39 What Is The Purpose Of The Peptide Bond That Is Shown In The Diagram?
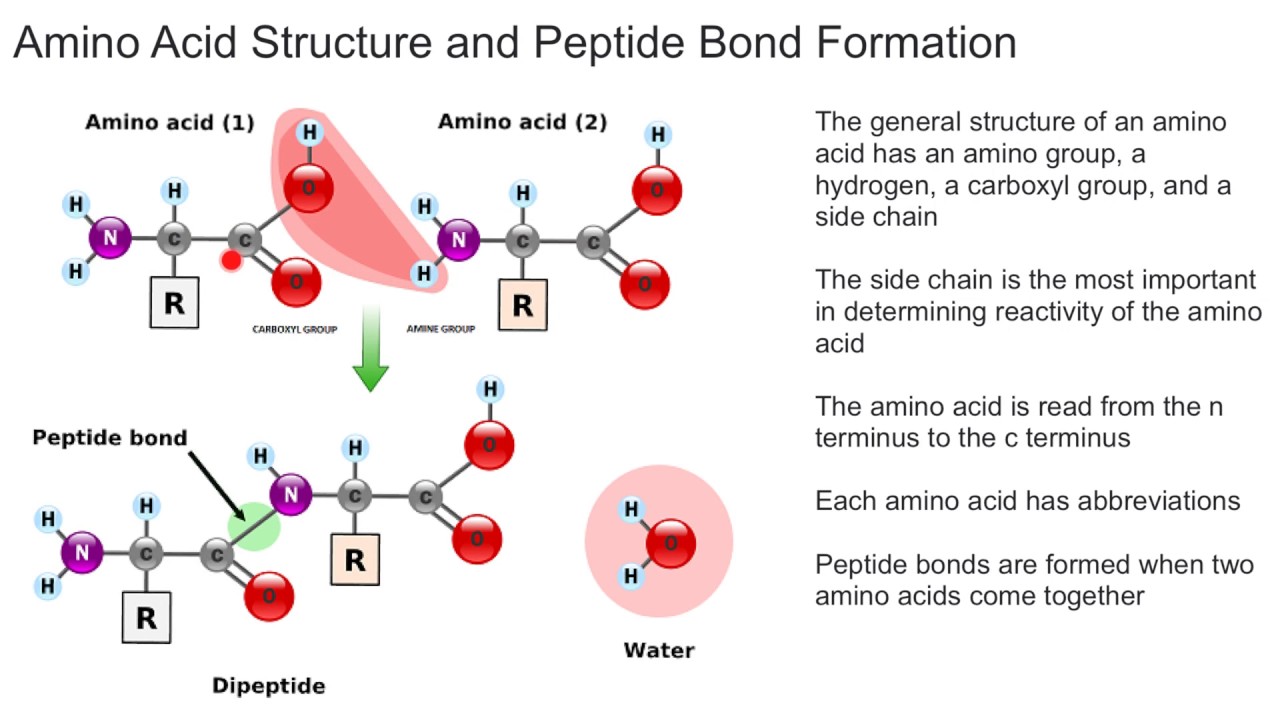
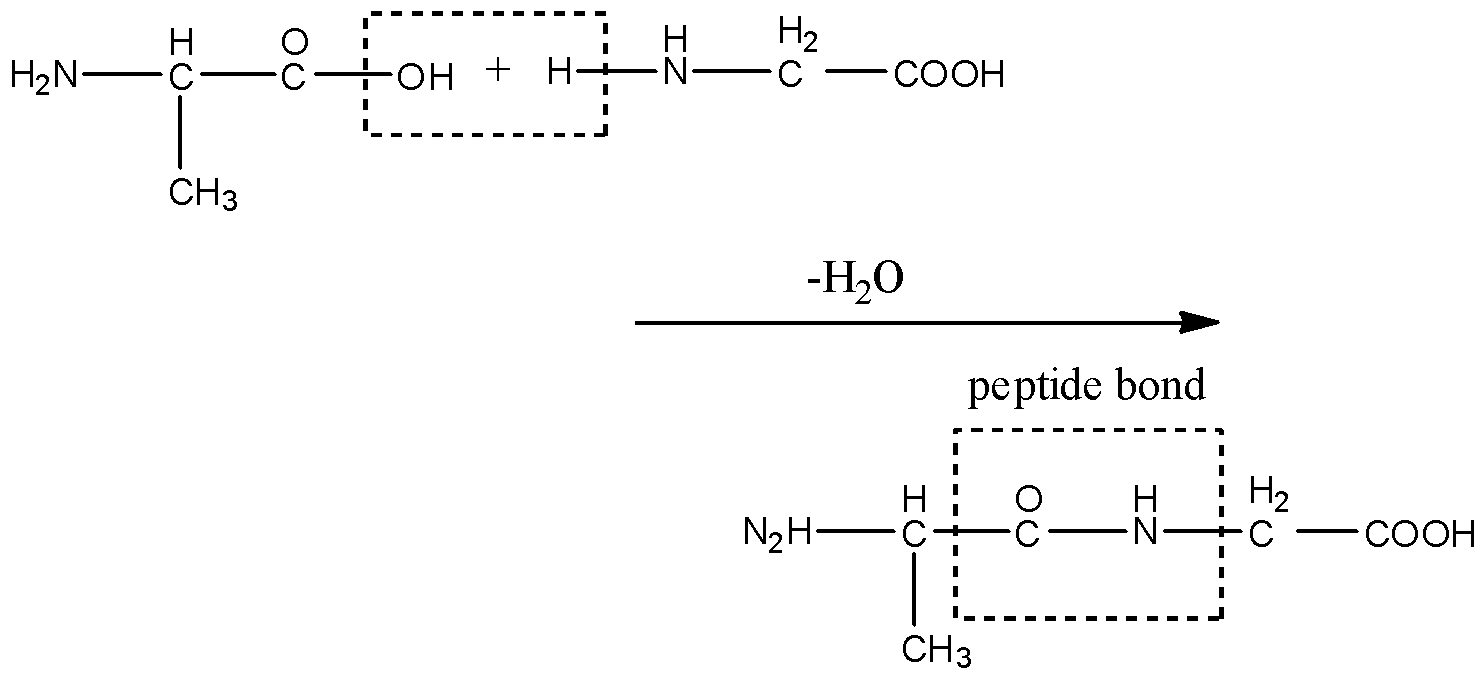
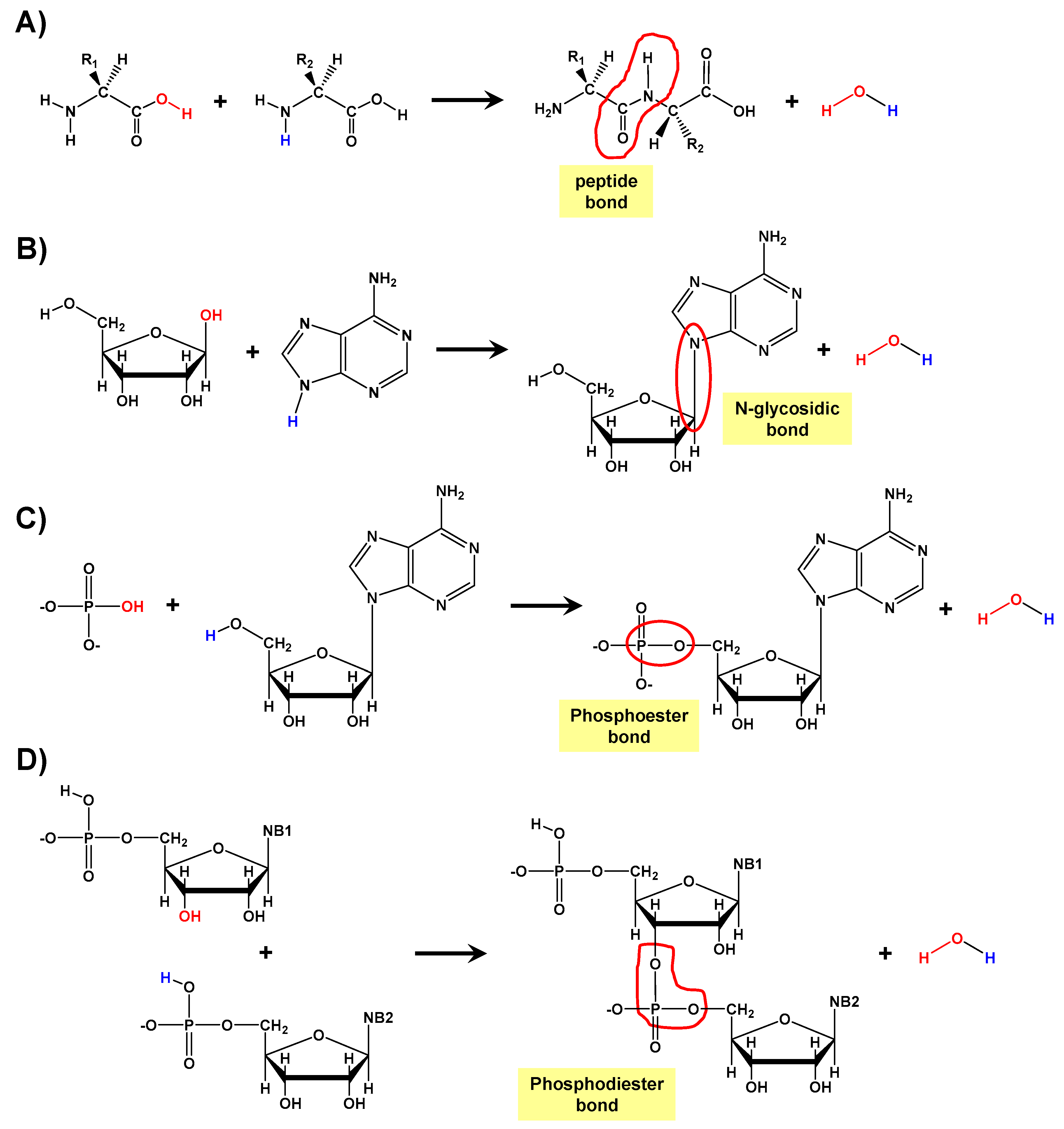
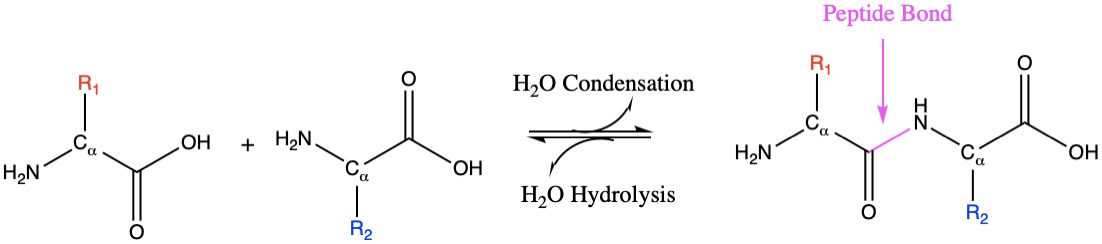
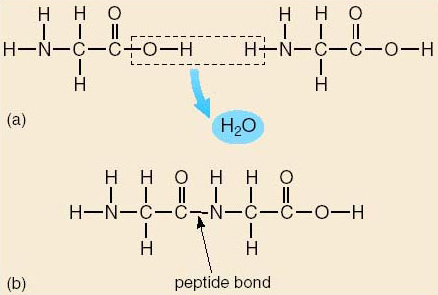
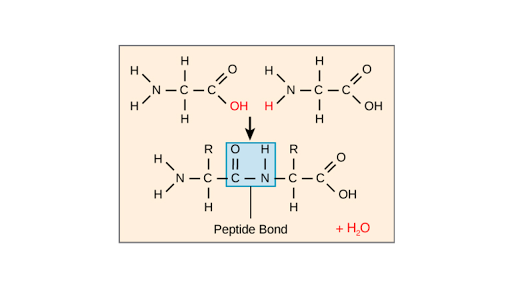
The Peptide Bond (Explained With Diagram) Proteins are composed of one or more chains of amino acids called polypeptides. The neighboring amino acids in the chain are linked together by peptide bonds; these bonds are formed, in effect, by the elimination of one molecule of water from the two amino acids linked by the bond, such that the a. A peptide bond is basically an amide-type of covalent chemical bond. This bond links two consecutive alpha-amino acids from C1 (carbon number one) of one alpha-amino acid and N2 (nitrogen number two) of another. This linkage is found along a peptide or protein chain. During the formation of this bond, there is a release of water (H 2 O) molecules.
