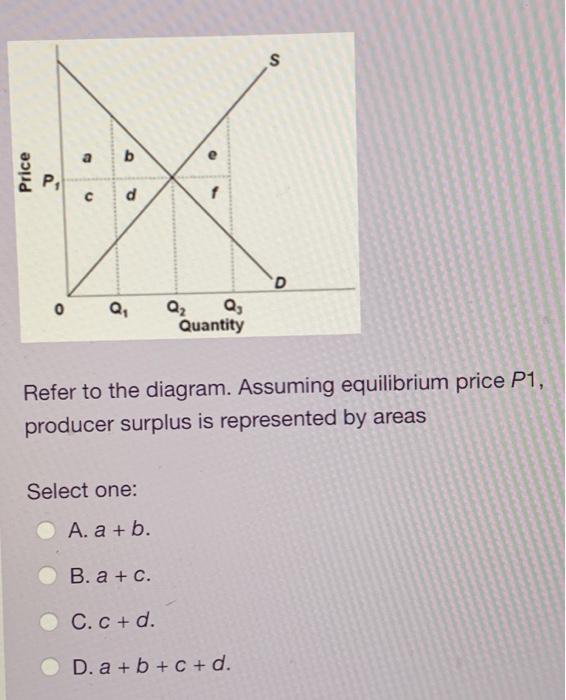
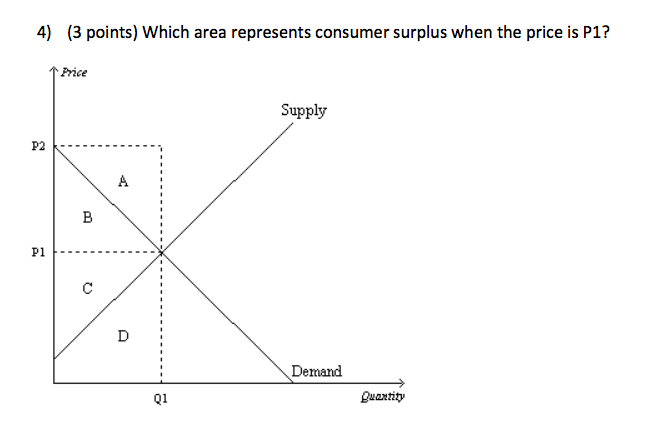
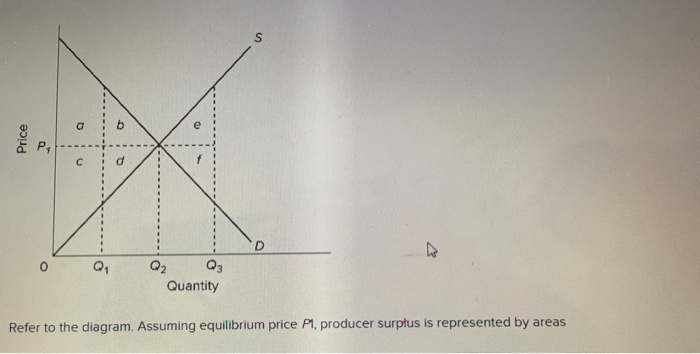
43 Refer To The Diagram. Assuming Equilibrium Price P1, Consumer Surplus Is Represented By Areas:
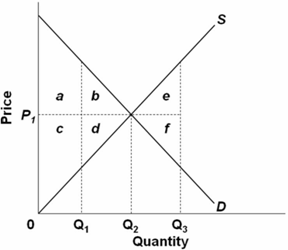
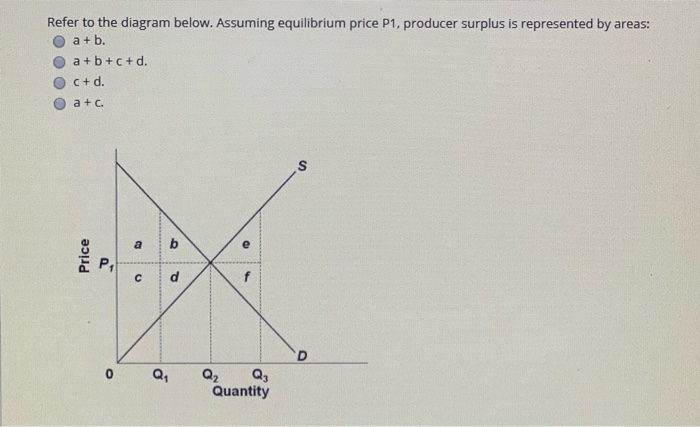
PLAY. Refer to the diagram. Assuming equilibrium price P1, consumer surplus is represented by areas: a + b. asymmetric information. Nice work! You just studied 20 terms! Now up your study game with Learn mode. At equilibrium, consumer surplus would be represented by the area. In the provided graph, the equilibrium point in the market is where the S and D curves intersect. At equilibrium, the producer surplus would be represented by the area. Refer to Figure 6.6, which shows a market for taxi medallions.
