40 Hertzsprung-russell Diagram Lab
The Hertzsprung - Russell Diagram Laboratory 11 Objective: In this laboratory a random sample of stars will be used to create a HR Diagram. From the diagram it will be determined which category certain stars belong to: Super Giants, Giants, and White Dwarfs. The properties of each category will be discussed as well as the Main Sequence, The main article for this category is Hertzsprung-Russell diagram. This page uses content from the English language Wikipedia. The original content was at Category:Hertzsprung-Russell classifications. The list of authors can be seen in the page history. As with this Familypedia wiki, the content of Wikipedia is available under the Creative.
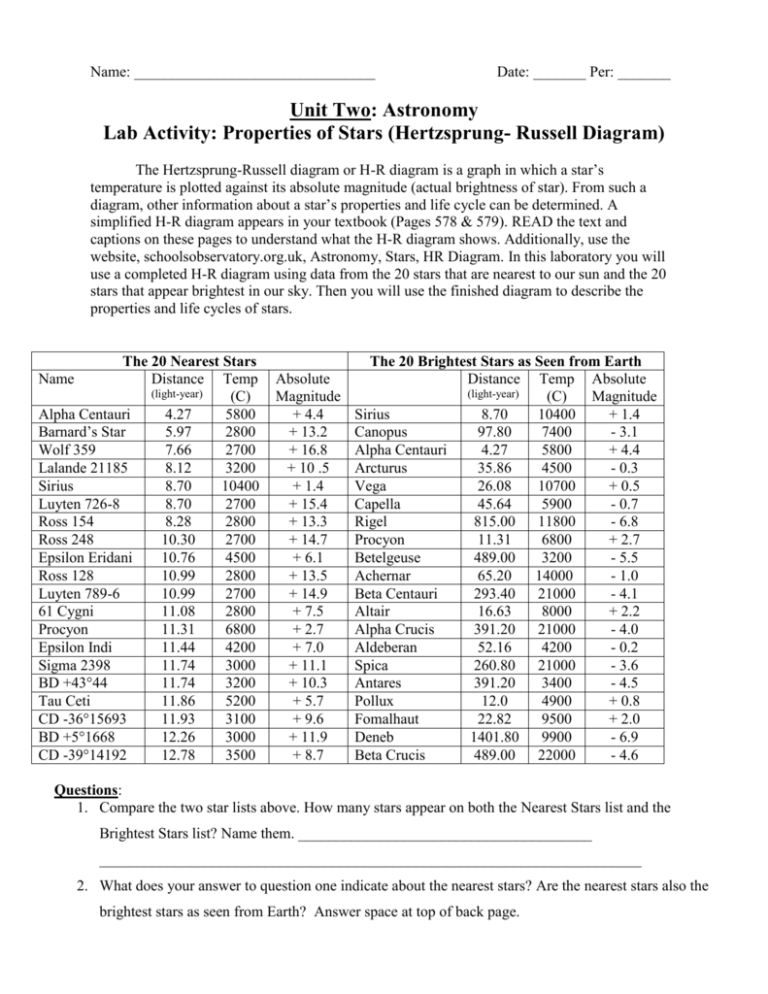
HR Diagram Lab. Course: Astronomy Of Stars And Galaxies (AST 132) Name: Adele Harris. HR Diagram – Student Gui de. Background Information. W ork through the background sections on Spec tral Classification, Luminosi ty, a nd the. Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram. Then complete the following questions related to the background.
Hertzsprung-russell diagram lab
Ursa Major constellation lies in the northern sky. Its name means “the great bear,” or “the larger bear,” in Latin. The smaller bear is represented by Ursa Minor.. Ursa Major is the largest northern constellation and third largest constellation in the sky. Its brightest stars form the Big Dipper asterism, one of the most recognizable shapes in the sky, also known as the Plough. Hertzsprung - Russell diagram. Procedure: 1. Take a look at the figure of the constellation Orion. The circles represent the stars of the constellation Orion. The diameter of the stars represents their magnitude. 2. Trace the stars on another sheet of paper. 3. Color each star with the appropriate color and then cut them out. Astronomy Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram Lab. STUDY. PLAY. graphs of intensity versus wavelength for an object; how much light is produced at each color. spectra. a complete rainbow of colors. continuous spectrum. a series of bright spectral lines against a dark background. emission line spectrum.
