40 Acl And Mcl Diagram
The medial collateral ligament (or MCL for short) connects the thigh bone (or femur) to the shin bone (or tibia) on the inside of the knee. It prevents your knee joint from moving sideways, particularly from forces on the outside of the knee. The MCL itself has two parts to it: Multiligament Knee Injury (ACL/PCL +/- MCL/PLC) Rehabilitation following surgery for multiligament knee injury (MLKI) or knee dislocation is an essential element of the treatment to achieve a full recovery. This protocol is intended to provide the user with instruction, direction, rehabilitative guidelines and functional goals. It is not meant
Jun 21, 2021 · Anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) avulsion fracture or tibial eminence avulsion fracture is a type of avulsion fracture of the knee. This typically involves separation of the tibial attachment of the ACL to variable degrees. Separation at the femo...

Acl and mcl diagram
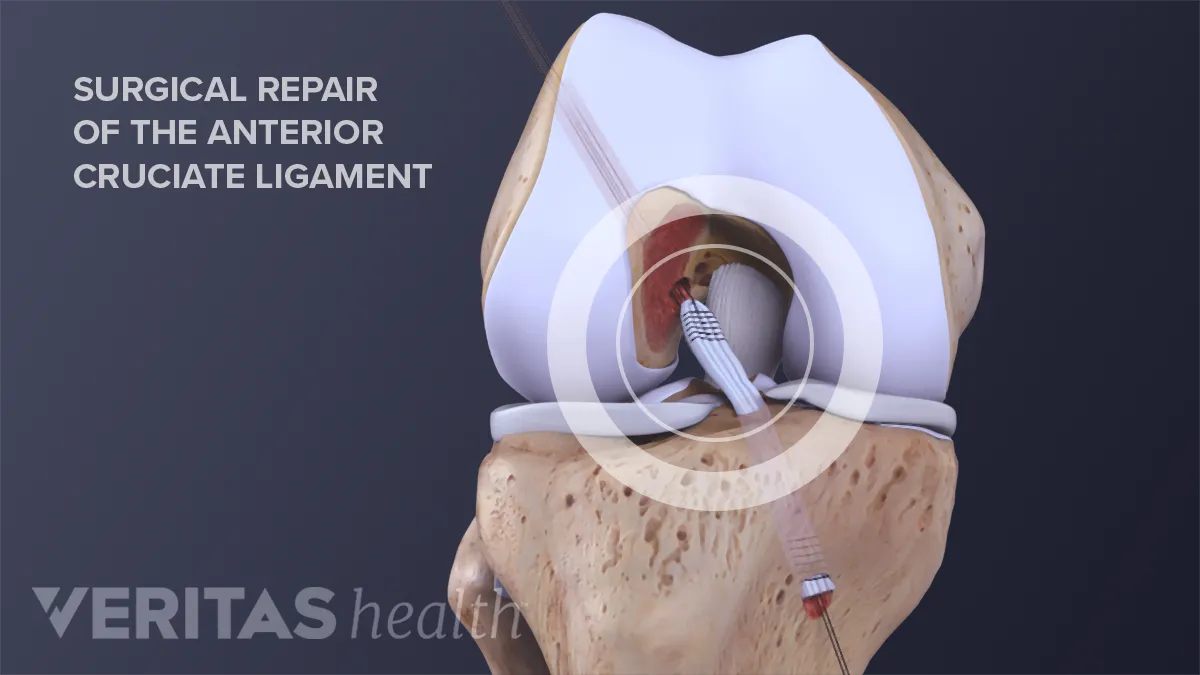
The anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) is one of a pair of cruciate ligaments (the other being the posterior cruciate ligament) in the human knee.The two ligaments are also called "cruciform" ligaments, as they are arranged in a crossed formation. In the quadruped stifle joint (analogous to the knee), based on its anatomical position, it is also referred to as the cranial cruciate ligament. staged for optimal outcomes. Surgery uses an allograft or autograft to reconstruct the torn ACL and PCL ligaments, and may repair the MCL, LCL, and/or posterolateral corner of the knee if needed as well. Long-term complications after surgery include chronic pain, knee instability, arthrofibrosis, and loss of knee flexion ROM. An anterior cruciate ligament injury occurs when the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) is either stretched, partially torn, or completely torn. The most common injury is a complete tear. Symptoms include pain, a popping sound during injury, instability of the knee, and joint swelling. Swelling generally appears within a couple of hours. In approximately 50% of cases, other structures of the.
