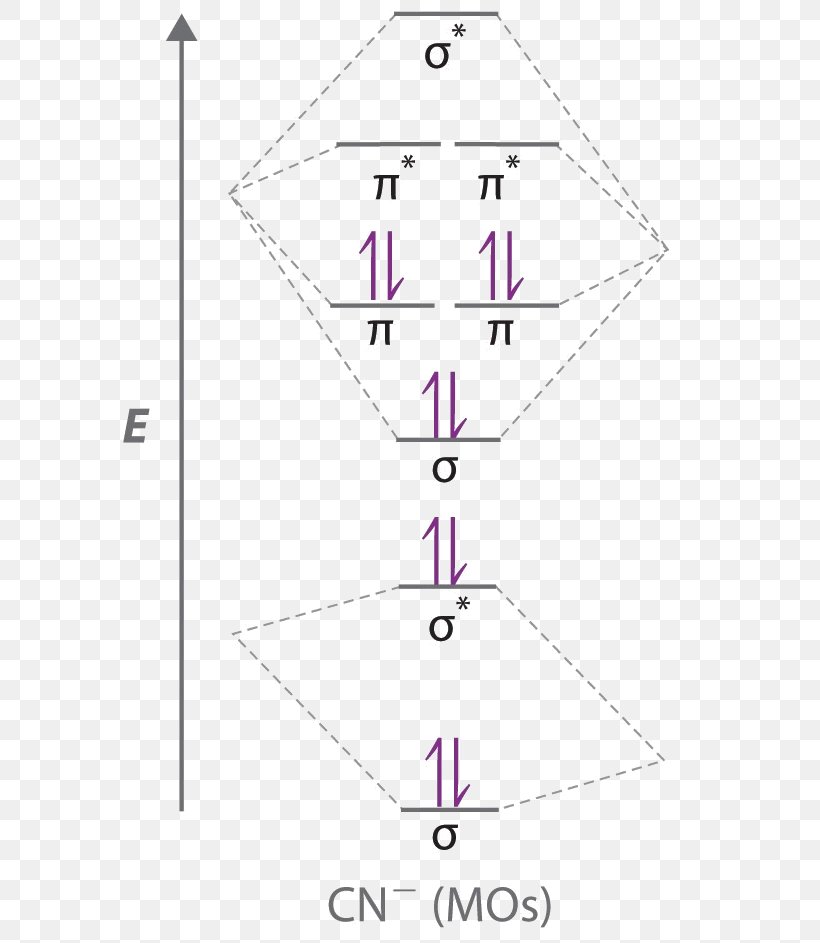
39 Mo Diagram For Cn-
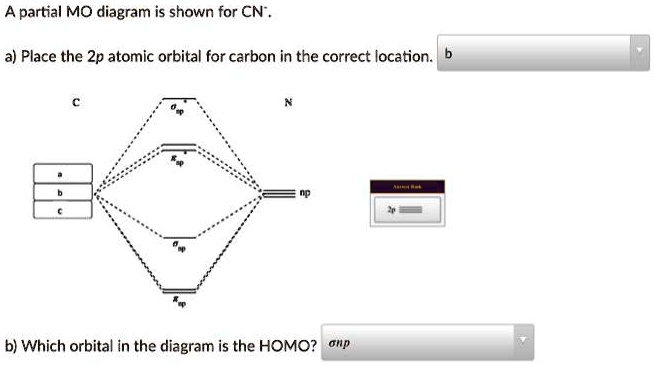
MO Theory • MO diagrams can be built from group orbitals and central atom orbitals by considering orbital symmetries and energies. • The symmetry of group orbitals is determined by reducing a reducible representation of the orbitals in question. This approach is used only when the group orbitals are not obvious by inspection. Science. Chemistry. Chemistry questions and answers. Assignment Score: 36.9% Resources Hint Check Answer < Question 7 of 16 > A partial MO diagram is shown for CN. Place the 2p atomic orbital for carbon in the correct location Which orbital in the diagram is the HOMO?
