41 Negative Feedback Loop Diagram
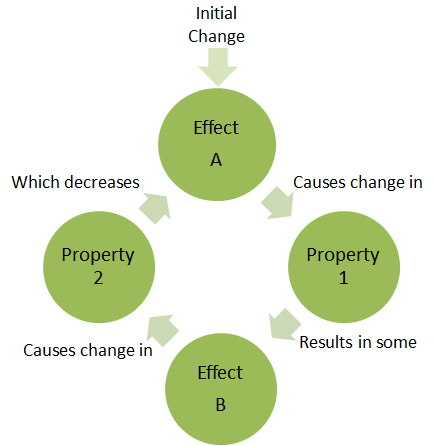
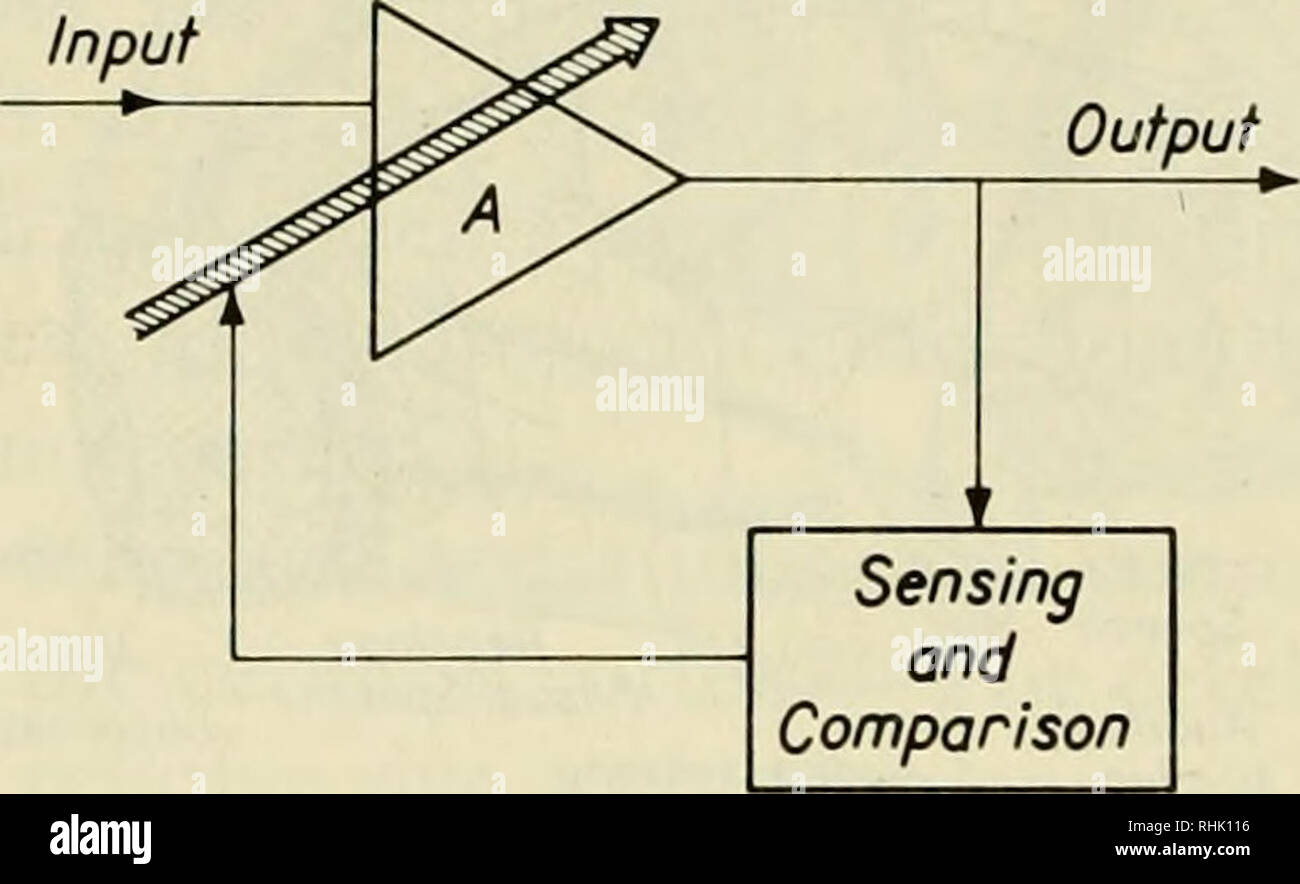
Negative feedback means that whenever a change occurs in a system, this automatically causes a corrective mechanism to start, which reverses the original change and brings the system back towards the set point (i.e. 'normal'). It also means that the bigger the change the bigger the corrective mechanism. Negative feedback The diagram will then be simplified through a process that is both graphical and algebraic. For exam-ple, equivalent blocks for a negative feedback loop are shown in Figure 8.9, along with an algebraic proof. Figure 8.9 A negative feedback block reduction Other block diagram equivalencies are shown in Figure 8.10 to Figure 8.16. In all
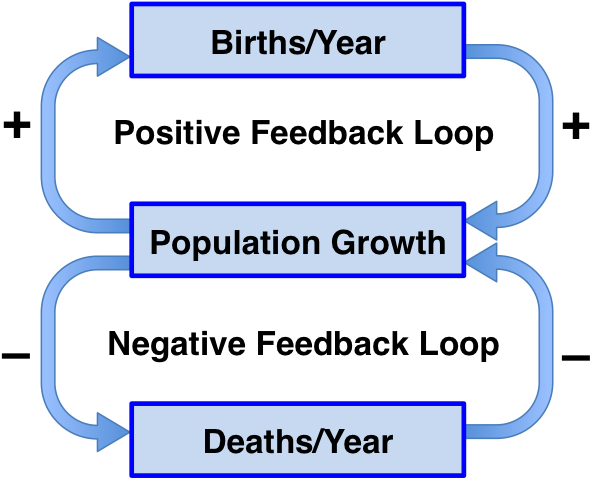
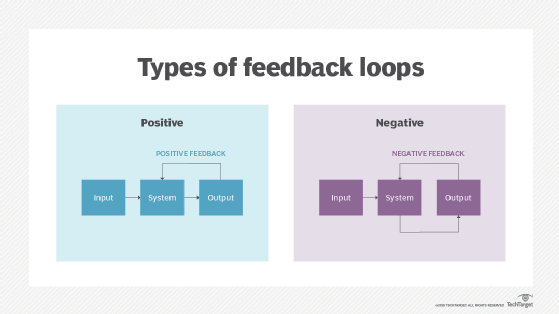
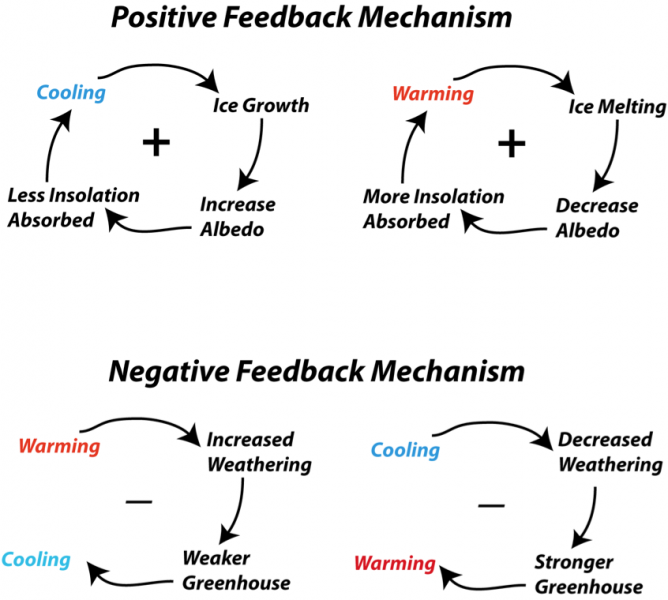
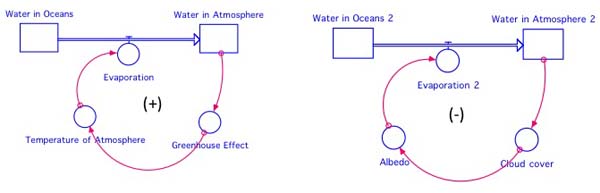
Feedback Loops can enhance or buffer changes that occur in a system.. Positive feedback loops enhance or amplify changes; this tends to move a system away from its equilibrium state and make it more unstable. Negative feedbacks tend to dampen or buffer changes; this tends to hold a system to some equilibrium state making it more stable.. Several examples are given here to help clarify feed.

Negative feedback loop diagram
Feedback loops can be divided into two types: positive and negative. Positive feedback loops are defined as amplifications away from a target level while negative feedback mechanisms attempt to maintain a target level. The latter are the most common. Don't let the name fool; negative feedback loop is a good thing when it comes to homeostasis. A negative feedback loop, also known as an inhibitory loop, is a type of self-regulating system. In a negative feedback loop, increased output from the system inhibits future production by the system. The body reduces its own manufacturing of certain proteins or hormones when their levels get too high. Negative feedback systems work to maintain. Negative Feedback Loops. A negative feedback loop occurs in biology when the product of a reaction leads to a decrease in that reaction. In this way, a negative feedback loop brings a system closer to a target of stability or homeostasis. Negative feedback loops are responsible for the stabilization of a system, and ensure the maintenance of a.
