44 nf+ molecular orbital diagram
PDF Miessler-Fischer-Tarr5e SM Ch 05 CM - Department of Chemistry Therefore, NF is predicted to be paramagnetic with a bond order of 2. The populations of the bonding (8 electrons) and antibonding (4 electrons) molecular orbitals in the diagram suggest a double bond. c. The 2s, 2s *, 2p, and 2p *orbitals exhibit C vsymmetry, with the NF bond axis the infinite-fold rotation axis. The 2pand 2p * Configuration interaction studies of NF and NF+ - ScienceDirect Journal of Molecular Spectroscopy. Volume 45, Issue 3, March 1973, Pages 358-365. Configuration interaction studies of NF and NF + ... + in the Born-Oppenheimer approximation with a configuration interaction method employing a minimal basis of Slater type orbitals. Resulting energy differences, vibrational and rotational constants are compared ...
Bond Order | Introduction to Chemistry - Lumen Learning Calculate a molecule's bond order given its molecular orbital diagram. Key Points Bond order is defined as half the difference between the number of bonding and antibonding electrons. Stable bonds have a positive bond order. Bond order is an index of bond strength and is used extensively in valence bond theory. Terms
Nf+ molecular orbital diagram
MO Diagrams for Diatomic Molecules Summary MO Theory • LCAO-MO Theory is a simple method for predicting the approximate electronic structure of molecules. • Atomic orbitals must have the proper symmetry and energy to interact and form molecular orbitals. • Photoelectron spectroscopy provides useful information on the energies of atomic orbitals. • Next we’ll see that symmetry will help us treat larger … PDF Answers to Molecular Orbitals Problem Set ANSWERS TO MOLECULAR ORBITALS PROBLEM SET 1. (a) N2 +(13 e-): σ2 1sσ*21sσ22sσ*22sπ22pπ22pσ12p N2 2+(12 e-): σ2 1sσ*21sσ22sσ*22sπ22pπ22p N2 (14 e-): σ2 1sσ*21sσ22sσ*22sπ22pπ22pσ22p N2-(15 e-): σ21sσ*21sσ22sσ*22sπ22pπ22pσ22pπ*12p N2 2-(16 e-): σ21sσ*21sσ22sσ*22sπ22pπ22pσ22pπ*12pπ*12p (b) Bond orders are: N2 + = 2.5 ; N 2 2+ = 2.0 ; N PDF MO Diagrams for Diatomic Molecules Summary MO Theory • LCAO-MO Theory is a simple method for predicting the approximate electronic structure of molecules. • Atomic orbitals must have the proper symmetry and energy to interact and form molecular orbitals. • Photoelectron spectroscopy provides useful information on the energies of atomic orbitals. • Next we'll see that symmetry will help us treat larger molecules in
Nf+ molecular orbital diagram. Solved: For each of the two species NF and NF+, (a) draw … Solutions for Chapter 9 Problem 34E: For each of the two species NF and NF+, (a) draw MO energy level diagrams; (b) write out electron configurations; (c) determine bond orders and predict relative stabilities; and (d) predict diamagnetism or paramagnetism. … Get solutions Get solutions Get solutions done loading Looking for the textbook? Answered: Molecule Ground state electron… | bartleby Solution for Molecule Ground state electron configuration NF (01s) (01s*) (023) (02,*) (72p) (02p * NF+ (015) (01s*) (02,*) (T2p) NF (613) (01s*)(025) (025*)… scilearn.sydney.edu.au › fychemistry › calculatorsMolecular Orbital Diagram Maker - University of Sydney Molecular Orbital Diagram Maker. ©2022 Prof Adam J Bridgeman | close window. More stable than the c2 ion b c2 has all paired The molecular orbitals of CO look similar to those of N2. The atomic orbitals of O are lower in energy than those of C because O is more electronegative. The bond order is ½(8 - 2) = 3. With no unpaired electrons, CO is diamagnetic. Putting It Together 51. ... The molecular electron configuration for NF+ is ...
