43 Orbital Filling Diagram For Silicon
The orbital filling diagram of boron. I skipped past beryllium because I was getting bored. The electron configuration of boron is 1s²2s²2p¹, which means that there are two electrons in the 1s orbital, two electrons in the 2s orbital, and one electron in the 2p orbitals. This gives us an orbital filling diagram of: Refer to the explanation. The electron configuration of manganese, atomic number 25, is "1s"^2"2"^2"2p"^6"3s"^2"3p"^6"3d"^5"4s"^2". The diagram below represents the electron configuration as an orbital diagram.
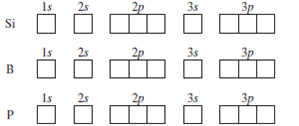
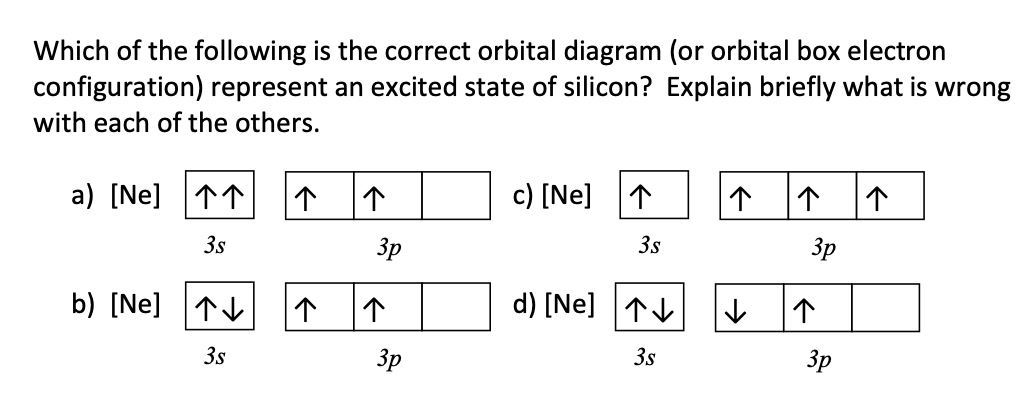
Orbital Filling Diagram Electron Configuration Electron Dot Diagram a. Boron b. Silicon c. Sulfur d. Calcium e. Iodine f. Rubidium g. Chromium h. Gallium Where are the Electrons? Write the full electron configuration, short-hand electron configuration, and fill in the orbital. Place the ending configuration and the dot diagram for the above.

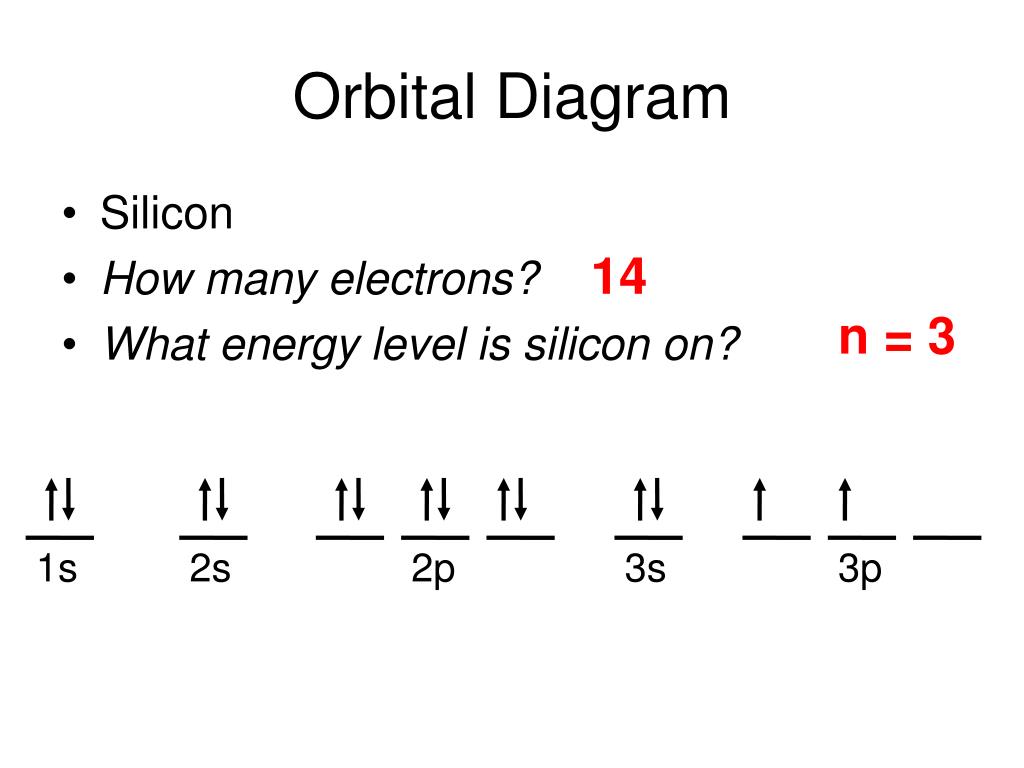
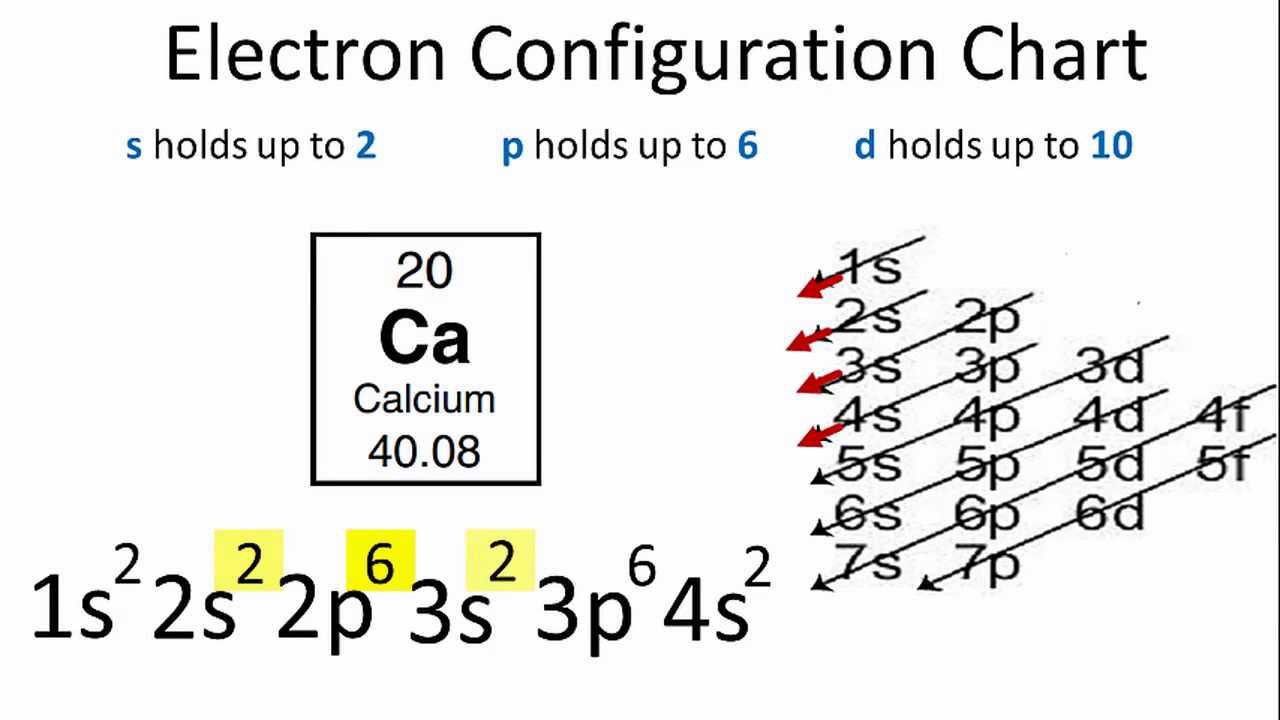
Orbital filling diagram for silicon
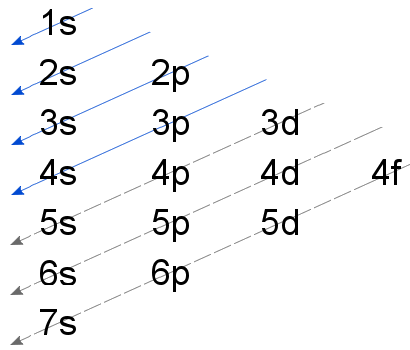
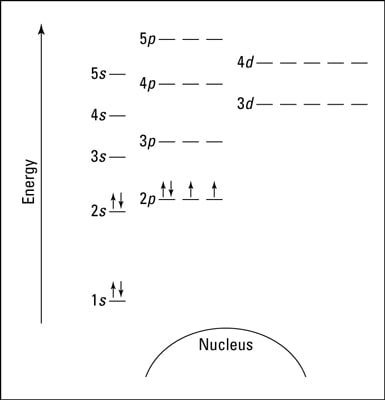
