39 Vapour Liquid Equilibrium Diagram
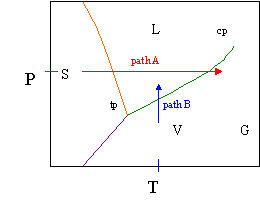
318 CHAPTER 10. Vapor/Liquid Eauilibrium: Introduction and KAC2, which represent the vapor pressure-vs.-T curves for pure species 1 and 2. More- over, the under and upper surfaces form a continuous rounded surface across the top of the diagram between Cl and C2, the critical points of pure species 1 and 2; the critical points of the The basis of distillation is phase equilibrium—specifically, vapor-liquid equilibrium (VLE) and in some cases vapor-liquid-liquid equilibrium (VLLE). Distillation can only. represents the vapor composition. The second diagram is a plot of x versus y. These types of diagrams are generated at a constant pressure. Because the pressure in a
Engineering; Chemical Engineering; Chemical Engineering questions and answers; Experiment 5: liquid vapour equilibria-phase diagram of propanol water Objective: To construct a phase diagram for the system n-propanol/water i.e to construct a boiling point versus composition diagram for the two liquids Experimental requirements Reflux setup inside heating mantle: -2 liebig condensers.
Vapour liquid equilibrium diagram
Vapor-liquid equilibrium data for Ethanol-Water* n-Buianol-Wator# Ethyl Aeeiate-Water# and n-Hexane-Ethanol at atmospheric pr 00 sura and £or n-Hoxana-Sthanol at 2f50 mnu, 59$ mm.* 1270 mm*# Ijbj mm** 2J10 mm.# 3.3 Phase Diagram for Water Vapor: Clausius-Clapeyron Equation. The Clausius-Clapeyron Equation. We can derive the equation for e s using two concepts you may have heard of and will learn about later: entropy and Gibbs free energy, which we will not go into here.Instead, we will quote the result, which is called the Clausius-Clapeyron Equation, Draw vapor-liquid equilibrium (VLE) and liquid-miscibility (LLE) phase diagrams, or calculate distillation processes. Over 300 organic compounds.
Vapour liquid equilibrium diagram. Apr 06, 2018 · (4) If a liquid is largely free of air, and the glass flask is clean and very smooth, the liquid may superheat, a condition in which the temperature of the liquid rises above its boiling point. In a superheated liquid it is hard to form vapour bubbles resulting in. Vapor/Liquid Equilibrium • Previous chapters dealt with pure substances or with constant composition mixtures (air). • But in chemical reactions and number of industrially mass-transfer operations the. composition changes are the desired outcome. (Process such as distillation, absorption and extraction bring phases of different Vapour Power Cycles. 415:. body Calculate called closed compression compressor constant constant pressure cooling cycle cylinder decreases defined Determine diagram difference effect efficiency energy engine enters enthalpy entropy equal equation equilibrium Example exhaust expansion expression final Find flow flow rate fluid fuel function ... Vapor refers to a gas phase at a temperature where the same substance can also exist in the liquid or solid state, below the critical temperature of the substance. (For example, water has a critical temperature of 374 °C (647 K), which is the highest temperature at which liquid water can exist.) If the vapor is in contact with a liquid or solid phase, the two phases will be in a state of.
Liquid, in physics, one of the three principal states of matter, intermediate between gas and crystalline solid. The most obvious physical properties of a liquid are its retention of volume and its conformation to the shape of its container. Learn more about the properties and behavior of liquids in this article. Vapor-Liquid Equilibrium Data. The experimental data shown in these pages are freely available and have been published already in the DDB Explorer Edition.The data represent a small sub list of all available data in the Dortmund Data Bank.For more data or any further information please search the DDB or contact DDBST.. Vapor-Liquid Equilibrium Data Set 615 The vapor-liquid equilibrium phase diagrams of Pb-Ag binary system in vacuum distillation are shown in Fig. 4. The agreement of the VLE phase diagrams with the experiment data indicates that the calculations method of VLE is reliable for the process of vacuum distillation of alloys, especially in liquid phase. The separation experiments of. The equilibrium state corresponds to the saturated vapor pressure curve p = p s (T), which is limited by a triple point (T tr P tr) and a critical point (T c,p c) of the substance.(In the presence of surface tension forces at the phase interface, pressures values p (1) and p (g) in coexisting phases are not equal.) The Clausius-Clapeyron equation follows from Eq.
