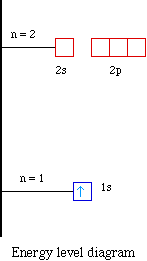
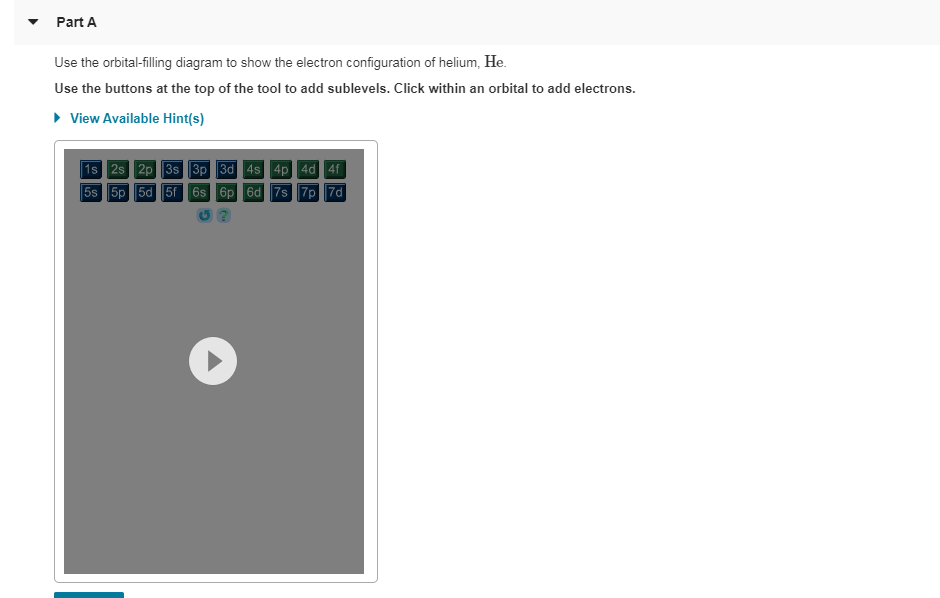
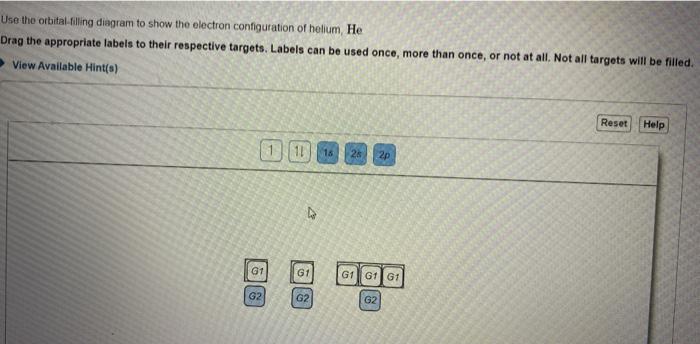
39 Use The Orbital-filling Diagram To Show The Electron Configuration Of Helium, He.
The electron configuration of boron is: B: 1s 2 2s 2 2p 1. Table 5.2 shows the electron configurations of the elements with atomic numbers 1 through 18. The electron configurations of elements with higher atomic number can be written by following the orbital-filling chart in Figure 5.9. Question: Use the orbital-filling diagram to show the electron configuration of helium, He. Drag the appropriate labels to their respective targets. Labels can be used once, more than once, or not at all. Not all targets will be filled. View Available Hint(s) Reset Help 1 1 1s 2s 2p Use the orbital-filling diagram to show the electron.
Part A Use the orbital-filing diagram to show the electron configuration of helium, He. Drag the appropriate labels to their respective targets. Labels can be used once, more than once, or not at all. Not all targets will be filled. View Available Hint (s) Reset Help 11 18 2s 2p G1 61 G1 G1 G1 G2 G2 G2 Submit Part B Use the orbital-filing.
Use the orbital-filling diagram to show the electron configuration of helium, he.