The formation of a covalent bond is the result of atoms sharing some electrons. The bond is created by the overlapping of two atomic orbitals [1]. This process is illustrated in Figure 3-4. In this type of bond, each shared electron will be counted toward both atoms’ valence shells for the purpose of satisfying the octet rule.

What is the purpose of the peptide bond that is shown in the diagram?
Nov 24, 2021 · Under these conditions, the peptide was completely soluble, and the resulting disulfide bond was stable (data not shown). Thus, the mixture was loaded on a C18 column. Two isocratic elutions, consisting of (a) 100% H 2 O (3 column volumes) and (b) 100% of 0.5% (v/v) AcOH in H 2 O (3 column volumes), completely removed ammonium trifluoroacetate. The diagram shows one step in the process of protein synthesis. mc015-1.jpg What is the purpose of the peptide bond that is shown in the diagram? It connects amino acids. During transcription, what happens to the RNA polymerase if a repressor protein attaches to the operator? What is the Purpose Of the Peptide Bond that is Shown In the Diagram? what is the purpose of the peptide bond that is shown in what is the purpose of the peptide bond that is shown in the diagram it connects amino acids it connects ribosomes it connects trna it connects anticodons the diagram shows one step in the process of protein the peptide bond is a special type of covalent bond form.
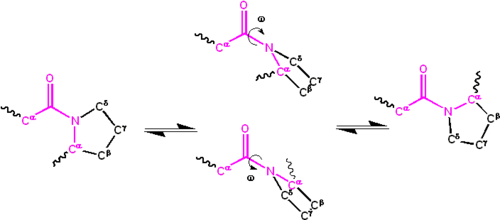
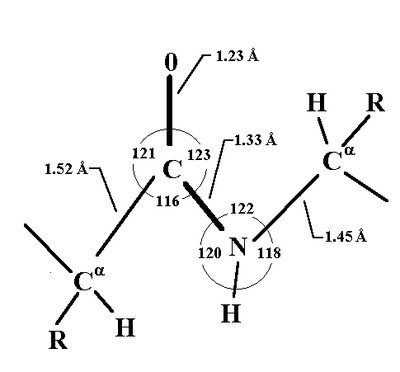
What is the purpose of the peptide bond that is shown in the diagram?. What is the purpose of the peptide bond that is shown in the diagram. When two amino acids form a dipeptide through a peptide bond it is type of condensation reaction. The peptide bond explained with diagram the neighboring amino acids in the chain are linked together by peptide bonds. It connects amino acids during transcription what happens. Matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs), also known as matrix metallopeptidases or matrixins, are metalloproteinases that are calcium-dependent zinc-containing endopeptidases; other family members are adamalysins, serralysins, and astacins.The MMPs belong to a larger family of proteases known as the metzincin superfamily.. Collectively, these enzymes are capable of degrading all kinds of. The figure to the right demonstrates a condensation reaction (dehydration synthesis, loss of water) showing the formation of a covalent peptide bond between two amino acids. In the figure to the left, the amino acids are shown in a generalized form, so the R-groups are only given as R1 and R2. Peptide bond, peptide plane, and the Ramachandran plot. (A) Peptide bond, peptide plane, phi and psi angles, and bond rotation involving two amino acids. The N C α and C α C bonds are not rigid and can freely rotate, being only limited by the size and character of the R-groups. (B) Diagram of a typical Ramachandran plot (φ/ψ plot).
