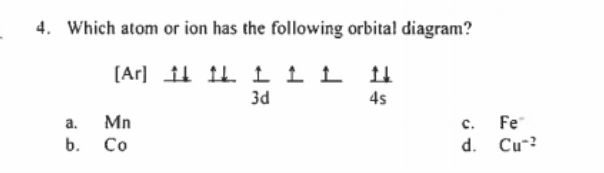
43 Orbital Diagram Of Fe
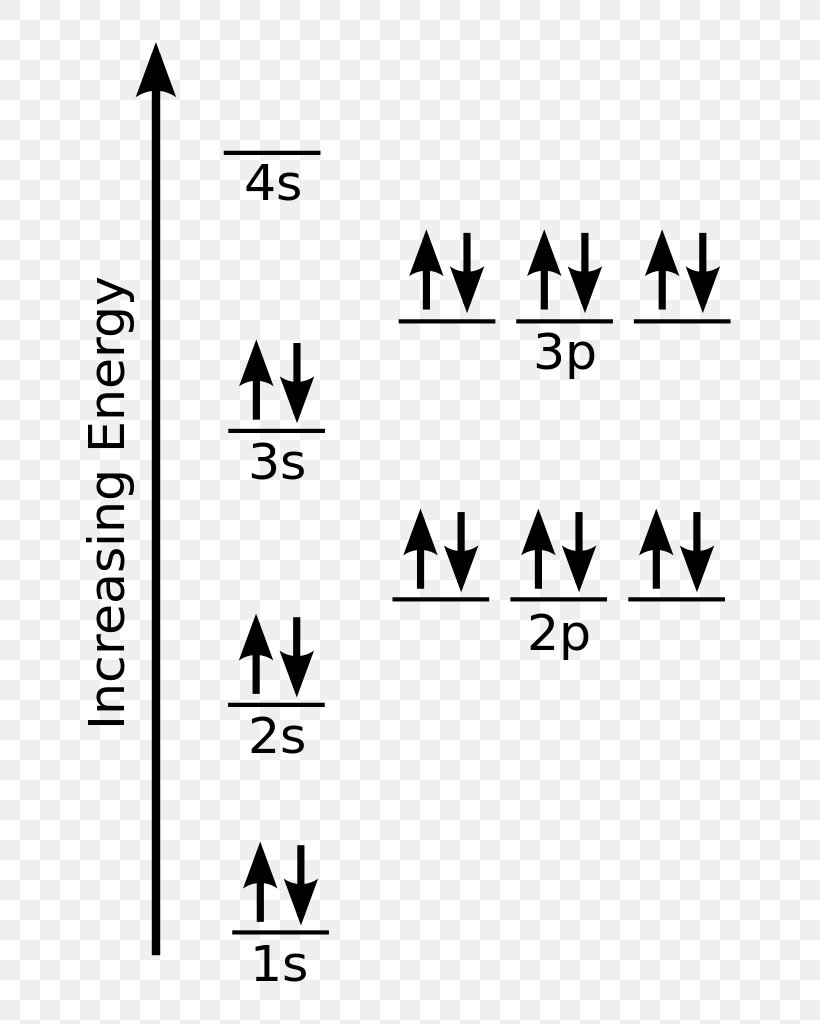
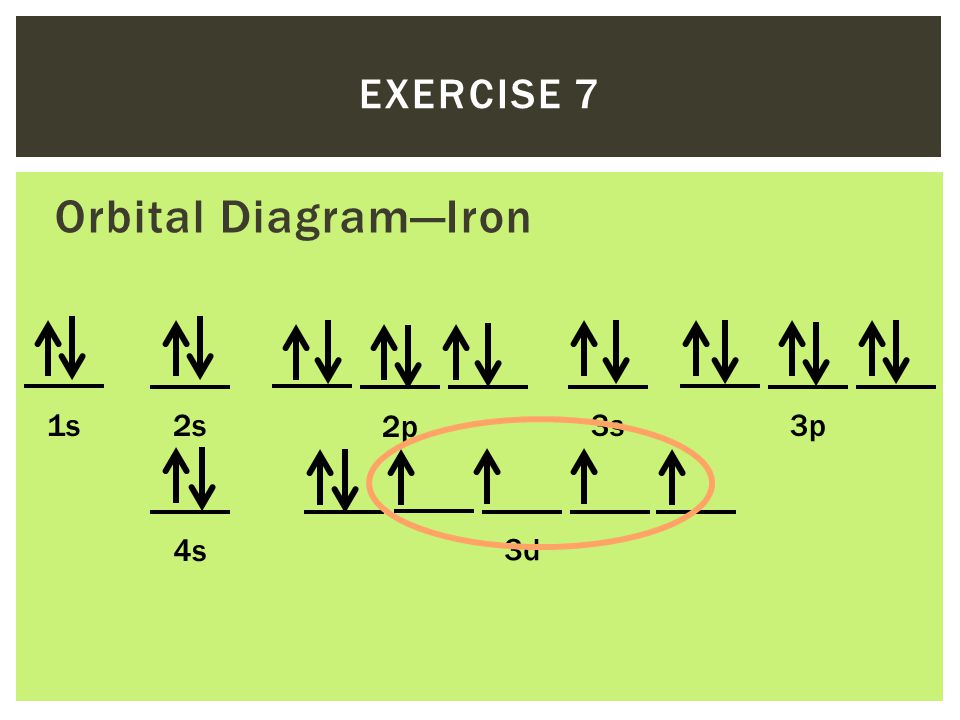
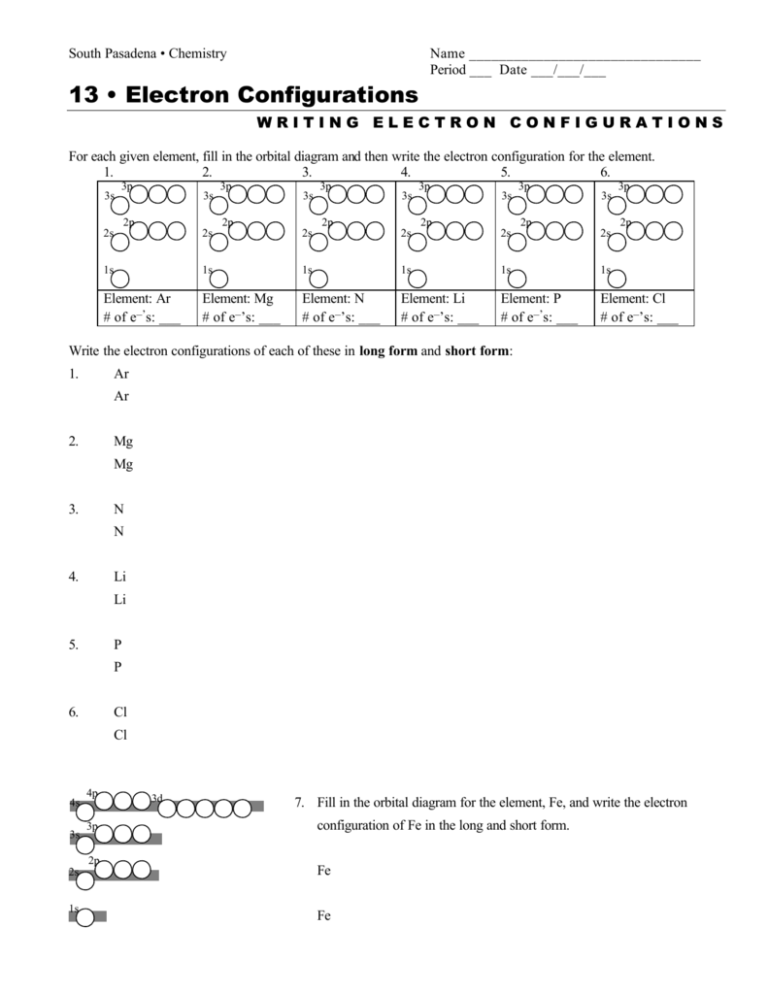
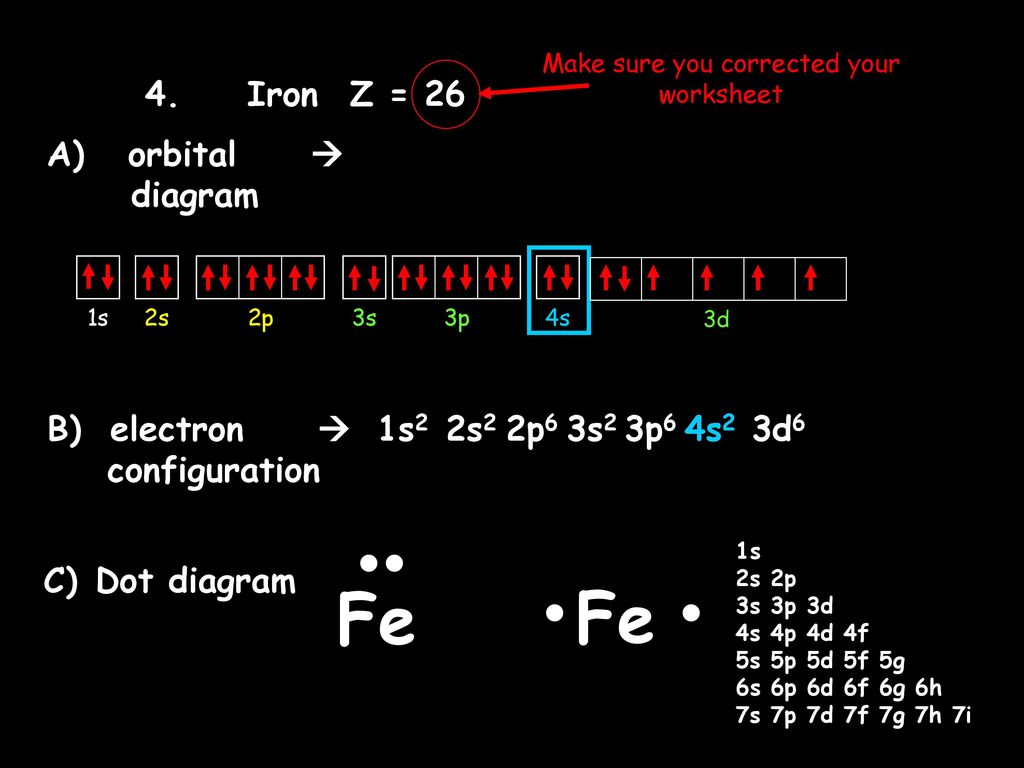
Iron has 26 electrons so its normal electron configuration would be: Fe 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p 6 4s 2 3d 6. When we make a 3+ ion for Iron,. Orbital Diagrams. Another way to represent the order of fill for an atom is by using an orbital diagram