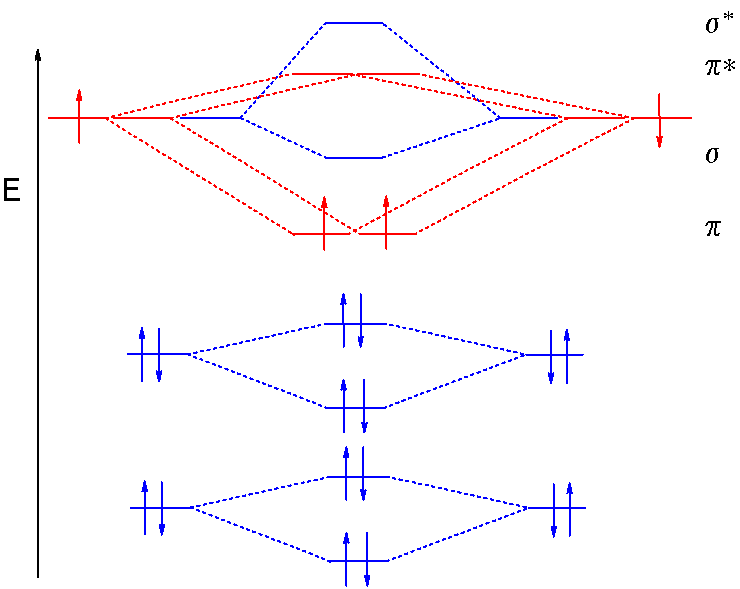
41 B2 2- Molecular Orbital Diagram
The molecular orbital electronic configuration, Magnetic property: Since bond order is zero, Be 2 molecule does not exist. It is diamagnetic due to the absence of any unpaired electron. B 2 molecule: The electronic configuration of B atom (Z = 5) is. B 2 molecule is formed by the overlap of atomic orbitals of both boron atoms. A number of. d. N a. 02 b. F e. Liz c. B2 - 15 minutes 9. Assuming that the molecular orbital energy diagram for a homonuclear diatomic molecules applies to heteronuclear diatomic species, use the MO diagrams in Model 2 to determine the bond order for the following. Use the first atom listed to select the diagram to use. Show your calculations! a. C e. BN b.
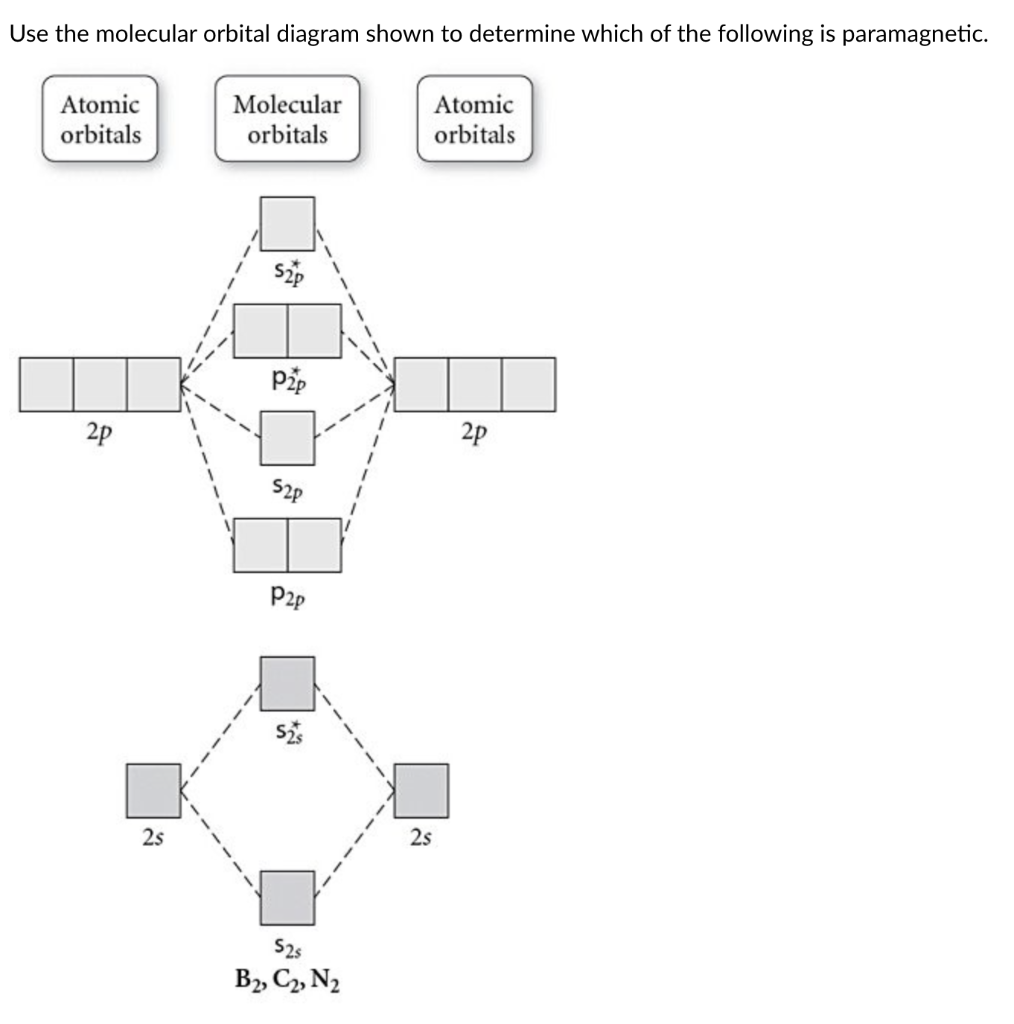
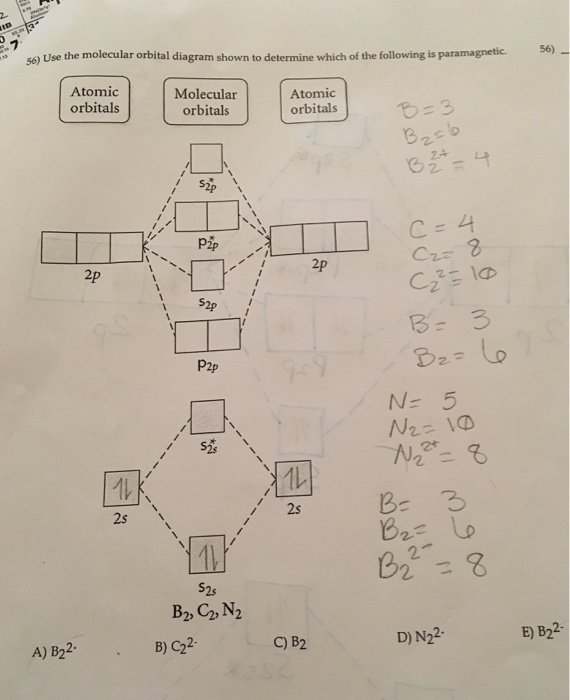
B) Ne2^2+ C) O2^2+ D) F2^2+ E) None of the above are paramagnetic; 3) Draw the molecular orbital diagram needed, and determine which of the following is paramagnetic. A) B2^2+ B) B2^2-C) N2^2+ D) C2^2-E) B2; 4) Draw the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which of the following is most stable.
B2 2- molecular orbital diagram
Molecular orbital diagram of b2. Bo 1 2 bonding e anti bonding e 1 2 8 4 2 lcao mo theory also predicts correctly that o2has two unpaired electrons. Molecular electron configuration for o2 σ2σ2σ2π4π2 we can also calculate the oo bond order. Molecular orbital diagrams of diatomic molecules draw the lewis structure for the following molecules. The number of unpaired electrons in the B2+ molecule is 2 (two) 1 (one) 3 (three) zero ; Question: Draw the molecular orbital diagram for B2+ (this is not B-B. it has an electron missing, so its B-B cation!) The number of unpaired electrons in the B2+ molecule is 2 (two) 1 (one) 3 (three) zero When two fluorine atoms bond, the sigma(2p) bonding molecular orbitals are lower in energy than the pi(2p) bonding orbitals.F2(2+) has a bond order of 2, so.