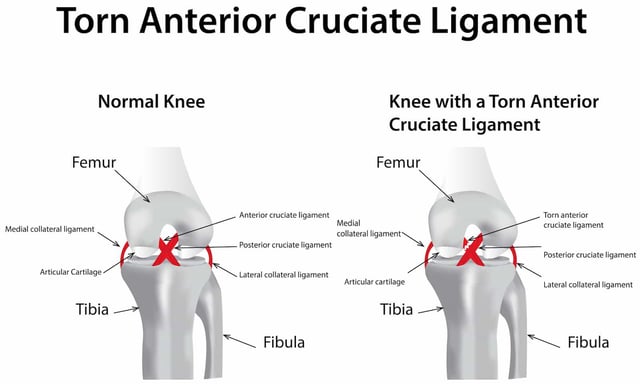
Acl and mcl diagram. staged for optimal outcomes. Surgery uses an allograft or autograft to reconstruct the torn ACL and PCL ligaments, and may repair the MCL, LCL, and/or posterolateral corner of the knee if needed as well. Long-term complications after surgery include chronic pain, knee instability, arthrofibrosis, and loss of knee flexion ROM. A knee ligament injury a sprain of one or more of the four ligaments in the knee, either the Medial Collateral Ligament (MCL), Lateral Collateral Ligament (LCL), Posterior Cruciate Ligament (PCL), or the Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL). ACL, PCL, MCL, and LCL injuries are caused by overstretching or tearing of a ligament by twisting or wrenching the knee. The medial collateral ligament (MCL) and lateral collateral ligament (LCL) are on the sides of the knee and prevent the joint from sliding sideways. The anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) and posterior cruciate ligament (PCL) form an "X" on the inside of the knee and prevent the knee from sliding back and forth. Diagram of a torn ACL A torn ACL or ACL injury is a common occurrence among athletes and others who participate in sports. Females are 2 to 8 times more likely to experience an ACL injury than a male, depending on which sport is involved.
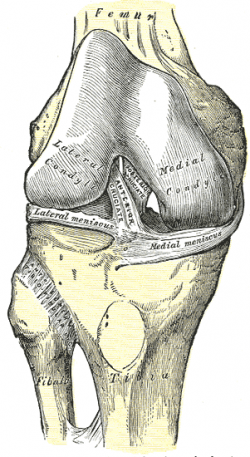
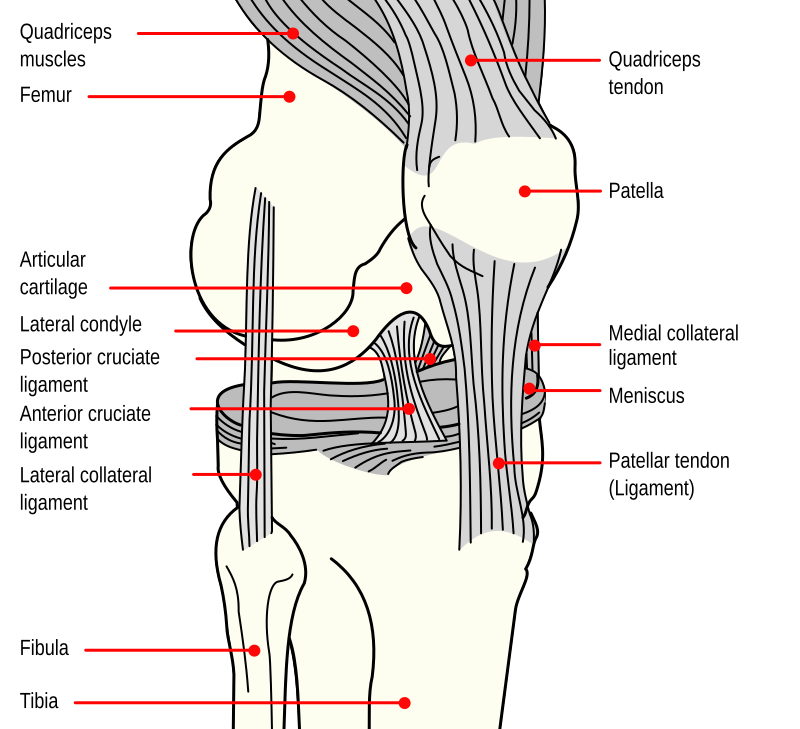
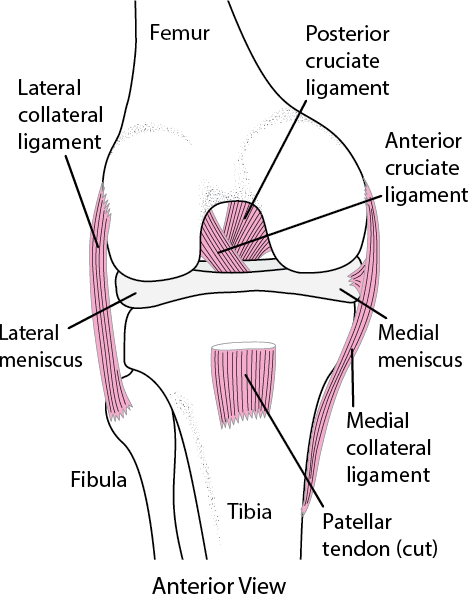
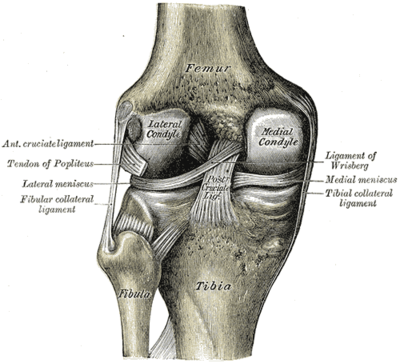
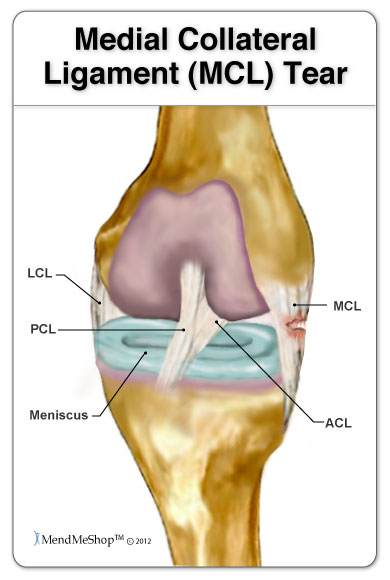
Medial collateral ligament Injury of the knee (MCL Tear) are the most common ligament injuries of the knee and are frequently associated with ACL tears. They are cause by either a direct blow (more severe tear) or a non-contact injury (less severe). Treatment is usually bracing unless there is gross varus instability in which case repair or reconstruction is performed. Assesses: MCL + ACL (Rotator Instability) The test is performed with the patient in a relaxed, supine position. The knee to be tested should be fully extended and the hip flexed to approximately 30 degrees. One of the examiners hands holds heel of the foot of the leg to be tested. The examiner’s other hand is