38 Diagram Of Sinus Cavity
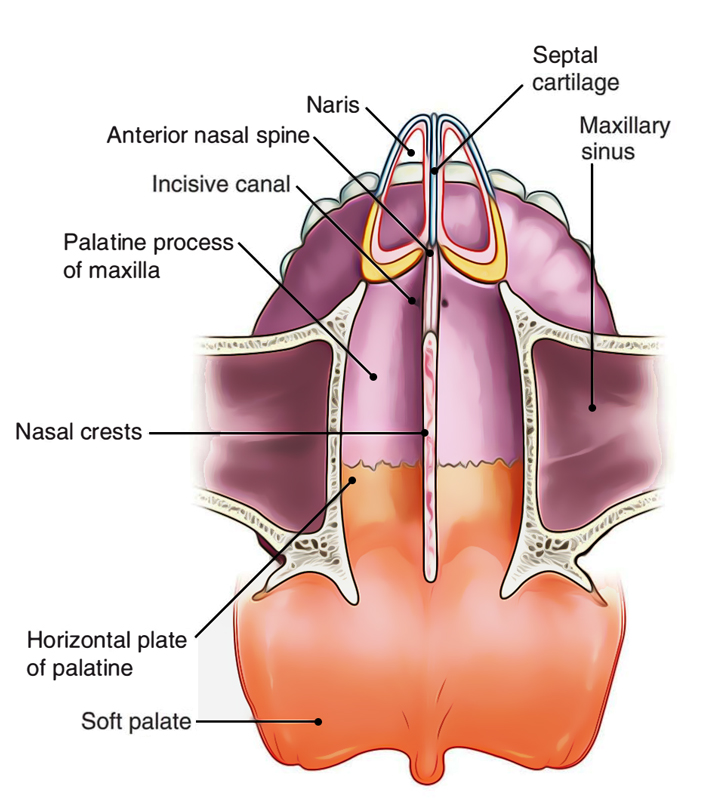
Maxillary Sinus (within the maxillary bones): The largest among all the paranasal sinuses [2], these two conical cavities are located on the two sides of the nose, above the upper teeth, and below the cheeks [4]. Ethmoid Sinus (within the ethmoid bones): Three to eighteen [5] air cells present in the ethmoid labyrinth, on both sides of the nose, between the eyes [6, 7]. Nasal cavity and paranasal sinus cancers are typically given a clinical stage based on the results of any exams, biopsies, and imaging tests that might have been done (as described in Tests for Nasal Cavity and Paranasal Sinus Cancers). If surgery has been done, the pathologic stage (also called the surgical stage) can be determined. The stages.
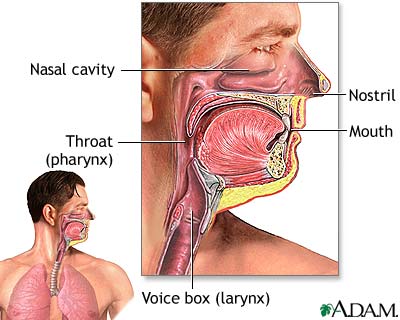
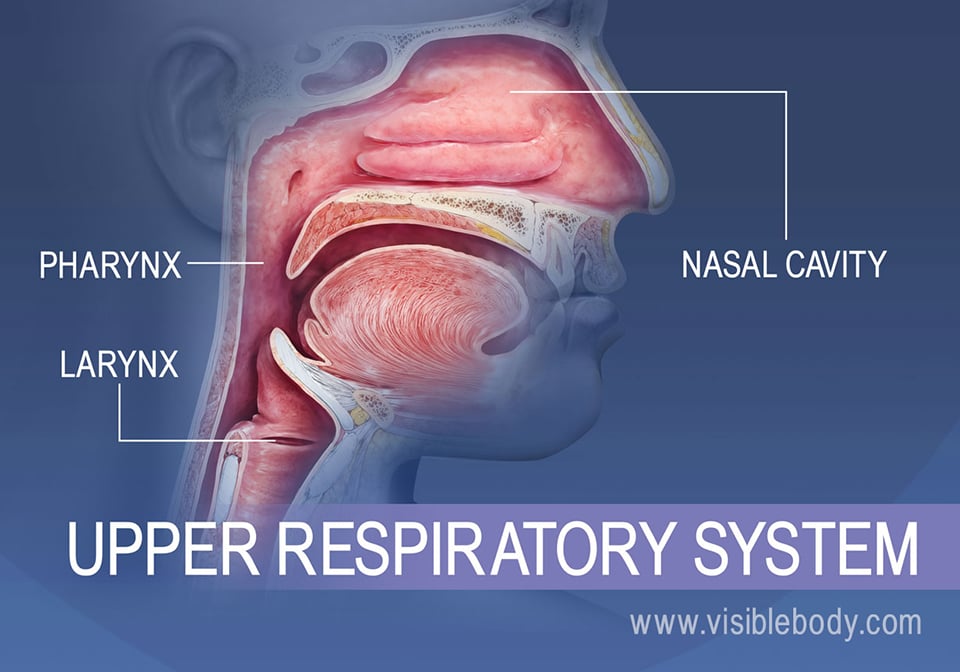
Nasal Cavity Definition. The nose is one of the primary sensory organs responsible for the sense of smell, while it also plays major roles in respiration and speech production [1].The nasal cavity lies just behind the two nostrils and forms the interiors of the nose.. It makes up the upper respiratory system along with the paranasal sinuses, oral cavity, pharynx, and larynx [2], and is the.