B2 2- molecular orbital diagram. Molecular orbital diagram of b2. Bo 1 2 bonding e anti bonding e 1 2 8 4 2 lcao mo theory also predicts correctly that o2has two unpaired electrons. Molecular electron configuration for o2 σ2σ2σ2π4π2 we can also calculate the oo bond order. Molecular orbital diagrams of diatomic molecules draw the lewis structure for the following molecules. A molecular orbital explicitly describes the spatial distribution of a single Energy Level Diagrams He2 has bond order 0 [ (2 − 2)/2 = 0], and we can make H+. According to the molecular orbital theory, in a supposed He2 molecule, both the if we draw its MOT DIAGRAM, 2 e's enter the Bonding molecular Orbital and 2. Re: M.O. Diagram for B2 Post by Chem_Mod » Tue Nov 11, 2014 11:21 pm As discussed in class the MO diagram for B 2 shows that it has two unpaired electrons (which makes it paramagnetic) and these electrons are in bonding molecular orbitals resulting in the equivalent bond strength of one bond. molecular orbital theory.. A2 + 4 B2 → 2 AB4.... The initial pressure, number of moles, and temperature of the gas are noted on the diagram. Which diagram (2)-(4) most closely represents the result of doubling the temperature while keeping the pressure and.
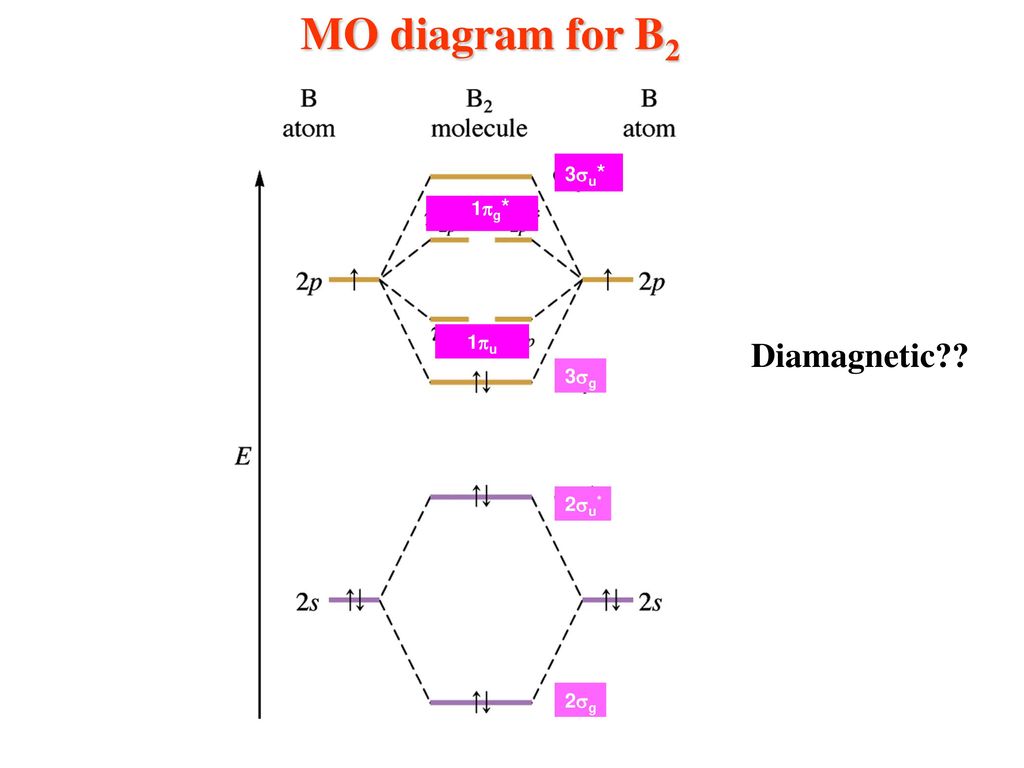
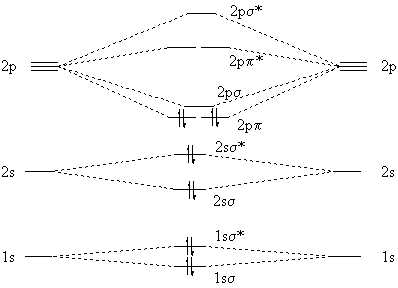
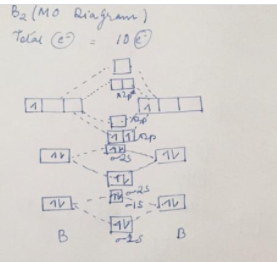
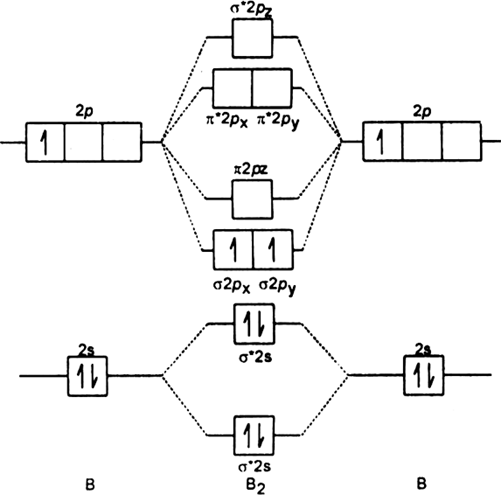