It is only an equilibrium if both liquid and vapour are present. The saturated vapour pressure of the liquid will force the mercury level down a bit. You can measure the drop - and this gives a value for the saturated vapour pressure of the liquid at this temperature. In this case, the mercury has been forced down by a distance of 760 - 630 mm. Two types of vapor-liquid equilibrium diagrams are widely used to represent data for two-component (binary) systems. The first is a "temperature versus x and y" diagram (Txy). The x term represents the liquid composition, usually expressed in terms of mole fraction. The y term represents the vapor composition. The second diagram is a plot of Vapor-liquid equilibrium, abbreviated as VLE by some, is a condition where a liquid and its vapor (gas phase) are in equilibrium with each other, a condition or state where the rate of evaporation (liquid changing to vapor) equals the rate of condensation (vapor changing to liquid) on a molecular level such that there is no net (overall) vapor-liquid interconversion. Vapor-liquid equilibrium data for Ethanol-Water* n-Buianol-Wator# Ethyl Aeeiate-Water# and n-Hexane-Ethanol at atmospheric pr 00 sura and £or n-Hoxana-Sthanol at 2f50 mnu, 59$ mm.* 1270 mm*# Ijbj mm** 2J10 mm.#
Ammonia - Properties at Gas-Liquid Equilibrium Conditions - Figures and tables showing how the properties of liquid and gaseous ammonia changes along the boiling/condensation curve (temperature and pressure between triple point and critical point conditions). An ammonia phase diagram are included.
The boiling point is defined as the temperature at which the saturated vapor pressure of a liquid is equal to the surrounding atmospheric pressure.For water, the vapor pressure reaches the standard sea level atmospheric pressure of 760 mmHg at 100°C. Since the vapor pressure increases with temperature, it follows that for pressure greater than 760 mmHg (e.g., in a pressure cooker), the.
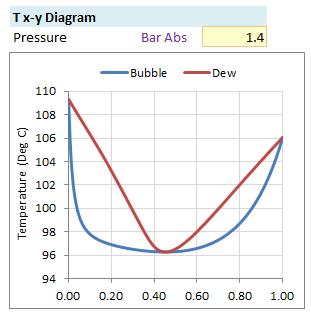
The vapor-liquid equilibrium relations for benzene (1)-toluene (2) at a total pressure of 200 kPa are given as a boiling-point Txy diagram shown in Figure 4.1-1. The upper curve is the saturated vapor curve (the dew-point curve) and the lower curve is the saturated liquid curve (the bubble-point curve).
Even at equilibrium, molecules are constantly in motion and, once in a while, a molecule in the liquid phase gains enough kinetic energy to break away from the liquid phase and enter the gas phase. Likewise, every once in a while a vapor molecule collides with the liquid surface and condenses into the liquid.
3: Three phases are in mutual equilibrium; liquid + Na 2K + a solid solution rich in Na (peritectic line) • b 3 → b 4: The amount of solid compound increases until at b4 the liquid reaches its eutectic composition. It solidifies to give a two-phase solid of a solid solution rich in K and solid Na2K 5.9 Liquid-solid phase diagrams
Draw vapor-liquid equilibrium (VLE) and liquid-miscibility (LLE) phase diagrams, or calculate distillation processes. Over 300 organic compounds.
Ammonia - Vapour Pressure at Gas-Liquid Equilibrium - Figures and table with ammonia saturation pressure at boiling points, SI and Imperial units. Ammonia Gas - Density vs. Temperature and Pressure - Online calculator with figures and tables showing density and specific weight of ammonia for temperatures ranging -50 to 425 °C (-50 to 800 °F.
SIMPLE MODELS FOR VAPOR/LIQUID EQUILIBRIUM 3.1 Raoult's Law • Assumptions: - The vapor phase is an ideal gas (low to moderate pressure) - The liquid phase is an ideal solution (the system are chemically similar) *Chemically similar: the molecular species are not too different in size and are of the same chemical nature. eg: n-hexane/n.