14.A public good: can be profitably produced by private firms. is characterized by rivalry and excludability. produces no positive or negative externalities. → is available to all and cannot be denied to anyone. 15. The market system does not produce public goods because: there is no need or demand for such goods. → private firms cannot.

Refer to the diagram. assuming equilibrium price p1, consumer surplus is represented by areas:
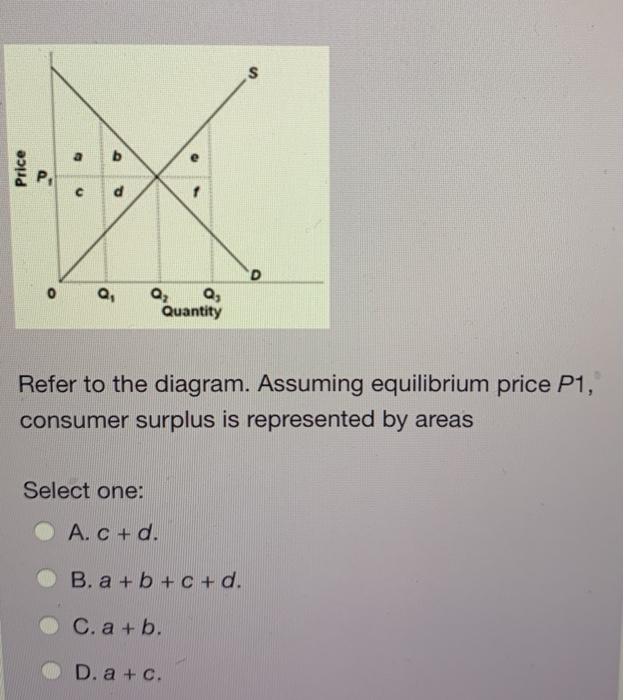
Exam 060204RR - Price, Efficiency, and Consumer Behavior. 1. Refer to the diagram above. Total revenue at price P1 is indicated by area (s) A. A + C. D. A + B. 2. Refer to the above diagram. Assuming equilibrium price P1, consumer surplus is represented by areas: a + b. Refer to the above diagram. Assuming equilibrium price P1, producer surplus is represented by areas: c + d. Refer to the above diagram. The area that identifies the maximum sum of consumer surplus and producer surplus is: Refer to the diagram. a b e Q, Q2 Q, Quantity Assuming equilibrium price P1, consumer surplus is represented by areas 1) a+ b. 2) a + b+ c+ d.
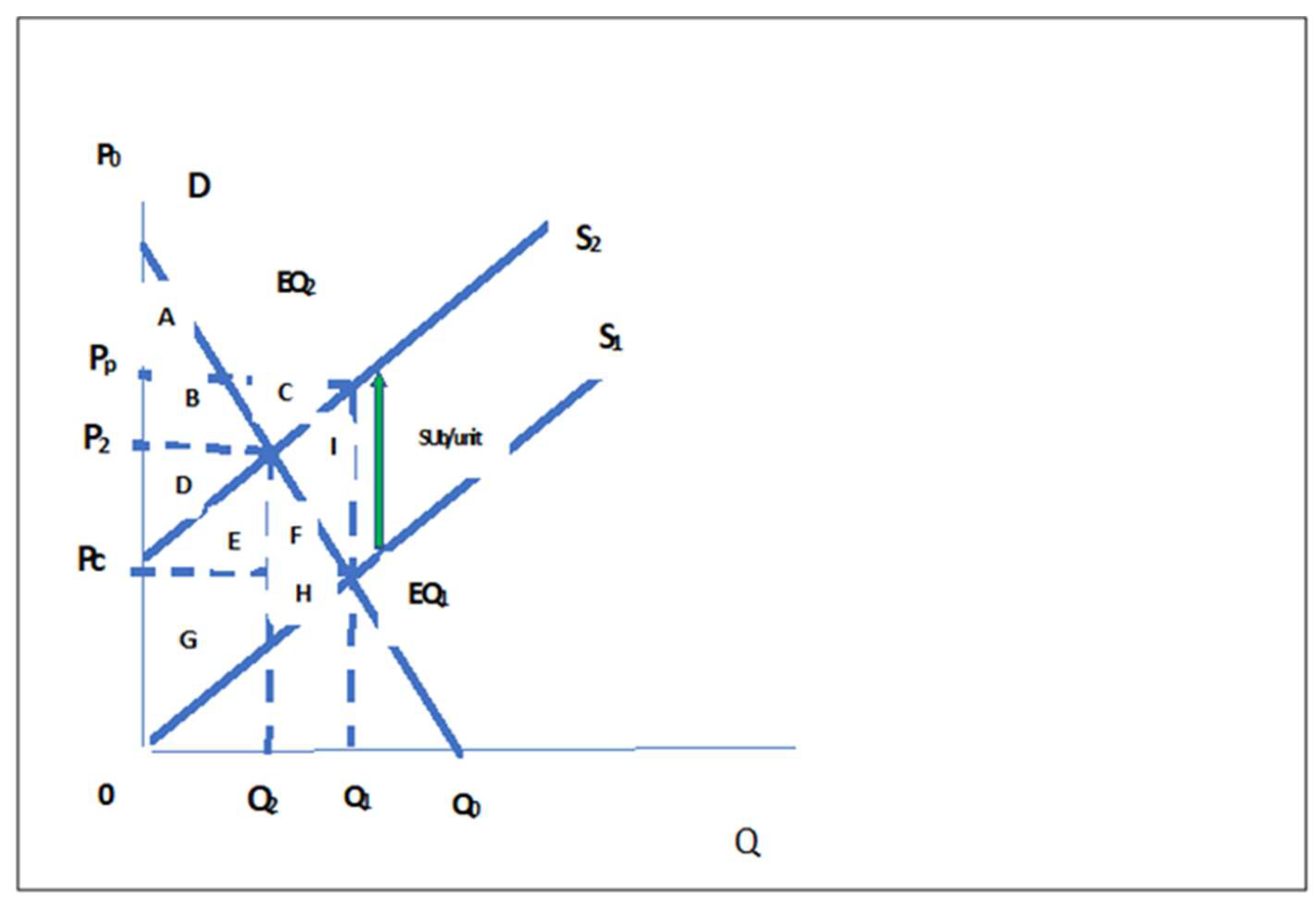
Refer to the diagram. assuming equilibrium price p1, consumer surplus is represented by areas:. A. marginal utility diminishes as more of a product is consumed. B. total utility falls below marginal utility as more of a product is consumed. C. the income and substitution effects precisely offset each other. D. time becomes less valuable as more of a product is consumed. 19. The price elasticity of supply measures how. Assuming equilibrium price P1, consumer surplus is represented by areas a + b a + b + c + c + d a + c d. References Multiple Choice Difficulty: 02 Medium Learning Objective: 04-02 Explain the origin of both consumer surplus and producer surplus, and explain how properly functioning markets maximize their sum, total surplus, while optimally. Refer to the above diagram. Assuming equilibrium price P1 producer surplus is represented by areas: (1) Solve