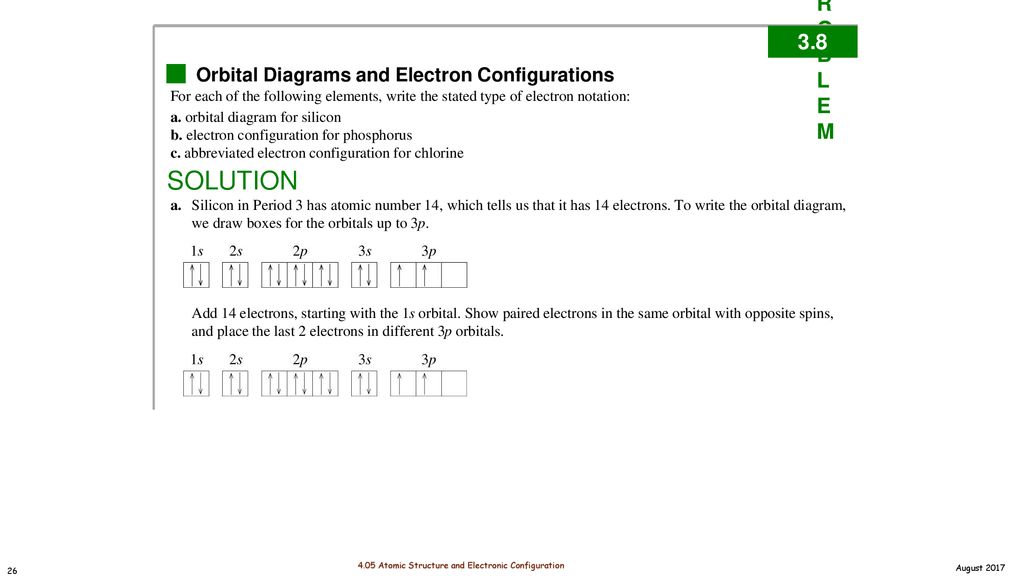
In an orbital filling diagram, the individual orbitals are shown as circles (or squares) and orbitals within a sublevel are drawn next to each other horizontally. Each sublevel is labeled by its principal energy level and sublevel. Electrons are indicated by arrows inside the circles.. What is the orbital diagram for silicon? Show the orbital-filling diagram for N (nitrogen).. Give the ground-state electron configuration for silicon (Si) using noble-gas shorthand. [Ne]3s^23p^2. Item 3: Part C Give the actual ground-state electron configuration for copper (Cu) using the complete form. 1s^22s^22p^63s^23p^63d^104s^1. For example, 1s2 2s2 2p1 is the electron configuration of boron. Use this tool to generate the electron configuration of arsenic (As). Item 15 150 Constants Period Review Use the orbital-filling diagram to show the electron configuration of aluminum, Al. Learning Goal: Relate orbital-filling diagrams to electron configurations.
Orbital filling diagram for silicon. 1. Write orbital filling diagrams, electron configurations, and electron dot diagrams for the following elements. Table: Element Orbital Filling Diagram Electron Configuration Electron Dot Diagram a. Boron b. Silicon c. Sulfur d. Calcium e. Iodine f. Rubidium g. Chromium h. Gallium This problem has been solved! Who are the experts? Experts are tested by Chegg as specialists in their subject area. We review their content and use your feedback to keep the quality high. plea.. View the full answer. Transcribed image text: Fill in the orbital energy diagram for silicon. How Many Valence Electrons are in Silicon. There are 4 electrons in the outer shell of Silicon so the number of valence electrons in silicon is 4. Silicon Orbital Diagram. Orbit diagram consists of a pair of electrons of the atom in the box i.e. Orbit diagram helps to define the ground-state electron configuration is an easy form. silicon only has 14 electrons The reason is that Silicon only has 14 electrons. When you start filling up the orbitals, you do that from the lowest energy and in this order: "1s" -> "2s" -> "2p" -> "3s" -> "3p" -> "4s" -> "3d".... As the levels get larger, their sublevels start to overlap. That's why 4s is at a lower energy than 3d sublevel. Each sublevel can accommodate a fixed number of.
