39 B2 Molecular Orbital Diagram
Printable O2 molecular orbital diagrams are available for you to guide your study in the molecular orbital lesson.This diagram is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of a molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) molecular orbital method in particular. Molecular orbital diagram for b2. B2 molecular orbital diagram. This also causes a large jump in energy in the 2p σ orbital. For example when two hydrogen atoms bond a σ1s bonding molecular orbital is for med as well as a σ1s antibonding molecular orbital. Valence bond model vs. The molecular orbital diagram for an o 2 molecule would there.
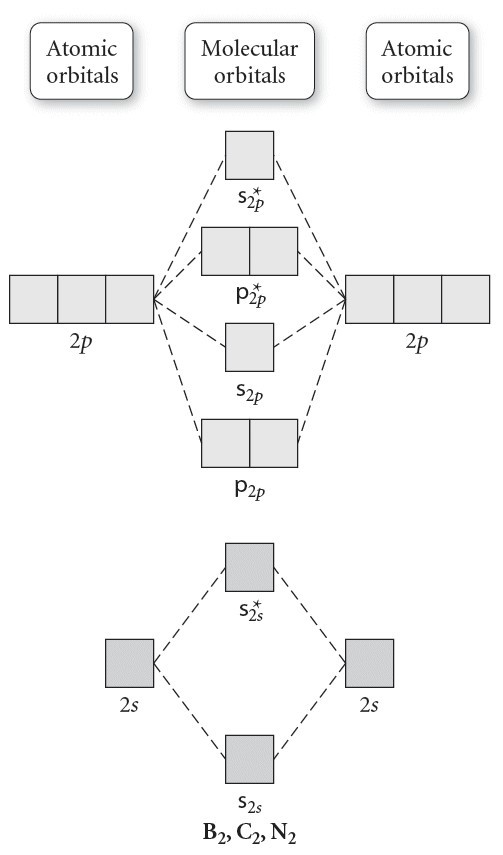
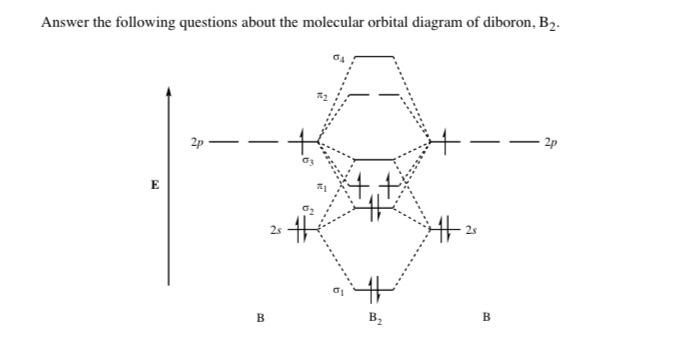
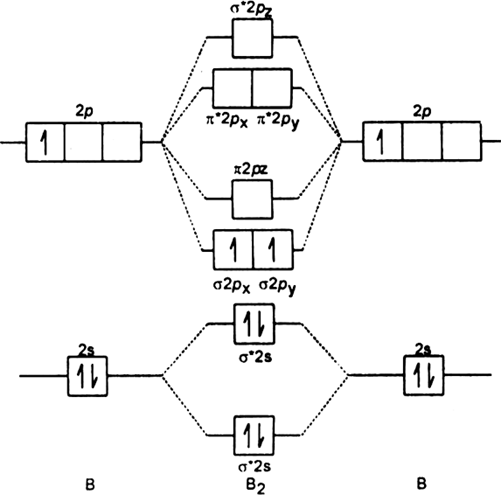
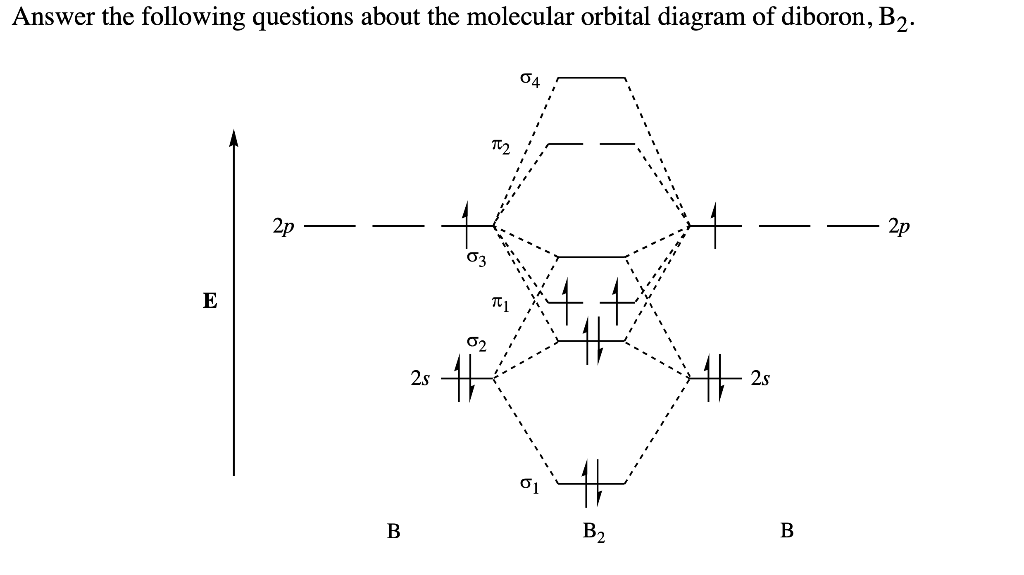
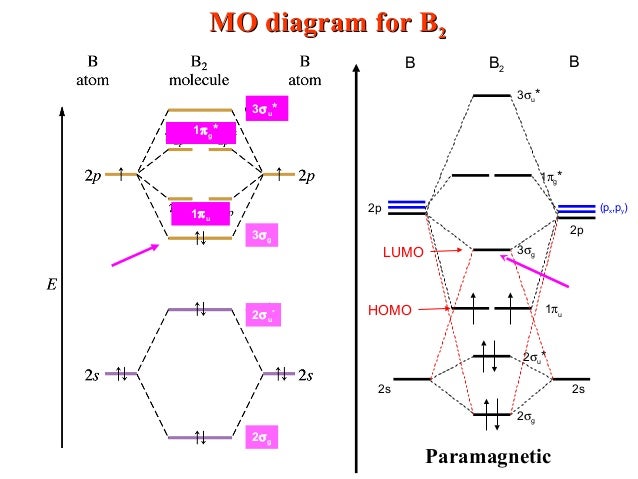
As discussed in class the MO diagram for B 2 shows that it has two unpaired electrons (which makes it paramagnetic) and these electrons are in bonding molecular orbitals resulting in the equivalent bond strength of one bond. As discussed in class it is not a bond. This example was covered in class to show the rare exception that this single bond is a bond.
B2 molecular orbital diagram
In this example problem, we show how to fill a molecular orbital diagram for a diatomic molecule and use molecular bond theory to compare bond order, bond st... + and Be2.A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) molecular orbital method in particular. 1. Draw the molecular orbital energy level diagram for each of the following. Molecular orbital diagram of b2. The next two would fill the 1 sigma e antibonding orbital. I can draw be2 but not this. B 2 molecule is formed by the overlap of atomic orbitals of both boron atoms. The electronic configuration of b atom z 5 is. It is diamagnetic due to the absence of any unpaired electron.