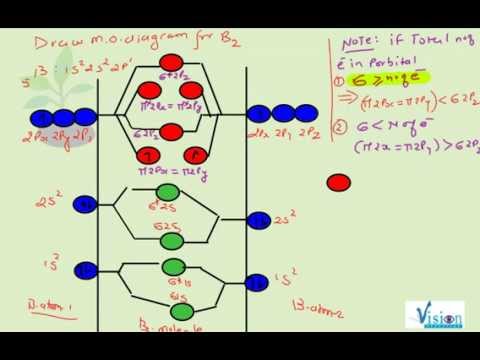
The molecular orbital diagram for B 2 molecule is as follows: We know that bond order is the difference between the number of bonds and the antibonds. Now, we have to calculate the bond order of B 2 molecule using the formula as follows: Bond order = 1 2 ( Number of electrons in BMO) − ( Number of electrons in ABMO) From the diagram, we can. Explain why the relative energy levels diagrams for Li2, Be2, B2, C2, N2 are different The molecular orbital theory of Li2 to F2 gives a graphical explanation. Energy level diagram for Molecular orbitals. May 25, By Mrs Shilpi Nagpal 9. It is paramagnetic in nature. 6)Li2. Molecular orbital energy level of Li2.Molecular orbitals of Li 2, Be 2. 5.9 a. A diagram is sketched at the right. Since the difference in valence orbital potential energy between the 2s of N (-25.56 eV) and the 2p of F (-18.65 eV) is 6.91 eV, the 2p orbital is expected to be higher in energy relative to the degenerate 2p set. b. NF is isoelectronic (has the same number of valence electrons) with O2. Therefore, NF. 1. Draw a molecular orbital diagram and determine the bond order expected for the molecule B. 2. For full credit on MO diagrams, • label increasing energy with an arrow next to the diagram. • pay attention to whether the question asks for valence electrons or all electrons.
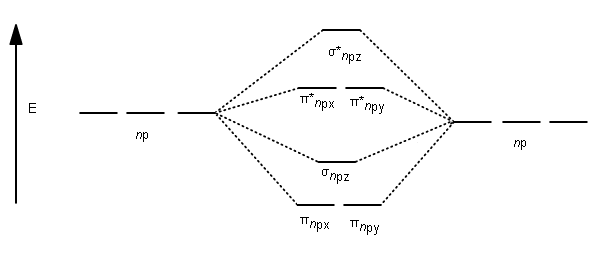
