39 O2 2- Mo Diagram
Oxygen is an element displayed by the symbol O, and atomic number 8. It is an essential element for human survival. Decreased oxygen levels may be treated with medical oxygen therapy. Treatment with oxygen serves to increase blood oxygen levels and also exerts a secondary effect of decreasing blood flow resistance in the diseased lung, leading to decreased cardiovascular workload in an attempt. CeO2 is Fluorite structured and crystallizes in the cubic Fm-3m space group. The structure is three-dimensional. Ce4+ is bonded in a body-centered cubic geometry to eight equivalent O2- atoms. All Ce–O bond lengths are 2.37 Å. O2- is bonded to four equivalent Ce4+ atoms to form a mixture of edge and corner-sharing OCe4 tetrahedra.
About Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy & Safety How YouTube works Test new features Press Copyright Contact us Creators.

O2 2- mo diagram
Relative AO Energies in MO Diagrams Use AO energies to draw MO diagram to scale (more or less). H He Li Be B C N O F Ne B C N O F Ne Na Mg Al Si P S Cl Ar Al Si P S Cl Ar 1s 2s 2p 3s 3p -19.4 eV -15.8 eV -32.4 eV -10.7 eV TDmeph IRSN Mephista nuclear database (0) TDnucl IRSN Nuclea nuclear database (0) SpMCBN Spencer Group M-C-N-B-Si alloys (837) MO-Schema O 2-(Superoxid)Energie 2p 2s 1s 1s * 1s b 2p 1s 2s b 2s * 2s b p x b p z *p x. Title: PowerPoint-Präsentation Author: A.Kelling Created Date: 6/30/2011 9:20:45 AM
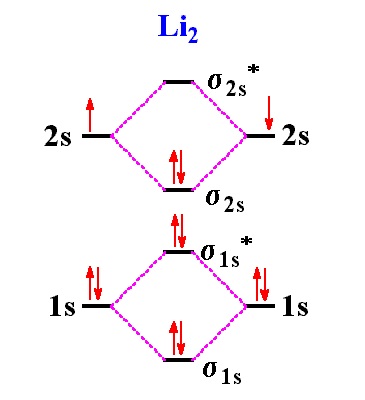
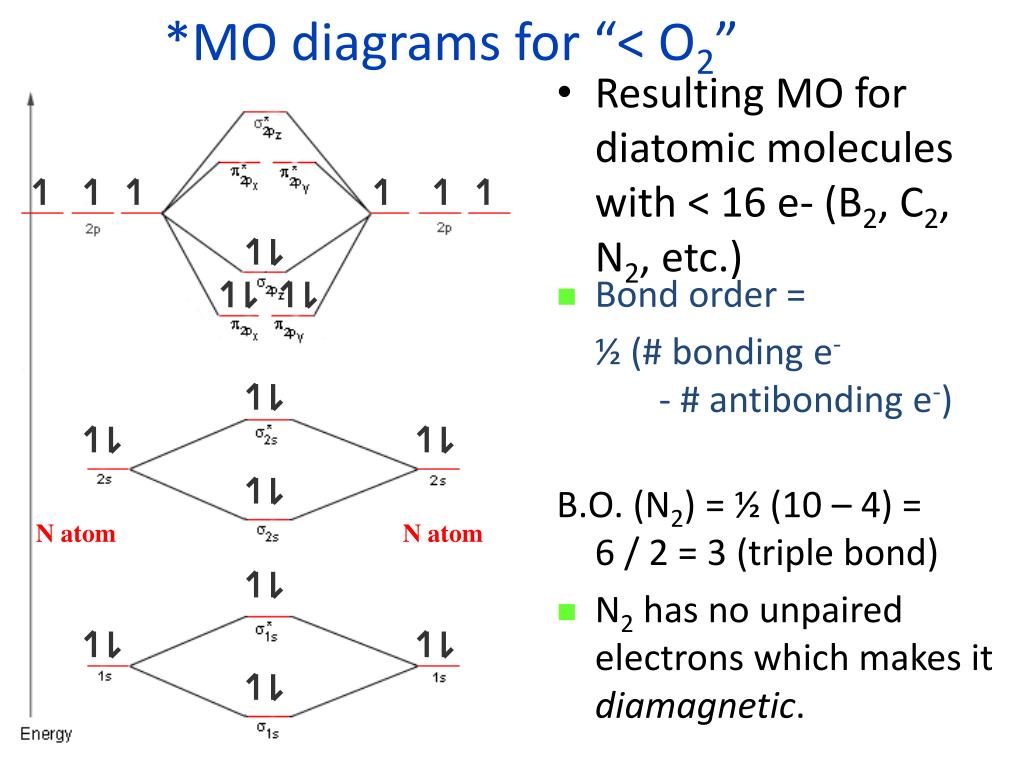
O2 2- mo diagram. Learn about the molecular orbital diagram for O2 using these free and printable molecular orbital diagram as your reference in understanding the MO of oxygen. A collection of printable MO diagram is available for you to help you study more about the topic. The following diagrams contain the MO of oxygen and you can get the picture by clicking