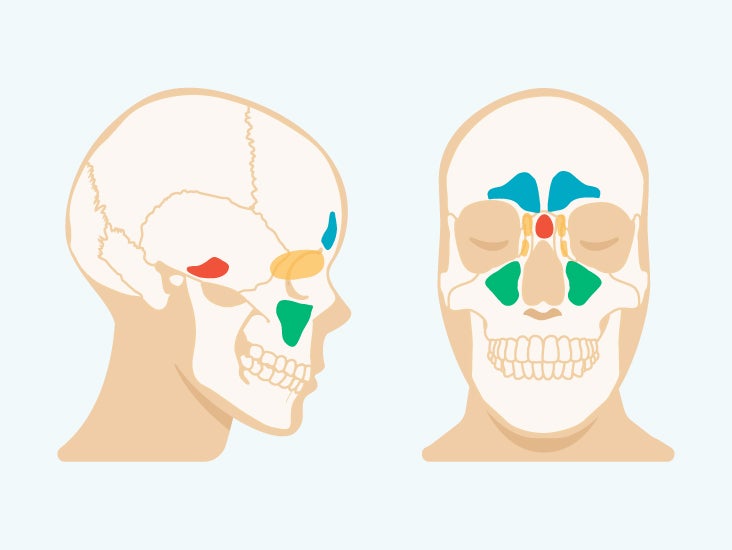
Diagram of sinus cavity
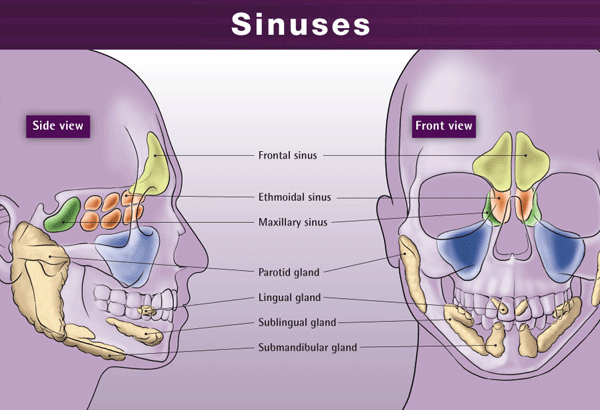
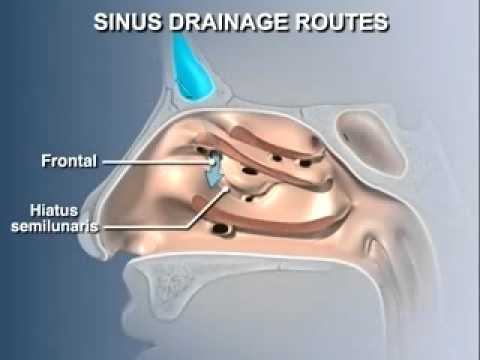
Sinuses are open cavities in the head, but they are not bare bones. Each sinus cavity has a mucous membrane lining that allows very slow ventilation into and out of the sinus. The slow ventilation allows the space in sinus cavities to be filled with a high concentration of carbon dioxide and a low level of oxygen. The maxillary sinuses are shaped like a pyramid and each contain three cavities, which point sideways, inwards, and downwards. The sinuses are small air-filled holes found in the bones of the face. The paranasal sinuses (“the sinuses”) are air-filled cavities located within the bones of the face. Each sinus is named for the bone in which it is located. Maxillary sinus: One sinus per side, located within the cheek bone (See Figures 1 & 2). Ethmoid sinus: A honeycomb-like structure of 6-12 small sinuses, located between the eyes.