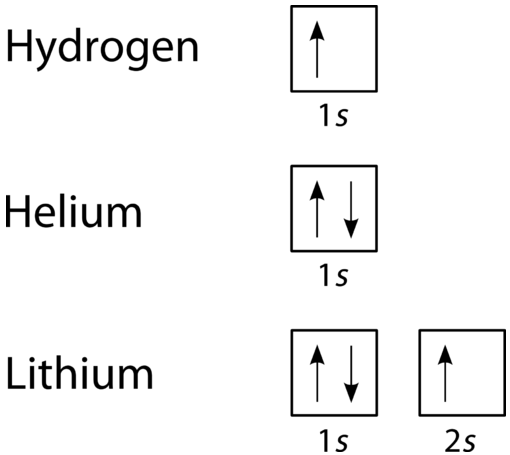
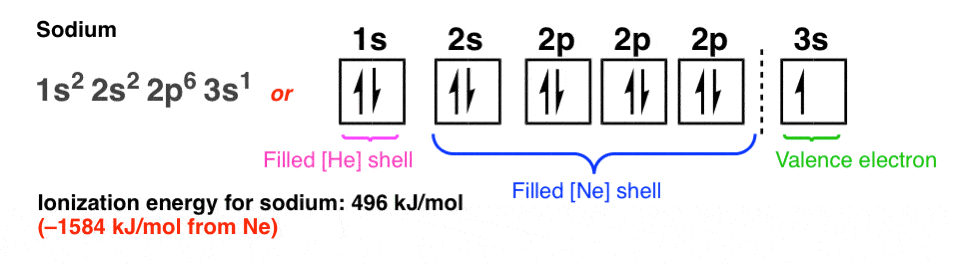
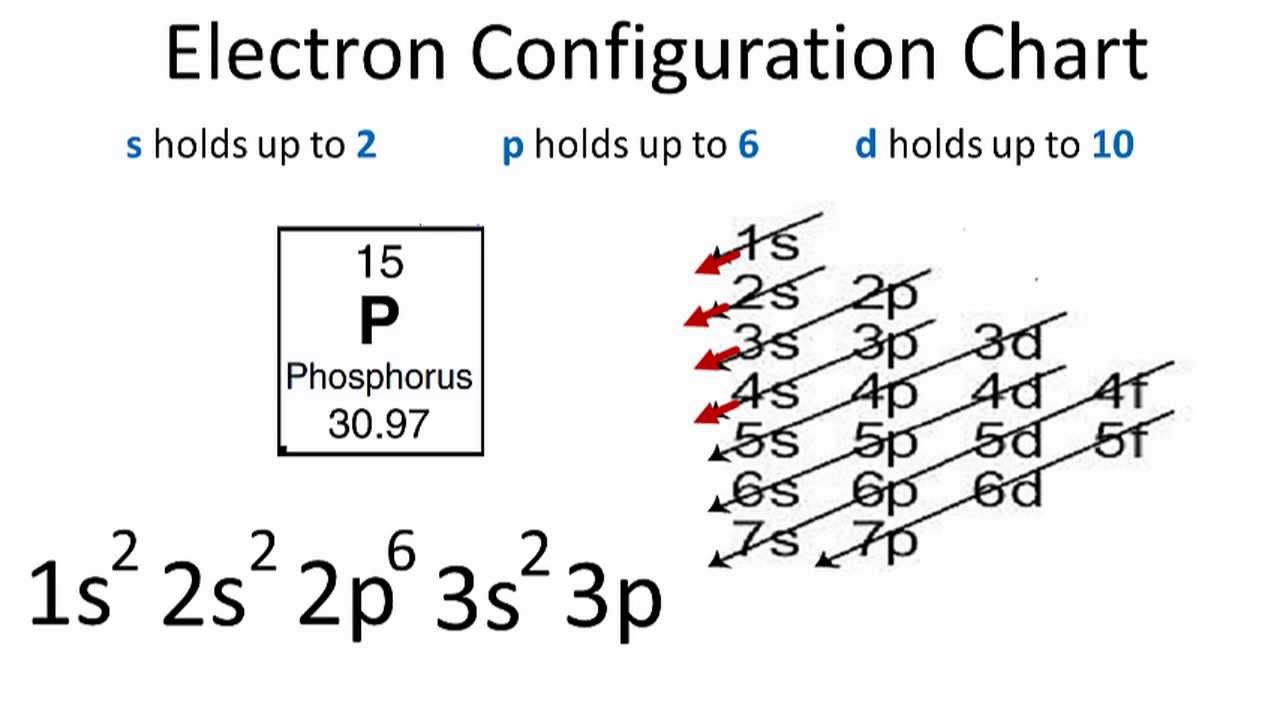
Electron configurations are a shorthand form of an orbital diagram, describing which orbitals are occupied for a given element. For example, 1s2 2s2 2p1 is the electron configuration of boron. Use this tool to generate the electron configuration of arsenic (As). Item 15 150 Constants Period Review Use the orbital-filling diagram to show the electron configuration of aluminum, Al. Learning Goal: Relate orbital-filling diagrams to electron configurations. An electron configuration shows the occupation of orbitals by electrons for a particular atom. For example, He has two electrons in the 18 orbital. Hydrogen only has one electron and therefore has a configuration of 1s 1.In order to fill it's energy level it only needs one more electron obtain a full outershell (1s 2).This is why we only put two electrons on Hydrogen atoms when drawing Lewis structures.