on the image. Follow me on instagram-https://www.instagram /trickychemistrysuman/?hl=enFollow me on facebook page-https://lm.facebook /l.php?u=https%3A%2F%2Ffb.me%2F... Answer (1 of 6): Here is the solution, > * For O2 molecule, > * For F2 molecule, Thanks for reading. Show activity on this post. I have been taught that the MO diagram is different for molecules with 14 or less electrons than the one used for molecules with 15 or more electrons. For N X 2 the orbitals in increasing energy are: σ 1 s < σ 1 s ∗ < σ 2 s < σ 2 s ∗ < π 2 p x, π 2 p y < σ 2 p z < π 2 p x ∗, π 2 p y ∗ < σ 2 p z ∗.
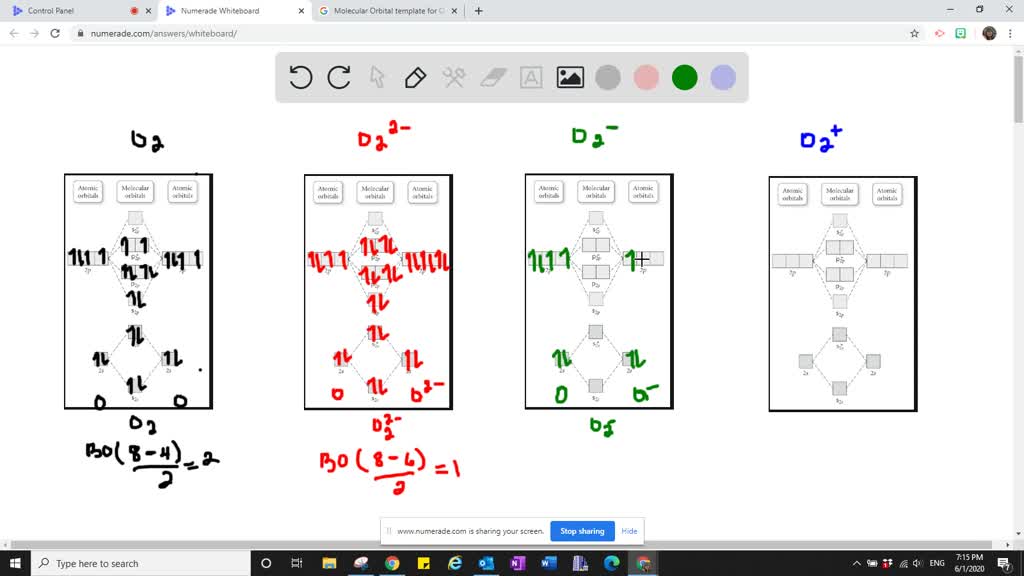
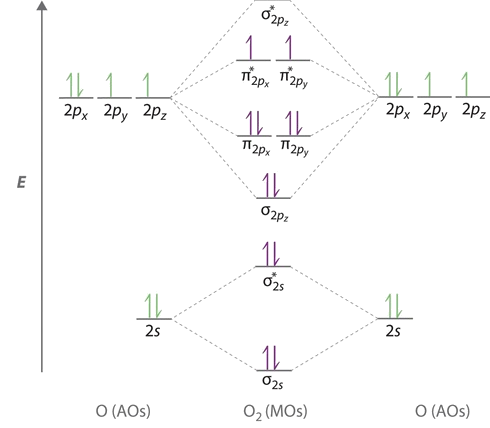
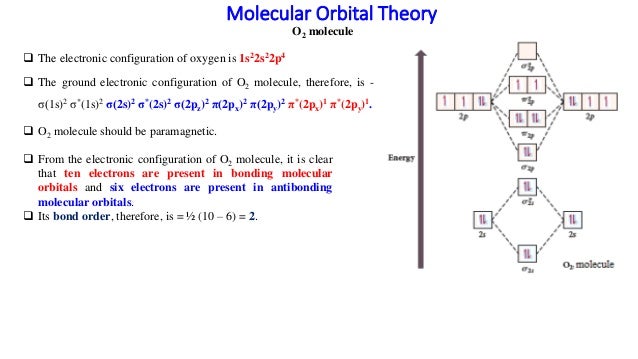
Molecular orbital diagram of b2. Bo 1 2 bonding e anti bonding e 1 2 8 4 2 lcao mo theory also predicts correctly that o2has two unpaired electrons. Molecular electron configuration for o2 σ2σ2σ2π4π2 we can also calculate the oo bond order. Molecular orbital diagrams of diatomic molecules draw the lewis structure for the following molecules. Electronic structure of oxygen atom is Leaving out the 4 electrons in the 1s orbitals of two oxygen atoms constituting the molecule (represented as KK), the molecular orbital energy diagram for remaining 12 electrons of oxygen as molecule is shown:(i) Electronic configuration:(ii) Bond order: Here Nb = 8; Na = 4The two oxygen atoms in a molecule of oxygen are united through two covalent bonds. There are two MO diagrams you need to memorize for diatoms (N2, O2, Ne2, etc). One is for the elements up to Nitrogen. The other is for AFTER nitrogen. The correlation diagrams for nitrogen and carbon monoxide and the first are nearly parallel to the corresponding orbital energy curves. Bond order for N2 is 3; bond order for N2- is and bond. MO-Schema O 2-(Superoxid)Energie 2p 2s 1s 1s * 1s b 2p 1s 2s b 2s * 2s b p x b p z *p x. Title: PowerPoint-Präsentation Author: A.Kelling Created Date: 6/30/2011 9:20:45 AM