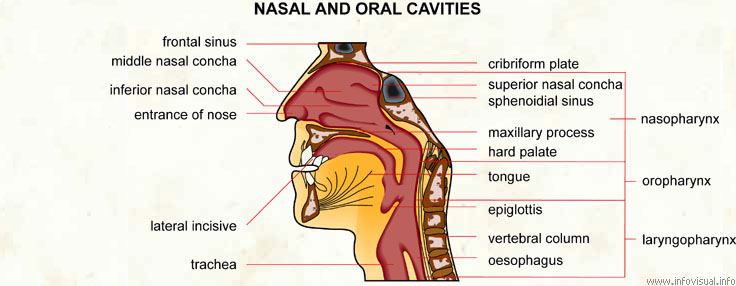
Diagram of sinus cavity. The Walls of the Nasal Cavity (p. 758) Click here for a diagram of the lateral wall of the nasal cavity. The medial wall is formed by the nasal septum; it is usually smooth. The lateral wall is uneven owing to the three longitudinal, scroll-shaped elevations, called the conchae (L. shells) or turbinates (L. shaped like a top). The maxillary sinuses are shaped like a pyramid and each contain three cavities, which point sideways, inwards, and downwards. The sinuses are small air-filled holes found in the bones of the face. Like the nasal cavity, the sinuses are all lined with mucus. The mucus secretions produced in the sinuses are continually being swept into the nose by the hair-like structures on the surface of. Review the sinuses anatomy Discern medical necessity for various sinus procedures Identify endoscopic sinus procedures Review the CPT® coding and modifier guidelines 1 