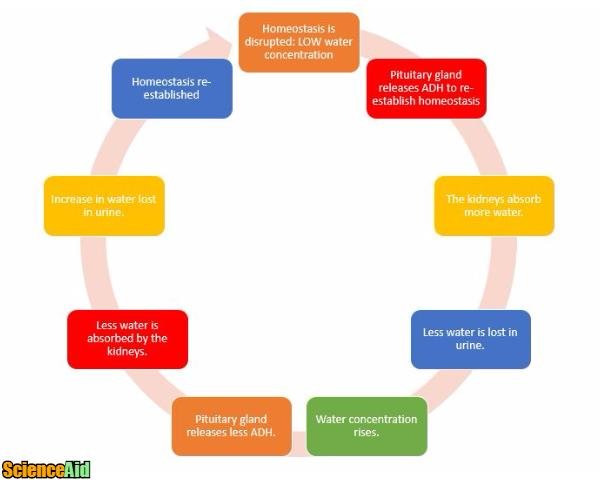
Negative feedback loop diagram. This means we can represent the negative feedback connection of two blocks with a single block. The transfer function of this single block is the closed loop transfer function of the negative feedback. The equivalent block diagram is shown below. Similarly, you can represent the positive feedback connection of two blocks with a single block. Figure 1.3.2 - Negative Feedback Loop: In a negative feedback loop, a stimulus—a deviation from a set point—is resisted through a physiological process that returns the body to homeostasis. (a) A negative feedback loop has four basic parts. (b) Body temperature is regulated by negative feedback. Negative Feedback in Nature. Dive into different negative feedback loops that you can find in nature. The carbon cycle - The equilibrium of this cycle will change in accordance with carbon dioxide emissions.; Plant photosynthesis - The photosynthesis in plants speeds up in response to increased levels of carbon dioxide.; Carbonation - Rain and carbon dioxide combine with limestone to make. A positive feedback loop increases the effect of the change and produces instability. In this case, the positive and negative naming of the loops do not indicate whether the feedback is good or bad. In climate change, a feedback loop is something that speeds up or slows down a warming trend. A positive feedback accelerates a temperature rise.
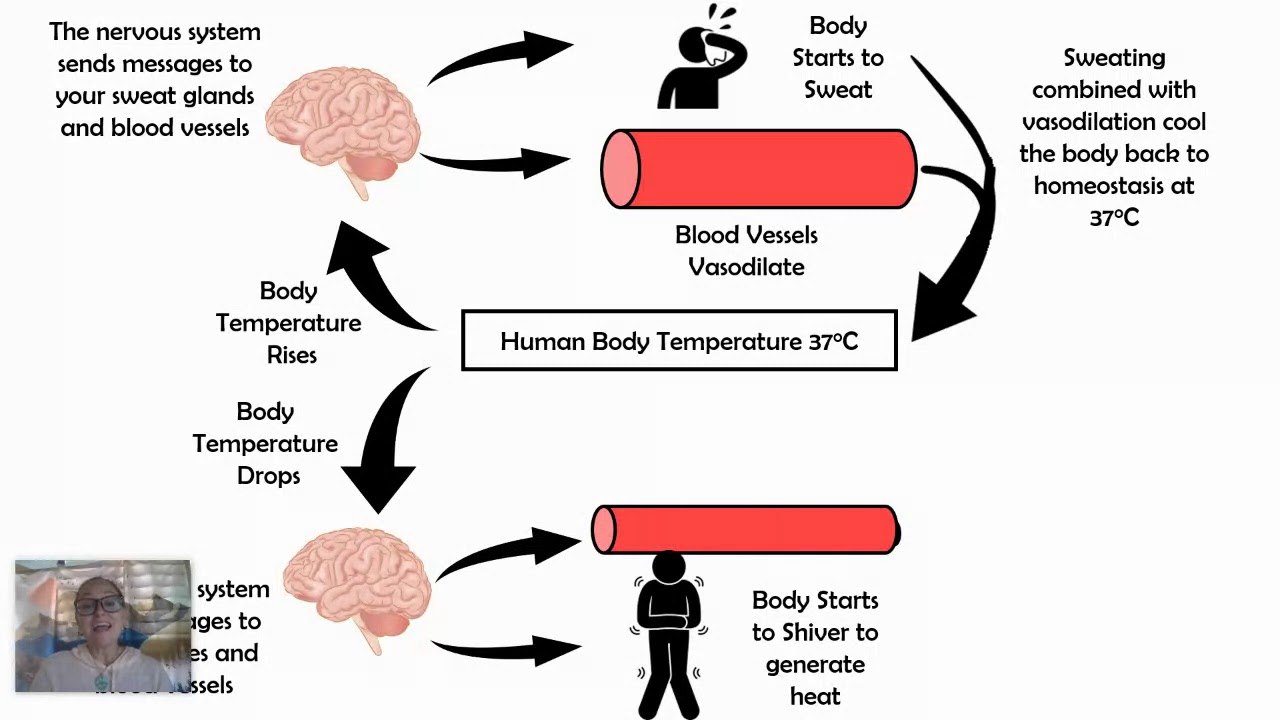
feedback path. Such a feedback loop is called a unity feedback loop. In general, we can put a dynamic element in the feedback loop (another open-looptransfer function) as presented in Figure 4.7b. For notational convenience, we will denote the transfer function in the feedback path by and the transfer function in the forward path by. Negative feedback system. A negative feedback system is defined as the negative feedback connected closed loop system. When the output of the system is increased more than the desired output, instead of increasing, we should control the output by decreasing the input. This can be achieved by using a negative feedback control. Traditionally([1], [2]) negative feedback circuits are introduced by putting showing the classical block diagram in Fig. 1, analyzing it, and showing that the closed loop gain This flowchart shows negative feedback regulation of temperature in a home with central heating and air-conditioning. Negative feedback maintains the regulated variable (room temperature) relatively constant at approximately the set point (20°C). The experiment provided will help you better understand about the negative feedback mechanism.