on the lateral aspect of the. The medial collateral ligament (MCL) is a flat band of connective tissue that runs from the medial epicondyle of the femur to the medial condyle of the tibia and is one of four major ligaments that supports the knee. MCL injuries often occur in sports, being the most common ligamentous injury of the knee, and 60% of skiing knee injuries involve the MCL). Here’s a diagram of the knee that explains what and where the various ligaments are: Anatomy of the Knee. ACL = Anterior Cruciate Ligament (this has gone on me) MCL = Medial Collateral Ligmanet (also gone) – this is on the inside of my right knee. LCL = Lateral Collateral Ligament (also gone – outside of my right knee)
The medial collateral ligament (MCL) is one of four ligaments that is responsible for keeping the knee joint stable. (The other three are the anterior and posterior cruciate ligaments [ ACL and PCL] and the lateral collateral ligament [ LCL ].) The MCL connects the inner (medial) surfaces of the thigh bone (femur) and the shin bone (tibia) and. We are pleased to provide you with the picture named Pcl Acl Lcl Mcl Meniscus Anatomy.We hope this picture Pcl Acl Lcl Mcl Meniscus Anatomy can help you study and research. for more anatomy content please follow us and visit our website: www.anatomynote . Anatomynote found Pcl Acl Lcl Mcl Meniscus Anatomy from plenty of anatomical pictures on the internet. Medial Collateral Ligament (MCL)... Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL)... Posterior Cruciate Ligament (PCL)... The outside joint capsule includes... the LCL and MCL. The inside joint capsule includes... the ACL and PCL. Sets found in the same folder. knee bones (pt1) 11 terms. Oct 19, 2021 · Bangor Daily News - a place for remembering loved ones; a space for sharing memories, life stories, milestones, to express condolences, and celebrate life of your loved ones
Jul 31, 2021 · Segond fracture is an avulsion fracture of the knee that involves the lateral aspect of the tibial plateau and is very frequently (~75% of cases) associated with disruption of the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL).On the frontal knee radiograph, it may be referred to as the lateral capsular sign.