often referred to as "the little boxes": Fe orbital Diagram. what is the orbital diagram for fe answers fe or iron has the atomic number of 26 i"highlight">diagram is 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d6. Wiki User. ∙ 2014-09-17 18:04:30. This answer is: Helpful.
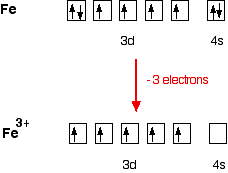
Transition Fe3+ ions and draw the orbital box diagrams for both ions. Using this. There for 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 3d5 is the electronic configration for Fe3+. half of electrons (there must be one electron in each orbital, and d has 5 orbitals). That's for filling up orbitals for ground state atoms.
Orbital diagram of fe
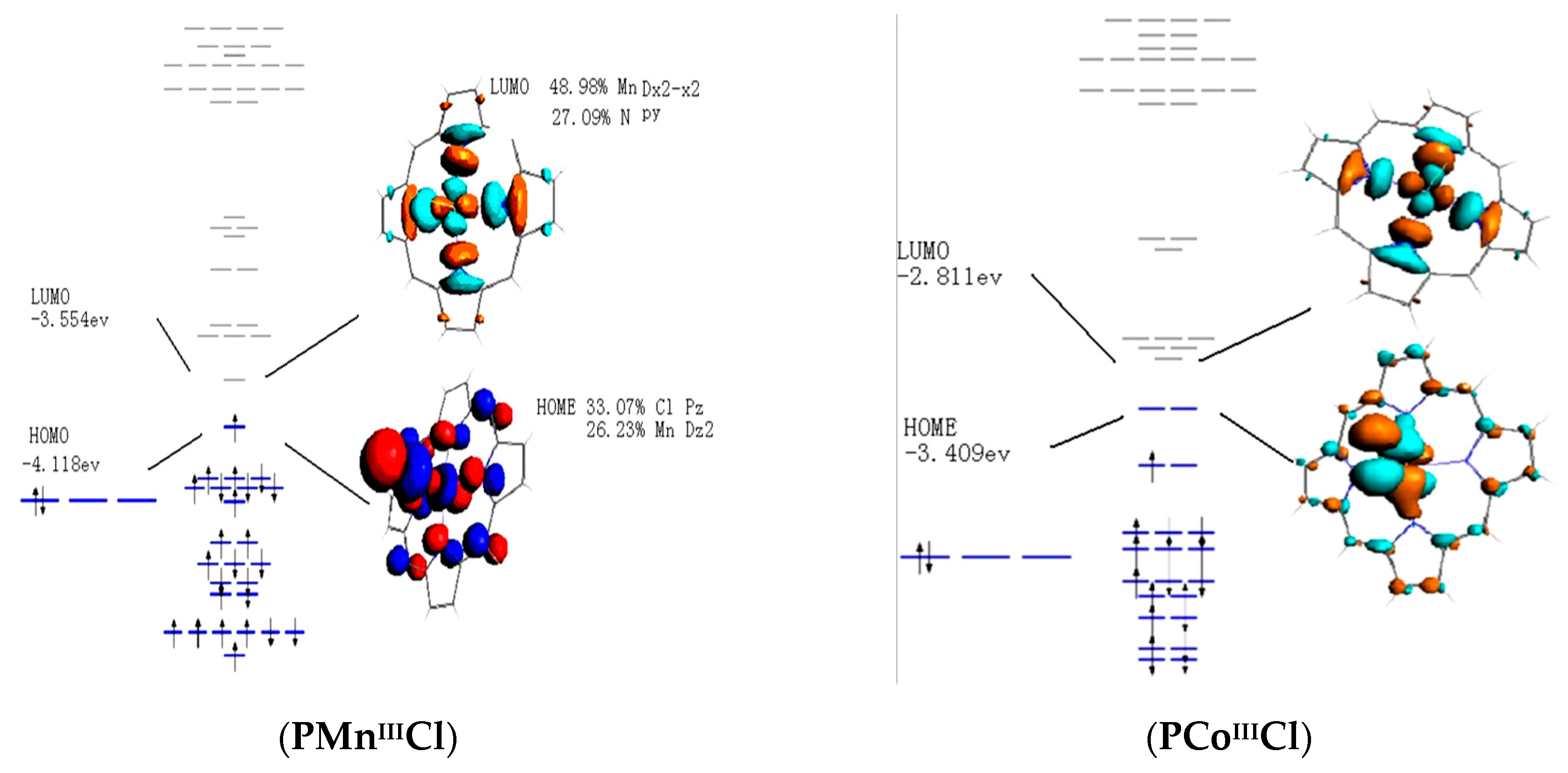
• The primary orbital interactions that form the metal‐ligand bonds in ferrocene occur between the Fed orbitalsand the ‐orbitals of the Cp ligand. • If D 5d symmetry is assumed,so that there is a centre of symmetry in the ferrocene molecule through the Fe atom there will be centro ‐symmetric (g)andanti‐ symmetric(u) combinations. Write the complete orbital configuration for iron (Fe). Orbital Configuration: Orbital configuration is the arrangement of electrons present in the atomic structure. Fe:1s^2 2s^2 2p^6 3s^2 3p^6 4s^2 3d^6 Recall that transition metals don't have "traditional" valence electrons. The valence electrons for a transition metal element are those of the highest ns and n−1d value, in this case those electrons in 4s and 3d. This means Fe has 8 valence electrons.