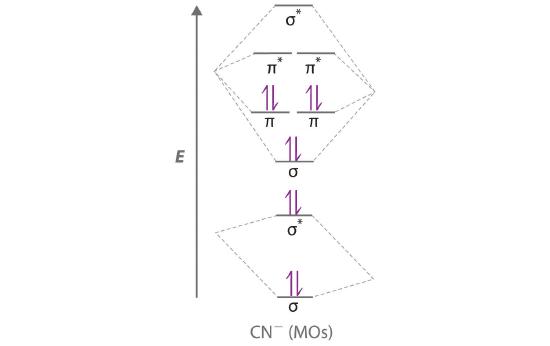
Answer (1 of 5): \text{Bond order} = \frac{n_{\text{bonding electrons}}-n_{\text{antibonding electrons}}}{2} Here is the molecular orbital diagram of CN-: There are 8 bonding electrons and 2 antibonding electrons, therefore B.O.=\frac{8-2}{2}=3 Here's a guide on how to construct MO diagrams, i...
Mo diagram for cn-
A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) method in particular. A fundamental principle of these theories is that as atoms bond to form molecules, a certain number of atomic orbitals combine to form the same number of. K3Fe(CN)6 crystallizes in the monoclinic P2_1/c space group. The structure is three-dimensional and consists of two iron molecules and one K(CN)2 framework. In the K(CN)2 framework, there are two inequivalent K1+ sites. In the first K1+ site, K1+ is bonded in a 4-coordinate geometry to six N3- atoms. There are a spread of K-N bond distances ranging from 2.89-3.29 Å. Answer (1 of 5): \text{Bond order} = \frac{n_{\text{bonding electrons}}-n_{\text{antibonding electrons}}}{2} Here is the molecular orbital diagram of CN-: There are 8 bonding electrons and 2 antibonding electrons, therefore B.O.=\frac{8-2}{2}=3 Here’s a guide on how to construct MO diagrams, i...
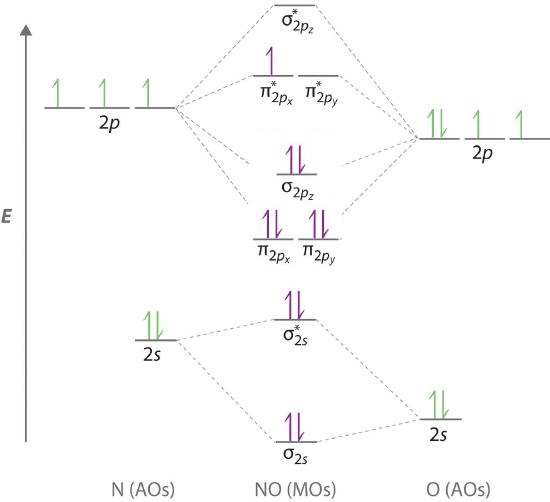
Mo diagram for cn-. The molecular orbital diagram of CN molecule is shown in the following figure: Reference: Essentials of Physical Chemistry /Arun Bahl, B.S Bahl and G.D. Tuli / multicolour edition. Molecular Orbitals for Heteronuclear Diatomic Molecules (MO Theory) Reviewed by تعرف على علم الكيمياء on 5/20/2019 Rating: 5 energy molecular orbital (σ*) will be empty (recall the Aufbau Principle). While there are only two. There would be four electrons to fill into our molecular orbital diagram and that would force us to fill in the bonding sigma MO and the anti-bonding sigma-star MO. What we gain in the bonding sigma MO, we lose in the anti-bonding sigma-star MO. MO Diagram for HF The AO energies suggest that the 1s orbital of hydrogen interacts mostly with a 2p orbital of fluorine. The F 2s is nonbonding. H–F nb σ σ* Energy H –13.6 eV 1s F –18.6 eV –40.2 eV 2s 2p So H–F has one σ bond and three lone electron pairs on fluorine Molecular Orbital Diagrams simplified. Megan Lim. Oct 26, 2016 · 3 min read. Drawing molecular orbital diagrams is one of the trickier concepts in chemistry. The first major step is understanding.
"O"_2 is well-known to be paramagnetic, and it is one of the successes of molecular orbital theory. You can see that "CO" is not (as it has zero unpaired electrons), but "NO" is (it has one unpaired electron). Well, the MO diagram for "O"_2 is: The bond order is already calculated in the diagram. So, in this article, we have learned about How to draw CN– lewis structure, its molecular orbital diagram (MO), formal charges, hybridization, and bond order. Here is a quick review of this article. The bond order of CN- is 3. CN– formal charge is -1 according to its lewis structure. A polyatomic ion is composed of multiple covalently bonded atoms. CO₃²⁻ is a polyatomic ion composed of a carbon atom and three oxygen atoms. Predict the chemical formula for the ionic compound formed by Au³⁺ and HSO₃⁻. Au (HSO3)3. Predict the chemical formula for the ionic compound formed by NH₄⁺ and PO₄³⁻. (NH4)3PO4. Molecular orbital diagram for hydrogen: For a diatomic molecule, an MO diagram effectively shows the energetics of the bond between the two atoms, whose AO unbonded energies are shown on the sides. The unbonded energy levels are higher than those of the bound molecule, which is the energetically-favored configuration.
