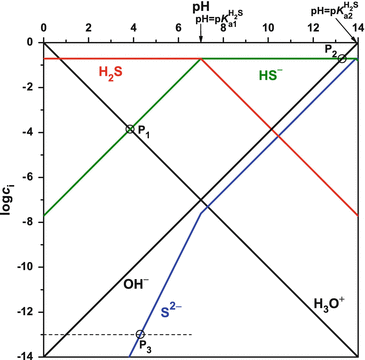
43 Log C Ph Diagram
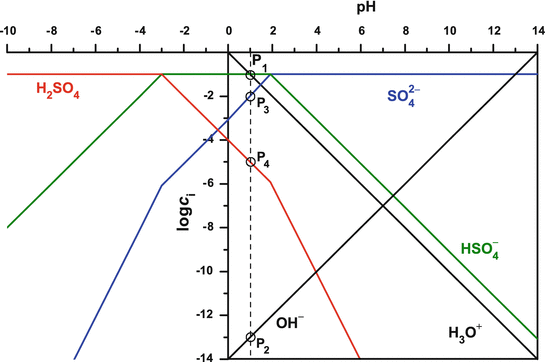
In electrochemistry, and more generally in solution chemistry, a Pourbaix diagram, also known as a potential/pH diagram, E H -pH diagram or a pE/pH diagram, is a plot of possible thermodynamically stable phases (i.e., at chemical equilibrium) of an aqueous electrochemical system.Boundaries (50 %/50 %) between the predominant chemical species (aqueous ions in solution, or solid phases) are. Similarly for over species present between pH 4 and 10 (see attached for Spreadsheet). Overlay Plot of Log C vs pH for Reduced Inorganic Nitrogen and Sulfur-10.-8.-6.-4.-2. 4.0 5.0 6.0 7.0 8.0 9.0 10.0 pH Log C (M) log C NH4+ log C NH3 log C H2S log C HS-solutions assign 2 2006
How to Construct a Log C Vs PH Diagram (monoprotic and Diprotic): This video will guide you on how to input the proper equations to build a log C vs pH diagram. Also I will go over the concepts involved between an open and closed system.