for the equilibrium price and quantity. Graph your results. Shade in the areas that represent consumer and producer surplus. Setting demand equal to supply, we find that: 38-P=P-2→𝑃. ∗ = $10, 𝑄. ∗ = 8 (2) Government officials fear that too much mead is being consumed at the market equilibrium, leading to
Assuming equilibrium price p1 producer surplus is represented by areas. Refer to the diagram above. 30 take highest consumer price minus lowest consumer price then subtract highest consumer price from actual price and add both prices. Some consumers who want a good do not obtain it because the price is higher than they are willing to pay. Refer to the diagram. assuming equilibrium price p1, producer surplus is represented by areas_. Consider this brinley is the hottest new pop singer but his agent discovers that internet sales of brinleys music have been poor due to internet piracy but concerts are regularly sold out and merchandise such as t shirts sells well. Assuming equilibrium price P1, consumer surplus is represented by areas O a+b. 4 DELL a+b+c+d. 5 a + c. 3 C + d. C 6 tt over 7 泉 Studio This problem has been solved! Refer to the diagram. Assuming equilibrium price P 1, consumer surplus is represented by areas:
Exam 060204RR - Price, Efficiency, and Consumer Behavior. 1. Refer to the diagram above. Total revenue at price P1 is indicated by area (s) A. A + C. D. A + B. 2. Experts are tested by Chegg as specialists in their subject area. We review their content and use your feedback to keep the quality high. 100% (3 ratings) Consumer surplus is measured as the area b.. View the full answer. Transcribed image text: Refer to the diagram Assuming equilibrium price P_1, consumer surplus is represented by areas. Refer to the diagram. a b e Q, Q2 Q, Quantity Assuming equilibrium price P1, consumer surplus is represented by areas 1) a+ b. 2) a + b+ c+ d. Refer to the diagram. Assuming equilibrium price P1, producer surplus is represented by areas A) a + b. B) a + b + c + d. C) c + d. D) a + c.