O2 is alpha oxygen-like structured and crystallizes in the monoclinic C2/m space group. The structure is zero-dimensional and consists of eight hydrogen peroxide molecules. O is bonded in a single-bond geometry to one O atom. The O–O bond length is 1.23 Å. TDmeph IRSN Mephista nuclear database (0) TDnucl IRSN Nuclea nuclear database (0) SpMCBN Spencer Group M-C-N-B-Si alloys (837) Molecular Orbital Diagram for Oxygen Gas (O2).Fill from the bottom up, with 12 electrons total.Bonding Order is 2, and it is Paramagnetic.sigma2s(2),sigma2s*... A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) method in particular. A fundamental principle of these theories is that as atoms bond to form molecules, a certain number of atomic orbitals combine to form the same number of.
Molecular orbital diagram for o2 2. Bonding order is 2 and it is paramagnetic. Which would be paramagnetic and which would be diamagnetic. Submit just now. This site might help you. Information from the mo diagram justify o2s stability and show that its bonding order is 2. Sketch the molecular orbital energy level diagram for o2 2.
Nov 20, 2021 · SO2 Molecular Orbital Diagram. The molecular orbital diagram of SO2 is attached below: A molecular orbital diagram gives us an idea about how the atomic orbitals of two different atoms can fuse and give rise to a new orbital. This further helps us to find out the bond order, bond length, and bond strength of any compound. In this MO we can see.
Answer (1 of 3): I modified the picture from this post: What's the MOT diagram of O2 +2 ion? and modified it to be O2 2+ (since sadly enough I am about as advanced with artistic programs on pc as a rock). How you basically do these questions is by first drawing the empty AO and MO, then counting.