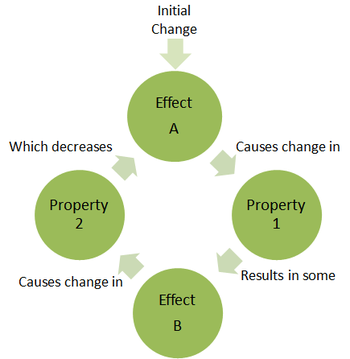
A causal loop diagram ( CLD) is a causal diagram that aids in visualizing how different variables in a system are causally interrelated. The diagram consists of a set of words and arrows. Causal loop diagrams are accompanied by a narrative which describes the causally closed situation the CLD describes. Closed loops, or causal feedback loops. Another common example of a negative feedback loop in biology is thyroid regulation of metabolism, which you can see in this diagram.This is a negative feedback loop that controls the release of. The Negative Feedback Amplifier in Closed Loop Mode A basic negative feedback arrangement is shown in Fig. 3.1.2 where the phase reversing amplifier has a fraction of its output (V out) fed back and added to the input (V in) so as to reduce the amplitude of the input signal. The arrows show the relative polarity of the signals and it can Causal loops show the interrelation causes and their effects. When finished you have a diagram of the positive and negative reinforcements which describe the system of behavior. The neat thing about causal loops is it is depersonalizing. People can point at the arrows in the loop that are reinforcing the problem instead of pointing at people.
There are two types of feedback loops in biology: negative feedback loops, and positive feedback loops. These act to either reduce or amplify the changes that occur in a given system. Let's see how feedback loops can be applied to thermoregulation. Imagine walking into a room that has an air conditioner on at full blast.
Have a look at the diagram above. It shows an op-amp with negative feedback. Ignoring the feedback loop for now, the voltage (pressure) coming from the 5V battery, acting on the inverting pin, should amount to 5V.
Typically, we divide feedback loops into two main types: positive feedback loops, in which a change in a given direction causes additional change in the same direction.For example, an increase in the concentration of a substance causes feedback that produces continued increases in concentration. negative feedback loops, in which a change in a given direction causes change in the opposite.
Feedback loops can be divided into two types: positive and negative. Positive feedback loops are defined as amplifications away from a target level while negative feedback mechanisms attempt to maintain a target level. The latter are the most common. Don't let the name fool; negative feedback loop is a good thing when it comes to homeostasis.
Negative Feedback Loops. A negative feedback loop occurs in biology when the product of a reaction leads to a decrease in that reaction. In this way, a negative feedback loop brings a system closer to a target of stability or homeostasis. Negative feedback loops are responsible for the stabilization of a system, and ensure the maintenance of a.