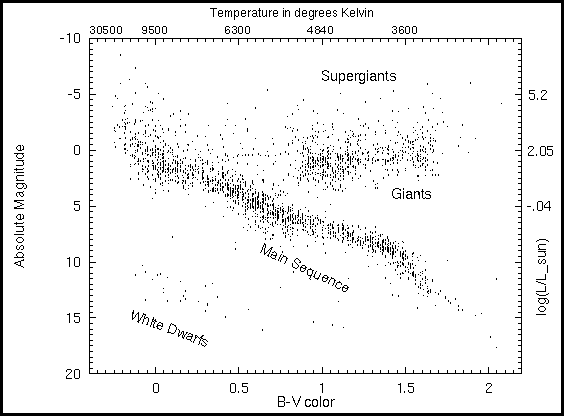
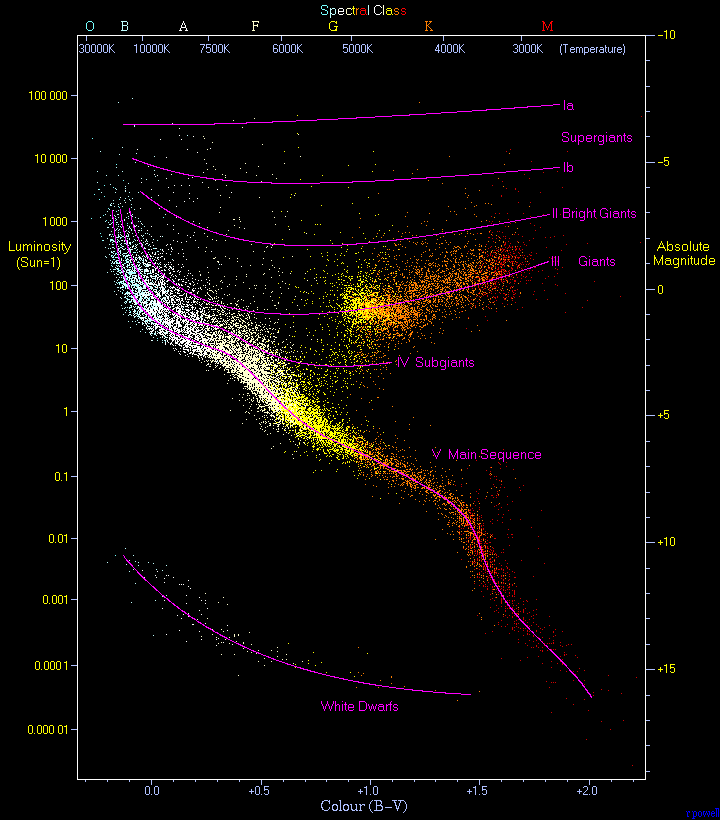
Hertzsprung-russell diagram lab. 49 Hertzsprung- Russell Diagram Hertzsprung- Russell Diagram. The Hertzsprung- Russell diagram , or the H-R diagram , is a graph which plots a star's brightness versus its color.This very-useful graphic was developed around 1910 by Danish astronomer Ejnar Hertzsprung and American astronomer Henry Norris Russell.The H-R diagram groups stars into four major classes, and shows stellar. An HR diagram reveals commonalities between stars and their properties, and it reveals the evolutionary life cycles of stars. By the end of this lab, students are expected to know: 1. The spectral classes of stars, and how they relate to the star's surface temperature 2. What an Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram is 3. The general life stages of. Stellarium Lab: Hertzsprung Russell Diagram Objectives: Upon the completion of this lab the student will be able to: Build an HR Diagram based on Absolute Magnitude and Color Index (B-V) data Discuss the Spectral Class of a star based on its B-V Color Index Calculate Surface Temperature of a star using Ballesteros' Formula Identify the Type of stars on an HR Diagram Calculate distance to a. (G) use the Hertzsprung-Russell diagram to plot and examine the life cycle of stars from birth to death. Colors of Stars activity Spectroscopy activities including H-R diagram Lives of Stars activity (link is on lower part of this page) Interview with a White Dwarf (activity components) -.
The Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram and Stellar Evolution AST 103 Galaxy Classification Lab See bottom row for classification guides ( Contact Irving K. With ANC, you’ll get only 5 hours of continuous Feb 01, 2020 · *This application is for Galaxy Buds+ and Galaxy Buds Live. 5.) Explain in 1-2 sentences what the Hertzsprung-Russell diagram shows (1 point). The HR Diagram shows the relationship between the brightness and temperature of stars. The majority of stars follow a main sequence trend line from red, cold, and dim to blue, hot, and bright with a few outliers like white dwarfs and red giants. Lab 14 Hertzsprung-Russel Diagram (Astronomy) DR. GREGG. WILKERSON. Questions on pages 156 and 157 can be answered on pages 158 and 159. p. 156, Introduction Hertzsprung-Russell Diagrams and Distance to Stars 10.1 Purpose In this lab, we will explore how astronomer classify stars. This classification is one way that can be used to determine the distance to stars that are more distant than those that can be measured using parallax. 10.2 Introduction
Native Apps. Executables (64-bit and 32-bit) for Windows and (64-bit) for Macintosh computers are available for all of our older projects (NAAP, ClassAction, & Ranking Tasks). The appropriate package for your (or your student's) computer system must be downloaded and installed locally. Note that these are actual applications that run in your. Ursa Major constellation lies in the northern sky. Its name means “the great bear,” or “the larger bear,” in Latin. The smaller bear is represented by Ursa Minor.. Ursa Major is the largest northern constellation and third largest constellation in the sky. Its brightest stars form the Big Dipper asterism, one of the most recognizable shapes in the sky, also known as the Plough. Print our Ninth Grade (Grade 9) worksheets and activities or administer as online tests. Our worksheets use a variety of high-quality images and some are aligned to Common Core Standards. Lab 6 The Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram and Stellar Evolution 6.1 Introduction On a clear, dark night, one might see more than two thousand stars. Unlike our distant ancestors, we recognize that each one is a huge ball of hot gas that radiates energy, like our own (very nearby) star, the Sun. Like the Sun, the stars shine by converting hydrogen