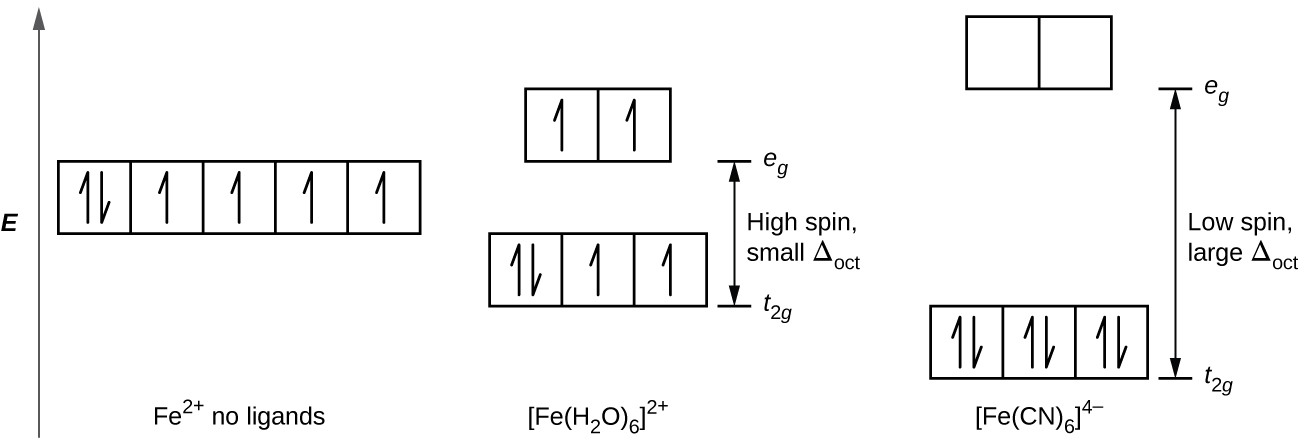
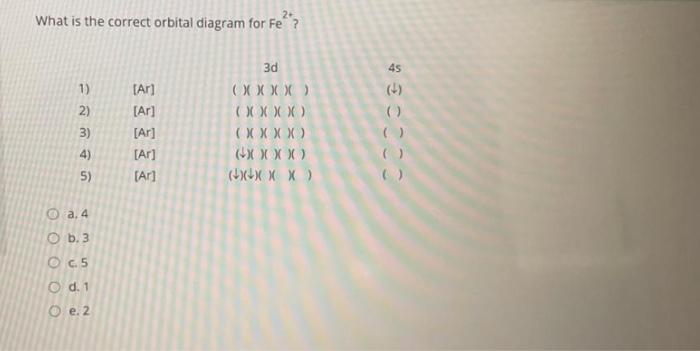
Orbital diagram of fe. What is the correct orbital diagram for Fe2+? Re: electron configuration for Fe2+ So the electron configuration for Fe is [Ar] 3d^6 4s^2. Fe^2+ means that 2 electrons are taken away. You start removing e- from the outermost shell. The outermost shell, in this case, is the 4s orbital. 22a. [Fe(CN) 6] 4− is low spin d6 and has all bonding orbitals filled. Irradiation with visible light leads to population of the e g* antibonding orbital, making the cyanides more labile. [Fe(CN) 6] 3− does not have as strong of a Fe-CN bond with only 5 electrons in the t 2g bonding orbital and they are therefore more labile. Orbital diagram of Iron (Fe) 27: Orbital diagram of Cobalt (Co) 28: Orbital diagram of Nickel (Ni) 29: Orbital diagram of Copper (Cu) 30: Orbital diagram of Zinc (Zn) 31: Orbital diagram of Gallium (Ga) 32: Orbital diagram of Germanium (Ge) 33: Orbital diagram of Arsenic (As) 34: Orbital diagram of Selenium (Se) 35: Orbital diagram of Bromine. Iron is on the fourth row of the periodic table, sixth column of the transition metals, atomic number 26. What we have is: Its core orbitals are the 1s, 2s, 2p's, 3s, and 3p's. Its valence orbitals are the 4s and 3d's. Writing the electron configuration, you really only need the valence orbitals, and you can omit the core orbitals by notating it via the noble gas shortcut.
