43 Simple Krebs Cycle Diagram
The Krebs cycle, also known as the Citric Acid cycle, is a very important process in cellular respiration. Without this portion, respiration would not be possible. This is because the Krebs cycle uses the pyruvate molecules from glycolysis to produce high energy molecules essential for the electron transport chain (ETC) which follows soon after. Krebs Cycle - Cellular Respiration. OVERVIEW. The Krebs cycle, also known as the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle or citric acid cycle, is the series of chemical reactions that generates energy through the oxidation of acetate. It was identified in 1937 by Hans Krebs, who was responsible for elucidating most of the pathway.
Krebs Cycle Steps. It is an eight-step process. Krebs cycle takes place in the matrix of mitochondria under aerobic condition. Step 1: The first step is the condensation of acetyl CoA with 4-carbon compound oxaloacetate to form 6C citrate, coenzyme A is released. The reaction is catalysed by citrate synthase.
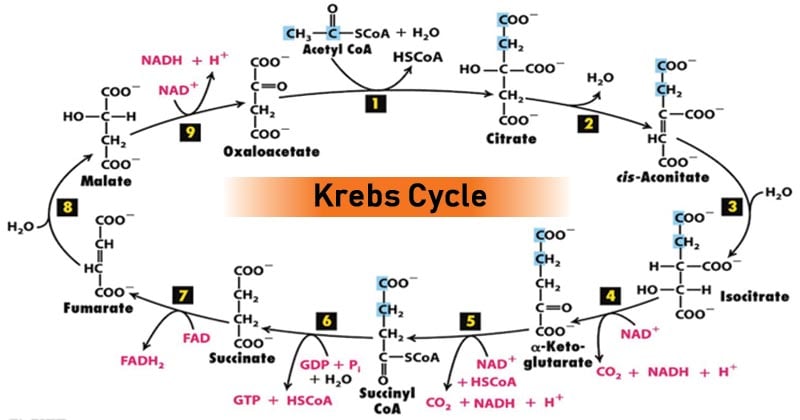
Simple krebs cycle diagram
The 2 carbons from pyruvate make up the acetyl part of acetylCoA. CoA is a big molecule that acts just as a carrier.) 3. Krebs Cycle. (2 AcetylCoA + 6 NAD + 2 FAD + 2 ADP + 2Pi -->. 4 CO2 + 6 NADH + 2 FADH2 + 2 ATP + 2 CoA + heat) 4. ETC. ( 10 NADH + 2 FADH2 + 34 ADP + 34 Pi + 6 O2-->. glycolysis: The cellular degradation of the simple sugar glucose to yield pyruvic acid and ATP as an energy source. The citric acid cycle, shown in —also known as the tricarboxylic acid cycle (TCA cycle) or the Krebs cycle—is a series of chemical reactions used by all aerobic organisms to generate energy through the oxidation of acetate. The Krebs cycle is the second stage of aerobic respiration, the first being glycolysis and last being the electron transport chain; the cycle is a series of stages that every living cell must undergo in order to produce energy. The enzymes that cause each step of the process to occur are all located in the cell's "power plant"; in animals, this power plant is the mitochondria; in plants, it is.
Simple krebs cycle diagram. The Krebs cycle (named after Hans Krebs) is a part of cellular respiration. The diagram below shows how this part of respiration is an ever-repeating cycle. a) Krebs cycle ccurs in matrix of mitochondria. The diagram below is a very simple outline of the Krebs Cycle showing the removal of CO2, and the making of 3. One cycle of the electron transport chain yields about 30 molecules of ATP (Adenosine triphosphate) as compared to the 2 molecules produced each via glycolysis and the citric acid cycle. The electron transport chain is made up of a series of spatially separated enzyme complexes that transfer electrons from electron donors to electron receptors. Krebs Cycle: The Krebs cycle yields six NADH, two FADH 2, and two ATP molecules.. Hope this article on simple cellular respiration diagram has helped you understand the process well. The process of cellular respiration is a very complex reaction that involves many enzymes, coenzyme, and molecules. Each and every step is a series of complex... Sep 07, 2011 · the Krebs cycle. b. lactic acid fermentation. d. the electron transport chain. Fill in the in the blanks within the diagram of respiration below. The terms you will need to use are: Kreb’s cycle, fermentation, mitochondria, cell membrane, cytoplasm, glucose and pyruvic acid... energy to convert carbon dioxide and water into simple sugars ...