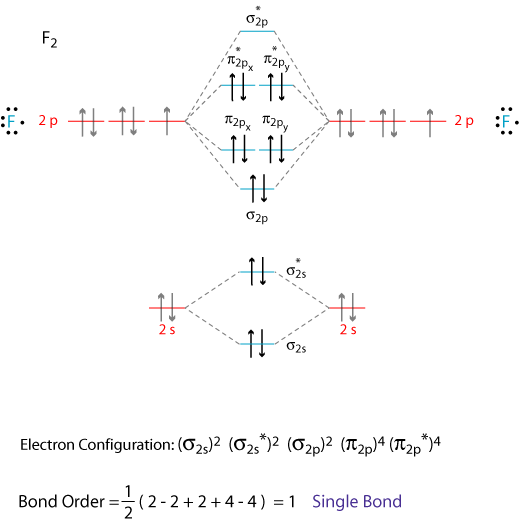
B2 molecular orbital diagram. In picture 1 we show the molecular orbital structure of F2. In picture 2 we show the overlapping p orbitals, which form the bond between the two fl uorine atoms, in red and green gradients. The dashed lines show the remaining p orbitals which do not take part in the bonding. σ z y x σ* x y z Construct the molecular orbital diagram for. Molecular orbital theory describes the distribution of electrons in molecules in much the same way that the distribution of electrons in atoms is described using atomic orbitals. Using quantum mechanics, the behavior of an electron in a molecule is still described by a wave function, Ψ, analogous to the behavior in an atom.Just like electrons around isolated atoms, electrons around atoms in. Answer to Construct the molecular orbital diagram for He2 and then identify the bond order. Bond order: Click within the blue boxe. A molecular orbital explicitly describes the spatial distribution of a single Energy Level Diagrams He2 has bond order 0 [(2 − 2)/2 = 0], and we can make H+. Before we get there it is worth while knowing a generic valence molecular orbital diagram where no s-p mixing occurs. This one pretty much applies to all main group elements heavier than nitrogen. The core orbitals, in case of lithium to neon these are the 1s orbitals, sodium to argon these are 1s, 2s, and 2p orbitals, are not included, as they.
Electron configuration orbital diagram worksheet answers. usin noble s notation Iron Orbital diagram Electron configuration E. 1s1 first 1 is the energy level, s is the type of orbital, and the second one is the number of the electrons in the orbital. elements in orbital notation, orbital notation with arrows and in short hand noble gas notation. Nov 17, 2021 · Molecular orbital diagram practice worksheet Molecular orbital diagram of b2. The next two would fill the 1 sigma e antibonding orbital. I can draw be2 but not this. B 2 molecule is formed by the overlap of atomic orbitals of both boron atoms. The electronic configuration of b atom z 5 is. It is diamagnetic due to the absence of any unpaired electron. B2 molecular orbital diagram. This also causes a large jump in energy in the 2p σ orbital. For example when two hydrogen atoms bond a σ1s bonding molecular orbital is formed as well as a σ1s antibonding molecular orbital. Valence bond model vs. The molecular orbital diagram for an o 2 molecule would therefore ignore the 1s electrons on both.
The molecular orbital diagram for B 2 molecule is as follows: We know that bond order is the difference between the number of bonds and the antibonds. Now, we have to calculate the bond order of B 2 molecule using the formula as follows: Bond order = 1 2 ( Number of electrons in BMO) − ( Number of electrons in ABMO) From the diagram, we can. A) The total number of molecular orbitals formed doesn't always equal the number of atomic orbitals in the set. B) A bond order of 0 represents a stable chemical bond. C) When two atomic orbitals come together to form two molecular orbitals, one molecular orbital will be lower in energy than the two separate atomic orbitals and one molecular. Draw the molecular orbital diagram for B2+ (this is not B-B. it has an electron missing, so its B-B cation!) The number of unpaired electrons in the B2+ molecule is 2 (two) 1 (one) 3 (three) zero ; Question: Draw the molecular orbital diagram for B2+ (this is not B-B. it has an electron missing, so its B-B cation!) The number of unpaired. Exercise 3.3.4. 3. Construct a qualitative molecular orbital diagram for chlorine, Cl 2. Compare the bond order to that seen in the Lewis structure (remember that an electron in an antibonding orbital cancels the stabilization due to bonding of an electron in a bonding orbital). Answer.
From the periodic table as we have already discussed the Molecular orbital diagrams of diatomic molecules of 1st two periods starting from Hydrogen to Neon..
Molecular Orbitals of the Second Energy Level. The 2s orbitals on one atom combine with the 2s orbitals on another to form a 2s bonding and a 2s * antibonding molecular orbital, just like the 1s and 1s * orbitals formed from the 1s atomic orbitals. If we arbitrarily define the Z axis of the coordinate system for the O 2 molecule as the axis along which the bond forms, the 2p z orbitals on the.
B2 molecular orbital diagram. Answer to question 1 by drawing molecular orbital diagrams for b2 c2 n2 o2 and f2 predict which of these homonuclear diatomi. Molecular orbitals are obtained by combining the atomic orbitals on the atoms in the molecule. Before we can draw a correlation diagram for b2 we must first find the in phase and out of.