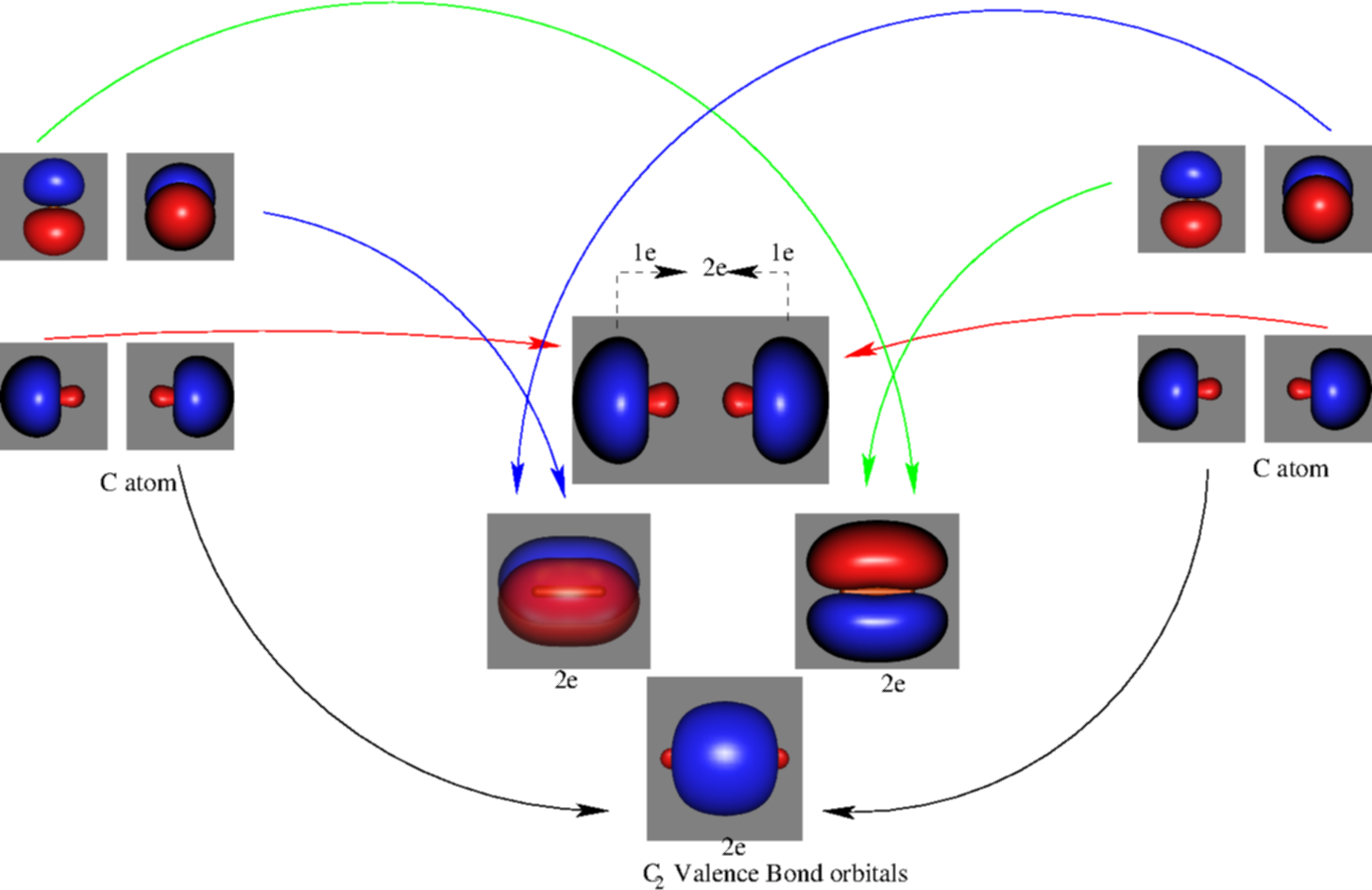
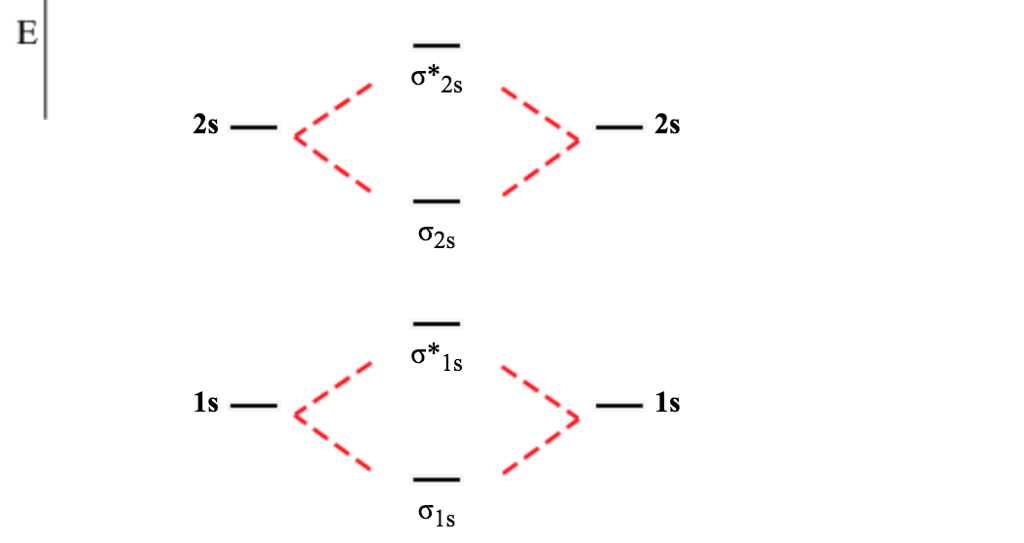
The following factors contribute to the position of one mo with respect to other mos. Molecular Orbital Theory - Part 1. Draw a molecular orbital energy diagram for each. B2-1. F 2. The magnetic property, bond order, and so on can be understood from its molecular orbital diagram. 5) Identify the bond and existence of molecule. From the molecular orbital diagram of N 2, predict its bond order and whether it is diamagnetic or paramagnetic. Answer: N 2 has a bond order of 3 and is diamagnetic. Example 3. Ion Predictions with MO Diagrams Give the molecular orbital configuration for the valence electrons in C 2 2. Chemistry questions and answers. Molecular Orbital theory predicts that the B2 2- ion would have a bond order of ________. If one of the highest valence electron (s) was excited into the next highest energy molecular orbital, it would_______. a. 1,strengthen the bonding in the molecule b. 2, have no effect on the bonding strength of the. Before we can draw a molecular orbital diagram for B₂, we must find the in-phase and out-of-phase overlap combinations for boron's atomic orbitals. Then we rank them in order of increasing energy. We can ignore the 1s orbitals, because they do not contain the valence electrons. Each boron atom has one 2s and three 2p valence orbitals. The 2s orbitals will overlap to form 2sσ and 2sσ.