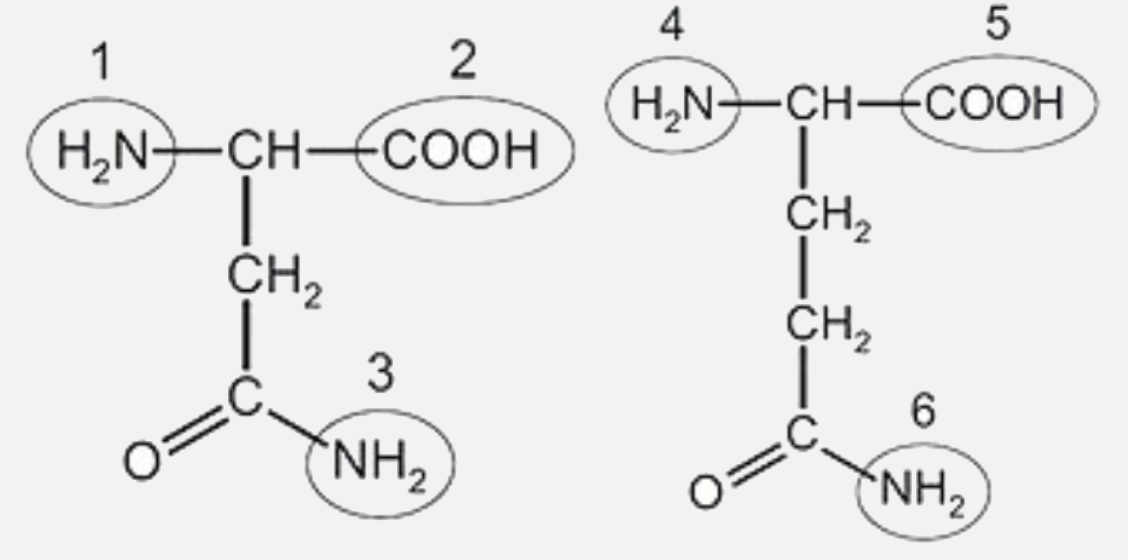
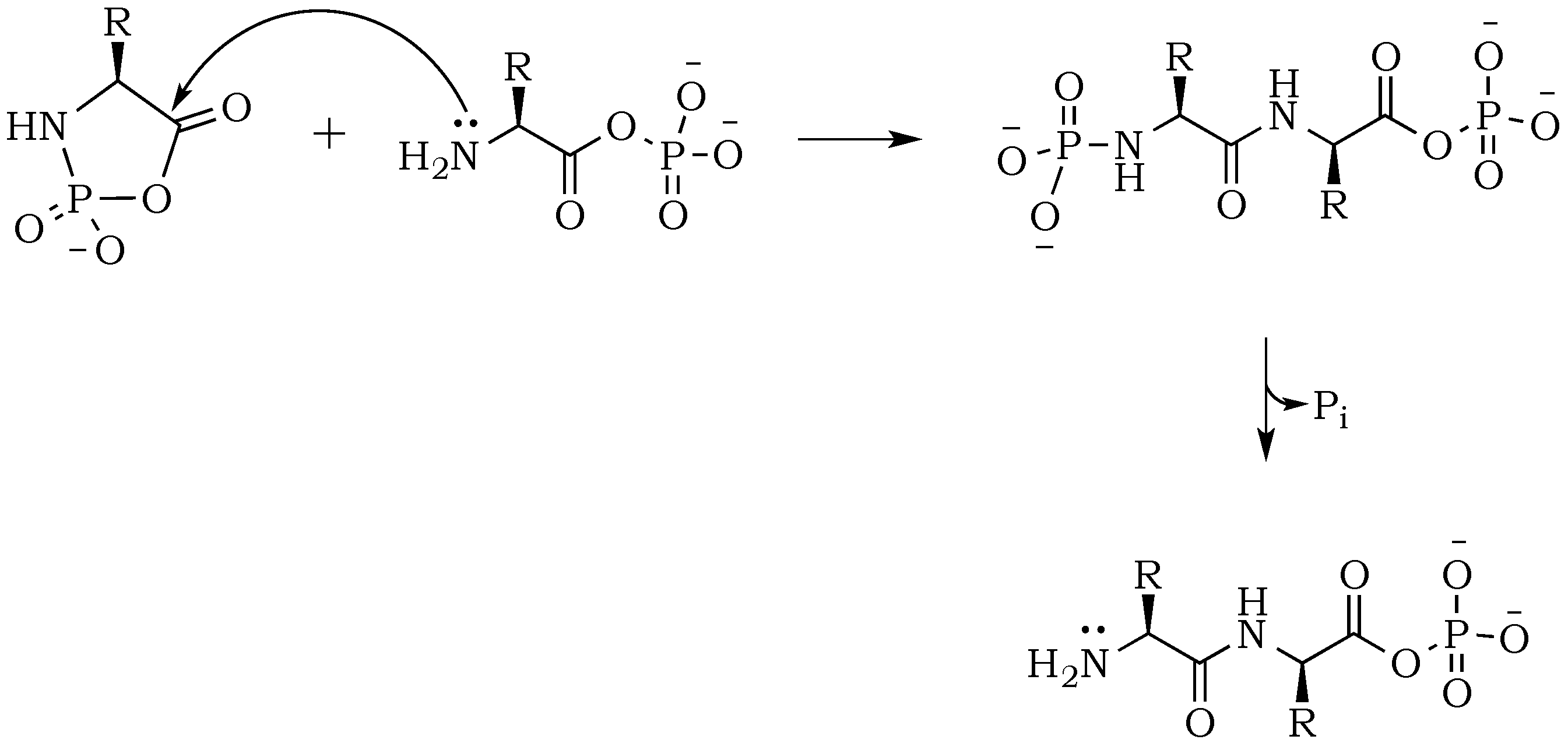
Peptide bond formation. Introduction to proteins and amino acids. Overview of protein structure. Tertiary structure of proteins. Orders of protein structure. This is the currently selected item. Practice: Proteins. Sort by: Top Voted. Tertiary structure of proteins. Proteins. Up Next. Proteins. Q. What is a peptide bond? answer choices. Bond that holds two amino acids together. A bond that holds hydrogen and oxygen molecules together.. Q. The diagram shows a bond forming between two amino acids. What is the name of this reaction? answer choices . Condensation. Hydrolysis. Pepysis. Oxidation. Tags: Question 10 . Which step is shown? transcription. During which process is mRNA converted into a sequence of amino acids for protein production? mRNA synthesis. The diagram shows one step in the process of protein synthesis. mc015-1.jpg. What is the purpose of the peptide bond that is shown in the diagram? it connects amino acids. A peptide bond is a covalent bond linking two amino acids together in a peptide. a. Circle the peptide bond in Model 1. b. Between which two atoms in the dipeptide is the peptide bond located? between C and N. c. Between what two functional groups is the peptide bond located? Carboxyl and amino groups. There are 22 different amino acids found.
Oct 14, 2021 · The structure of amylose, including its glycosidic bond, is shown in Diagram 6. Can you spot the type of glycosidic bond being used to form an amylose chain? It's an O-glycosidic bond. The diagram shows one step in the process of protein synthesis. A step in the process of protein synthesis is shown. A peptide bond is shown. What is the purpose of the peptide bond that is shown in the diagram? It connects amino acids. It