Anatomy of the Facial Sinuses Nasal septum Ethmoid (right and left) Maxillary sinus (right and left) Turbinates (concha) • Superior • Middle • Inferior 2
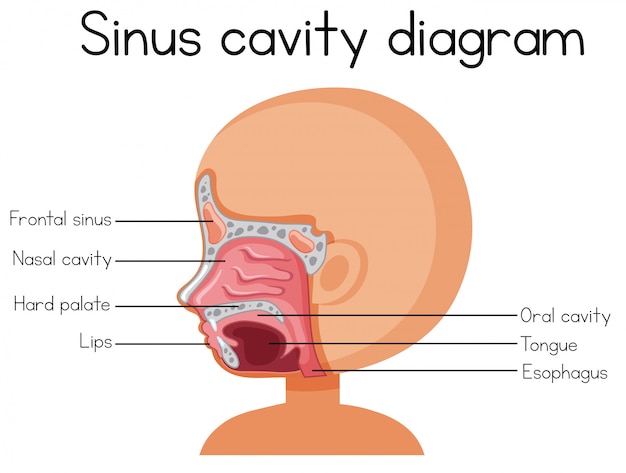
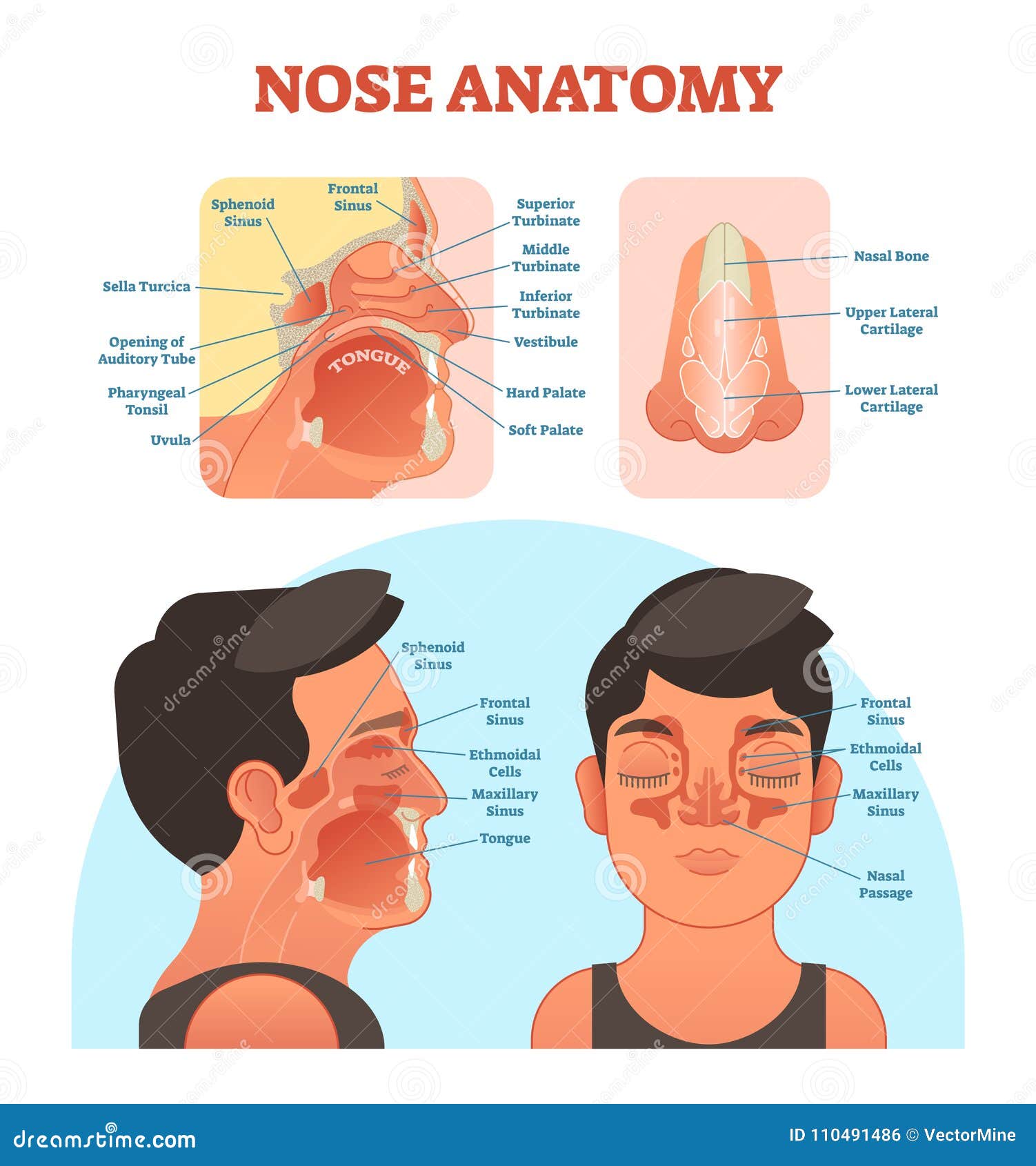
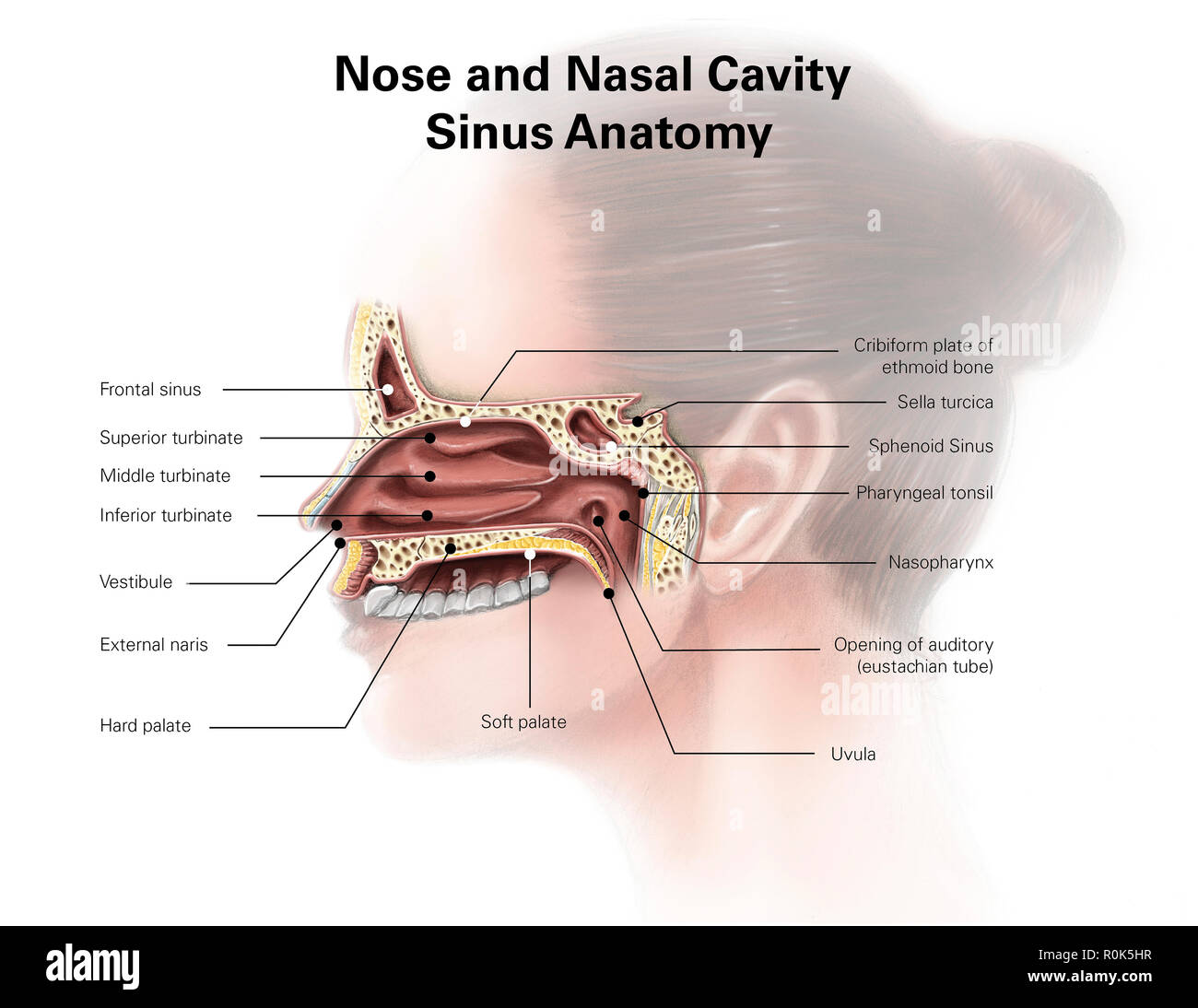
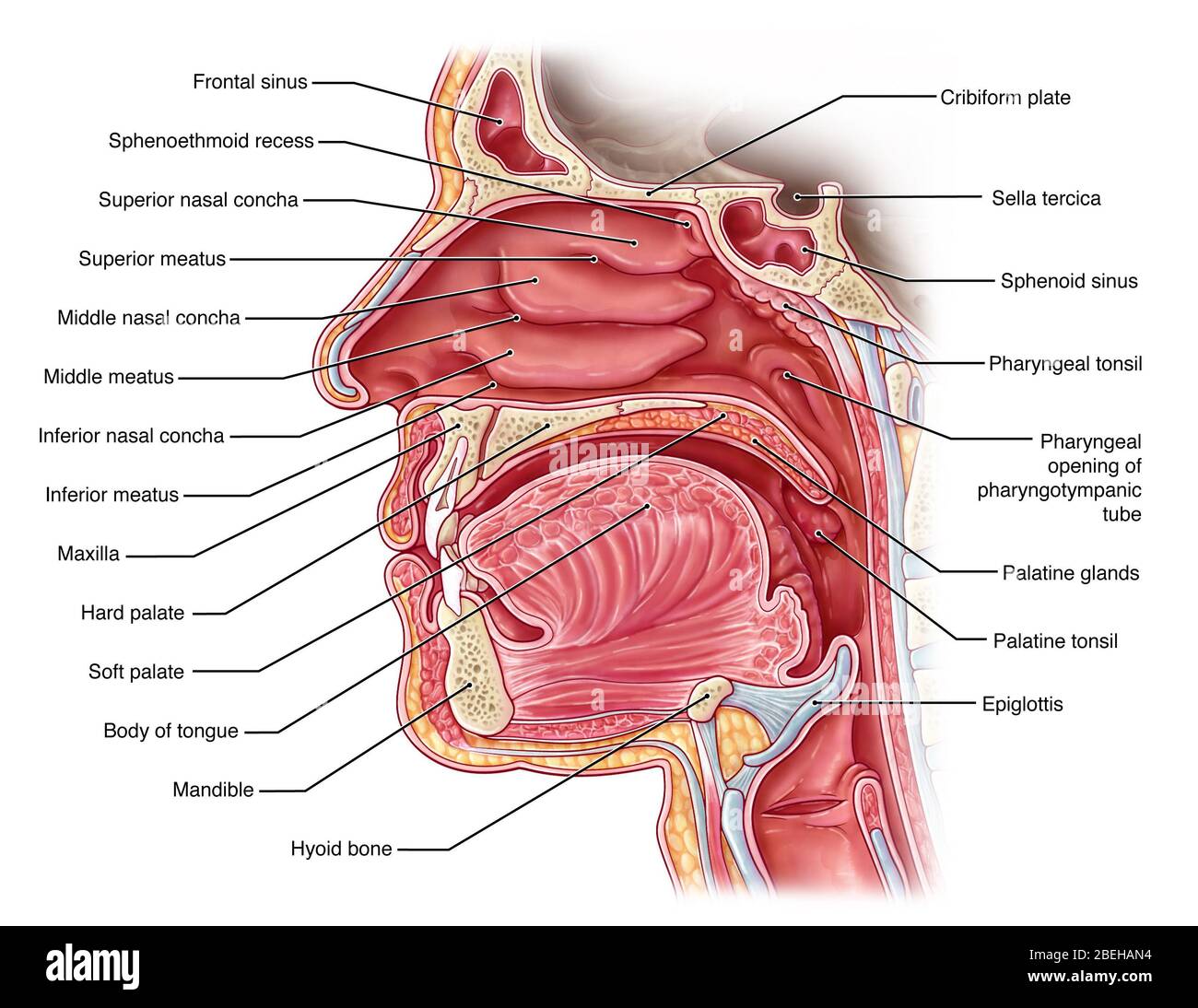
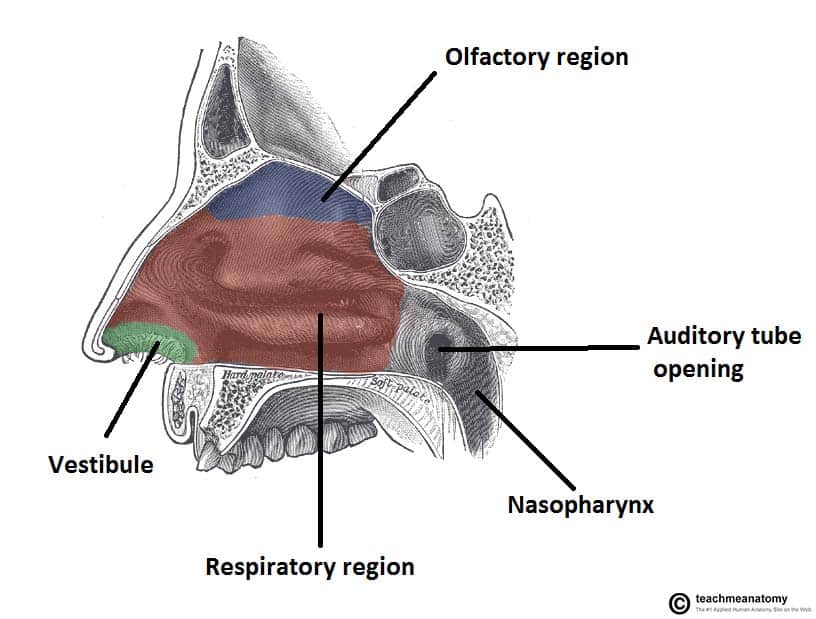
The nasal cavity (or cavity of nose, Latin: cavum nasi, cavitas nasi) is an irregular, bilateral air-filled space located above the roof of the mouth forming the internal part of the nose.The nasal cavity is an initial part of the respiratory tract and it also lodges the olfactory receptors providing the sense smell.. Nasal cavity by Anatomy Next. Most of the nasal cavity is lined with mucosa. Jan 27, 2015 · Like the nasal cavity, the sinuses are all lined with mucus. The mucus secretions produced in the sinuses are continually being swept into the nose by the hair-like structures on the surface