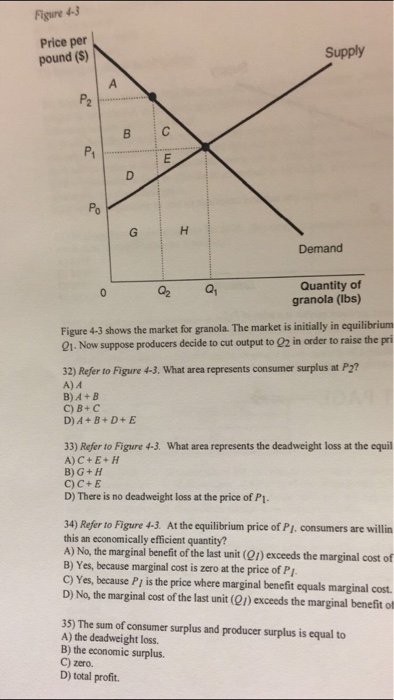
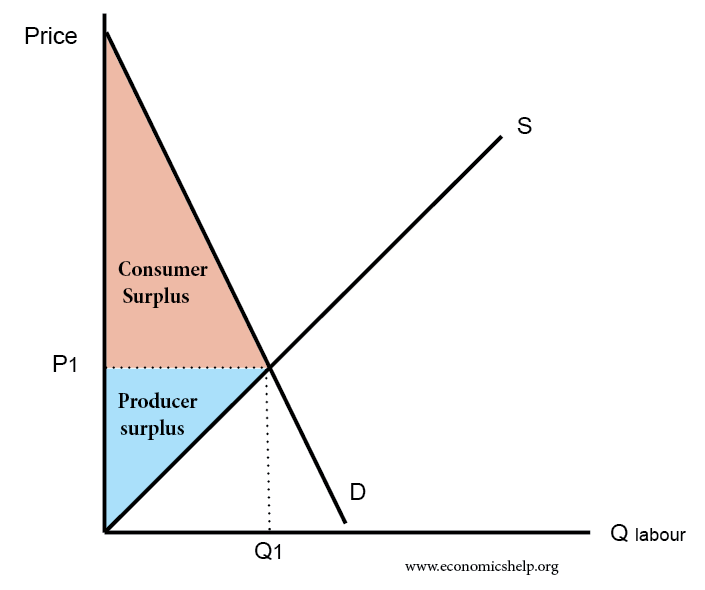
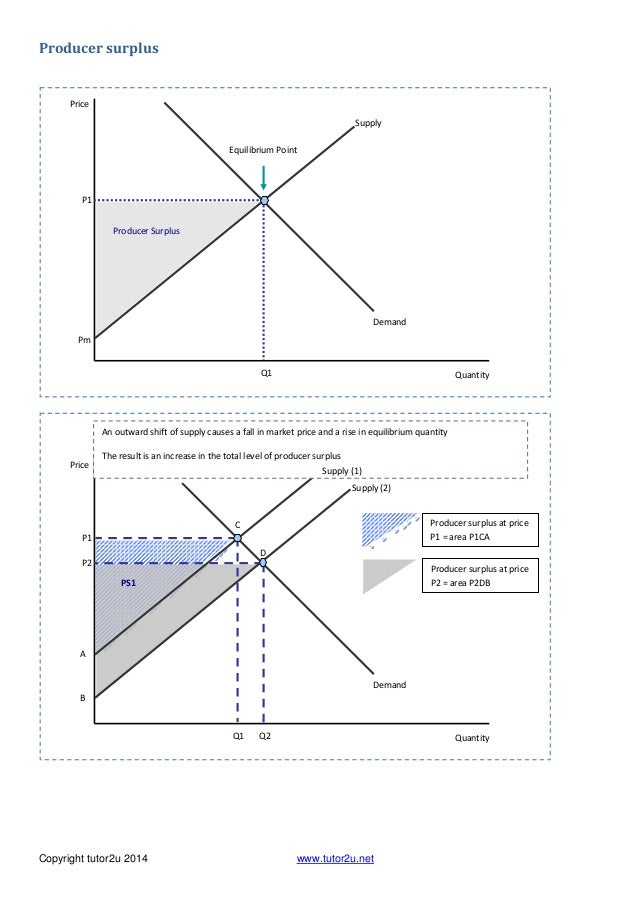
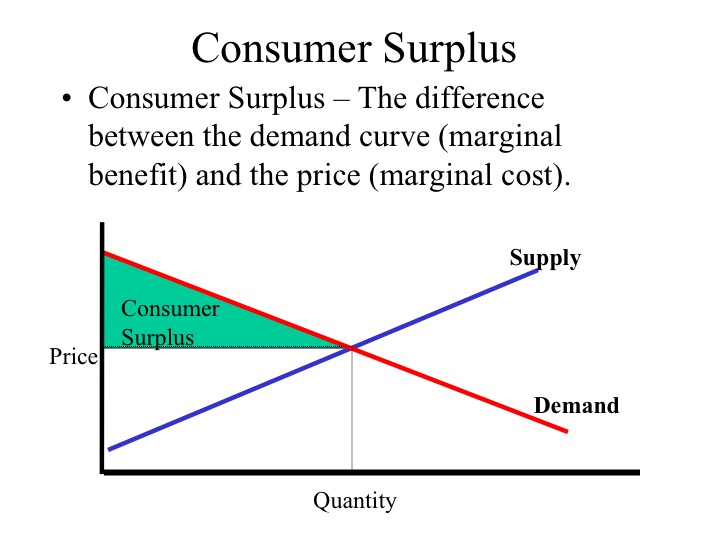
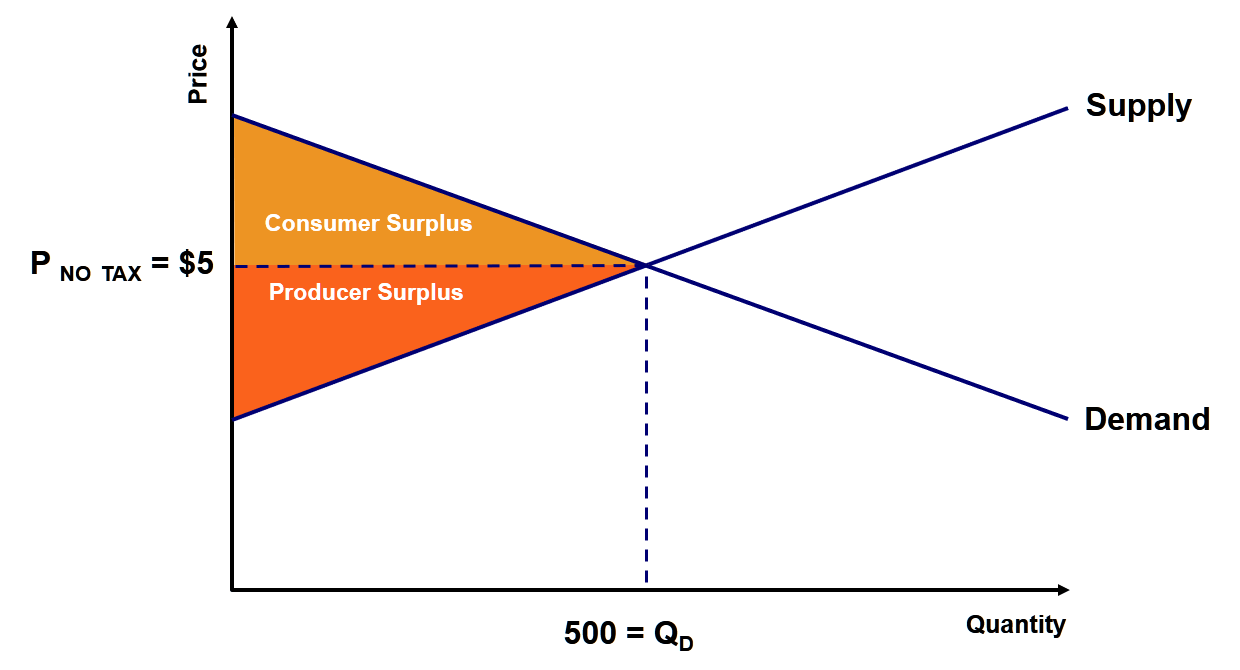
Graph 1. The red triangle in the above graph represents producer surplus. Producer surplus exists when the price goods are sold for is greater than what it costs the firms to manufacture those goods. Producer surplus is defined by the area above the supply curve, below the price, and left of the quantity sold. Graph 2. The yellow triangle in the above graph represents consumer surplus.