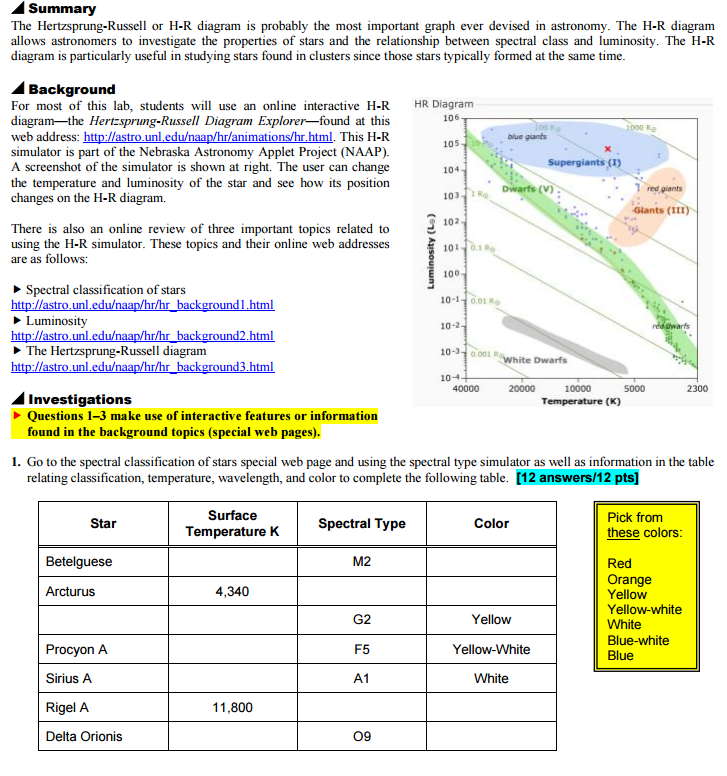
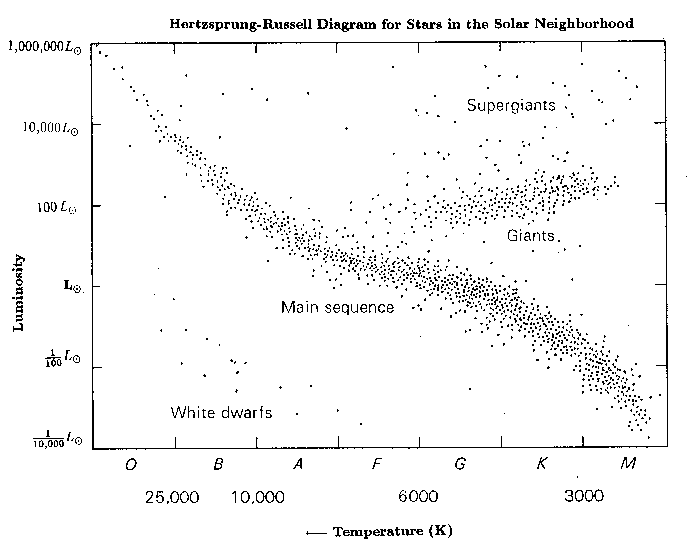
INSIDE LAB 7: Plotting Stars on the Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram OBJECTIVE: To become familiar with the Hertzsprung-Russell diagram and the method of spectroscopic parallax. DISCUSSION: The Hertzsprung-Russell diagram (H-R diagram) is a plot of the luminosity of a star versus its spectral classification.
Astronomy Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram Lab. STUDY. PLAY. graphs of intensity versus wavelength for an object; how much light is produced at each color. spectra. a complete rainbow of colors. continuous spectrum. a series of bright spectral lines against a dark background. emission line spectrum.
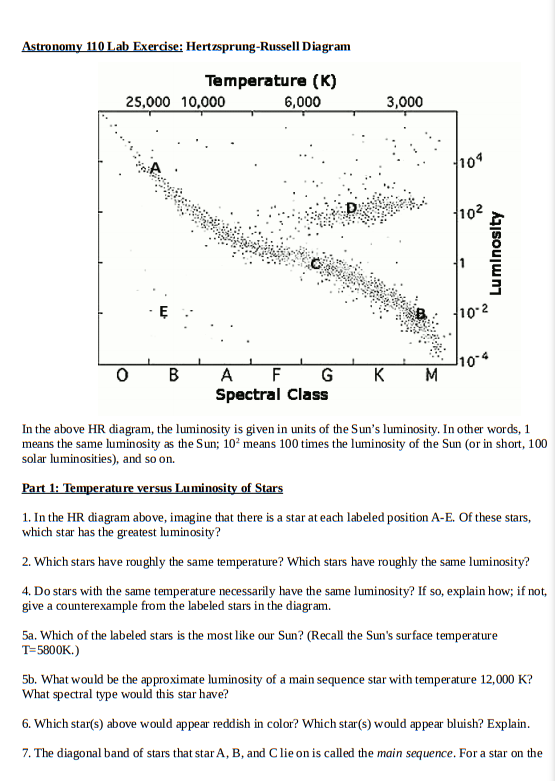
Period _____ Lab _____ THE HERTZSPRUNG-RUSSELL DIAGRAM Astronomers use two basis properties of stars to classify them. These two properties are luminosity and surface temperature. Luminosity usually refers to the brightness of the star relative to the brightness of our sun.
Indoor lab: The Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram and Selection Effects. 1. Use the program "The Sky" to select 40 stars at random, and record the following properties in an Excel table. Note: do not include stars whose distances are not given. star name (use ANY of the names given) (put in Excel column 1) visual magnitude, m (col. 2),
The waves of light in the figure are represented as rings, similar to the waves in a pond. If the source of a wave is stationary, the space between each ring (the wavelength) should be constant, and the rings should appear completely circular.An observer located anywhere around the source will record the wave arriving at her location with a wavelength equal to the wavelength as it was emitted.
The purpose of this lab is to have you identify the main characteristics used to classify stars, and the five main types of stars. You will also become familiar with the use of the Hertzsprung-Russell (HR) diagram used for the classification of stars.