Use the orbital-filling diagram to show the electron configuration of helium, he.. Item 15 150 Constants Period Review Use the orbital-filling diagram to show the electron configuration of aluminum, Al. Learning Goal: Relate orbital-filling diagrams to electron configurations. An electron configuration shows the occupation of orbitals by electrons for a particular atom. For example, He has two electrons in the 18 orbital. Hydrogen only has one electron and therefore has a configuration of 1s 1.In order to fill it's energy level it only needs one more electron obtain a full outershell (1s 2).This is why we only put two electrons on Hydrogen atoms when drawing Lewis structures. Chemistry questions and answers. Part A Use the orbital-filling diagram to show the electron configuration of helium, He. Use the buttons at the top of the tool to add sublevels. Click within an orbital to add electrons. View Available Hint (s) 15 23 22 35 3p 3d 4s 4p 4d 4 55 5P 5d 5f 6s 6p 6d 75 7P 7d Part B Use the orbital-filling diagram to. Use the orbital-filling diagram to show the electron configuration of helium, He. Use the buttons at the top of the tool to add sublevels. Click within an orbital to add electrons. Sign up to view answer. Our mission is to help you succeed in your Chemistry class. Sign up for free to see the solution.
Electron configuration notation eliminates the boxes and arrows of orbital filling diagrams. Each occupied sublevel designation is written followed by a superscript that is the number of electrons in that sublevel. For example, the hydrogen configuration is 1s 1, while the helium configuration is 1s 2. Multiple occupied sublevels are written. Electron Configuration -The Electron Configuration of an Element Describes how Electrons are Distributed in their Atomic Orbitals. In Electronic Configuration electrons are arranged in various shells, Subshell and Orbital by following certain rules. To Learn how to Write Electronic Configurations, Detailed Explanation, Filling of orbital with FAQs, Visit BYJU'S for detailed explanation. Answer: 3 📌📌📌 question The electron configuration for Helium (He) is shown below. 1S2 Which diagram shows the correct distribution of electrons in the electron shells of a helium atom? - the answers to estudyassistant After the 4s is full we put the remaining six electrons in the 3d orbital and end with 3d6. Therefore the Iron electron configuration will be 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p 6 4s 2 3d 6. Note that when writing the electron configuration for an atom like Fe, the 3d is usually written before the 4s. Both of the configurations have the correct numbers of.
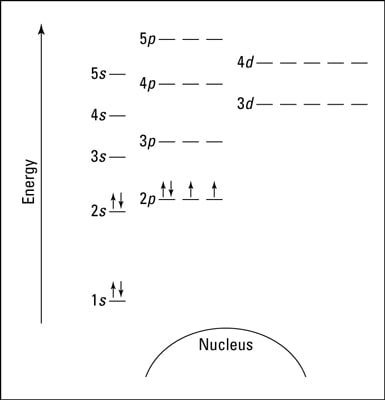
According to the Aufbau process, sublevels and orbitals are filled with electrons in order of increasing energy. Since the s sublevel consists of just one orbital, the second electron simply pairs up with the first electron as in helium. The next element is lithium and necessitates the use of the next available sublevel, the 2s.. The filling diagram for carbon is shown in the Figure below. In writing the electron configuration for Silicon the first two electrons will go in the 1s orbital. Since 1s can only hold two electrons the next 2 electrons for Silicon go in the 2s orbital. The nex six electrons will go in the 2p orbital. The p orbital can hold up to six electrons. We'll put six in the 2p orbital and then put the next two. The orbital filling diagram for helium. The electron configuration for helium is 1s². This means that we have two electrons in the 1s orbital, which looks like this: This diagram is exactly the same as the one for hydrogen, except that there’s a second arrow added to the 1s orbital. The nex six electrons will go in the 2p orbital. The p orbital can hold up to six electrons. We'll put six in the 2p orbital and then put the next two electrons in the 3s. Since the 3s if now full we'll move to the 3p where we'll place the remaining electron. Therefore the Aluminium electron configuration will be 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p 1.
Write orbital filling diagrams electron configurations and electron dot diagrams for the following elements. Since the s sublevel consists of just one orbital the second electron simply pairs up with the first electron as in helium. The 2px orbital lies on the x-axis. Is 2s lectron Is 4s on 2s a o o gurations or ome Orbital filling elected.
Use the orbital-filling diagram to show the electron configuration of helium, He. Use the orbital-filling diagram to show the electron configuration of oxygen, O. Use the orbital-filling diagram to show the electron configuration of gallium, Ga.