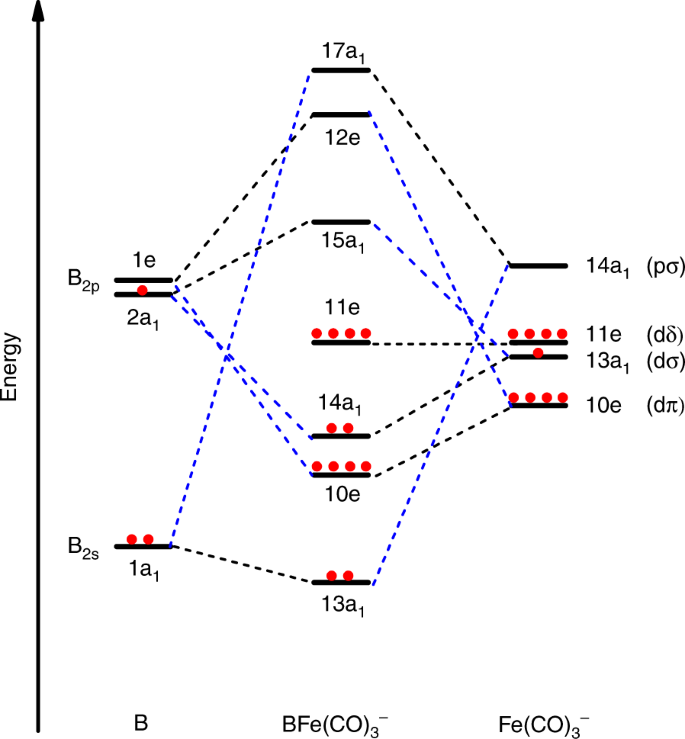
Fe:1s^2 2s^2 2p^6 3s^2 3p^6 4s^2 3d^6 Recall that transition metals don't have "traditional" valence electrons. The valence electrons for a transition metal element are those of the highest ns and n−1d value, in this case those electrons in 4s and 3d. This means Fe has 8 valence electrons. Orbital Interaction Diagram 1. Plot atomic valence orbital en ergies (or fragment orbitals for More complex molecules). 2. Determine which orbitals can interact (those with S 0). 3. Determine magnitude of each interaction: scales directly with magnitude of overlap scales inversely with orbital energy difference 4. Plot MO energies and draw orbitals As is apparent from the molecular orbital diagram of excited Fe(CO) 4 in Fig. 2b, these transitions entail negative energy transfer because the incident photon energy is smaller than the scattered. A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) molecular orbital method in particular.electron configuration for Fe2+ - CHEMISTRY COMMUNITYMolecular orbital diagram - Wikipedia.
The 3d_(xy) orbital of "Fe" does not match up with any of "O" atom's atomic orbital symmetries, so it is nonbonding. The 4s and 3d_(x^2 - y^2) are mostly nonbonding, because the 2p_z orbital has already been used, and no other orbitals on "O" that are of that symmetry are available to pair up with these orbitals on "Fe". Answer (1 of 8): To determine hybridization of Co ordination compound first of all we will have to write electronic configuration of central metal. Thereafter orbital diagram is sketched. * If strong ligand is present then pairing of electron occurs, otherwise no pairing occurs.