Configuration interaction studies of NF and NF Mar 01, 1973 · JOURNAL OF MOLECULAR SPECTROSCOPY 45, 358-365 (1973) Configuration Interaction Studies of NF and NF+ ANDREAS ANDERSENt AND YNGVE OHRN Quantum Theory Project, Departments of Chemistry and Physics, University of Florida, Gainesville, Florida 32601 Full potential energy curves and wavefunctions are calculated for NF and NF+ in the … Molecular Orbital Diagram Maker - University of Sydney Molecular Orbital Diagram Maker. ©2022 Prof Adam J Bridgeman | close window. 4 draw the valence molecular orbital diagram for nf State the bond order, the molecular orbital configuration and determine whether each of the following molecules/ions is paramagnetic or diamagnetic. (6 points) a) Molecular Orbital Diagram b) Bond Order _____ c) Molecular orbital configuration _____ d) Consider NF, NF +, and NF-. Which of these is paramagnetic and diamagnetic? Solved: For each of the two species NF and NF+, (a) draw MO ... - Chegg Solutions for Chapter 9 Problem 34E: For each of the two species NF and NF+, (a) draw MO energy level diagrams; (b) write out electron configurations; (c) determine bond orders and predict relative stabilities; and (d) predict diamagnetism or paramagnetism. … Get solutions Get solutions Get solutions done loading Looking for the textbook?
Question about diamagnetism and paramagnetism - CHEMISTRY COMMUNITY Is there a way to determine if a molecule is diamagnetic or paramagnetic without drawing it's molecular orbital diagram? For example, in the workbook there is a question that asks you to identify the non-paramagnetic molecule out of OF+, NO+, CO+, NF+, and CF. ... NF+, and CF. It seems that there is no correlation between an odd/even number of ... › file › p55lheq4 draw the valence molecular orbital diagram for nf - Course Hero State the bond order, the molecular orbital configuration and determine whether each of the following molecules/ions is paramagnetic or diamagnetic. (6 points) a) Molecular Orbital Diagram b) Bond Order _____ c) Molecular orbital configuration _____ d) Consider NF, NF +, and NF-. Which of these is paramagnetic and diamagnetic? Tudo sobre orbitais moleculares #2 Diagrama de moléculas ... - YouTube Na aula de hoje vamos aprender a montar um diagrama de orbitais moleculares de moléculas homonucleadas - H2, O2, N2 etcAprenderemos também o conceito de orde... PDF Quantum Mechanical Study -of Molecules - Nasa The molecular orbitals, g's, are expressed as linear combination of atomic orbitals, X*S, (1) where a ip are undetermined coefficients. ... NF+ 4 l-I : 10 2 2u 2 302 4a2 502 l-I; l-Ix l-I* X II; * The nomenclature and configurations of the different states of NE were derived from the corresponding states of the isoelectronic O2 molecule. ...
web.stanford.edu › ~kaleeg › chem32Chem 32 Virtual Manual - Stanford University Structure and Bonding Solutions: #4. 4.* (1997 1 7) Consider the diatomic molecule NF. Draw its molecular orbital energy diagram. A. Using the LCAO-MO scheme, indicate the ground-state MO description for NF, i.e. complete the following: 1 ( s) 2 . . . The LCAO-MO description is: 1s 2 2s 2 3s 2 4s 2 5s 2 1p 4 2p 2. B.
Bond Order | Introduction to Chemistry - Lumen Learning bond orderthe number of overlapping electron pairs between a pair of atoms. antibondingan atomic or molecular orbital whose energy increases as its constituent atoms converge, generating a repulsive force that hinders bonding. Bond order is the number of chemical bonds between a pair of atoms; in diatomic nitrogen (N≡N) for example, the bond ...
Use molecular orbital theory to complete the ... - Study.com Answer to: Use molecular orbital theory to complete the ground state electron configuration for each of the molecules: a. NF b. NF+ c. NF- The MO diagram of ...1 answer · Top answer: The MO diagram of the NF molecule can be drawn as below The energies of the atomic orbital of N and F are different. The atomic orbitals of F are...
Solved Use molecular orbital theory to complete this table. | Chegg.com Question: Use molecular orbital theory to complete this table. Molecule Ground state electron configuration Bond order Number 700 Number NF (s) (02s) ( () (2 Number NF ( () (02 ()2) (T2) Drag a number into each of the blank boxes above. Classify these species according to their magnetic properties. Diamagnetic Paramagnetic NF NF NF.