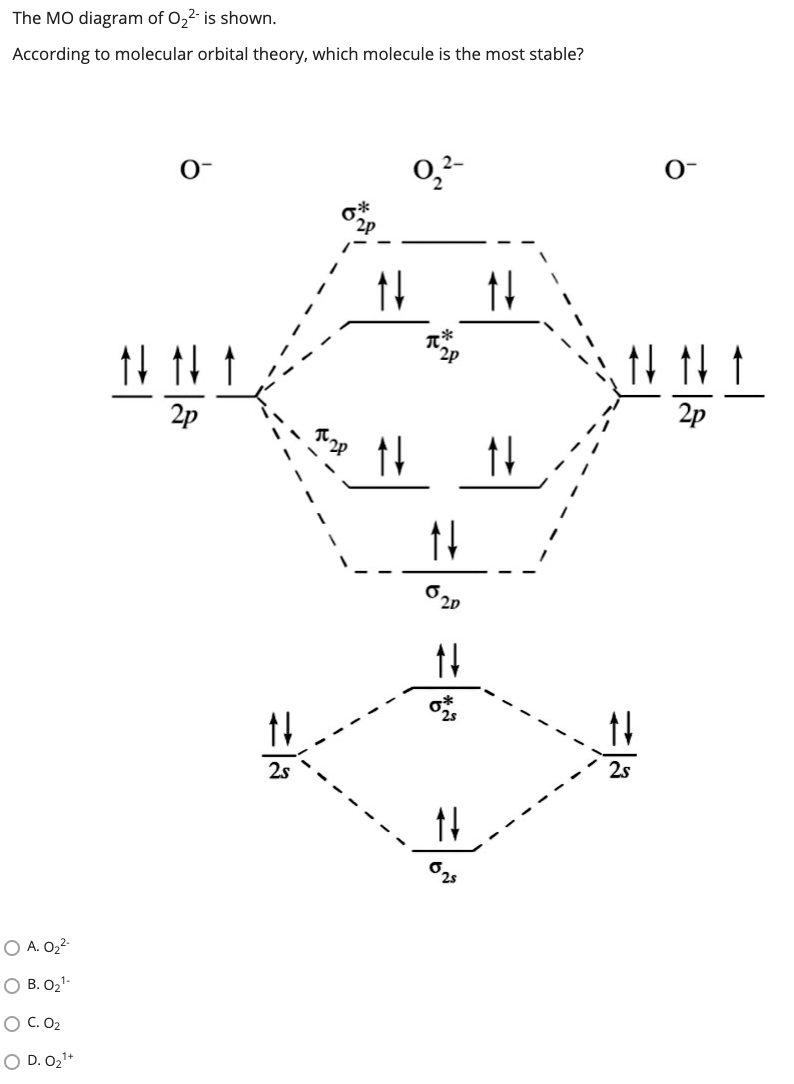
Bond order (B.O) 1/2 × [Number of an electron in antibonding molecular orbitals] – [Number of electrons in bonding molecular orbitals] The higher the order of the bond the greater the pull between the two atoms and the shorter the length of the bond. (1) B.O for O 2 = 1/2 × [10 – 6] B.O for O 2 = 2 (2) B.O for O 2 – = 1/2 × [10 – 7]
A molecular orbital explicitly describes the spatial distribution of a single electron orbitals, and σ∗. 1s is higher in energy. Draw this out using an energy level diagram: 2 He2 has bond order 0 [ (2 − 2)/2 = 0], and we can make H+. 2,. H−.A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical.
Oxygen is the chemical element with the symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group in the periodic table, a highly reactive nonmetal, and an oxidizing agent that readily forms oxides with most elements as well as with other compounds.Oxygen is Earth's most abundant element, and after hydrogen and helium, it is the third-most abundant element in the universe.
2- = Molecular orbital for N2, N2+, O2, H2 and He2 by Thomas Wells - December 5, Brian Verfuerth 0. Ozone Lewis diagrams and by avatar Claire Bridget. The correlation diagrams for nitrogen and carbon monoxide and the first are nearly parallel to the corresponding orbital energy curves.
Remember: When two oxygen atoms bond, the pi(2p) bonding molecular orbitals are lower in energy than the sigma(2p) bonding orbitals. They are flipped compare...