The exact location of MCL can be described as within the inner part of the knee from the bottom of the thighbone to a point on the top of shinbone, which is about 4-6 inches from the knee. The locations of ACL and MCL and where it can be torn are indicated in the following diagram: ACL vs. MCL Tears
Anterior to the intercondyloid eminence of the tibia, being blended with the anterior horn of the medial meniscus. The tibial attachment is in a fossa in front of and lateral to anterior spine, a rather wide area from 11 mm in width to 17 mm in AP direction.. For more detail on the anatomy of the ACL, please see this page: Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) - Structure and Biomechanical Properties
ACL Tear and MCL Tear Treatment and Healing Time. For an ACL Tear: Treatment for an ACL tear will vary on two main factors: (a) The severity of the injury, and (b) the patient's lifestyle. For minor injuries or for a person who has either a sedentary lifestyle or low activity level, conservative treatment such as physical therapy may suffice.
Anterior cruciate ligament (ACL). (LCL and MCL) don't need surgery. However, when a cruciate ligament (ACL or PCL) is completely torn or stretched beyond its limits, the only option is...
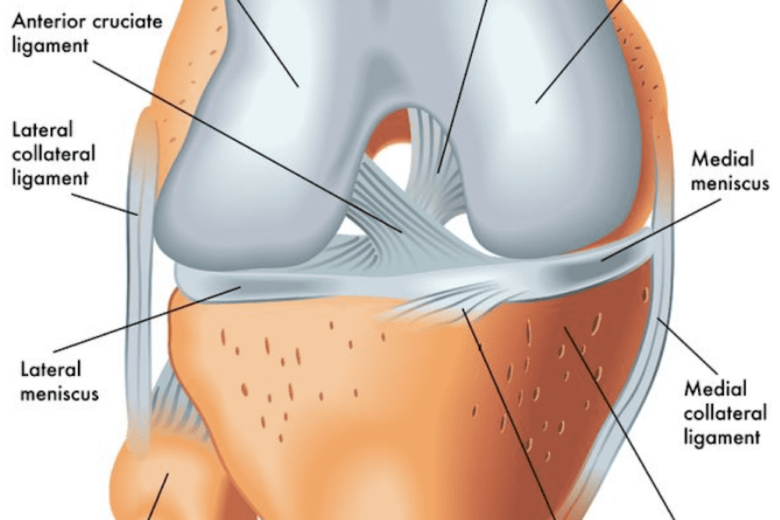
The meniscus has two distinct areas: White Zone: the inner portion of the knee meniscus.It is avascular, meaning it d oes not have a blood supply; Red Zone: the outer portion of the knee meniscus. This part does have a reasonable blood supply being vascularised by the joint capsule.