A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) method in particular. A fundamental principle of these theories is that as atoms bond to form molecules, a certain number of atomic orbitals combine to form the same number of. molecular orbital energy-level diagram for the NO molecule. We assume that orbital order is the same as that for N2. The bond order is 2.5. Figure 9.42: The molecular orbital energy-level diagram for both the NO+ and CN-ions. Figure 9.43: A partial molecular orbital energy-level diagram for the HF molecule. The MO diagram for "NO" is as follows (Miessler et al., Answer Key): (The original was this; I added the orbital depictions and symmetry labels. For further discussion on the orbital energy ordering being "N"_2-like, see here and comments.) Quick overview of what the labels correspond to what MOs: 1a_1 is the sigma_(2s) bonding MO. 2a_1 is the sigma_(2s)^"*" antibonding MO. 1b_1 is the pi_(2p. CN Lewis Structure, Molecular Geometry, Hybridization, Polarity, and MO Diagram. CN is known as cyanide which exists as a pseudohalide anion. It belongs to the cyano group and consists of carbon and a nitrogen atom having a triple bond. It carries a charge of -1 and is a conjugate base of hydrogen cyanide (HCN).
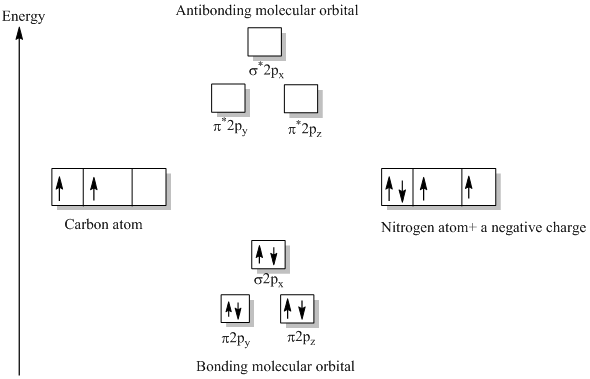
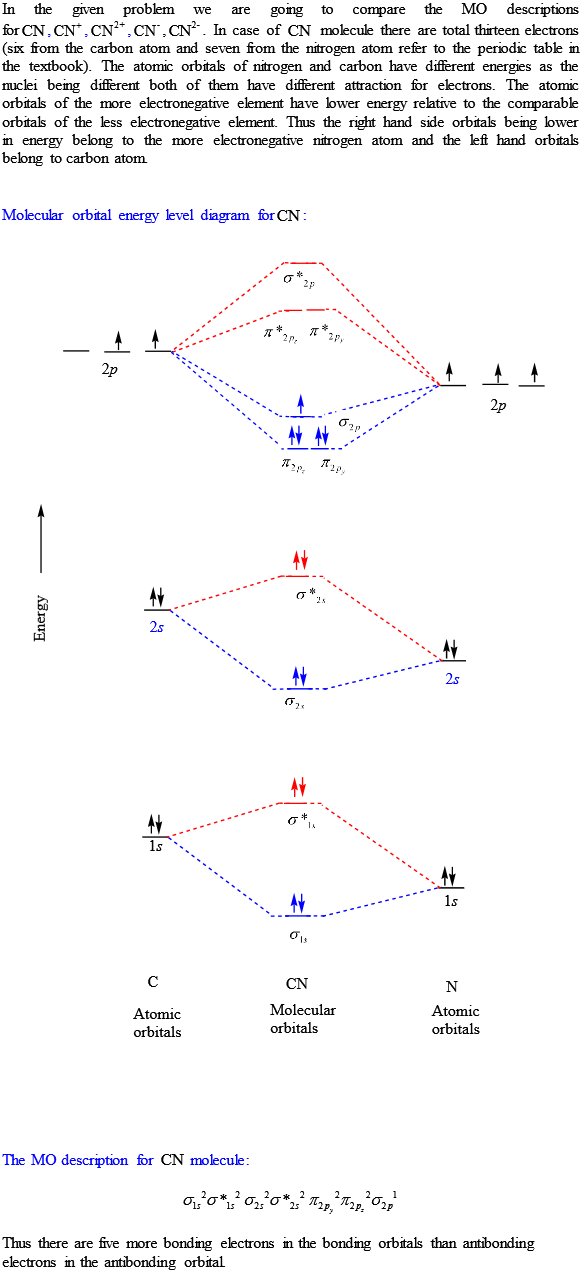
The molecular orbital energy level diagram provided shows the energies of the orbitals for the valence electrons in the free radical CN. Indicate on this diagram the ground state electronic configuration of CN using the arrow notation for electron spins. * C has 4 valence electrons and N has 5 valence electrons, giving a total of 9
Obtain the molecular orbital diagram for a homonuclear diatomic ion by adding or subtracting electrons from the diagram for the neutral molecule. Figure 11. This shows the MO diagrams for each homonuclear diatomic molecule in the second period. The orbital energies decrease across the period as the effective nuclear charge increases and atomic.