The MO diagram for "NO" is as follows (Miessler et al., Answer Key): (The original was this; I added the orbital depictions and symmetry labels. For further discussion on the orbital energy ordering being "N"_2-like, see here and comments.) Quick overview of what the labels correspond to what MOs: 1a_1 is the sigma_(2s) bonding MO. 2a_1 is the sigma_(2s)^"*" antibonding MO. 1b_1 is the pi_(2p.
1 Answer. Truong-Son N. Apr 25, 2018. (σ2s)2(σ* 2s)2(σ2pz)2(π2px)2(π2py)2(π* 2px)1. Your first answer option is for N− 2. Your second answer option is for O+ 2. Your third answer option is for N2. You should be able to draw the MO diagram for N− 2 given the information below. You'll need the molecular orbital (MO) diagram of O2.
About Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy & Safety How YouTube works Test new features Press Copyright Contact us Creators.
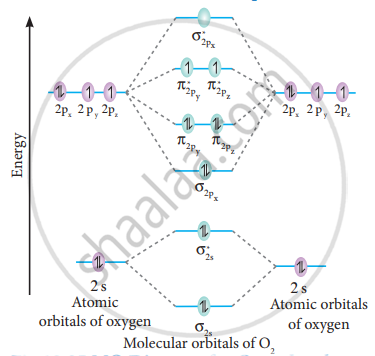
This phenomenon is explained by s-p mixing. All the elements in the second period before oxygen have the difference in energy between the 2s and 2p orbital small enough, so that s-p mixing (combination) can occur lowering the energy of the σ(2s) and σ*(2s) and increasing the energy of the σ(2p) and σ*(2p) molecular orbitals.