Consumer surplus: A. is the difference between the maximum prices consumers are willing to pay for a product and the lower equilibrium price.. Refer to the diagram. Assuming equilibrium price P1, consumer surplus is represented by areas: A. a + b.... Refer to the diagram. Assuming equilibrium price P1, producer surplus is represented by ...
Assuming equilibrium price P1, producer surplus is represented by areas. asked Sep 13, 2019 in Economics by Common.. Assuming equilibrium price P1, consumer surplus is represented by areas. asked Sep 13,... Refer to the information provided in Figure 26.6 below to answer the question(s) that follow. ...
Chapter 5 Quiz.docx - Question 1 Refer to the above diagram Assuming equilibrium price P1 producer surplus is represented by areas a b a b c d c d a c A
53. Producer surplus: is the difference between the maximum prices consumers are willing to pay for a product and the lower equilibrium price. rises as equilibrium price falls. → is the di fference between the minimum prices producers are willing to accept for a product and the higher equilibrium price.
Refer to the diagram. Assuming equilibrium price P1, consumer surplus is represented by areas A) a + b. B) a + b + c + d. C) c + d. D) a + c.
Assuming equilibrium price P1 consumer surplus is represented by areas: a + b. Refer to the above diagram. Assuming equilibrium price P1 producer surplus is represented by areas: c + d. Refer to the above diagram. The area that identifies the maximum sum of consumer surplus and producer surplus is:
Assuming equilibrium price p1 consumer surplus is represented by areas a a b. Under the demand curve and above the actual price. Refer to the above diagram in which s is the market supply curve and s1 is a. A b. 2030 2 Practice Under The Demand Curve And Above The Actual Price Above The Supply
Refer to the diagram. Assuming equilibrium price P1, producer surplus is represented by areas A) a + b+c+ d. B) a + b. C) a +c. D) c+ d. Forks.
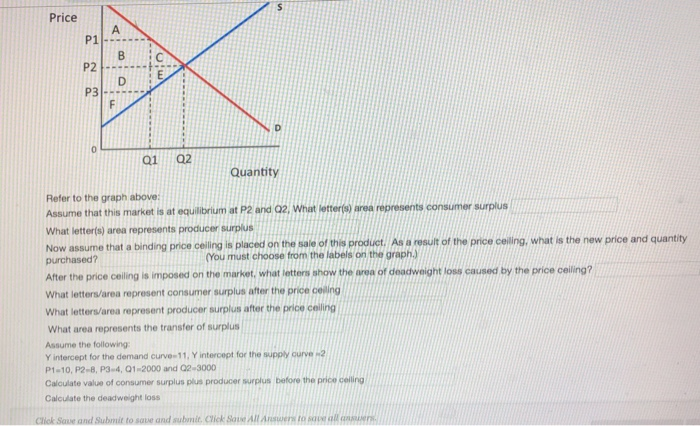
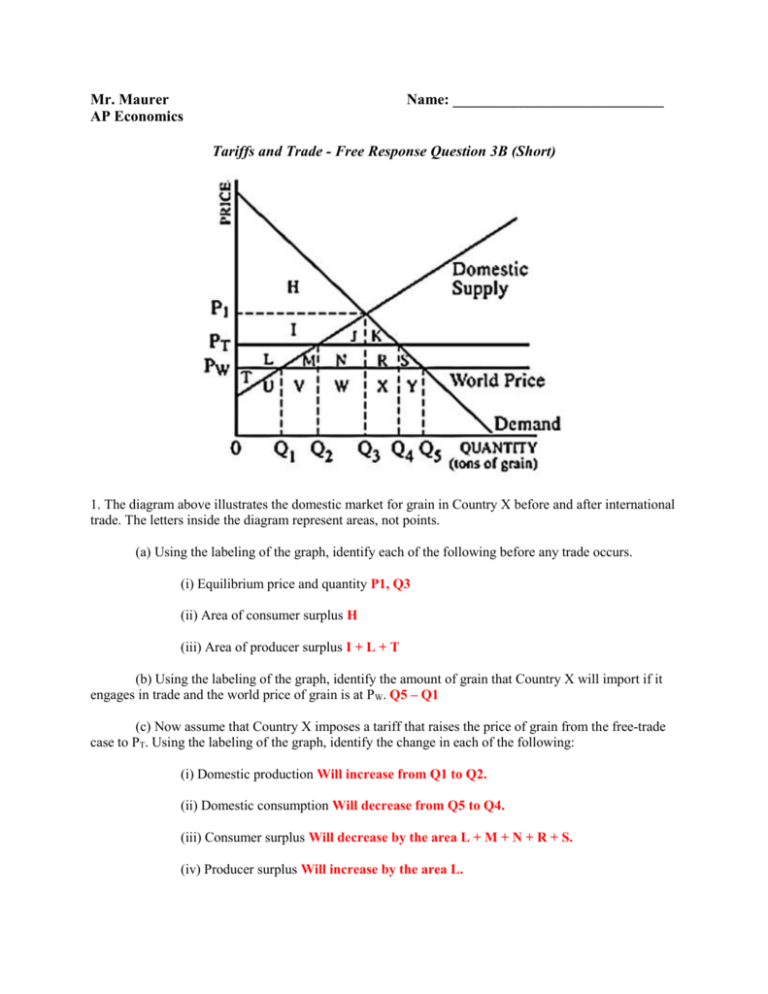
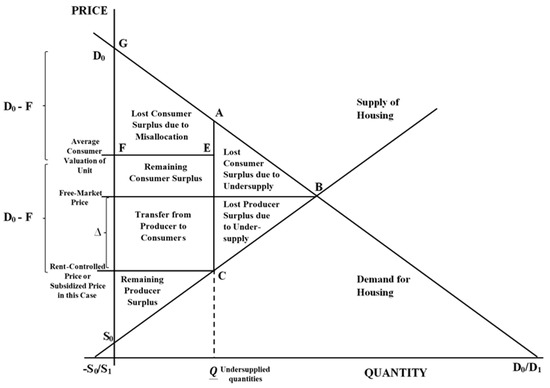
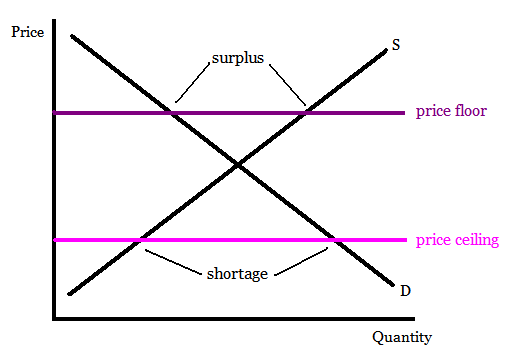
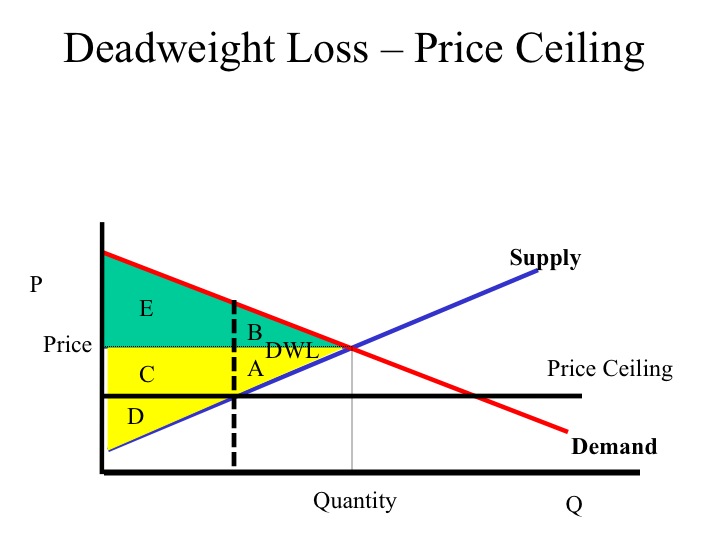
A minimum price set above the market equilibrium price is known as _____. 7. A reduction in net benefits as a result of a market intervention is known as. refer to the graph below. 14. In the graph above, setting a maximum price of P 1... Consumer surplus is now areas (A+C). Producer surplus is now area E. Total market benefits are now
B) a consumer surplus of $10, and Tony experiences a producer surplus of $190 Refer to the diagram. Assuming equilibrium price P1, consumer surplus is represented by areas
a consumer surplus of $10 and Tony experiences a producer surplus of $190. Refer to the diagram. Assuming equilibrium price P1, consumer surplus is represented by areas:
60 seconds. Q. When a price floor is imposed, it has an impact on a market if it is set: answer choices. Below the equilibrium price. Above the equilibrium price because quantity supplied exceeds quantity demanded. Above the equilibrium price because quantity demanded exceeds quantity supplied. At the equilibrium price.