of. Sinus Pressure Points for Sinus Relief. Below are a number of sinus trigger points to help alleviate the discomfort from sinus pressure; some will even help mucus drain. A sinus pressure points diagram is also included to assist you in finding the location accurately on your face: The nasal cavity The nares serve as the entryway to the nasal cavities, which open posteriorly into the nasopharynx via the choanae. The walls of the nasal cavity include the following features: Roof: The roof is divided into three parts: frontonasal, ethmoidal, and sphenoidal. Each part corresponds to the underlying bone of the same name.
The sinus venosus is a large quadrangular cavity which precedes the atrium on the venous side of the chordate heart.In mammals, it exists distinctly only in the embryonic heart, where it is found between the two venae cavae.However, the sinus venosus persists in the adult. In the adult, it is incorporated into the wall of the right atrium to form a smooth part called the sinus venarum, which. SINUS CAVITIES DIAGRAM by Sinus Help. www.sinusinfectionrelief . Fundamentally situated in the skull, human sinus cavities are the passageways mainly found in the areas around the face. the nasal cavity, has a rich neurovascular supply, and is lined by respiratory epithelium composed mainly of ciliated and mucous cells; •the olfactory region is small, is at the apex of each nasal cavity, is lined by olfactory epithelium, and contains the olfactory receptors. •In addition to housing receptors for the Dec 06, 2017 · Nasal Cavity. The nasal cavity is the space behind the nostrils and the beginning of the respiratory tract [6].It is separated into the right and left nasal cavities by the nasal septum. There are three sections of the cavity: Nasal Vestibule: The area lying just behind the nasal cavities, the nasal vestibule is lined with skin tissue, unlike the rest of the nasal cavity.