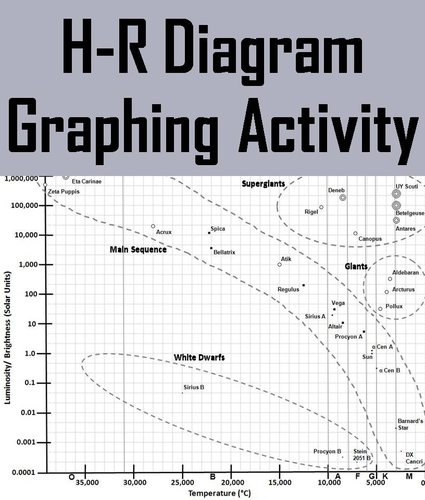
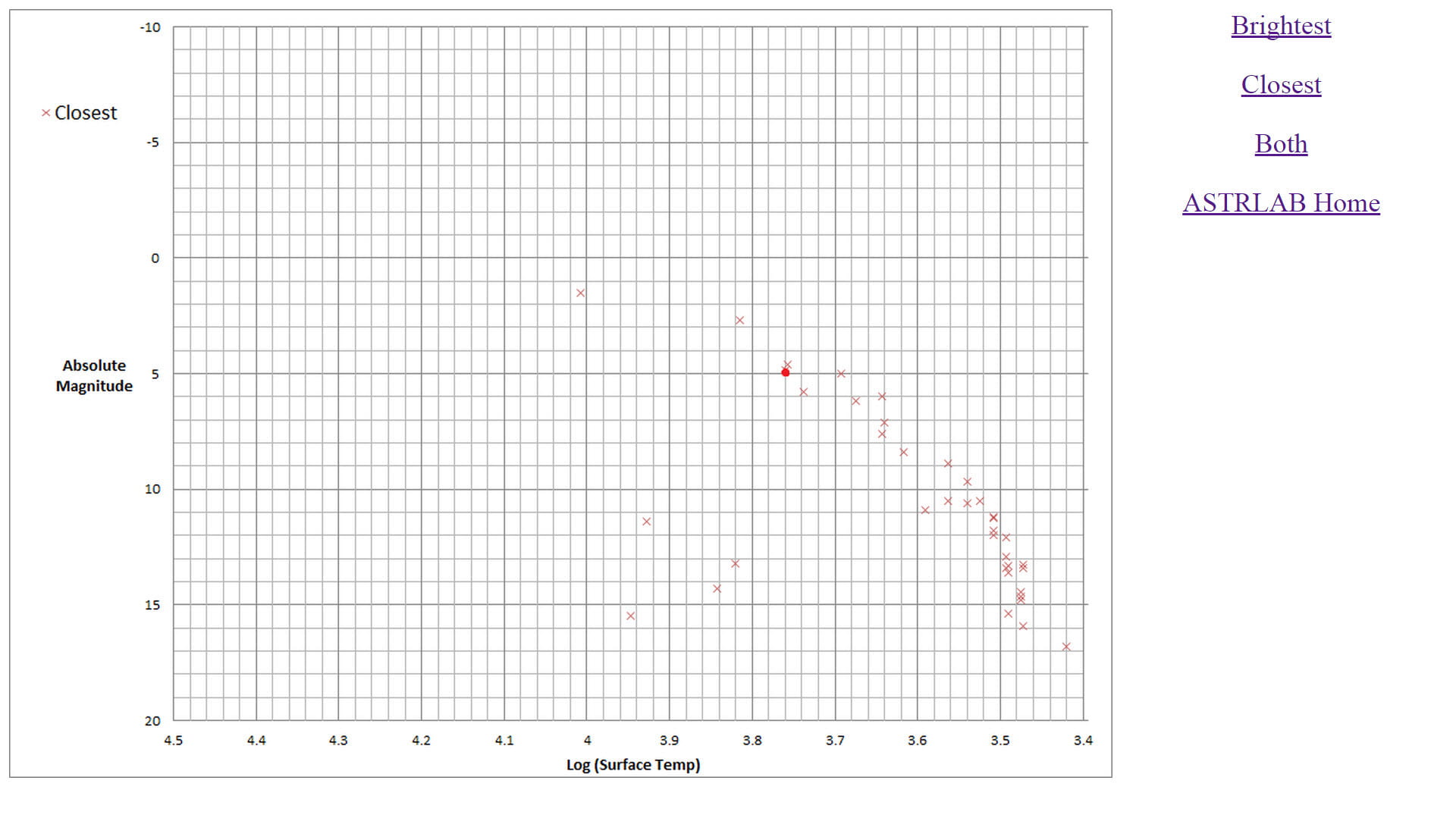
Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram Lab. Click on graph to view full size. HR Diagram of both Brightest and Closest Stars. HR Diagram of Brightest stars only.