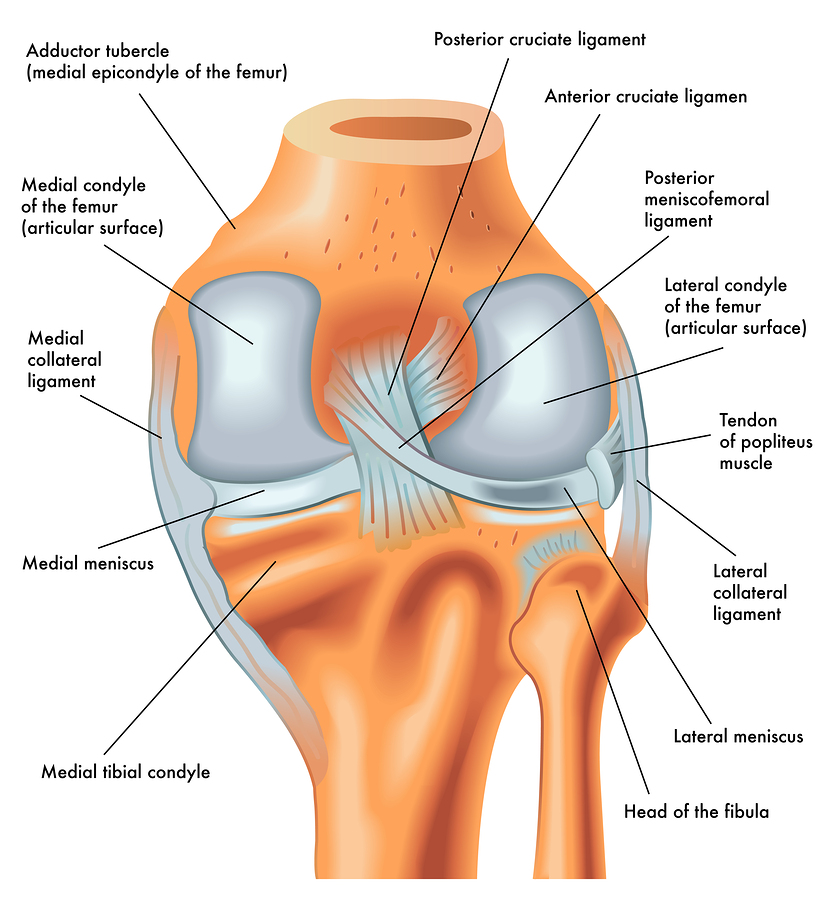
Mar 29, 2021 · The intercondylar fossa is the location for 2 important knee ligaments: the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) and the posterior cruciate ligament (PCL). The ACL attaches to the medial aspect of the lateral femoral condyle. The PCL attaches to.
Download scientific diagram | Postoperative X-ray after ACL reconstruction and MCL ligament bracing from publication: Acute MCL and ACL injuries: first results of minimal-invasive MCL ligament.
Symptoms of a Torn MCL Diagram. Functions of the PCL and ACL. Mechanisms of Injury in the Knee. Diagram of a Torn PCL. First Healing Phase in a Knee Injury. Torn ACL Diagram. PLC and ACL Injury Treatment. Signs of a Torn PLC and ACL. ACL Tear Surgery Diagram. ACL, Medial Meniscus, and MLC Injury Diagram. Ligaments of the Knee Diagram.
ACL vs. MCL tears: Although symptoms of ACL and MCL tears are similar, a few key differences will help identify whether the injury affected the ACL or MCL. An ACL tear will have a more distinctive and loud popping sound than an MCL tear. The location of your pain and swelling could indicate either an ACL or MCL tear.
Download scientific diagram | Deep and superficial MCL, and ACL double bundle anatomy from publication: Consideration of growth factors and bio-scaffolds for treatment of combined grade II MCL and.
Unhappy Triad: Torn ACL, MCL and Meniscus An injury to a ligament in the knee often entails damage to other structures as well because of the complex construction of the joint. Surgeons refer to the so-called Unhappy Triad of torn ACL, MCL and meniscus— a triple-pronged injury that is often seen in knee patients.