Orbital filling diagram for silicon. So you put 8 electrons into your energy level diagram. You can represent electrons as arrows. Also the crystalline form is used in semiconductors. If you havent yet learned electron configurations you really need to go ahead. Commercial production depends on a reaction between sand sio2 and carbon at a. Orbital Filling Diagram Electron Configuration Electron Dot Diagram a. Boron b. Silicon c. Sulfur d. Calcium e. Iodine f. Rubidium g. Chromium h. Gallium Where are the Electrons? Write the full electron configuration, short-hand electron configuration, and fill in the orbital diagrams, for the following elements. 1. Orbital filling diagram Silicon - Long e- config: 2 Short e- config: Orbital filling diagram 2s2z 3 G Gold - Long e- config: Short e- config: Xe - Long e- config: Short e- config: U short e-config: Oxygen long e-config: Ba short e-config: Pb long e-config: Label the adjacent pictures as highest & lowest frequency longest & shortest wavelength Orbital diagram of Carbon (C) 7: Orbital diagram of Nitrogen (N) 8: Orbital diagram of Oxygen (O) 9: Orbital diagram of Fluorine (F) 10: Orbital diagram of Neon (Ne) 11: Orbital diagram of Sodium (Na) 12: Orbital diagram of Magnesium (Mg) 13: Orbital diagram of Aluminum (Al) 14: Orbital diagram of Silicon (Si) 15: Orbital diagram of Phosphorus.
Orbital Diagram, electron configuration, and the noble gas notation for a silicon (Si) atom. Orbital Diagram For Arsenic. Because the 4p section has 3 orbitals, but Arsenic ends with 4p3. It'll want to leave as few orbitals empty, so you have three arrows pointing up. The orbital diagram of arsenic can be written as 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s23p6 4s2 3d10 4p3. Arsenic has 33 electrons, including 3 in itsoutermost shell. schematron ! Show the orbital-filling diagram for (bromine).Status: Resolved. Show the orbital-filling diagram for S (sulfur). Stack the subshells in order of energy, with the lowest-energy subshell at the bottom and the highest-energy subshell at the top%(15). 1. Describe the two differences between a 2p x orbital and a 3p y orbital. For example, 1s2 2s2 2p1 is the electron configuration of boron. Use this tool to generate the electron configuration of arsenic (As). Item 15 150 Constants Period Review Use the orbital-filling diagram to show the electron configuration of aluminum, Al. Learning Goal: Relate orbital-filling diagrams to electron configurations.
Si orbital Diagram. electron configuration of silicon si orbital diagram orbital diagram electron configuration and the noble gas notation for a silicon si atom electron configuration for silicon si how to write the electron configuration for silicon si since 1s can only hold two electrons the next 2 electrons for silicon go in the 2s orbital.
This video shows how to draw the orbital diagram of Titanium (Ti). It also shows how to write the electron configuration of titanium and the shorthand noble...
Show the orbital-filling diagram for N (nitrogen).. Give the ground-state electron configuration for silicon (Si) using noble-gas shorthand. [Ne]3s^23p^2. Item 3: Part C Give the actual ground-state electron configuration for copper (Cu) using the complete form. 1s^22s^22p^63s^23p^63d^104s^1.
Orbital filling diagram for silicon. Well put six in the 2p orbital and then put the next two. Silicon carbide sic is one of the hardest substances known and used in polishing. Sources makes up major portion of clay granite quartz sio2 and sand. Visit the post for more. Since 1s can only hold two electrons the next 2 electrons for silicon go in.
Just so, what is the orbital diagram for silicon? Silicon has 14 electrons in the following orbital configuration 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p2 when neutral in charge. Also the crystalline form is used in semiconductors. Phosphorus 1s 2s 2p 3s 3p 4s 3d 4p. In writing the electron configuration for silicon the first two electrons will go in the 1s orbital.
Orbital Filling Diagram For Silicon Written By JupiterZ Friday, November 6, 2020 Add Comment Edit. Silicon Wikipedia. 8 4 Molecular Orbital Theory Chemistry. Nature Of Traps Responsible For The Memory Effect In Silicon. Arrangements Of Electrons In The Orbitals Of An Atom Is Called Its.