The students will use a Hertzsprung-Russell(HR) Diagram simulation/animation from a website for this lab. This site allows the student to manipulate the variables of stars from the HR diagram (temperature, color, spectral type, size/mass, luminosity), in order to understand how stars can be classified/categorized.
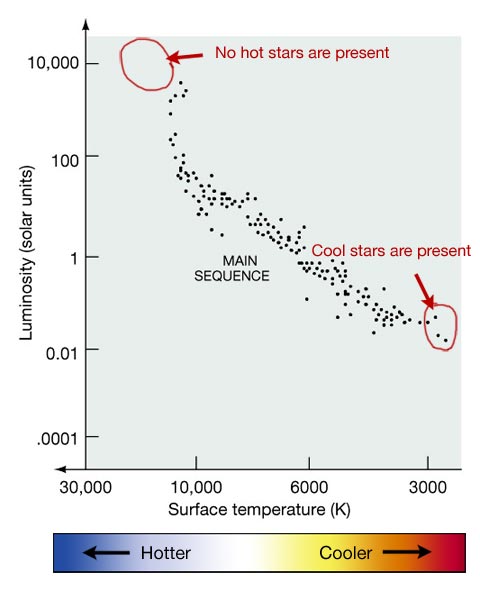
The Hertzsprung-Russell diagram (or HR diagram) is constructed in logarithmic coordinates. In this graphic construction, each star is a point marked on the ordinate by its brightness (luminosity or absolute magnitude) and on the abscissa by its spectral type (or surface temperature). By making such a graph for a cluster of stars, H.N. Russell publishes an article in Nature in 1914 where he.
7. According to the HR diagram, a massive star with a surface temperature of 20,000 K that is nearly a million times brighter than the sun would mostly likely be classified as a _____ 8. Which type of star is dimmer than the Sun? _____ 9.
The Hertzsprung-Russell diagram, abbreviated as H-R diagram, HR diagram or HRD, is a scatter plot of stars showing the relationship between the stars' absolute magnitudes or luminosities versus their stellar classifications or effective temperatures.The diagram was created independently around 1910 by Ejnar Hertzsprung and Henry Norris Russell, and represented a major step towards an.
Lab #6. The Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram and Stellar Evolution. Students explore the basic phases of stellar evolution on and beyond the Main Sequence, and learn to utilize a Hertzsprung-Russell (color-magnitude) diagram to understand the relationship between fundamental parameters for stars such as mass, luminosity, temperature, and age.
Study the Hertzsprung-Russell diagram in the LINK and answer the question that follows. The temperature of a star is 6000K and its luminosity is 1000. Which type of star is it?. lab 12 bacteriology. 17 terms. lesley_jimenez3. protists lab 13. 37 terms. lesley_jimenez3. lab 17 fungi. 22 terms. lesley_jimenez3. Other Quizlet sets. Pediatric...
Hertzsprung- Russell Diagram. The Hertzsprung- Russell diagram , or the H-R diagram , is a graph which plots a star's brightness versus its color.This very-useful graphic was developed around 1910 by Danish astronomer Ejnar Hertzsprung and American astronomer Henry Norris Russell.The H-R diagram groups stars into four major classes, and shows stellar evolution: how stars change as they fuse.
The Hertzsprung-Russell (HR) Diagram is commonly viewed by students as simply another graph to make or even worse, simply another graph to observe and memorize. The day that my students create and interpret the Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram is one of my absolute favorite days of the year.