Vapour-liquid equilibrium diagrams Figure 5.1 presents the behaviour of a pure species that can exist as solid, liquid or vapour in a pressure-temperature diagram.We may have three types of two-phase equilibrium solid/liquid, vapour/liquid and solid/vapour.There is a point where all three phases coexist, designated by the triple point.Here the phase rule gives F=C+2-P= +2-3=Q degrees of freedom.
Drawing Vapor-Liquid Equilibrium Diagrams - posted in Student: I am asked to calculate and draw the vapor-liquid equilibrium (VLE) diagram of a binary mixture of acetone and glycerol, given only the total pressure, P = 1 atm (760 mmHg). It says for me to explicitly plot the mole fraction of acetone versus the mole fraction of glycerol. I have no idea where to start.
Vapor-Liquid Equilibrium Diagram for Non-Ideal Mixtures. This simulation shows P-x-y and T-x-y diagrams for vapor-liquid equilibrium (VLE) of a benzene/ethanol mixture. This liquid mixture is non-ideal, and the system has an azeotrope (a condition where liquid and vapor have the same composition). The blue curve represents the liquid-phase.
Calculation of vapor-liquid equilibrium (VLE) and drawing of phase diagrams. Name of substance. CAS-nr. Formula. Type of substance. acetone. 67-64-1. C 3 H 6 O. ketone.
The main objective of this practical is to determine the Vapour-Liquid Equilibrium for the given real system of two miscible liquids. it is also to construct the isobaric diagram and the equilibrium diagram of the two components. The other objective is to calculate the Raoul t’s activity coefficients.
3.3 Phase Diagram for Water Vapor: Clausius-Clapeyron Equation. The Clausius-Clapeyron Equation. We can derive the equation for e s using two concepts you may have heard of and will learn about later: entropy and Gibbs free energy, which we will not go into here.Instead, we will quote the result, which is called the Clausius-Clapeyron Equation,
Thus the sizes, particularly the height, of distillation columns are determined by the vapour liquid equilibrium (VLE) data for the mixtures. Vapour-Liquid-Equilibrium (VLE) Curves. Constant pressure VLE data is obtained from boiling point diagrams. VLE data of binary mixtures is often presented as a plot, as shown in the figure on the right.
A schematic three-dimensional diagram illustrating these surfaces for VLE is shown in Fig. 10.1. This figure shows schematically the P-T-composition surfaces which contain the equilibrium states of saturated vapor and saturated liquid for a binary system.
Vapor Pressure Diagrams and Boiling Diagrams We are now ready to begin talking about phase diagrams involving two components. Our first few phase diagrams will involve only the liquid and gas (or vapor) phases. Later we will discuss two-component phase diagrams involving liquids and solids.
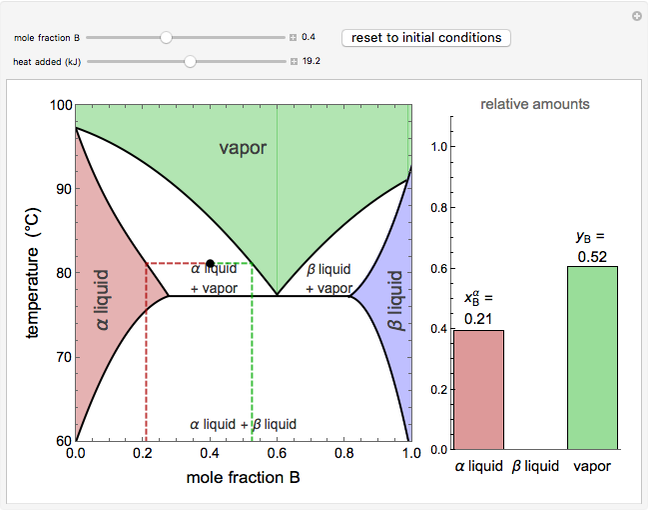
This Demonstration shows phase equilibrium for a binary system of two partially miscible liquids, A and B. Because of the partial miscibility, vapor-liquid equilibrium (VLE), liquid-liquid equilibrium (LLE), and vapor-liquid-liquid equilibrium (VLLE) are present on the phase diagram. You can vary the mole fraction of component B and the heat.