Free Energy from Hydrolysis of ATP Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is the energy currency of life and it provides that energy for most biological processes by being converted to ADP (adenosine diphosphate). Since the basic reaction involves a water molecule, ATP + H 2 O → ADP + P i. this reaction is commonly referred to as the hydrolysis of ATP.The change in Gibbs free energy in the reaction is. The Krebs cycle is the second stage of aerobic respiration, the first being glycolysis and last being the electron transport chain; the cycle is a series of stages that every living cell must undergo in order to produce energy. The enzymes that cause each step of the process to occur are all located in the cell's "power plant"; in animals, this power plant is the mitochondria; in plants, it is. The vector stencils library "Citric acid cycle (TCA cycle)" contains 26 symbols of metabolites for drawing metabolic pathway maps and biochemical shematic diagrams of the citric acid cycle (TCA cycle, tricarboxylic acid cycle, Krebs cycle) and diagrams of metabolism processes. "The citric acid cycle - also known as the tricarboxylic acid cycle (TCA cycle), or the Krebs cycle, - is a series of. I have an exam tomorrow and would like a simple review of glycolysis cycle Molecules in Citric Cycle NADH: An energy shuttle which delivers high-energy electrons to the electron transport chain where they will eventually power the production of 2 to 3 ATP molecules.
JOIN our channel for LECTURE HANDOUT & FLASHCARDS New Video on GLYCOLYSIS TRICK : https://youtu.be/C5wNfdWr4tkKREBS CYCLE MADE EASY.The Krebs cycle (named a... Step 1. In the first step of the citric acid cycle, acetyl joins with a four-carbon molecule, oxaloacetate, releasing the group and forming a six-carbon molecule called citrate. Step 2. In the second step, citrate is converted into its isomer, isocitrate. The Krebs cycle is simply another name for the Citric Acid Cycle, so named for the researcher who identified the complete cycle in 1937. This cycle describes a series of chemical reactions that. The citric acid cycle (CAC) – also known as the TCA cycle (tricarboxylic acid cycle) or the Krebs cycle – is a series of chemical reactions to release stored energy through the oxidation of acetyl-CoA derived from carbohydrates, fats, and proteins.The TCA cycle is used by organisms that respire (as opposed to organisms that ferment) to generate energy, either by anaerobic respiration or.
The Krebs cycle uses the two molecules of pyruvic acid formed in glycolysis and yields high-energy molecules of NADH and flavin adenine dinucleotide (FADH 2 ), as well as some ATP. The Krebs cycle occurs in the mitochondrion of a cell (see Figure 6-1). This sausage-shaped organelle possesses inner and outer membranes and, therefore, inner and.
The TCA cycle is a central pathway that provides a unifying point for many metabolites, which feed into it at various points. It takes place over eight different steps: Step 1: Acetyl CoA (two carbon molecule) joins with oxaloacetate (4 carbon molecule) to form citrate (6 carbon molecule).
In aerobic respiration both glycolysis and the Krebs cycle are involved whereas in anaerobic respiration only glycolysis takes place. The flow diagram shows that every time a stage produces two hydrogen atoms, in the presence of oxygen, three ATP molecules are produced. The role of these hydrogen atoms is shown in the electron carrier system.
In this article we will discuss about the functions of the Krebs cycle, explained with the help of diagrams. Krebs made an outstanding contribution to the discovery of the operating mechanisms of this cycle which is also called tricarboxylic cycle or citric cycle, owing to the participation of various tricarboxylic acids, including citric acid.
Krebs (Citric Acid) Cycle Steps by Steps Explanation. It is also known as TriCarboxylic Acid (TCA) cycle. In prokaryotic cells, the citric acid cycle occurs in the cytoplasm; in eukaryotic cells, the citric acid cycle takes place in the matrix of the mitochondria. The cycle was first elucidated by scientist "Sir Hans Adolf Krebs" (1900 to.
The Krebs cycle, named after 1953 Nobel Prize winner and physiologist Hans Krebs, is a series of metabolic reactions that take place in the mitochondria of eukaryotic cells.Put more simply, this means that bacteria do not have the cellular machinery for the Krebs cycle, so it limited to plants, animals and fungi.
The Krebs and Calvin cycles Venn diagram graphic organizer is a great way for students to compare and contrast these two biochemical processes.Includes two versions:Version 1. Students cut and paste labels onto the correct part of the Venn diagram.Version 2. Students write the correct statement into.
glycolysis: The cellular degradation of the simple sugar glucose to yield pyruvic acid and ATP as an energy source. The citric acid cycle, shown in —also known as the tricarboxylic acid cycle (TCA cycle) or the Krebs cycle—is a series of chemical reactions used by all aerobic organisms to generate energy through the oxidation of acetate.