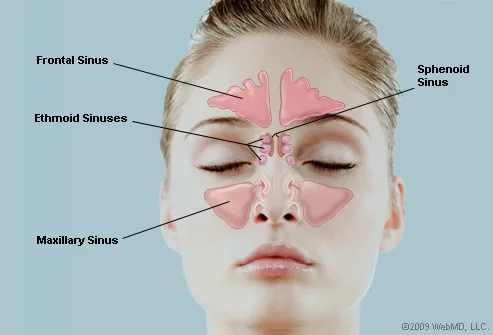
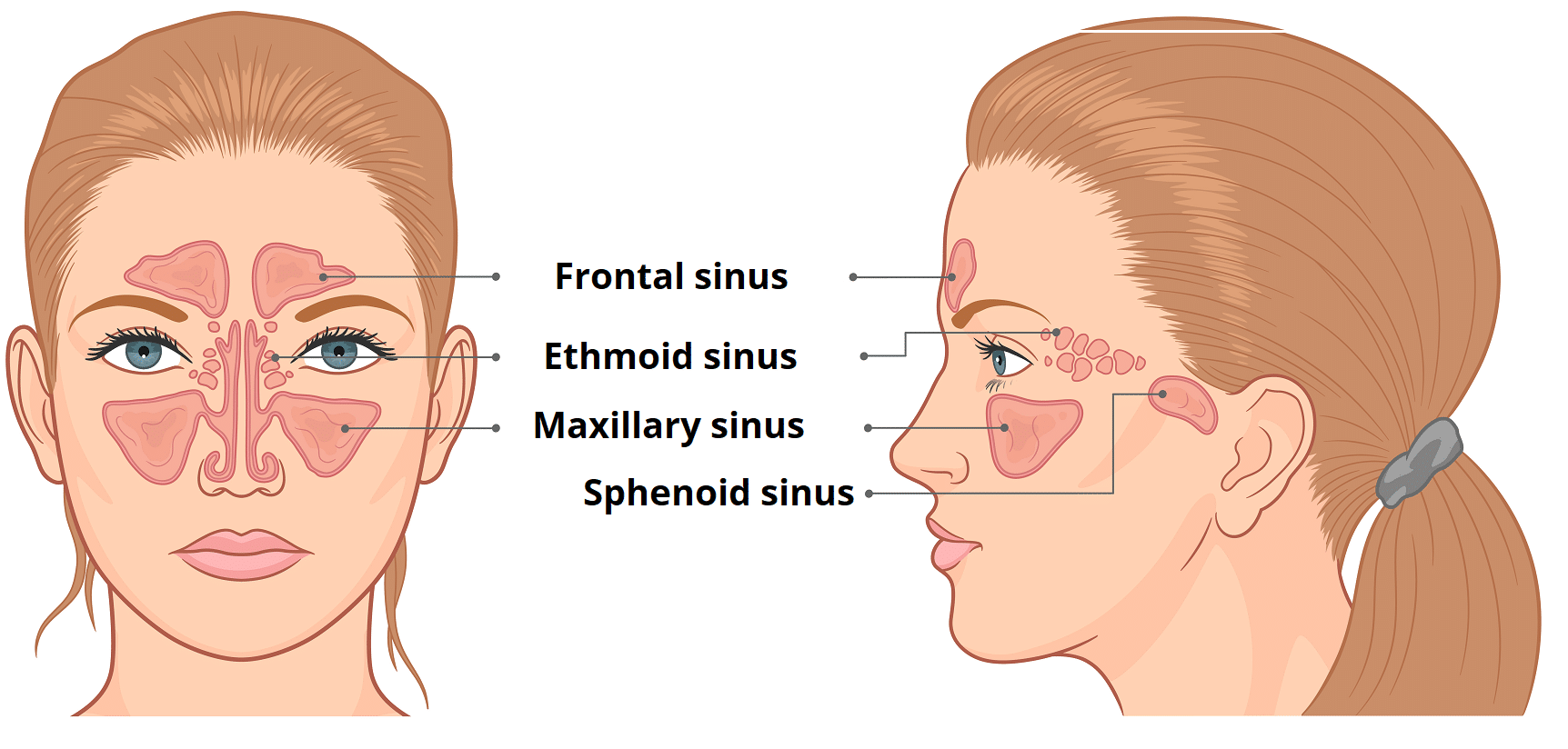
Sinuses are hollow, air-filled cavities that are located throughout the skull. There are several sets of sinuses in the head. The maxillary sinuses are behind the cheeks. The ethmoid sinuses lie under the inside corners of the eyes. The sphenoid sinuses are located behind the ethmoid sinuses. The frontal sinuses lie behind the forehead above.
human respiratory system, the system in humans that takes up oxygen and expels carbon dioxide.. The design of the respiratory system. The human gas-exchanging organ, the lung, is located in the thorax, where its delicate tissues are protected by the bony and muscular thoracic cage.The lung provides the tissues of the human body with a continuous flow of oxygen and clears the blood of the.
A sinus is a sac or cavity in any organ or tissue, or an abnormal cavity or passage caused by the destruction of tissue.In common usage, "sinus" usually refers to the paranasal sinuses, which are air cavities in the cranial bones, especially those near the nose and connecting to it. Most individuals have four paired cavities located in the cranial bone or skull.
Sinuses are open cavities in the head, but they are not bare bones. Each sinus cavity has a mucous membrane lining that allows very slow ventilation into and out of the sinus. The slow ventilation allows the space in sinus cavities to be filled with a high concentration of carbon dioxide and a low level of oxygen.
View nasal cavity diagram videos. Browse 35 nasal cavity diagram stock illustrations and vector graphics available royalty-free, or start a new search to explore more great stock images and vector art. antique illustration: head throat section - nasal cavity diagram stock illustrations. cutaway diagram of human respiratory system, including.