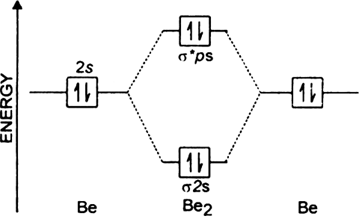
Draw the molecular orbital energy level diagram for each of the following species Be2+, Be2, and Be Indicate theirnumbers of unpaired electron and mention their magnetic diagramweb ate their bond orders, and state which species is moststable% (1). Molecular orbitals of Li 2, Be 2, to F 2 The molecular orbital theory (MO) has been introduced.
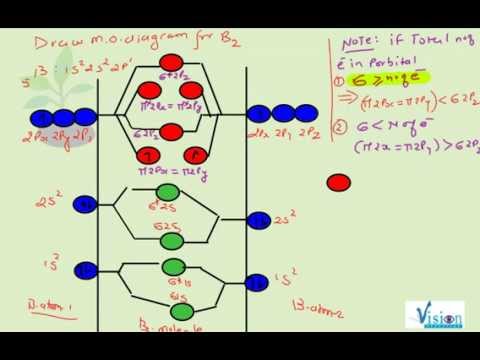
This video discusses how to draw the molecular orbital (MO) diagram for the B2 (boron) molecule. The bond order of the boron molecule is also calculated and.
(i) Be2 molecule: The electronic configuration of Be(Z = 4) is: 4 Be 1s 2 2s 1 Be 2 molecule is formed by the overlap of atomic orbitals of both beryllium atoms. Number of valence electrons in Be atom = 2 Thus in the formation of Be 2 molecule, two outer electrons of each Be atom i.e. 4 in all, have to be accommodated in various molecular orbitals in the increasing order of their energies.
Science. Chemistry. Chemistry questions and answers. -. Draw complete Molecular orbital diagram - Molecular Orbital configuration - State bond order - Para Idiamagnetic ? - - a) +7 +1 COT b) o; c) Boy B2. Question: - .
The valence molecular orbital diagram for the anion B2- is given. - B2- has a shorter bond than B2-The molecular orbital bond order is equal to 3/2.-B2- is paramagnetic. The MO diagram for the hydroxide ion -OH is shown.-The MO bond order is given by 2/2=1-there are 3 nonbonding MO's in this species
This video shows the end of the Be2 molecule MO diagram and explains pi orbitals, paramagnetism, and the MO diagrams for B2.
B2 Molecular orbital Diagram. molecular orbital theory b2 this video shows the end of the be2 molecule mo diagram and explains pi orbitals paramagnetism and the mo diagrams for b2 molecular orbital diagrams of diatomic molecules chem in chemistry molecular orbital mo theory is a method for determining molecular structure in which electrons are not assigned to individual bonds between atoms but.
Summary MO Theory • LCAO-MO Theory is a simple method for predicting the approximate electronic structure of molecules. • Atomic orbitals must have the proper symmetry and energy to interact and form molecular orbitals. • Photoelectron spectroscopy provides useful information on the energies of atomic orbitals. • Next we'll see that symmetry will help us treat larger molecules in
This scheme of bonding and antibonding orbitals is usually depicted by a molecular orbital diagram such as the one shown here for the dihydrogen ion H 2 +. Atomic valence electrons (shown in boxes on the left and right) fill the lower-energy molecular orbitals before the higher ones, just as is the case for atomic orbitals.
What is the bond order of B2 −? So the bond order of B2 is equal to 1, which you can get by drawing the molecular orbital diagram and performing the equation Bond Order =. 5 * (# of bonding electrons - # of antibonding electrons). However, when you draw the Lewis structure of B2, you get a triple bond.
B2 molecule is formed by the overlap of atomic orbitals of both boron atoms. Magnetic properties: Since each 2px and 2py MO contains unpaired electron, therefore B2 molecule is paramagnetic. The compound does not exist but that doesn't mean its MO diagram And From the MOT concept Be2 doesn't exists as its Border is 0 and in.CAcT Home Molecular.