Answer (1 of 4): The atomic number of fluorine is 9, so a (neutral) F2 molecule has a total of 18 electron, or 14 valence electrons (excluding the four 1s electrons). The (F2)- ion has one more valence electron, or 15. The orbital diagram for a diatomic molecule is To find the bond order, add th...
It is sigma2s(2)sigma2s*(2)sigma2p(2)pi2p(4)pi2p*(4)Bond order 1. It is stable. In fact, it's the perioxide ion.Check me out: http://www.chemistnate
Relative AO Energies in MO Diagrams Use AO energies to draw MO diagram to scale (more or less). H He Li Be B C N O F Ne B C N O F Ne Na Mg Al Si P S Cl Ar Al Si P S Cl Ar 1s 2s 2p 3s 3p -19.4 eV -15.8 eV -32.4 eV -10.7 eV
Answer (1 of 4): O2^+2 means it loses 2 e-,there are 4 e- in p_orbitals.According to MOT(molecular orbital theory) 6 e- are in bonding molecular orbitals BMO and 2 e- are in antibonding molecular orbitals ABMO Formula to find bond order is No.of e in BMO — NO. of e in ABMO/2 So, if we calculat...
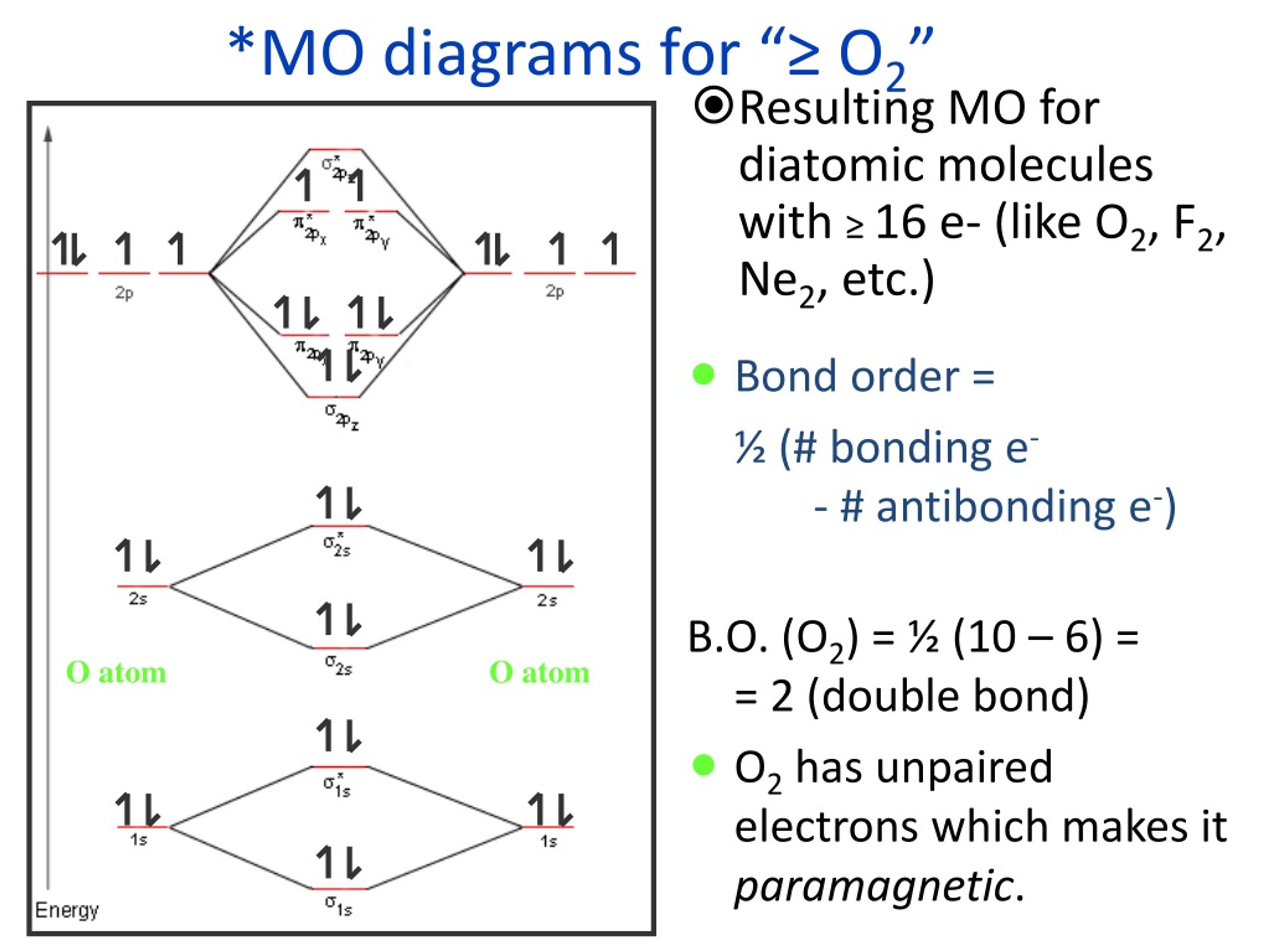
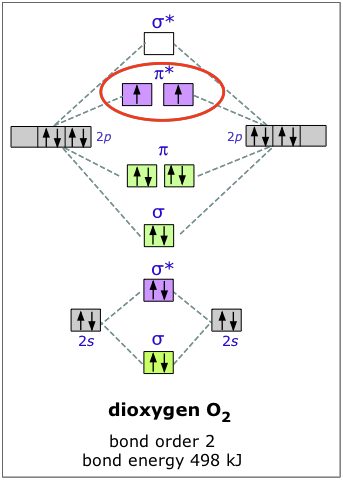
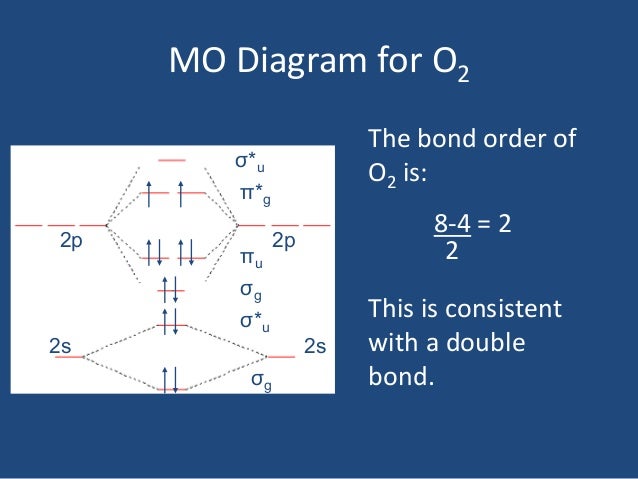
MO diagrams explain why some molecules exist and others do not. By looking at the O2 molecular orbital diagram, we can see that oxygen has BO of 2 because it has 10 bonding and 6 anti-bonding. Experiments show that each O2 molecule has two unpaired electrons. We can also notice the magnetic property of diamagnetic or paramagnetic.