(ligand contain... What is electron configuration of Fe? [Ar] 3d6 4s2. How many d electrons are in FE? From the periodic table, iron has atomic number 26 , meaning that there are 26 electrons in each ground state iron atom. 2⋅5=10 electron in each d orbital, and so on so forth. After the 4s is full we put the remaining six electrons in the 3d orbital and end with 3d6. Therefore the Iron electron configuration will be 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p 6 4s 2 3d 6. Note that when writing the electron configuration for an atom like Fe, the 3d is usually written before the 4s. Both of the configurations have the correct numbers of.
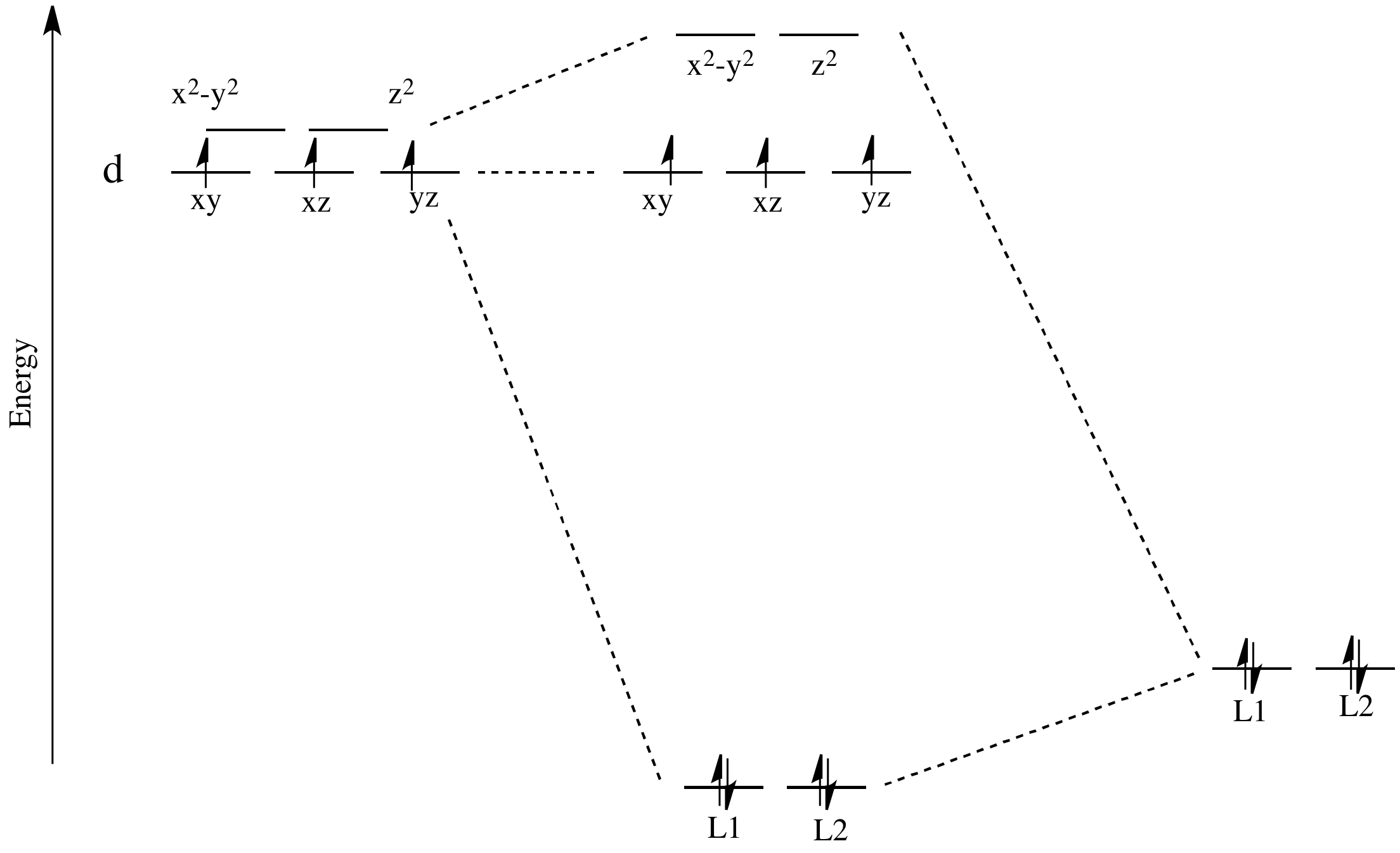
d-orbital diagram for [Fe(H 2 O) 6] 3+: The first three electrons go into t 2g orbitals unpaired. The 4th and 5th electrons must choose whether to pair up with electrons already in t 2g (which costs energy) or to go into higher energy e g orbitals (which also costs energy). In this case, the splitting energy is less than the pairing energy so the 4th and 5th electrons go into the e g orbitals.
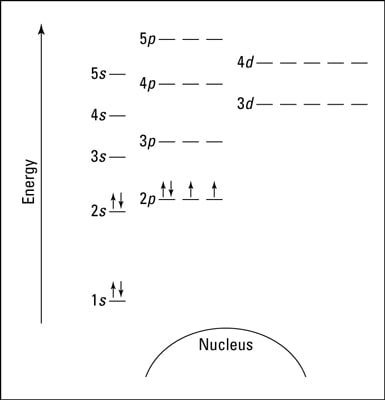
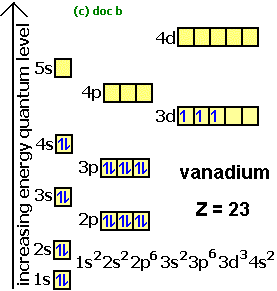
Orbital diagrams are a visual way to show where the electrons are located within an atom. Orbital diagrams must follow 3 rules: The Aufbau principle, the Pau...
Orbital Notation for Iron (Fe). Mr. Causey shows you step by step how to write the orbital notation for iron (Fe).http://yourCHEMcoach SUBSCRIBE for more.
Orbital diagram of iron. See Answer. Best Answer. Copy. The electron configuration of iron (Fe) has an argon (Ar) core. The electron configuration of Fe is [Ar]3d^6 4s^2 2 8 14 2. Wiki User. ∙.
Fe:[Ar]3d⁵. How many valence electrons does an arsenic atom have?. Which principle or rule is violated by the following orbital diagram of an atom in its ground state? ** the second 2p orbital is empty. Hund's rule. The element whose atoms in the ground state have 2 half-filled orbitals is. Po.