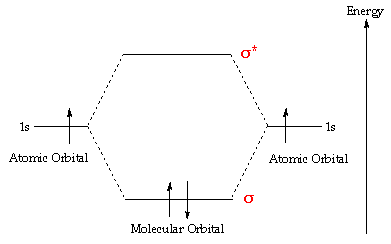
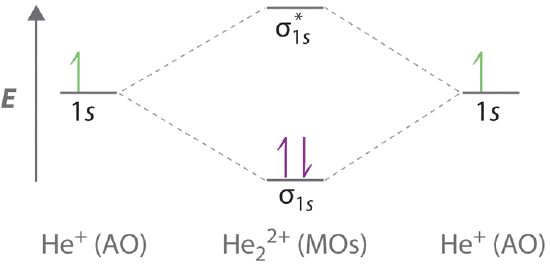
A molecular orbital explicitly describes the spatial distribution of a single Energy Level Diagrams He2 has bond order 0 [ (2 − 2)/2 = 0], and we can make H+. According to the molecular orbital theory, in a supposed He2 molecule, both the if we draw its MOT DIAGRAM, 2 e's enter the Bonding molecular Orbital and 2.
Rule 3 : Once the first shell is full then the next electron is added to the next shell and so on. That means the shell number one i.e, 'K' can hold only two electrons, the shell number two i.e, 'L' can hold eight electrons, and so on. The given atom is, helium with electronic configuration,.
Transcribed image text: Part B Use the orbital-filling diagram to show the electron configuration of oxygen, O. Drag the appropriate labels to their respective targets. Labels can be used once, more than once, or not at all. Not all targets will be filled. View Available Hint(s) Reset Help 1 11 1s 2s 3s 2p 3p G1 G1 G1 || G1G1 G1 G1G11 G1 G2 G2 G2 G2 G2 Electron Configurations Part C Use the.
Live. •. Helium only has 2 electrons and therefore it has a configuration of 1s 2. Because the 1s orbital is full with 2 electrons and any additional electrons would go in a new energy level. The electron configuration for Helium shows a full outer shell and is Helium is therefore called a Nobel Gas. This means it will not react with other atoms.
The placement of the next electron must follow Hund's rule. The orbital diagram shows three unpaired electrons. The electron configuration for nitrogen is 1s 2 2s 2 2p 3. For oxygen the eighth electron must pair with one of the electrons in the 2p orbitals. The orbital diagram for oxygen is shown on the left.
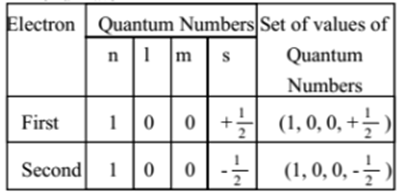
The electron configuration and the orbital diagram are: Following hydrogen is the noble gas helium, which has an atomic number of 2. The helium atom contains two protons and two electrons. The first electron has the same four quantum numbers as the hydrogen atom electron ( n = 1, l = 0, ml = 0, ms = +1 2 m s = + 1 2 ).
Electron orbital diagrams and written configurations tell you which orbitals are filled and which are partially filled for any atom. The number of valence electrons impacts on their chemical properties, and the specific ordering and properties of the orbitals are important in physics, so many students have to get to grips with the basics.
Question: MULUI3627beabcb0ad8867dcf2d783aa0c#10001 Text Use the orbital-filling diagram to show the electron configuration of helium, He.
Electron configurations are a shorthand form of an orbital diagram, describing which orbitals are occupied for a given element. For example, 1s2 2s2 2p1 is the electron configuration of boron. Use this tool to generate the electron configuration of arsenic (As).
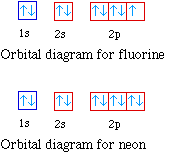
Use the orbital-filling diagram to show the electron configuration of helium, He. What is the electron configuration of helium Which diagram shows the correct electron configuration for fluorine (F)
The electron configuration for Gallium, Ga is 1s^2 2s^2 2p^6 3s^2 3p^6 3d^10 4s^2 4p^1 Gallium, Ga has 31 protons and 31 electrons. The superscripts represent the electrons present in each region of the periodic table. The sum of these superscripts should equal the atomic number for a neutral atom. The last electron is in the 4th period, in the p region and the first electron in that region.
smilodon. As you can see in the picture presented below, Helium (He) is a noble gas with a stable 1s2 electron configuration. This means that an atom of Helium has two electrons that are orbiting the atom's core in the first, S orbit. The two electrons are in the same orbit, but they orbit in opposite directions, they have an opposite spin.
Orbital Filling Element 1s 2s 2p x 2p y 2p z 3s Configuration Electron Configurations Electron H He Li C N O F Ne Na 1s1 1s 22s 2p63s1 1s22s22p6 1s 22s 2p5 1s 22s 2p4 1s22s22p3 1s22s22p2 1s22s1 1s2 NOT CORRECT Violates Hund’s Rule 2 6 1 2 6 2 2 4 2 3 2

















0 Response to "39 Use The Orbital-filling Diagram To Show The Electron Configuration Of Helium, He."
Post a Comment