connects ribosomes. It connects tRNA. It connects anticodons The peptide bond explained with diagram the neighboring amino acids in the chain are linked together by peptide bonds. Peptide Bond Definition And Formation Biology Dictionary An oxygen atom acts as an electrophile. What is the purpose of the peptide bond that is shown in the diagram. Show transcribed image text shown below is an arrow pushing. 2.2 Peptide Bond Formation and Primary Protein Structure. Within cellular systems, proteins are linked together by a large enzyme complex that contains a mixture of RNA and proteins. This complex is called the ribosome. Thus, as the amino acids are linked together to form a specific protein, they are placed within a very specific order that is.
Vancomycin is an antibiotic medication used to treat a number of bacterial infections. It is recommended intravenously as a treatment for complicated skin infections, bloodstream infections, endocarditis, bone and joint infections, and meningitis caused by methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Blood levels may be measured to determine the correct dose.
Chymotrypsin is a member of a family of enzymes all of which cleave peptide bonds through the action of an active site serine (the serine proteases). This family includes the pancreatic enzymes chymotrypsin, trypsin and elastase as well as a variety of other proteases (e.g. cocoonase, thrombin, acrosomal protease, etc).
This showed a lack of understanding of covalent bonds and hydrogen bonds. The requirement for candidates to know that fatty acids do not dissolve in water because it is polar was questioned in a G2. This would be covered in 3.1.5 under solvent properties of water, 3.2.7 under use of lipids in energy storage and again in 2.4.2 when explaining.