Fe2+ Orbital Diagram. For midterm question Q5C, why the electron configuration for Fe2+ is not [Ar]3d^5 4S^1? The outermost shell, in this case, is the 4s orbital. You're removing 2 electrons from it to generate the Fe2+ ion, which are removed from the 4s orbital first (this is always the case in transition chemistry - as far as.
Orbital diagrams are pictorial descriptions of the electrons in an atom. Orbital Diagram Ar Wiring Diagrams The pauli exclusion principle says that only two electrons can fit into an single orbital. Fe orbital diagram. What is the electron configuration and orbital diagram of. Three rules are useful in forming orbital diagrams.
Write the complete orbital configuration for iron (Fe). Orbital Configuration: Orbital configuration is the arrangement of electrons present in the atomic structure.
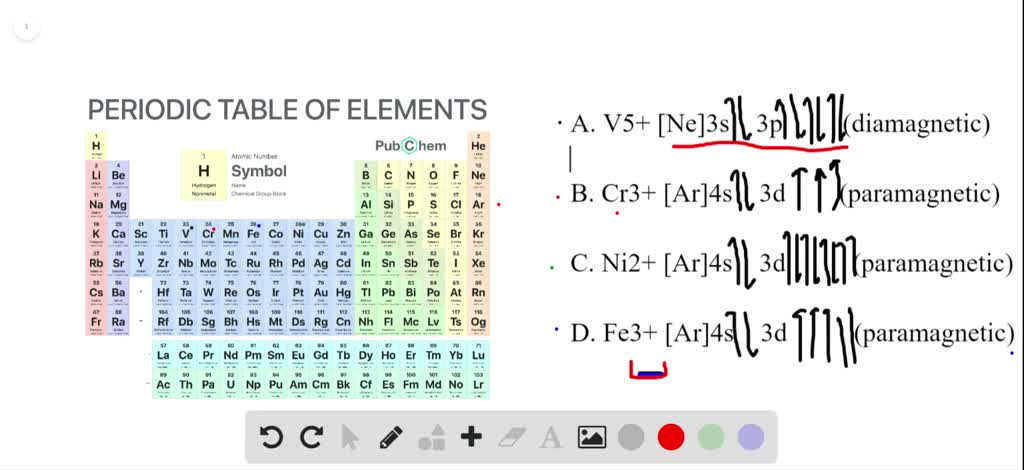
Write Out The Electron Configuration For The Uncharged Fe Atoms And The Fe2 And Fe3 Ions Also Write Out The Orbital Diagram To Show The Unpaired Electrons Is Each Species Paramagnetic Or Dia 54006
• The primary orbital interactions that form the metal‐ligand bonds in ferrocene occur between the Fed orbitalsand the ‐orbitals of the Cp ligand. • If D 5d symmetry is assumed,so that there is a centre of symmetry in the ferrocene molecule through the Fe atom there will be centro ‐symmetric (g)andanti‐ symmetric(u) combinations.
Example: Constructing MOs for Titanium Tetraiso propoxide, Ti(OiPr) pp , 4 • The OiiPrSALCs are compridised of fill dfilled p d bit l th O t x an p y orbitals on e a oms. • Ti bonding AOs E: (3dz 2, 3dx2‐y ) T 2: (4p x , 4p y, 4p z) (3dxy, 3dxz, 3dyz) • The T 1 SALC is non‐bonding. • Significant overlap occurs between the E SALC 2and the e AOs on Ti (3dz2, 3dx2‐y )
Orbital Diagram For Fe3+. There for 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 3d5 is the electronic configration for Fe3+. half of electrons (there must be one electron in each orbital, and d has 5 orbitals). Fe3+ loses an electron from the d You take electrons out of the 4s orbital, before you take them out of the 3d orbital, because it is lower. -3,-2,-1,0,1,2,3 c.
Orbital-Filling Diagram for Bromine. Bromine has 35 electrons, so it will have 35 arrows placed in its orbital-filling diagram as in figure The order bottom to top.Show the orbital-filling diagram for Br (bromine). Stack the subshells in order of energy, with the lowest-energy subshell at the bottom and the highest-energy subshell at the top.
























0 Response to "43 Orbital Diagram Of Fe"
Post a Comment