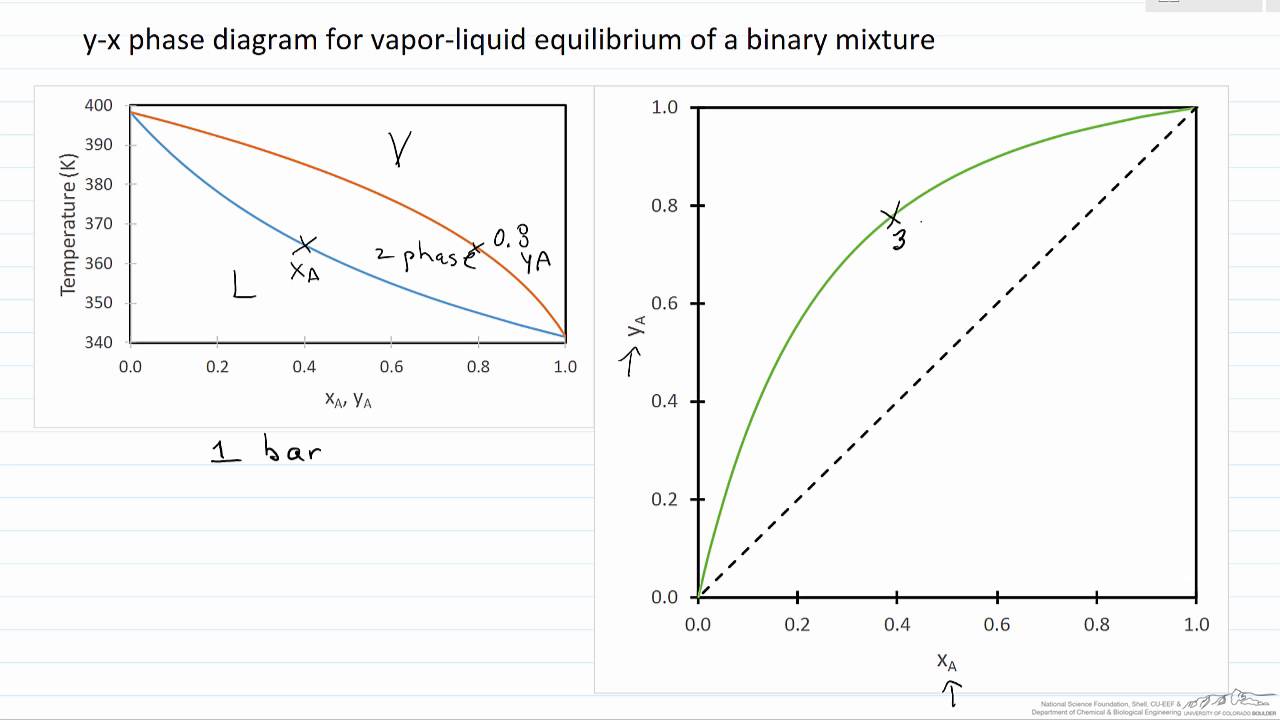
Vapor-liquid equilibrium diagrams For each component in a binary mixture, one could make a vapor-liquid equilibrium diagram. Such a diagram would graph liquid mole fraction on a horizontal axis and vapor mole fraction on a vertical axis. What happens when a liquid vapor system at equilibrium? The pressure exerted by a vapor in equilibrium.
Summary: A vapor containing 90 mol% pentane (y = 0.9) could be compressed to 7.5 atm (at 400 K), at which point it would be a saturated vapor (red line), and it would begin to condense.The saturated liquid (blue line) in equilibrium with the vapor contains less of the more volatile component, n-pentane.The composition of this saturated liquid is 65 mol% n-pentane (y = 0.65).
The vapor-liquid equilibrium (VLE) behavior of an -hexane/ -octane mixture is demonstrated in and diagrams. The blue line represents the liquid-phase boundary (bubble point) and the green line represents the vapor-phase boundary (dew point). Click and drag the black dot on either diagram and the bar chart shows the amounts of liquid (blue) and.
Using Gibbs Energy to Understand Phase Diagram The resulting phase behaviour shows three regions: When x a is small, the equilibrium state is as a single liquid phase. When x a is large, the equilibrium state is as a single vapour phase. When x a is between the minima, the Gibbs energy can be lowered if the system separates into two phases.
A liquid-vapor phase diagram plots temperature of mixture versus the mole fraction or composition. A phase diagram of 2 components that will have differing molecular interactions causing mixture's boiling point to rise/drop will show an azeotrope, in which there will be 2 lobes that either concave down/up depending on if there's positive.