#3. Draw the MO diagram for `O_2^+` This is a bit of a curveball, but a perfectly valid problem. Recall that a cation indicates a loss of `1` electron. `O_2^+` is just the ionized form of `O_2`; that is, it's `O_2` with `1` missing electron. The MO diagram will be the same as the MO diagram of `O_2`, except with `1` less electron.
Lecture 3 Ligands and Bonding and Electron Counting in Organo-Transition Metal Compounds. Stable electronic configurations: MO Energy Level Diagrams Reviewed
The Molecule. CO is a very stable 10-valence-electron molecule, isoelectronic with [CN] - and with N 2, which has a slightly lower bond dissociation energy than CO. The formal bond order of CO is 3, from about one σ- bond and two π- bonds. Its most important property is burning in air to give CO 2 , in the combustion of fossil fuels.
Cyanide Molecular Orbital Diagram. MO Theory: the bonding orbital will be lower in energy, the an7bonding The resul7ng MO diagram looks like this. CN– (Cyanide ion), NO+ (Nitrosonium ion ). The molecular orbital diagram of (if order of molecular orbital is like that in) is as shown below. We must remember that total number of electrons in.
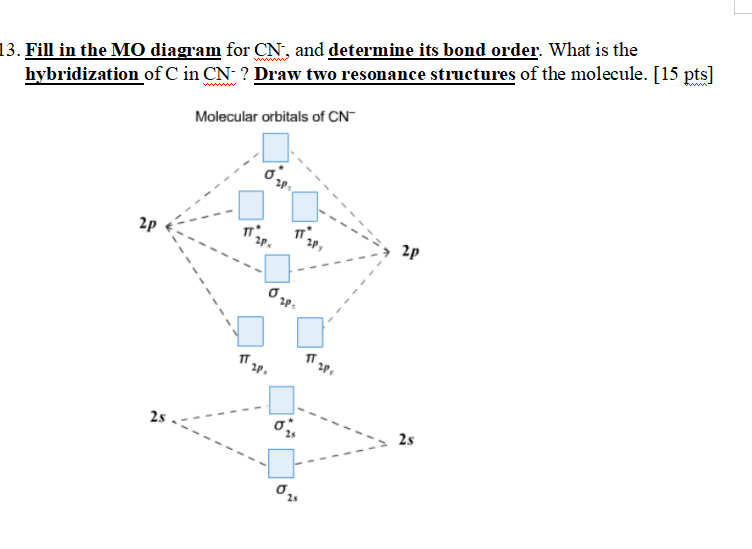
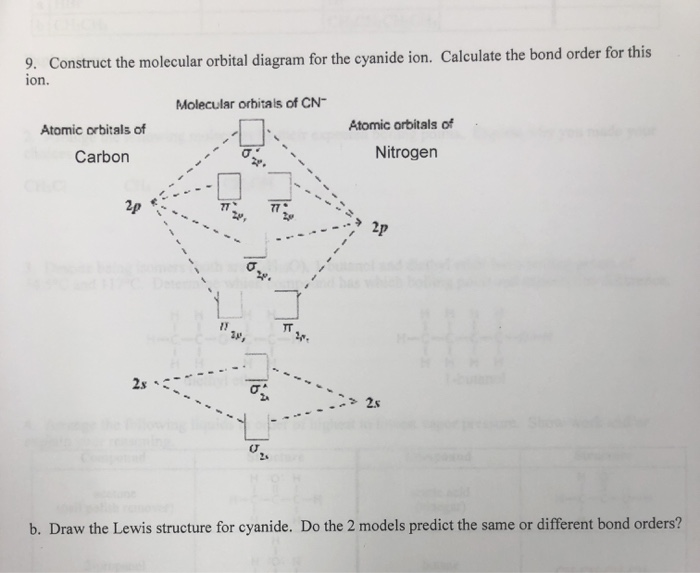
Problem 5.8 1: (a) Prepare a molecular orbital diagram for the cyanide ion. Use sketches to show clearly how the atomic orbitals interact to form MO's. (b) What is the bond order, and how many unpaired electrons does cyanide have? (c) Which molecular orbital of CN - would you predict to interact most strongly with a hydrogen 1 s orbital to form an H-C bond in the reaction CN - + H + HCN?