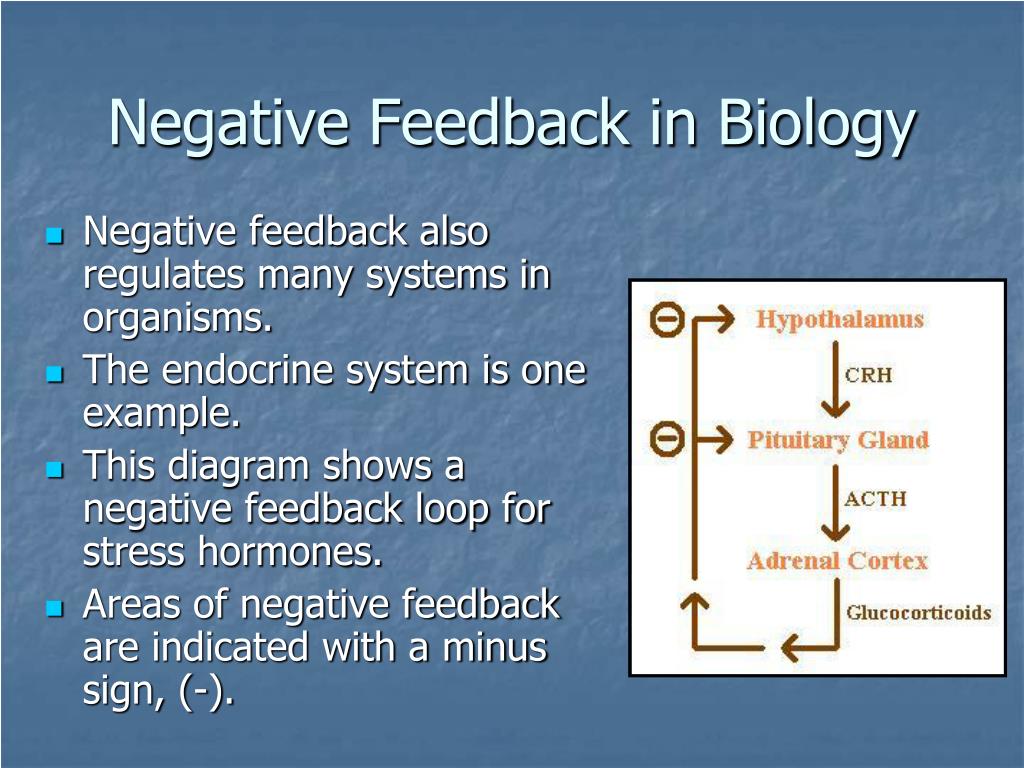
Feedback loops are used extensively to regulate secretion of hormones in the hypothalamic-pituitary axis. An important example of a negative feedback loop is seen in control of thyroid hormone secretion. The thyroid hormones thyroxine and triiodothyronine ("T4 and T3") are synthesized and secreted by thyroid glands and affect metabolism.
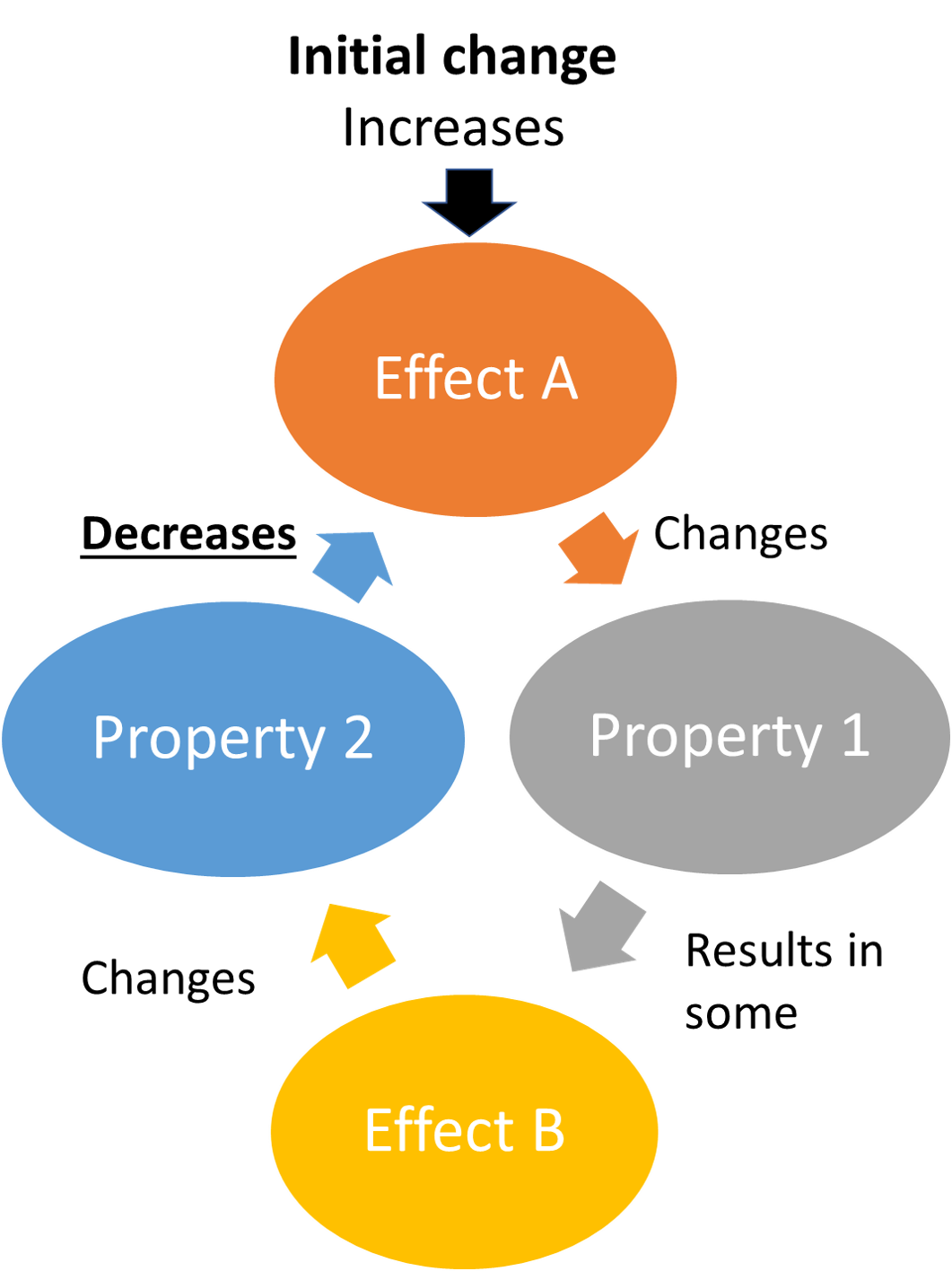
A negative feedback loop' (sometimes referred to as a " balancing feedback loop") creates conditions that slow down and/or dampen the initial change or perturbation. This type or feedback tends to push a system towards stability. Other words and phrases associated with balancing feedback loops are dampening, restores balance, and reducing.
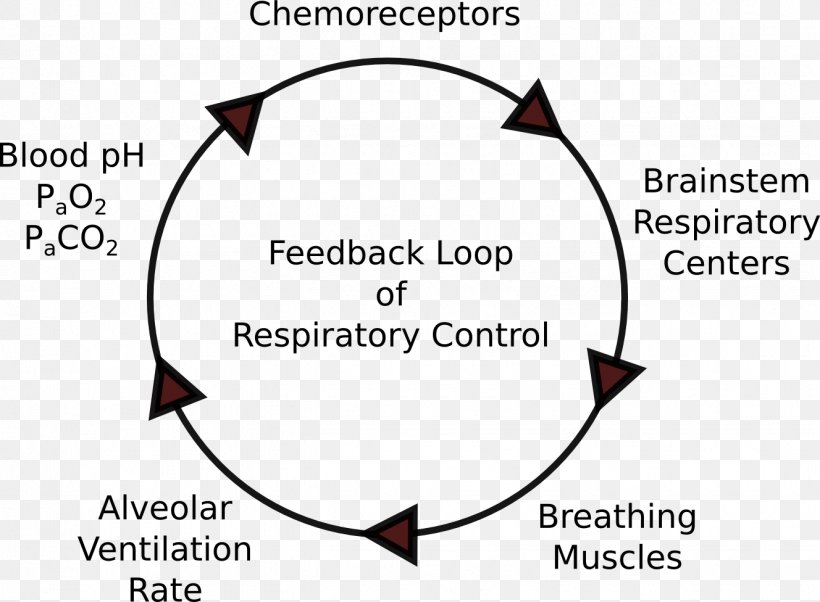
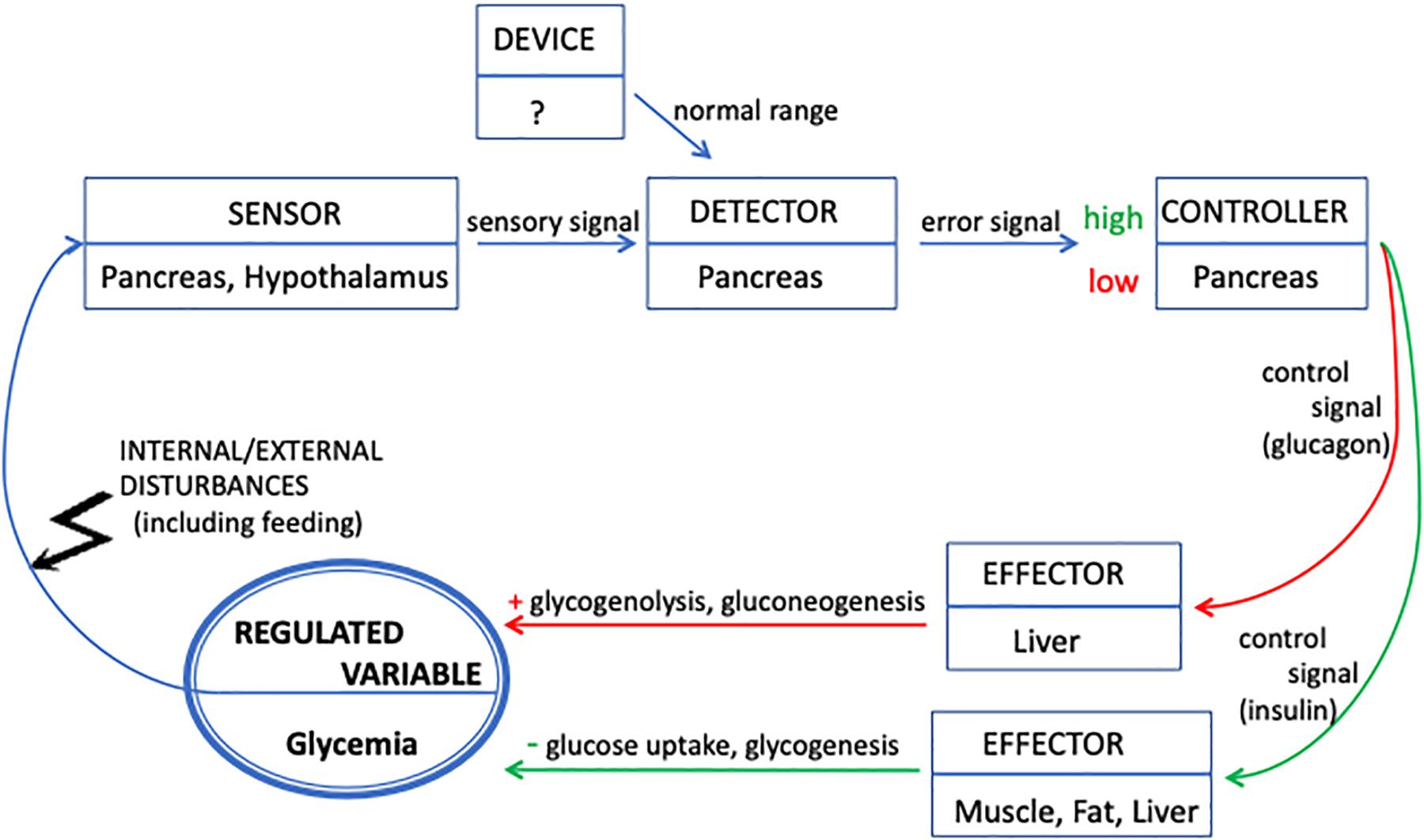
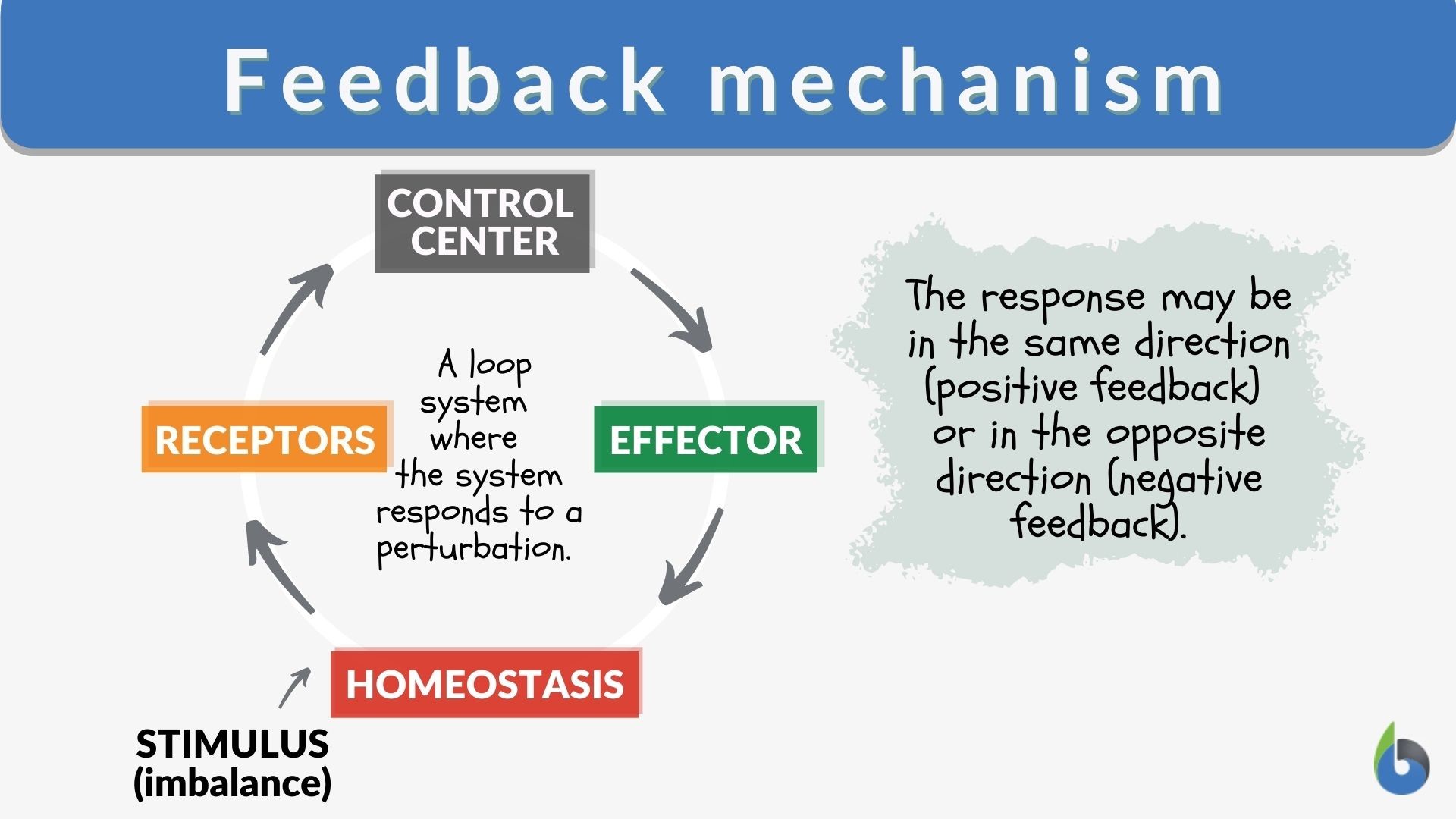
A negative feedback control system responds when conditions change from the ideal or set point and returns conditions to this set point. There is a continuous cycle of events in negative feedback.