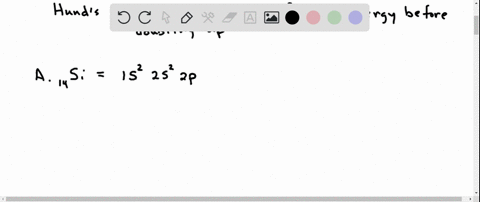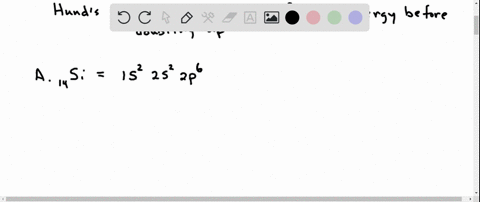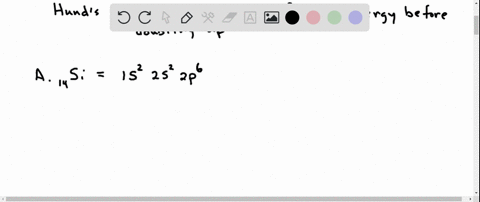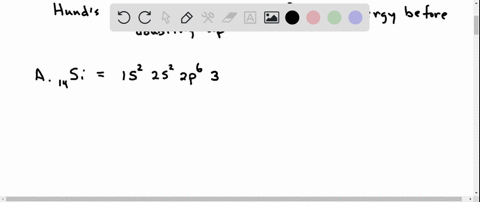
Hund©s Rule & Orbital Filling Diagram Complete the orbital diagram for each element. 2) calcium 1s 2s 4s 3s 3d 2p 4p 3p 1) sodium 1s 2s 4s 3s 3d 2p 4p 3p 3) nickel 1s 2s 4s 3s 3d 2p 4p 3p 4) silicon 1s 2s 4s 3s 3d 2p 4p 3p 5) iron 6) copper 1s 2s 4s 3s 3d 2p 4p Answer key 3p 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 1s 2s 4s 3s 2p 4p 3p 3d.
To see the orbital filling diagram, click on the "Orbital Filling Diagram" button and click on element "53": iodine. Once you have clicked on it, click on "electron configuration" and you'll see the rbital filling diagram of iodine! Powered by Create your own unique website with customizable templates.
Orbital Filling Diagrams. An orbital filling diagram is the more visual way to represent the arrangement of all the electrons in a particular atom. In an orbital filling diagram, the individual orbitals are shown as circles (or squares) and orbitals within a sublevel are drawn next to each other horizontally.
Silicon orbital diagram. Show the orbital-filling diagram for S sulfur. It is a hard brittle crystalline solid with a blue-grey metallic lustre and is a tetravalent metalloid and semiconductorIt is a member of group 14 in the periodic table. Also the crystalline form is used in semiconductors. Three rules are useful in forming orbital diagrams.
Fill in the blank for the condensed electron configuration of Sr (Z=38). [_____]5s^2. Draw the orbital filling diagrams for silicon. Enter a number for the the electrons that are paired or unpaired in each of the sublevels.
In writing the electron configuration for Silicon the first two electrons will go in the 1s orbital. Since 1s can only hold two electrons the next 2 electrons for Silicon go in the 2s orbital. The nex six electrons will go in the 2p orbital. The p orbital can hold up to six electrons. We'll put six in the 2p orbital and then put the next two.
Orbital Filling Diagrams An orbital filling diagram is the more visual way to represent the arrangement of all the electrons in a particular atom. In an orbital filling diagram, the individual orbitals are shown as circles (or squares) and orbitals within a sublevel are drawn next to each other horizontally.
Orbital-Filling Diagram for Bromine. Bromine has 35 electrons, so it will have 35 arrows placed in its orbital-filling diagram as in figure The order bottom to top.Show the orbital-filling diagram for Br (bromine). Stack the subshells in order of energy, with the lowest-energy subshell at the bottom and the highest-energy subshell at the top.
This preview shows page 2 - 3 out of 3 pages. Table: Element Orbital Filling Diagram Electron Configuration Electron Dot Diagram a. Boron b. Silicon c. Sulfur d. Calcium e. Iodine f. Rubidium g. Chromium h. Gallium.
In an orbital filling diagram, the individual orbitals are shown as circles (or squares) and orbitals within a sublevel are drawn next to each other horizontally. Each sublevel is labeled by its principal energy level and sublevel. Electrons are indicated by arrows inside the circles.. What is the orbital diagram for silicon?
1. Write orbital filling diagrams, electron configurations, and electron dot diagrams for the following elements. Table: Element Orbital Filling Diagram Electron Configuration Electron Dot Diagram a. Boron b. Silicon c. Sulfur d. Calcium e. Iodine f. Rubidium g. Chromium h. Gallium



























0 Response to "43 Orbital Filling Diagram For Silicon"
Post a Comment