View Notes - 2Review Test Submission_ Quiz 02 - Fall 2016 ECON231-50_. from ECON 231 at Western Carolina University. 9/11/2016 ReviewTestSubmission:Quiz02Fall2016ECON23150:. Home H SupportResources
Refer to the above diagram. Assuming equilibrium price P1, consumer surplus is represented by areas: a + b. Refer to the above diagram. Assuming equilibrium price P1, producer surplus is represented by areas: c + d. Refer to the above diagram. The area that identifies the maximum sum of consumer surplus and producer surplus is:
the minimum prices producers are willing to accept for a product and the higher equilibrium price. Refer to the diagram. Assuming equilibrium price P1, consumer surplus is represented by areas.
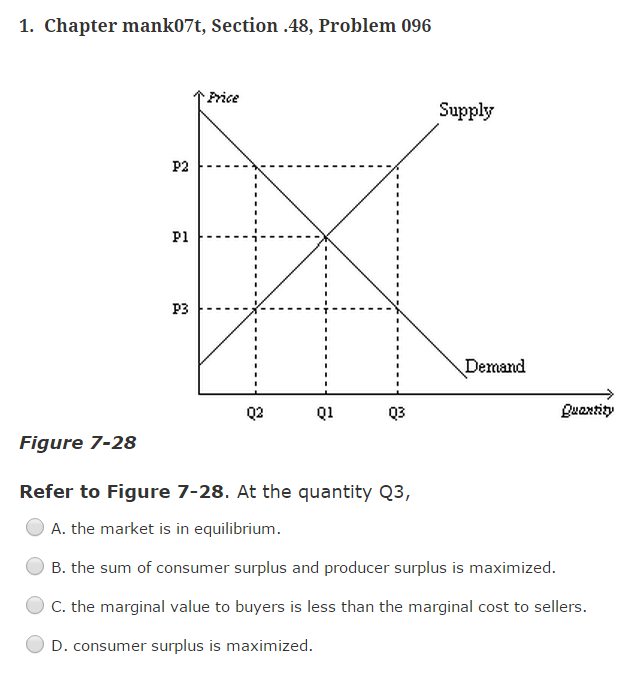
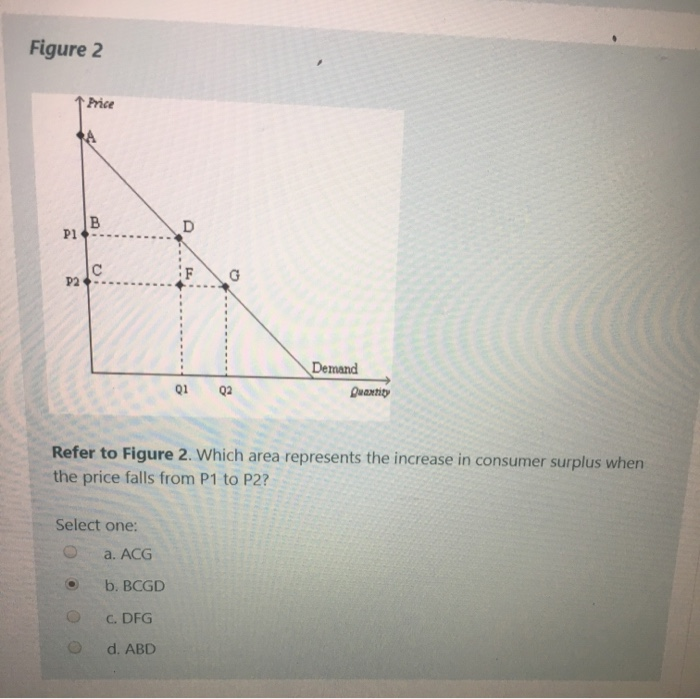
If the price of this good is $60, what will consumer surplus equal? a) $50. b) $100. c) $150. d) $200. The following question refers to the diagram below, which illustrates an individual's demand curve for a good. If the price of this good falls from P1 to P2, then consumer surplus will by areas. a) increase; B+D. b) decrease; B+D. c.











/producer_surplus_final-680b3c00a8bb49edad28af9e5a5994ef.png)




0 Response to "43 Refer To The Diagram. Assuming Equilibrium Price P1, Consumer Surplus Is Represented By Areas:"
Post a Comment