Answer (1 of 5): \text{Bond order} = \frac{n_{\text{bonding electrons}}-n_{\text{antibonding electrons}}}{2} Here is the molecular orbital diagram of CN-: There are 8 bonding electrons and 2 antibonding electrons, therefore B.O.=\frac{8-2}{2}=3 Here’s a guide on how to construct MO diagrams, i...
121AP. Draw the molecular orbital diagram for the cyanide ion (CN − ). (Assume the ordering of moleculer orbitals to be like that in N 2.) Write the electron configuration of the cyanide ion (CN − ). Step-by-step solution. Step 1 of 4. The molecular orbital diagram of (if order of molecular orbital is like that in ) is as shown below.
How to make molecular Orbital diagramhttps://www.youtube /watch?v=UYC-ndQ6Lww&t=6s
This video is about MO Diagram #3 - CN-
Who are the experts? Experts are tested by Chegg as specialists in their subject area. We review their content and use your feedback to keep the quality high. Transcribed image text: 2. Draw Lewis structures and MO diagrams for CN+ CN-, and CN. According to the Lewis model, which molecule is most stable? According to MO theory, which molecule.
K3Fe(CN)6 crystallizes in the monoclinic P2_1/c space group. The structure is three-dimensional and consists of two iron molecules and one K(CN)2 framework. In the K(CN)2 framework, there are two inequivalent K1+ sites. In the first K1+ site, K1+ is bonded in a 4-coordinate geometry to six N3- atoms. There are a spread of K-N bond distances ranging from 2.89-3.29 Å.
Molecular orbital Diagram Cn-mo diagram of cn hunt research group right you have been asked to draw the mo diagram for cn a heteronuclear diatomic don t panic take it one step at a time and you will have a plete mo diagram before you know it this is meant to be an interactive exercise so arrange for some pieces of blank paper a pencil a pen and an eraser molecular orbital theory heteronuclear.
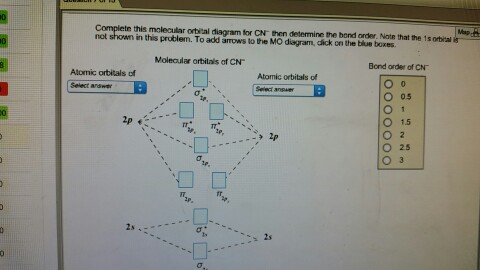
Complete this molecular orbital diagram for CN - then determine the bond order. Note that the 1s orbital is not shown in this problem. Note that the 1s orbital is not shown in this problem. Learn this topic by watching MO Theory: Heteronuclear Diatomic Molecules Concept Videos
The MO diagram for the diatomic carbon monoxide, CO, shows it to be isoelectronic with nitrogen, N 2: The heteronuclear diatomic ions cyanide ion, CN -, and nitrosonium ion, NO +, are also electronic with nitrogen, N 2, and carbon monoxide. The only difference between the MO diagrams are the relative energies of the orbitals.
Molecular orbital theory is also able to explain the presence of Figure \(\ PageIndex{6}\): Molecular Orbital Energy-Level Diagram for HCl. to describe the bonding in the cyanide ion (CN −). mix atomic orbitals on different atoms to get Molecular Orbitals. The resul7ng MO diagram looks like this. CN– (Cyanide ion), NO+ (Nitrosonium ion).














0 Response to "39 Mo Diagram For Cn-"
Post a Comment