In thermodynamics and chemical engineering, the vapor–liquid equilibrium (VLE) describes the distribution of a chemical species between the vapor phase and a liquid phase.. The concentration of a vapor in contact with its liquid, especially at equilibrium, is often expressed in terms of vapor pressure, which will be a partial pressure (a part of the total gas pressure) if any other gas(es.















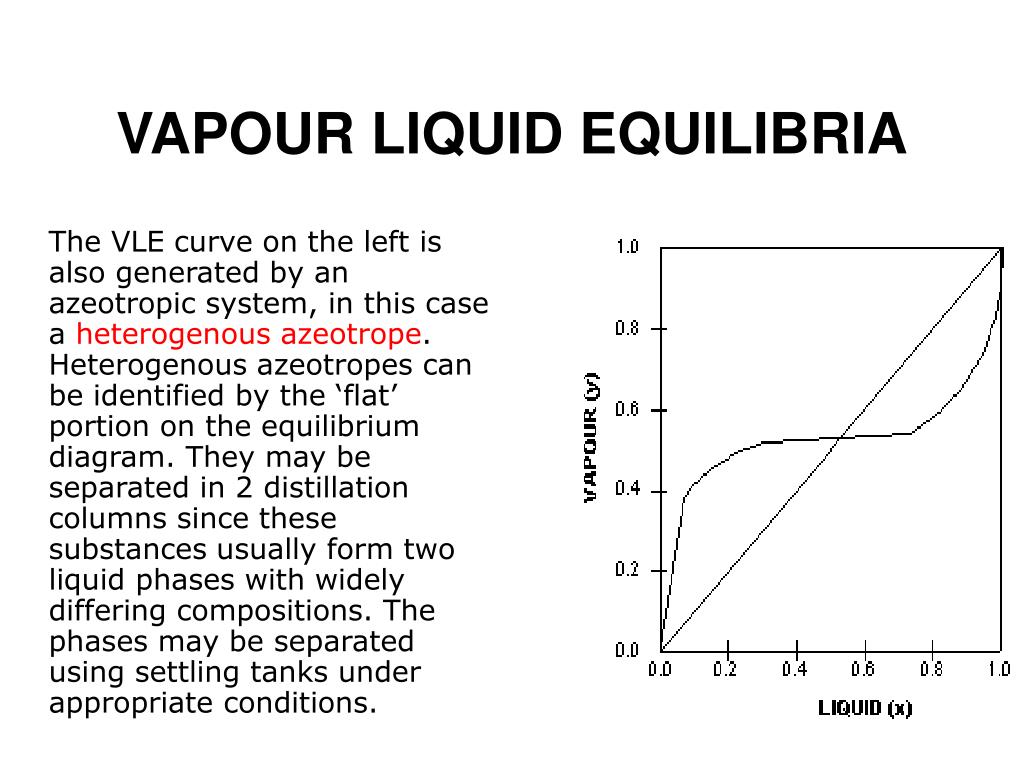



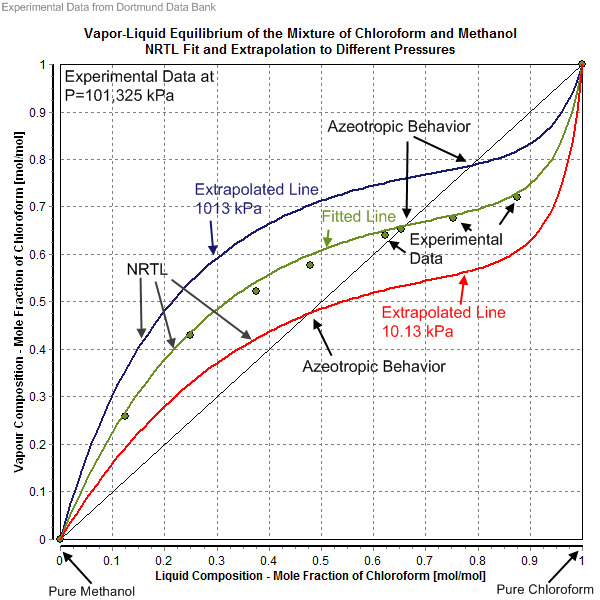

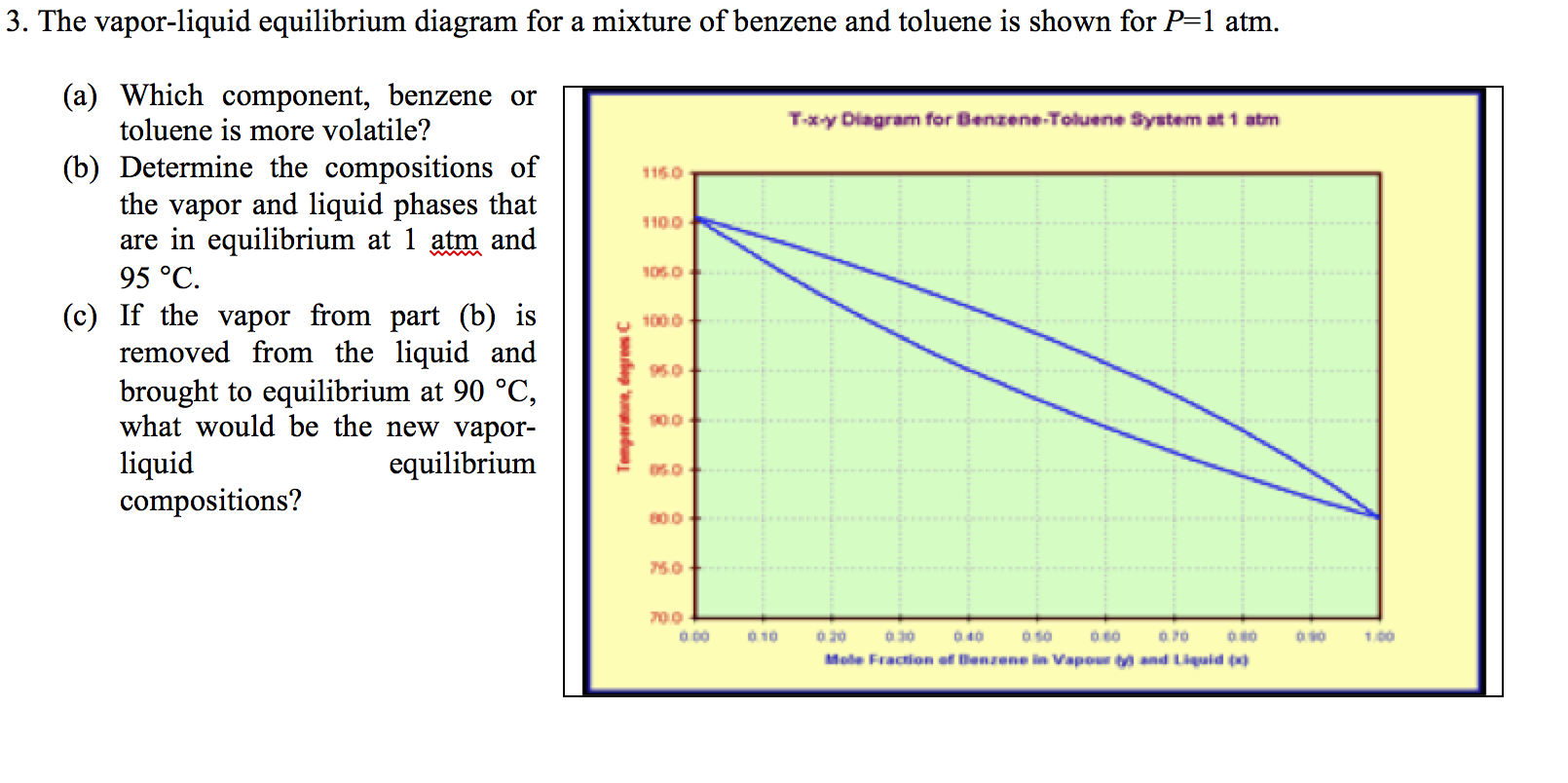
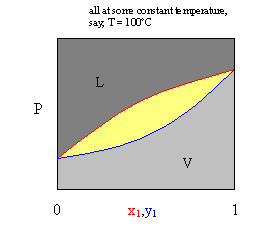
0 Response to "39 Vapour Liquid Equilibrium Diagram"
Post a Comment