Krebs Cycle Definition. The Krebs Cycle, also called the citric acid cycle, is the second major step in oxidative phosphorylation.After glycolysis breaks glucose into smaller 3-carbon molecules, the Krebs cycle transfers the energy from these molecules to electron carriers, which will be used in the electron transport chain to produce ATP.. Krebs Cycle Overview
The Krebs Cycle LSM 2.2-3 Krebs Cycle enters the cycle and then combines with to make the six-carbon compound. During the eight steps of the Krebs cycle, undergoes a number of reactions, releasing and in a number of steps. is eventually converted into so it can be used again during the Krebs cycle. Pyruvate Oxidation
The TCA cycle or Krebs' cycle (after H. A. Krebs) is a cyclic sequence of reactions through which pyruvic acid produced in the EMP and EDP is oxidized. The cycle operates in aerobic organisms including animals, plants and microorganisms. The main function of the cycle is to generate energy by oxidation of acetic acid which is produced by.
Krebs Cycle (TCA or Citric Acid Cycle): It is the common pathway for complete oxidation of carbohydrates, proteins and lipids as they are metabolised to acetyl coenzyme A or other intermediates of the cycle.The Acetyl CoA produced enters the Tricarboxylic acid cycle or Citric acid cycle. Glucose is fully oxidised in this process. The acetyl CoA combines with oxaloacetate (4C) to form citrate (6C).
The Krebs Cycle Step 1: In the first step of the Krebs cycle, acetyl CoA is added to oxaloacetate to form citrate. Note that coenzyme A (CoA-SH) is removed in the process. Step 2: Citrate is isomerized forming isocitrate, which is less stable than citrate. During this step, one water molecule is
Krebs Cycle. This is also known as the citric acid cycle or the tricarboxylic acid cycle. For each glucose molecule, there were 2 pyruvic acid molecules formed, (and therefore 2 acetylCoA molecules formed) so the whole cycle takes place twice for every glucose molecule respired. Each acetylCoA ( 2C) combines with an oxaloacetic acid ( 4C) to.
Krebs Cycle Diagram Easy. The Krebs cycle, also known as the Citric Acid cycle, is a very important process in cellular respiration. Without this portion, respiration would. Glycolysis- 10 steps explained steps by steps with diagram. This step involves a simple rearrangement of the position of the phosphate group of oxygen will continue on to.
The Krebs cycle (named after Hans Krebs) is a part of cellular respiration.Its other names are the citric acid cycle, and the tricarboxylic acid cycle (TCA cycle).. The "Krebs cycle" is a series of chemical reactions used by all aerobic organisms in their energy conversion processes. It is important to many biochemical pathways. This suggests that it was one of the earliest parts of cellular.
Physics Symbols. ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with Physics solution from the Science and Education area is a powerful software for creating various physics diagrams. Physics solution provides all tools that you can need for physics diagrams designing. It includes 3 libraries with predesigned vector physics.
2) Krebs Cycle 3) The Electron Transport Chain (ETC) This is a very simple overview of these 3 stages: Glycolysis (Stage 1) Glycolysis is the process where 1 glucose molecule, in the cell’s cytoplasm, is broken down (through several steps) into 2 molecules of pyruvate, which is then used in the Kreb’s Cycle (stage 2). This break down also
The 2 carbons from pyruvate make up the acetyl part of acetylCoA. CoA is a big molecule that acts just as a carrier.) 3. Krebs Cycle. (2 AcetylCoA + 6 NAD + 2 FAD + 2 ADP + 2Pi -->. 4 CO2 + 6 NADH + 2 FADH2 + 2 ATP + 2 CoA + heat) 4. ETC. ( 10 NADH + 2 FADH2 + 34 ADP + 34 Pi + 6 O2-->.
Krebs Cycle. By A* Biology on June 2, 2017 in. The Krebs cycle involves a series of oxidation-reduction reactions that take place in the matrix of the mitochondria. 1. A 2 carbon acetylcoenzyme A from the link reaction combines with a 4 carbon molecule to produce a 6 carbon molecule. 2.
Glycolysis, which is the simple sugar glucose, broke down in the cytosol. Pyruvate, which is the product from glycolysis transfer into acetyl CoA in the mitochondria. The Citric Acid Cycle, where acetyl CoA modifies to produce energy for the next step.
new vid on krebs cycle : https://youtu.be/o2h7xsnq1kiget lecture handouts and other downloadable content from this videosupport us on patreon or join here on...
Krebs cycle The Krebs cycle, also known as the citric acid cycle or the tricarboxylic acid cycle, is one of the most important reaction sequences in biochemistry. Not only is this series of reactions responsible for most of the energy needs in complex organisms, the molecules that are produced in these reactions can be used as building blocks for a large number of important processes.

0 Response to "43 Simple Krebs Cycle Diagram"
Post a Comment