Use molecular orbital theory to complete the ground state el Use molecular orbital theory to complete the ground state electron configuration for each of the molecules. Molecule Ground state electron configuration NF ...1 answer · Top answer: **NF** $$ \sigma_1s^2\sigma_1^*s^2\sigma_2s^2\sigma_2^*s^2\pi_2p^4\sigma_2p^2\pi_2^*p^2 $$ • *NF+** $$ \sigma_1s^2\sigma_1^*s^2\sigma_2s^2\sigma_2^*s^2\pi_2 ...
3 Ways to Calculate Bond Order in Chemistry - wikiHow In molecular orbital theory, bond order is defined as half of the difference between the number of bonding and antibonding electrons. Bond order = [ (Number of electrons in bonding molecules) - (Number of electrons in antibonding molecules)]/2. 2 Know that the higher the bond order, the more stable the molecule.
Molecular Orbitals Flashcards | Quizlet How are molecular orbitals different from atomic orbitals. because the electrons filling them are under the influence of two or more nuclei rather than just one nucleus. Electron density increases between. 2 nuclei in bonding molecular orbitals. Electron density decreases between.

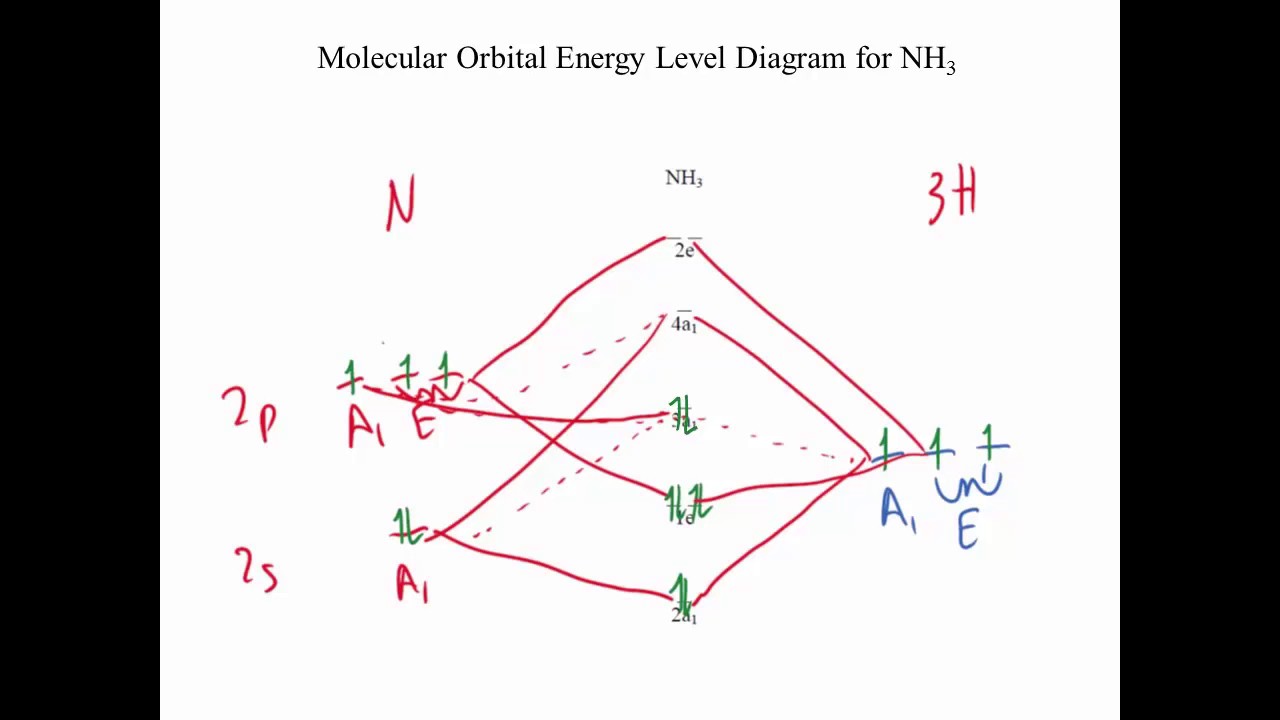

0 Response to "44 nf+ molecular orbital diagram"
Post a Comment