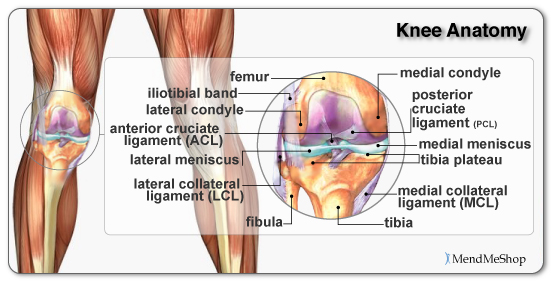
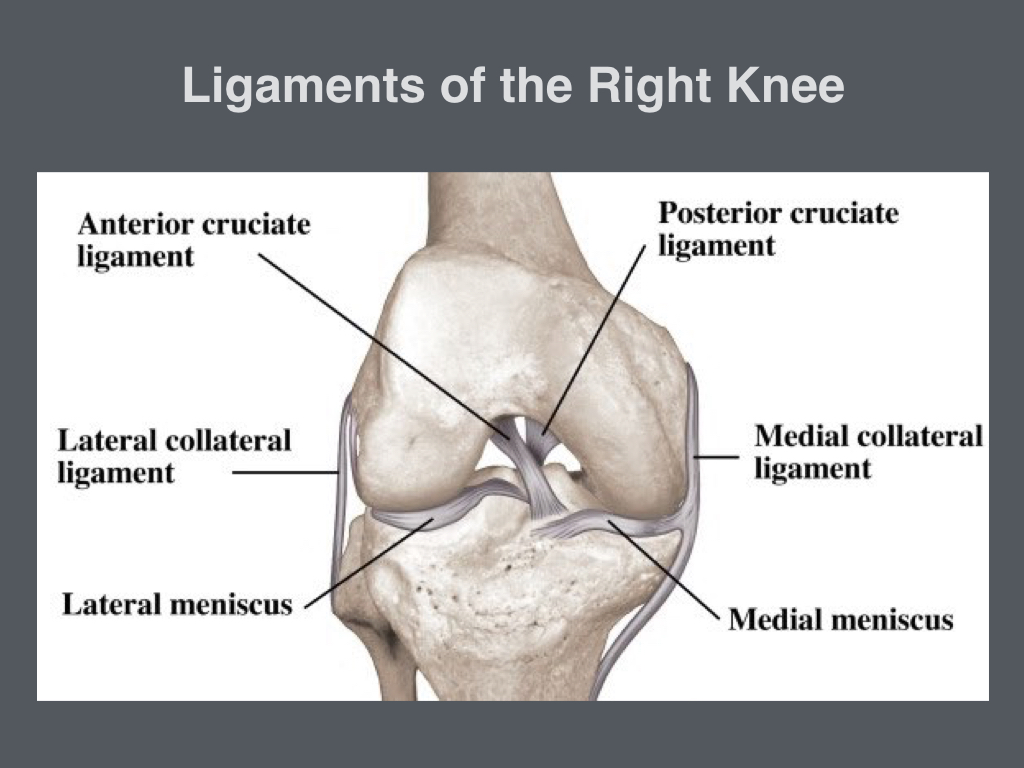
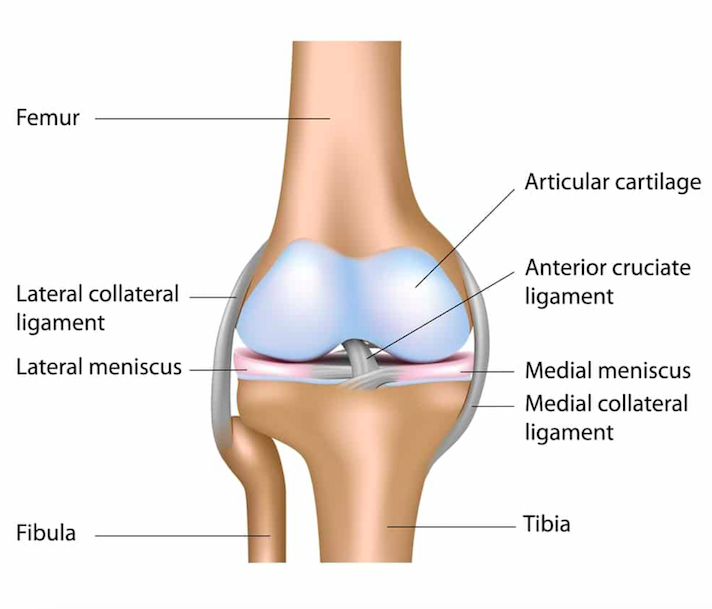
An anterior cruciate ligament (ACL): Inside of the knee and crosses to the front. A posterior cruciate ligament (PCL): Inside of the knee and crosses to the back. The MCL and the LCL sit on the sides of the knee, and they help give stability to the knee if your knee gets hit from the sides. Knee bones, ligaments, and meniscus
An ACL tear often leads to the knee “giving out,” and may require surgical repair. PCL (posterior cruciate ligament) strain or tear: PCL tears can cause pain, swelling, and knee instability.
Jan 23, 2018 · Anterior cruciate ligament (ACL). (MCL) Lateral collateral ligament (LCL) Posterior cruciate ligament (PCL) Damage to the ACL, such as a tear,.
