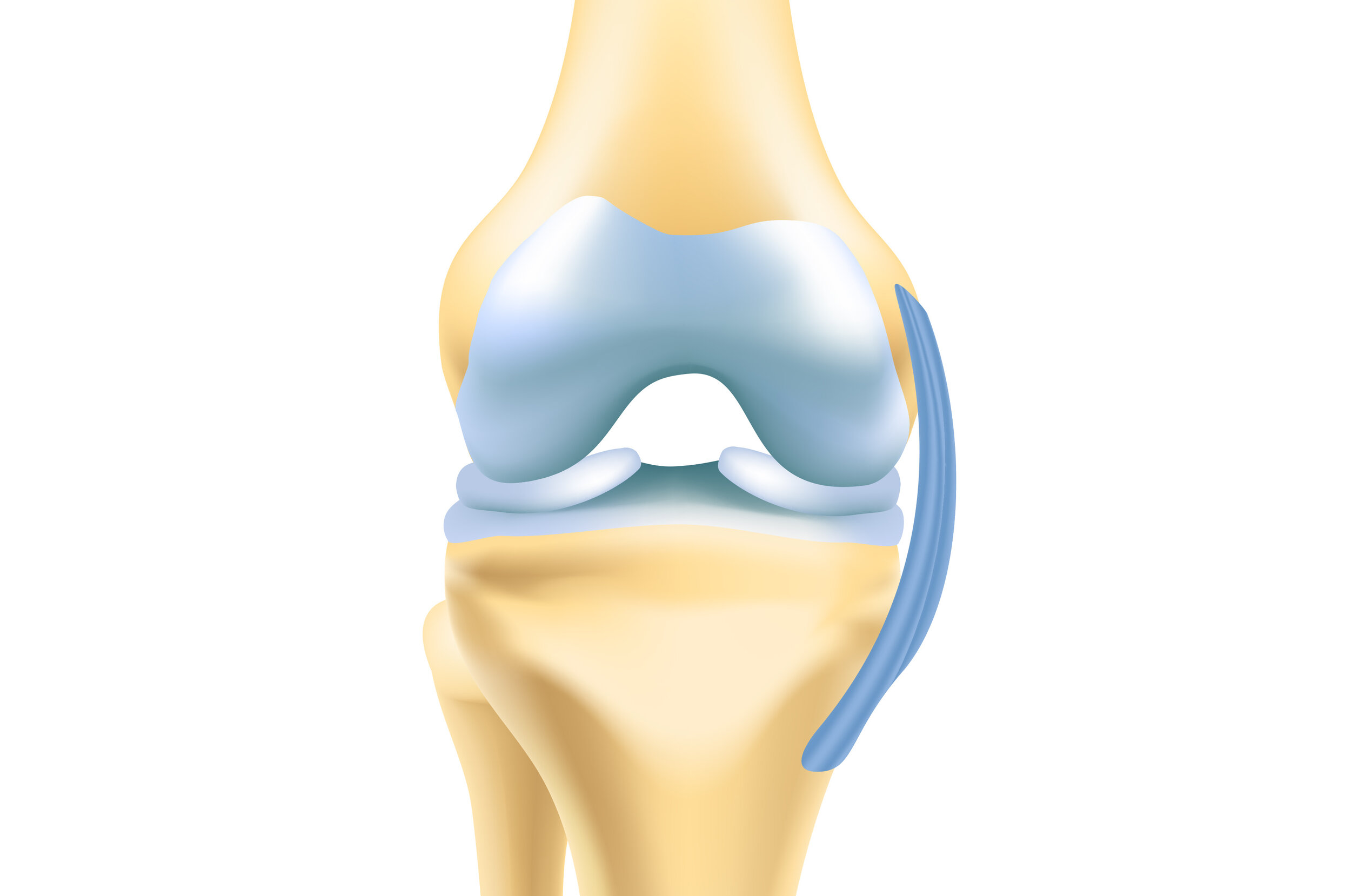
Torn anterior cruciate ligament diagram. In this image, you will find Medial side (inside of knee), Femur (thigh bone), Lateral side (outside of knee), Posterior cruciate ligament (PCL), Anterior cruciate ligament (ACL), Lateral collateral ligament, Fibula, Torn ACL, Tibia (shin bone), Medial collateral ligament in it.
The MCL (medial collateral ligament) and PCL (posterior cruciate ligament) are two of the four ligaments (ACL, MCL, PCL, and LCL) that provide stability to the knee as well as prevent the knee from moving too far in a specific direction. The MCL is a ligament on the inside of the knee. It prevents your knee from bending inward (valgus).
The posterior cruciate ligament (PCL) runs diagonally opposite of the ACL, crossing its path to make an “X” in the middle of the knee. Unlike the ACL, the PCL restricts excessive posterior translation, or sliding backward of the tibia on the femur. This ligament is nearly twice as thick as the ACL, meaning that it is almost twice as strong.
What is the LCL? Like the ACL and the PCL, the MCL and the lateral collateral ligament (LCL) work together to stabilize the knee joint. The collateral ligaments are located on the outside of the knee and help control the sideways movement of the knee. The LCL is located on the outside of the knee, while the MCL is located on the inside of the.
Aug 05, 2021 · This diagram illustrates some areas covered by the main branches, any of which can produce RSI symptoms. RSI can be complicated. Because you have so many nerve fibres that exit from your neck and travel through your arm, the symptoms of this problem can vary wildly. You may experience pain almost anywhere. Nerve-related pain misdiagnosis can occur.
The medial collateral ligament (MCL) is a flat band of connective tissue that runs from the medial epicondyle of the femur to the medial condyle of the tibia and is one of four major ligaments that supports the knee. MCL injuries often occur in sports, being the most common ligamentous injury of the knee, and 60% of skiing knee injuries involve the MCL).




















/knee-pain-instability-2549493-5c04aaf946e0fb00010b8e7a-b0ef89c536aa4cd7a9db3f927d72597b.png)


0 Response to "42 Acl Mcl Pcl Lcl Diagram"
Post a Comment