2 In picture 1 we show the molecular orbital structure of F2. In picture 2 we show the overlapping p orbitals, which form the bond between the two fl uorine atoms, in red and green gradients. The dashed lines show the remaining p orbitals which do not take part in the bonding. σ z y x σ* x y z Construct the molecular orbital diagram for.
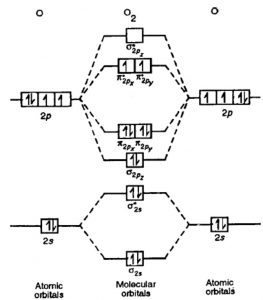
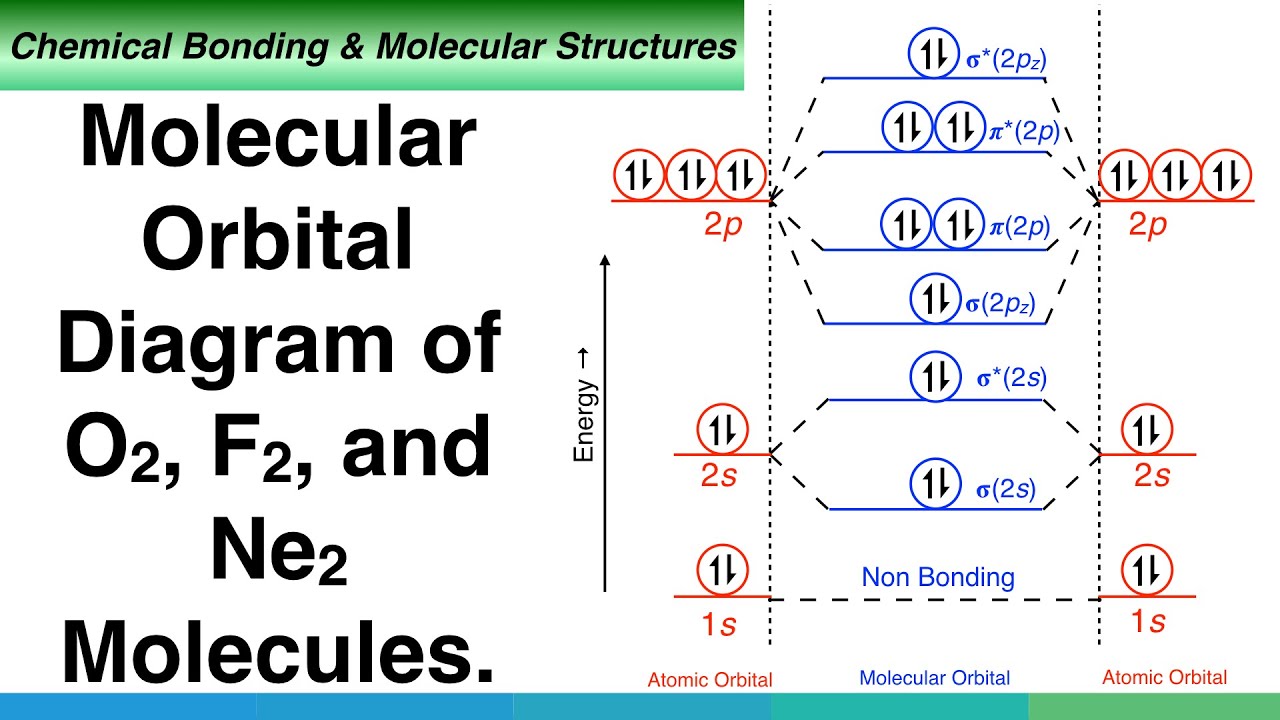
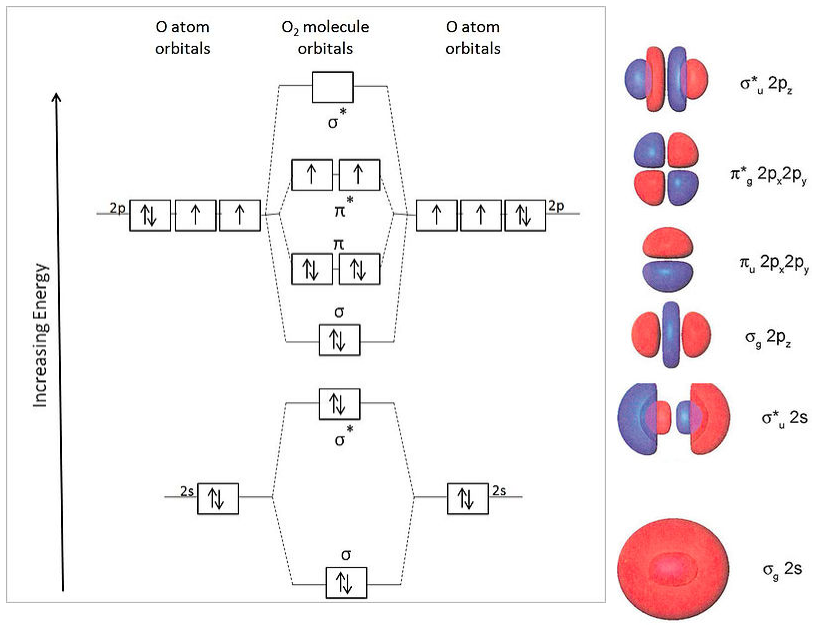
Molecular orbital diagram for b2. By drawing molecular orbital diagrams for b2 c2 n2 o2 and f2 predict which of these homonuclear diatomic molecules are magnetic. The molecular orbital diagram for an o 2 molecule would therefore ignore the 1s electrons on both oxygen atoms and concentrate on the interactions between the 2s and 2p valence orbitals.
Molecular orbital diagram for ne2 2. 2s. I know ill need a 2p orbital but theres orbital mixing going on so i have 2 choices. Wiki User Answered 2012-03-05 06:41:57. Because According to molecular orbital theory O 2 + has 15 electrons &it has one electron in antibonding orbital. Side by Side Comparison – Homo vs Lumo in Tabular Form 5. C 2 c.
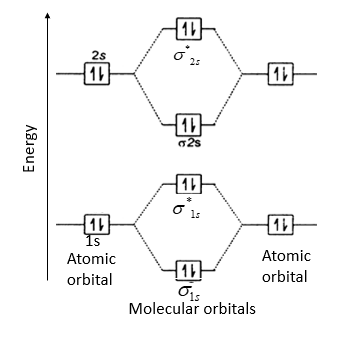