存储一些密码字典(其实就是水仓库的,以后再水一些其他的分享之类的)
Treatment for ACL and PCL injuries essentially is the same, but will differ depending on the severity, or grade, of the injury: Grade 1: The ligament is slightly stretched but the knee is stable. Grade 2: The ligament has become loose or is partially torn. Grade 3: There is a complete rupture of the ligament. Depending on the grade, the injury.
Acl And Mcl Diagram. Signs and symptoms of a medial collateral ligament (MCL) injury include The anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) and posterior cruciate ligament. The MCL is one of four major ligaments that supports the knee. either partial or complete ruptures in the ligament significantly increases the load on the ACL.
MCL Tear Symptoms. Just as with an ACL tear, you may hear a popping sound when the injury occurs. Some of the most common symptoms of an MCL tear include: Pain on the inner side of the knee. Feeling the knee “give out”. Swelling. The knee feels unstable. Pain when putting weight on the knee. Locked knee.
The anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) is one of a pair of cruciate ligaments (the other being the posterior cruciate ligament) in the human knee.The two ligaments are also called "cruciform" ligaments, as they are arranged in a crossed formation. In the quadruped stifle joint (analogous to the knee), based on its anatomical position, it is also referred to as the cranial cruciate ligament.
Ligaments are strong, elastic-like tissues that connect bone to bone and provide stability and protection to your knee joint by limiting the forward and backward movement of the shin bone. There are four ligaments in the knee joint that connect the femur and tibia; the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL), the posterior cruciate ligament (PCL), the medial collateral ligament (MCL), and the lateral.
The Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) and Medial Collateral Ligament (MCL) are two important structures in the knee. Along with other ligaments, the ACL and MCL work together to help keep the knee stable and moving properly. A torn ACL can occur in conjunction with a Grade 1, 2, or 3 MCL tear.
The lateral collateral ligament is much shorter than the medial collateral ligament making it much less common to injure the LCL than the MCL. Cruciate Knee Ligaments. The cruciates are the most important knee ligaments in providing stability of the knee. There are two cruciate ligaments, anterior (ACL) and posterior (PCL).
There are four types of ligaments namely Medial Collateral Ligament (MCL), Lateral Collateral Ligament (LCL), Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) and Posterior Cruciate Ligament (PCL). MCL provides stability to the inner knee and LCL provides stability to the outer part. ACL and PCL are present in the center of the knee.
An anterior cruciate ligament injury occurs when the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) is either stretched, partially torn, or completely torn. The most common injury is a complete tear. Symptoms include pain, a popping sound during injury, instability of the knee, and joint swelling. Swelling generally appears within a couple of hours. In approximately 50% of cases, other structures of the.
Oct 13, 2021 · The knee is made up of 4 very important ligaments, these include the ACL (Anterior cruciate ligament, PCL (posterior cruciate ligament), LCL.
Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL).ACL, PCL, MCL, and LCL injuries are caused by overstretching or tearing of a ligament by twisting or wrenching the knee. 31.07.2021 · Segond fracture is an avulsion fracture of the knee that involves the lateral aspect of the tibial plateau and is very frequently (~75% of cases) associated with disruption of the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL).On the frontal.