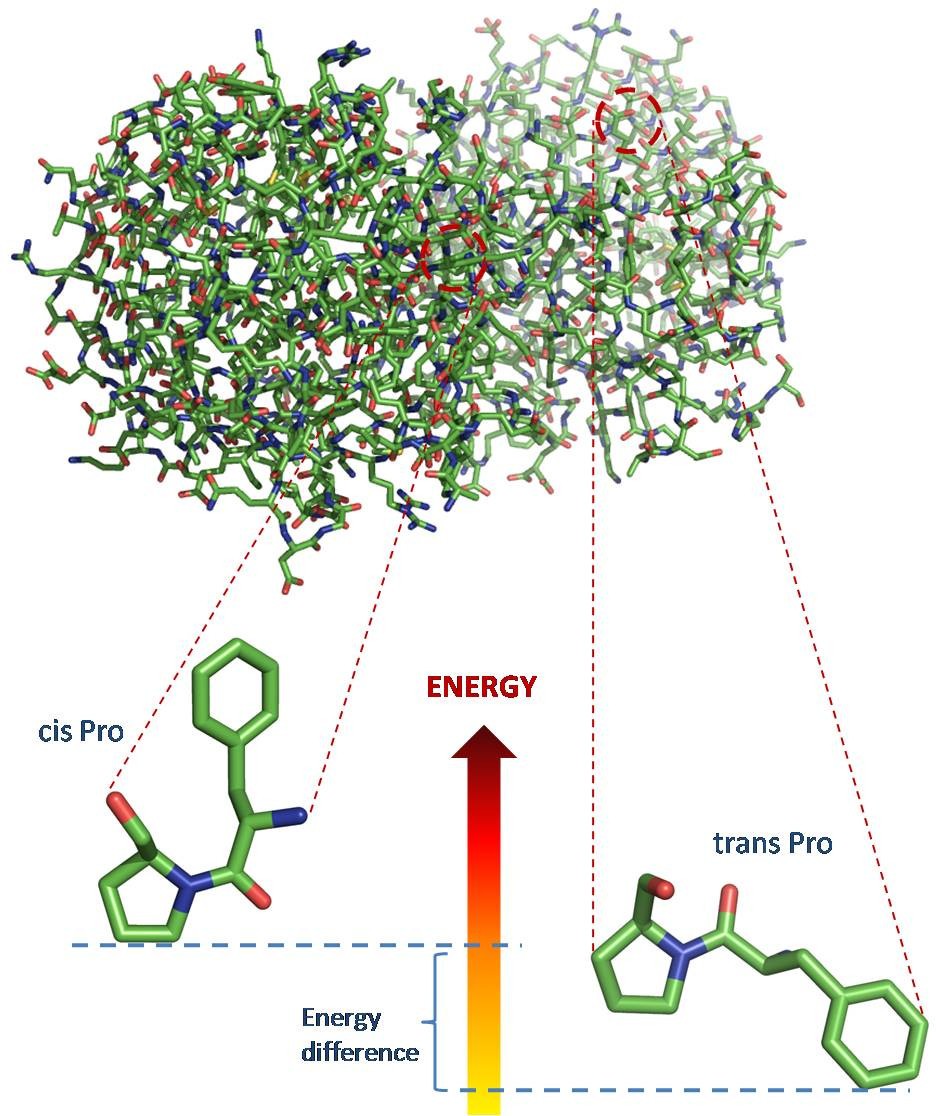
Idealize adjusts peptide bond angles and lengths, such as the ones shown in this diagram. See the text below for a detailed explanation of the features shown in the diagram. The Idealize tool adjusts the lengths and angles of peptide bonds in the protein backbone.The lengths and angles, also known as "degrees of freedom", can vary, but only within a narrow range.
Which type of molecule is shown in the diagram below? A. Peptide B. Carbohydrate C. Lipid. For what purpose is the enzyme lactase useful?... C. Peptide bond D. Semi-conservative bond. What characteristic shows that this steroid molecule is a lipid? A. It is made of carbon rings.
Apr 12, 2019 · Introduction. Bayliss and Starling first described the connection between the pancreas, the gut and incretin hormones in the early part of the twentieth century ().When the incretin hormone glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) was subsequently shown to account for up to 70% of insulin secretion in response to nutrient intake (), its potential as a therapeutic target in type 2 diabetes (T2D) was.
Peptide bonds: special chemical bonds that hold amino acids together ; Carboxyl group: a group of atoms made up of a carbon that is double bonded to an oxygen and is also bound to an oxygen and a.
The right answer is It connects amino acids.. Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins. • There are 21 amino acids, but only one type of binding used to connect them: it is the peptide bond. • The peptide bond is formed during the translation step by a covalent bond between an α-amino group of an amino acid and the carboxylic group of another amino acid.