Hertzsprung - Russell diagram. Procedure: 1. Take a look at the figure of the constellation Orion. The circles represent the stars of the constellation Orion. The diameter of the stars represents their magnitude. 2. Trace the stars on another sheet of paper. 3. Color each star with the appropriate color and then cut them out.
(c) A sketch of a Hertzsprung-Russell diagram is shown below. l u m i n o s i t y t e m p e r a t u r e On the diagram above, identify the (i) main sequence (label this M); (ii) red giant region (label this R); (iii) white dwarf region (label this W). (2) (d) In a Hertzsprung-Russell diagram
The Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram Stellar Evolution: Mass dependence Before returning to open clusters and globular clusters, we are going to revisit the topic of.
Nebraska Astronomy Applet Project: Hertzsprung-Russel Diagram Lab. published by the Astronomy Education at the University of Nebraska. written by Kevin M. Lee. This simulation explores the Hertzsprung-Russell diagram and those topics necessary to understand the diagram. These topics include the different kinds of spectrum, spectral.
Access the lab content at Name: _Jamie Machtmes The H-R Diagram Background Information Work through the background sections on Spectral Classification, Luminosity, and the Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram. Then complete the following questions related to the background information. Remember to type your answer in blue text.
The Hertzsprung-Russell diagram is one of the most important tools in the study of stellar evolution.Developed independently in the early 1900s by Ejnar Hertzsprung and Henry Norris Russell, it plots the temperature of stars against their luminosity (the theoretical HR diagram), or the colour of stars (or spectral type) against their absolute magnitude (the observational HR diagram, also known.
Q. Use the Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram to answer the following question. Sirius B is a _____. Q. Use the Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram to answer the following question. Epsilon Eridani is a _____. Q. John observes three different colored stars. What can John infer about the three stars.
This video demonstrates the use of the Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram Simulator created by the Nebraska Astronomy Applet Project. The simulator can be downloade...
use models such as the Hertzsprung -Russell diagram for classification 8.9(B) relate plate tectonics to the formation of crustal features 8.9(C) interpret topographic maps and satellite views to identify land and erosional features and predict how these features may be reshaped by weathering
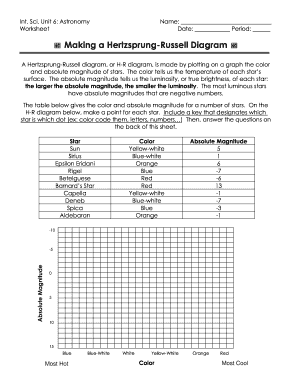
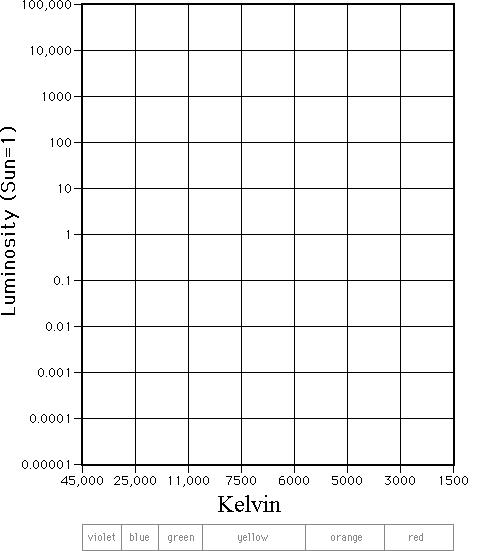
H. R. Diagram Lab Directions Step #1: Look at the chart on the next page to identify each star's temperature and luminosity. Plot the characteristics of each star on the chart titled, "Characteristics of Stars". Be sure to label each star's name next to its data point on the chart. Step #2: The color that a star appears is based upon its.
Students will use a Venn diagram to compare lightning and static electricity. Then, students will experiment with static electricity and read nonfiction passages about lightning and lightning rods. Finally, they will apply their learning to construct a model of a lightning rod system that protects a house from a lightning-induced fire.



















0 Response to "40 Hertzsprung-russell Diagram Lab"
Post a Comment