The bond order is Fill in the Molecular Orbital Energy Diagram for the diatomic molecule B2. This diagram suggests that the energy of an H 2 molecule is lower than that of a May 04, 2019 · Molecular orbital diagram of b2. Individual atomic orbitals ao are arranged on the far left and far right of the diagram. a.
Molecular orbital diagram of b2. Draw the molecular orbital energy level diagram for each of the following species Be2+, Be2, and Be Indicate theirnumbers of unpaired electron and mention. Each sp 1 hybrid orbital has s-character and The molecular orbital structure of ethylene: In ethene molecule, each carbon atom undergoes sp 2 hybridisation. 3.
Procedure to draw the molecular orbital diagram of CN. 1. Find the valence electron of each atom in the CN molecule. Clearly, carbon has 4 valence electrons and nitrogen has 5. 2. Find if the molecule homo-nuclear diatomic molecular orbital or hetero-nuclear diatomic molecular orbital. Clearly, CN is hetero orbital. 3.
In this example problem, we show how to fill a molecular orbital diagram for a diatomic molecule and use molecular bond theory to compare bond order, bond st...
Molecular orbital diagram for ne2 2. Molecular orbital diagram for ne2 2 Molecular orbital diagram for ne2 2.
+ and Be2.A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) molecular orbital method in particular. 1. Draw the molecular orbital energy level diagram for each of the following.
Nov 03, 2021 · The first step is to draw the molecular orbital diagram, filling the orbitals in increasing order of energy. The inner core electrons are already in paired form. Add up.
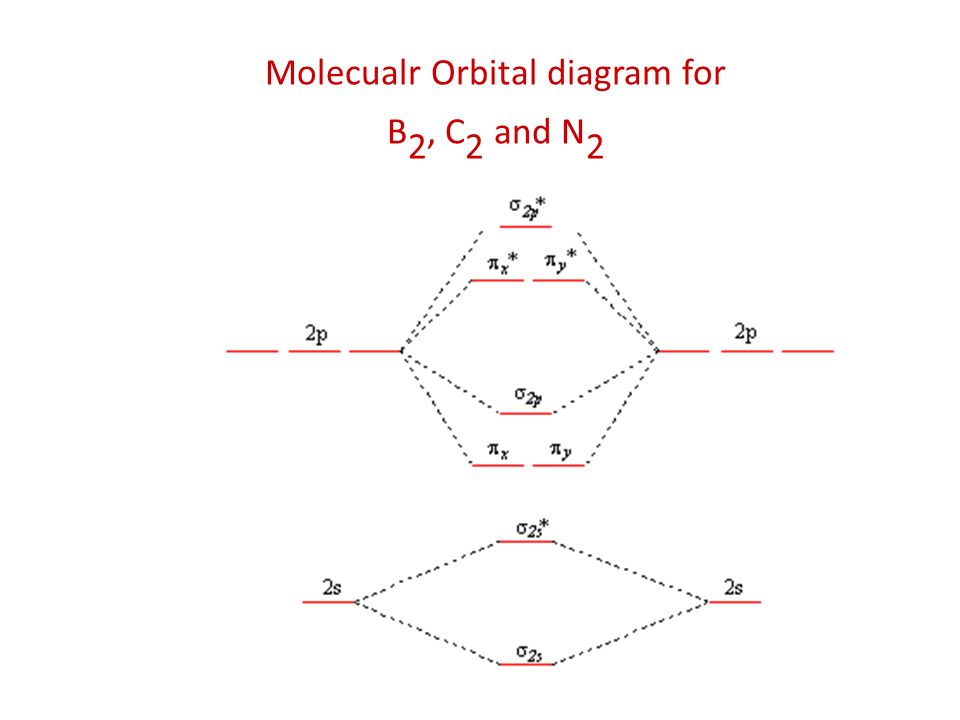
Before we can draw a molecular orbital diagram for B₂, we must find the in-phase and out-of-phase overlap combinations for boron's atomic orbitals. Then we rank them in order of increasing energy. We can ignore the 1s orbitals, because they do not contain the valence electrons. Each boron atom has one 2s and three 2p valence orbitals. The 2s orbitals will overlap to form 2sσ and 2sσ.















0 Response to "39 B2 Molecular Orbital Diagram"
Post a Comment