The tertiary structure of a protein gives a specific three-dimensional shape to the polypeptide chain including interactions and cross-links between different parts of the peptide chain The tertiary structure is stabilized by:hydrophobic and hydrophilic interactions, salt bridges hydrogen bonds and disulfide bonds The primary structure of a protein is the particular sequence of amino acids
V.N. Uversky, in Brenner's Encyclopedia of Genetics (Second Edition), 2013 Chemical Extension of the Genetic Code. Protein synthesis occurs during a process called ‘translation’. Posttranslational modification (PTM) of proteins, being one of the later stages in protein biosynthesis, refers to the reversible or irreversible chemical changes proteins may undergo after translation.
Hydrogen bond HO2C CH2 N H 9. Locate the primary structure of the polypeptide in Model 2. a. Draw an arrow to two different peptide bonds in the diagram. b. Circle three separate amino acids that were joined together to make the polypeptide. 4 POGIL ª Activities for AP* Biology 10.
His57 then donates its extra proton to the γ oxygen of Ser195 as it leaves the substrate acyl carbon, forming the second product and completing the peptide bond hydrolysis. Upon release of the P1 fragment from the enzyme active site, a new peptide substrate can bind to the enzyme, and the hydrolytic mechanism can be reiterated.
Jan 12, 2021 · Nonribosomal peptide synthetases containing starter condensation domains direct the biosynthesis of nonribosomal lipopeptides, which generally exhibit wide bioactivities. The acyl chain has strong.
Peptides & Proteins. 1. The Peptide Bond. If the amine and carboxylic acid functional groups in amino acids join together to form amide bonds, a chain of amino acid units, called a peptide, is formed. A simple tetrapeptide structure is shown in the following diagram. By convention, the amino acid component retaining a free amine group is drawn.
What is the Purpose Of the Peptide Bond that is Shown In the Diagram? what is the purpose of the peptide bond that is shown in what is the purpose of the peptide bond that is shown in the diagram it connects amino acids it connects ribosomes it connects trna it connects anticodons the diagram shows one step in the process of protein the peptide bond is a special type of covalent bond form.
The diagram shows one step in the process of protein synthesis. mc015-1.jpg What is the purpose of the peptide bond that is shown in the diagram? It connects amino acids. During transcription, what happens to the RNA polymerase if a repressor protein attaches to the operator?
Q. What is the bond labeled 5 known as? answer choices. a peptide bond. a hydrogen bond. an ionic bond. a carboxyl bond. Tags: Question 8 . SURVEY . 30 seconds . Report an issue . Q. The diagram represents a step in protein synthesis. If a sequence of nitrogenous bases on DNA strand I is T-A-G-C-C-T-A, the corresponding sequence on the RNA.
Apr 10, 2013 · The use of organic solvents during trypsin digestion has been shown to improve digestion efficiency based on peptide identifications, protein sequence coverage, and trypsin specificity on protein complex purifications 78–79 and complex proteomic mixtures. 80 SDS remains one of the best protein solubilizers, but is detrimental to LC-MS peptide.
A tRNA molecule with the appropriate anti-codon then attaches at the starting point and this is followed by a series of adjacent tRNA attachments, peptide bond formation and shifts of the ribosome along the mRNA chain to expose new codons to the ribosomal chemistry. The following diagram is designed as a slide show illustrating these steps.
The left diagram is a projection on the plane of the H-bonded N-H···O=C groups of the ß-sheet and the right diagram is a projection of the same part of the protein rotated by about 90° along the Y-axis of the figure. The first set of four peptides is shown starting at the N-terminal of the protein.
What is the purpose of the peptide bond that is shown in the diagram? - 7611651 kirti4858 kirti4858 13.01.2019 Biology Secondary School answered The diagram shows one step in the process of protein synthesis. What is the purpose of the peptide bond that is shown in the diagram? 1 See answer Advertisement Advertisement kirti4858 is waiting for.
Nov 24, 2021 · Under these conditions, the peptide was completely soluble, and the resulting disulfide bond was stable (data not shown). Thus, the mixture was loaded on a C18 column. Two isocratic elutions, consisting of (a) 100% H 2 O (3 column volumes) and (b) 100% of 0.5% (v/v) AcOH in H 2 O (3 column volumes), completely removed ammonium trifluoroacetate.



















0 Response to "39 What Is The Purpose Of The Peptide Bond That Is Shown In The Diagram?"
Post a Comment