Molecular orbital diagram for beryllium dimer be2 fill from the bottom up with 4 electrons total. The electronic configuration of b atom z 5 is. View a full sample. Since bond order is zero be 2 molecule does not exist. This video shows the end of the be2 molecule mo diagram and explains pi orbitals paramagnetism and the mo diagrams for b2.
The AO energies suggest that the 1s orbital of hydrogen interacts mostly with a 2p orbital of fluorine. The F 2s is nonbonding. H-F nb σ σ* Energy H -13.6 eV 1s F -18.6 eV -40.2 eV 2s 2p So H-F has one σ bond and three lone electron pairs on fluorine
This video shows the end of the Be2 molecule MO diagram and explains pi orbitals, paramagnetism, and the MO diagrams for B2.
Nov 10, 2021 · Terms in this set (13) Linear. This is composed of a σ framework and a π-bond. A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) method in particular.
Answer (1 of 7): The diatomic molecules having less than or equal to 14 electrons in all show s-p mixing. Eg:- N_2,CO,C_2,BN, etc. In such molecules, the energy difference between 2s and 2p orbitals is quite less and due to it the 2s orbital and 2p_z orbital tend to overlap. Due to this, the ene...
A) The total number of molecular orbitals formed doesn't always equal the number of atomic orbitals in the set. B) A bond order of 0 represents a stable chemical bond. C) When two atomic orbitals come together to form two molecular orbitals, one molecular orbital will be lower in energy than the two separate atomic orbitals and one molecular.