Molecular orbital (MO) theory explains the construction of molecular orbital diagram on the basis of following main points. 1.Formation of MOs: Atomic orbitals(AOs) linearly combine with each other to form equal number of molecular orbitals (MOs). 2.Energy of MOs: Half of the molecular orbitals (MOs) having energy lower than the atomic orbitals are called…
Some Species With Two Oxygen Atoms Only Are The Oxygen Molecule Mathrmo 2 The Peroxide Ion Mathrmo 2
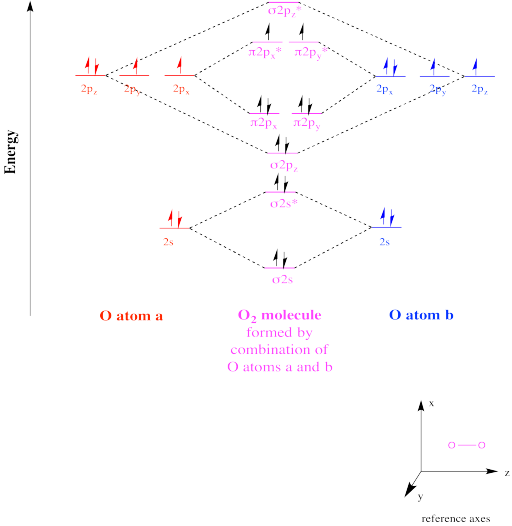
Molecular Orbitals of the Second Energy Level. The 2s orbitals on one atom combine with the 2s orbitals on another to form a 2s bonding and a 2s * antibonding molecular orbital, just like the 1s and 1s * orbitals formed from the 1s atomic orbitals. If we arbitrarily define the Z axis of the coordinate system for the O 2 molecule as the axis along which the bond forms, the 2p z orbitals on the.
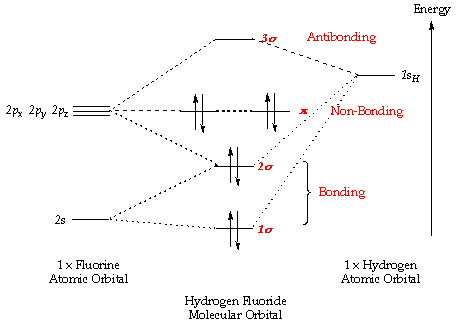
MO Diagram for HF The AO energies suggest that the 1s orbital of hydrogen interacts mostly with a 2p orbital of fluorine. The F 2s is nonbonding. H–F nb σ σ* Energy H –13.6 eV 1s F –18.6 eV –40.2 eV 2s 2p So H–F has one σ bond and three lone electron pairs on fluorine
Answer (1 of 3): I modified the picture from this post: What's the MOT diagram of O2 +2 ion? and modified it to be O2 2+ (since sadly enough I am about as advanced with artistic programs on pc as a rock). How you basically do these questions is by first drawing the empty AO and MO, then counting.
This problem has been solved! See the answer. See the answer See the answer done loading. Draw MO diagram, give MO configuration, state bond order and whether it is para/diamagnetic for each: O 2-1, B 2+1 , CO +1. Show transcribed image text.
Nov 27, 2021 · Molecular Orbital (MO) Diagram of O2. The molecular orbital diagram shows the energy state at each level where the excited state increases from the bottom to the top. The left-hand side diagram is of O2 at ground level whereas the right-hand side diagram is of rearranged electrons as per the Lewis structure within the O2 molecule.
As it can be seen from the MOT of O 2 , The electrons in the highest occupied molecular orbital are unpaired therefore it is paramagnetic in nature. Also, the bond order can be calculated as [N b − N a ] / 2 = [1 0 − 6] / 2 = 2. Therefore there is a double bond present as O = O.















0 Response to "39 O2 2- Mo Diagram"
Post a Comment