A diagram of the sinuses and an explanation is given here if you want to learn the names and see the locations of the different sinus cavities( frontal, maxillary, ethmoid, and sphenoid). This might be helpful, for example, to understand a doctor's diagnosis or your X-ray.
The paranasal sinuses are air-filled extensions of the nasal cavity. There are four paired sinuses - named according to the bone in which they are located - maxillary, frontal, sphenoid and ethmoid. Each sinus is lined by a ciliated pseudostratified epithelium, interspersed with mucus-secreting goblet cells.
Browse 37 nasal cavity diagram stock photos and images available, or start a new search to explore more stock photos and images. antique illustration: head throat section - nasal cavity diagram stock illustrations. cutaway diagram of human respiratory system, including nasal and mouth cross section. - nasal cavity diagram stock illustrations.
Sinus Cavity Diagram Teeth What is Sinusitis? Sinusitis is caused by an inflammation of your sinus cavities that causes redness, swelling, mucus, and pain. There are two types of sinusitis: Acute sinusitis - an infection that is often triggered by the flu or cold. The flu or cold virus attacks your sinuses causing them to swell and become narrow.
The paranasal sinuses (“the sinuses”) are air-filled cavities located within the bones of the face. Each sinus is named for the bone in which it is located. Maxillary sinus: One sinus per side, located within the cheek bone (See Figures 1 & 2). Ethmoid sinus: A honeycomb-like structure of 6-12 small sinuses, located between the eyes.
Nasal steroid spray: These medications ease tissue swelling and help prevent the regrowth of nasal polyps after sinus surgery. Nasal washes: They rinse mucus from the nasal cavities and sinuses.
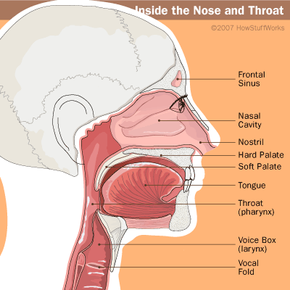
Nov 05, 2019 · The soft palate is the muscular part of the roof of the mouth. This article provides a diagram of the soft palate and discusses its anatomy and functions, as well as the conditions that affect it.
The nasal cavity consists of all the bones, tissues, blood vessels and nerves that make up the interior portion of the nose. The most important functions of the nasal cavity include warming and humidifying the air as you breathe and acting as a barrier for the immune system to keep harmful microbes from entering the body.
A CBCT scan of the sinuses shows a patient's paranasal sinus cavities. Paranasal sinuses are a group of four paired air-filled spaces that surround the nasal cavity. With a CBCT scanner, our allergists are able to see the sinuses located under the eyes, above the eyes, between the eyes, and behind the eyes.
A hematoma may create the buccal space, e.g. due to hemorrhage following wisdom teeth surgery. Buccal space abscesses typically cause a facial swelling over the cheek that may extend from the zygomatic arch above to the inferior border of the mandible below, and from the anterior border the masseter muscle posteriorly to the angle of the mouth anteriorly.
The cavernous sinuses are 1 cm wide cavities that extend a distance of 2 cm from the most posterior aspect of the orbit to the petrous part of the temporal bone.They are bilaterally paired collections of venous plexuses that sit on either side of the sphenoid bone.Although they are not truly trabeculated cavities like the corpora cavernosa of the penis, the numerous plexuses, however, give the.
Sinus Cavities Diagram. 1. SINUS CAVITIES DIAGRAM by Sinus Help www.sinusinfectionrelief . 2. Fundamentally situated in the skull, human sinus cavities are the passageways mainly found in the areas around the face. Also known as paranasal sinuses, they are hollow, irregular air cavities which sit adjacent to and are attached to the nose and.
Title: how to draw nasal cavity | how to draw nasal cavity easy | how to draw nasal cavity step by step@AsapKNOWLEDGE Hello Friends in this video I tell you...
Aug 12, 2019 · There are four pairs of sinuses (named for the skull bones in which they're located). Interactive diagrams show sinus cavity locations and help visualize sinusitis, the most common type of sinus.
The maxillary sinuses are the pockets near the cheeks. This sinus is located in the maxilla bone under the eye, contains three recesses, and is shaped like a pyramid. The frontal sinuses are over the forehead and above the eyes. These are absent at birth, and in approximately 5% of the adult population. The ethmoid sinuses are actually several.
Sep 29, 2019 · The nose is an olfactory and respiratory organ. It consists of nasal skeleton, which houses the nasal cavity. The nasal cavity has four functions: Warms and humidifies the inspired air.; Removes and traps pathogens and particulate matter from the inspired air. Responsible for sense of smell. Drains and clears the paranasal sinuses and lacrimal ducts.






















0 Response to "38 Diagram Of Sinus Cavity"
Post a Comment