Negative feedback loops require a receptor, a control center, and an effector. A receptor is the structure that monitors internal conditions. For instance, the human body has receptors in the blood vessels that monitor the pH of the blood.
An example of the use of negative feedback control is the ballcock control of water level (see diagram), or a pressure regulator.In modern engineering, negative feedback loops are found in engine governors, fuel injection systems and carburettors.Similar control mechanisms are used in heating and cooling systems, such as those involving air conditioners, refrigerators, or freezers.
A negative feedback loop, also known as an inhibitory loop, is a type of self-regulating system. In a negative feedback loop, increased output from the system inhibits future production by the system. The body reduces its own manufacturing of certain proteins or hormones when their levels get too high. Negative feedback systems work to maintain.
An important aspect of homeostasis is maintaining a normal body temperature. Describe the homeostatic feedback system that would be activated in response to a decreased external temperature. Yes, homeostasis is important to keep everything in the body balanced. The temperature of the body is around 37ºC at all times.
4. Diagram the short loop and long loop negative feedback control of the anterior pituitary hormone secretion. Predict changes in the secretory rates of hypothalamic, anterior pituitary and target gland hormones caused by over secretion or under secretion of any of these hormones or receptor deficit for any of these hormones. 5.
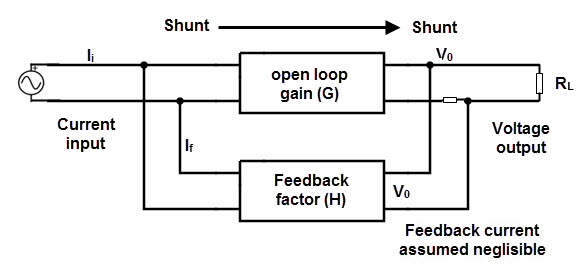
The basic block diagram of the negative feedback system is shown below with X, Y, Z as input, output and feedback loops respectively. Transistor feedback circuits The disadvantage in the circuits designed with transistors is that, the properties like gain, distortion, input and output resistance and the signal to noise ratio depend upon the.
Since AMPK-dependent inhibition of mTOR is already well-known [13,27], an extra double negative feedback loop might be generated between mTOR and AMPK (see AMPK ┤ mTOR ┤ AMPK in Figure 1). This so called bistable toggle switch is a common feature of biochemical regulatory networks describing an irreversible cellular transition between two.
Diagram the negative feedback loop involved with thyroxine blood level regulation. Take some time with this one! I expect you to be able to predict what will happen to the levels of TRH, TSH, and T3/T4 if any one of these hormones rises or falls! List AND describe the major metabolic effects of thyroid hormone.
Negative feedback occurs when a system's output acts to reduce or dampen the processes that lead to the output of that system, resulting in less output. In general, negative feedback loops allow systems to self-stabilize. Negative feedback is a vital control mechanism for the body's homeostasis.






















0 Response to "41 Negative Feedback Loop Diagram"
Post a Comment