:strip_icc():format(jpeg)/kly-media-production/medias/3107265/original/099932600_1587383541-ACL_1.jpg)











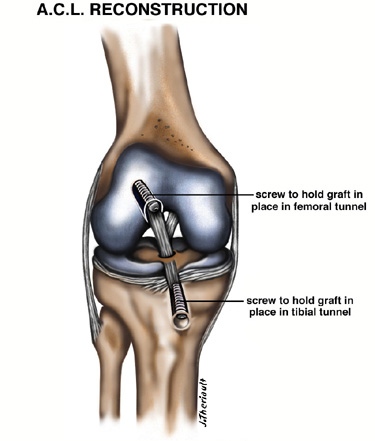
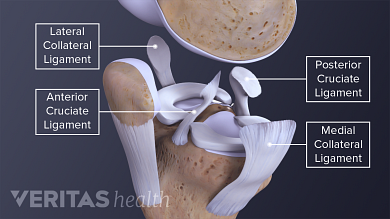


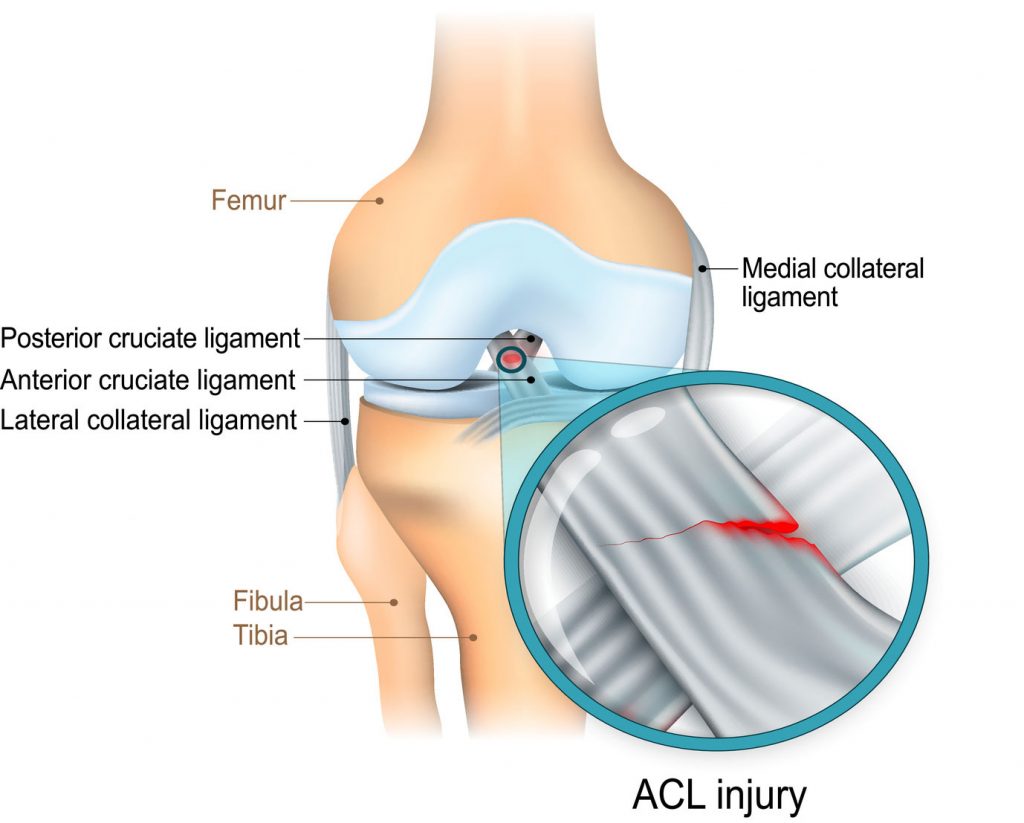
/knee-pain-instability-2549493-5c04aaf946e0fb00010b8e7a-b0ef89c536aa4cd7a9db3f927d72597b.png)

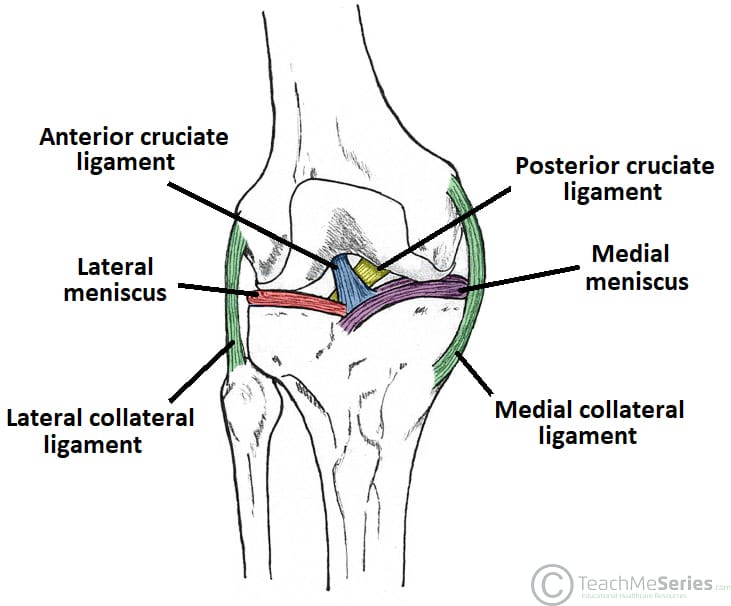


0 Response to "40 Acl And Mcl Diagram"
Post a Comment