Molecular orbital diagram of b2. The next two would fill the 1 sigma e antibonding orbital. I can draw be2 but not this. B 2 molecule is formed by the overlap of atomic orbitals of both boron atoms. The electronic configuration of b atom z 5 is. It is diamagnetic due to the absence of any unpaired electron.
Procedure to draw the molecular orbital diagram of CN. 1. Find the valence electron of each atom in the CN molecule. Clearly, carbon has 4 valence electrons and nitrogen has 5. 2. Find if the molecule homo-nuclear diatomic molecular orbital or hetero-nuclear diatomic molecular orbital. Clearly, CN is hetero orbital. 3.
2 linear. BH2. 2a1. 21b2. 23a1. MO Diagram for BeH2. Be 2p. Be 2s. -. +. BeH2 MOs bonding MOs antibonding MOs non-bonding orbitals. Be AOs. H LCAOs g u u bonding nonrbonding. a complex MO diagram: B2H6 MO diagrams combine two fragments. Symmetry.. fragment =5e therefor keep up to b2 orbital z x y b1 a1 a1 b2. BH2. Fig.
The molecular orbital diagram for $\\ce{O2}$ says that the sigma 2p bonding molecular orbital is lower in energy than the pi 2p bonding molecular orbital. Why is this not the case in the $\\ce{B2}$ MO
B2 molecular orbital diagram. Since bond order is zero be 2 molecule does not exist. This was on a quiz and i somehow got the bond order and the lumo indicated wrong. I also calculated the bond order of this molecule to be 32. B 2 molecule is formed by the overlap of atomic orbitals of both boron atoms.
The number of unpaired electrons in the B2+ molecule is 2 (two) 1 (one) 3 (three) zero ; Question: Draw the molecular orbital diagram for B2+ (this is not B-B. it has an electron missing, so its B-B cation!) The number of unpaired electrons in the B2+ molecule is 2 (two) 1 (one) 3 (three) zero
"BO" = 1/2 Boron atom is atomic number 5 in the periodic table, so it has five electrons. Thus, B_2 carries ten total electrons. The atomic orbitals each boron contributes consists of the 1s, 2s, and 2p. The ns orbitals combine to give a portion of the molecular orbital (MO) diagram like this: where sigma^"*" indicates an antibonding sigma (sigma) MO, and sigma is the bonding MO.
When two fluorine atoms bond, the sigma(2p) bonding molecular orbitals are lower in energy than the pi(2p) bonding orbitals.F2(2+) has a bond order of 2, so.
The bond order of B2, C2, and N2 are 1, 2, and 3, respectively. B2 has two unpaired electrons with the same spin and therefore is paramagnetic. C2 and N2 are...
Molecular orbital diagram of b2. Draw the molecular orbital energy level diagram for each of the following species Be2+, Be2, and Be Indicate theirnumbers of unpaired electron and mention. Each sp 1 hybrid orbital has s-character and The molecular orbital structure of ethylene: In ethene molecule, each carbon atom undergoes sp 2 hybridisation. 3.
B2 molecular orbital diagram. This also causes a large jump in energy in the 2p σ orbital. For example when two hydrogen atoms bond a σ1s bonding molecular orbital is formed as well as a σ1s antibonding molecular orbital. Valence bond model vs. The molecular orbital diagram for an o 2 molecule would therefore ignore the 1s electrons on both.
Molecular Orbital (MO) Theory helps us to explain and understand certain Part B - Molecular Orbital Energy Diagrams & Bond Order. + and Be2.A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic.
4 Lecture 2 Pi bond (π): bonding molecular orbital -The bonding electron density lies above and below, or in front and in back of the bonding axis, with no electron directly on the bonding axis, since 2p orbitals do not have any electron density at the nucleus.
Nov 17, 2021 · Molecular orbital diagram practice worksheet
The electron configuration of the C− 2 ion will be. The molecular orbital diagram for C 2 molecule is :. The electronic configuration of C 2 is K K (σ2s) 2 (σ * 2s) 2 n(2px) 2 n(2py) 2. The C 2 molecule is diamagnetic because all electrons are paired there are no unpaired electrons. Molecular orbital diagram for c2 2-. The bond order of B2, C2











0 Response to "41 B2 2- Molecular Orbital Diagram"
Post a Comment