Log c ph diagram
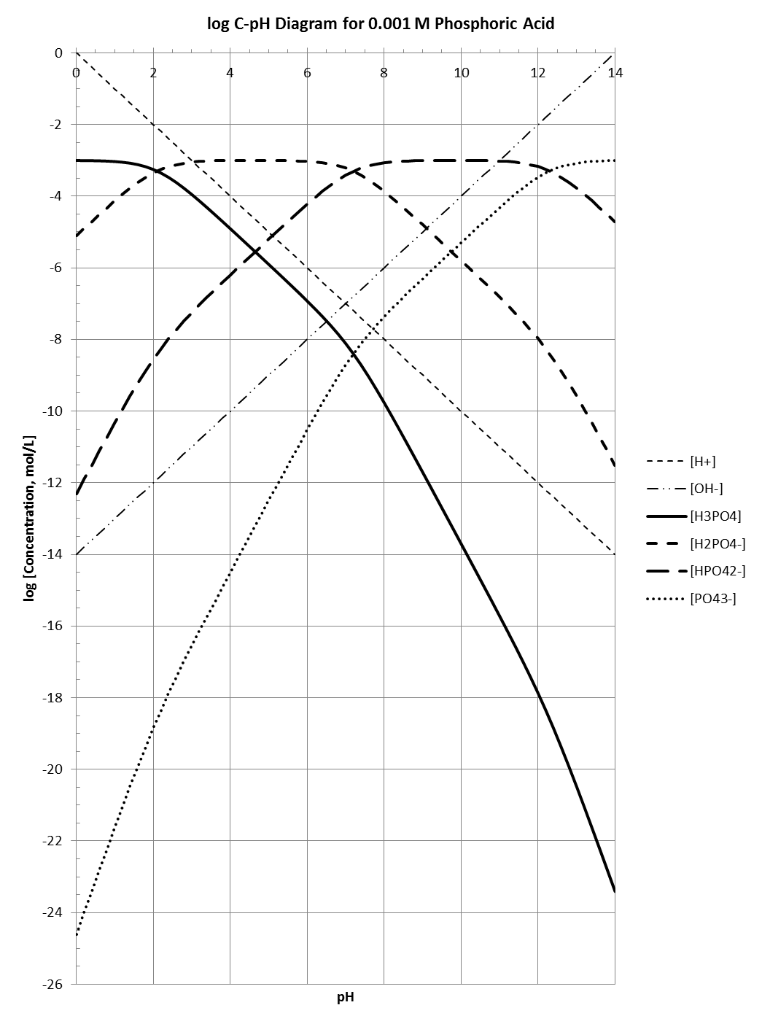
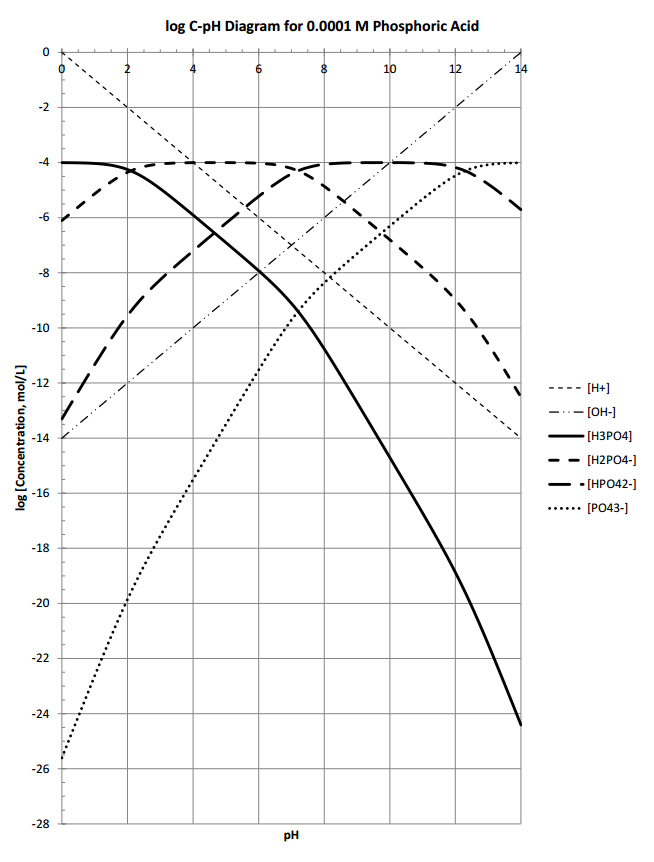
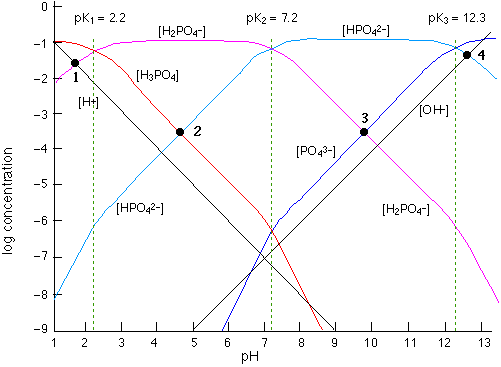
Fe III species and the revised potential - pH diagram of Fe - H 2 O system at 25º C, 1 bar and a [Fe] = 10 - 6 mol l - 1 are plotted. Aqueous chemistry of iron is studied very widely. Engineering; Chemical Engineering; Chemical Engineering questions and answers; 1. Use the attached 10-5 M phosphoric acid log C-pH diagram to obtain equilibrium compositions for the following aqueous solutions: (a) 10 5 M H3PO4 (b) 10-5 M NaH2PO4 (c) 10-5 M Na2HPO4 (d) 10-5 M Na3PO4 (e) 5 x 10-6 M NaH2PO4 + 5 x 10 M H3PO4 (f) 5 x 10-6 MH3PO4 +5 x 10-6 M Na2HPO4 We looked at this in class. Prepare a solubility diagram (log C vs pH) for a water that is potentially in equilibrium with zinc hydroxide and zinc carbonate. Assume the water has 10 -3 M total carbonates. Show all soluble species along with the Zn T line and indicate where precipitation will occur and the type of precipitate.
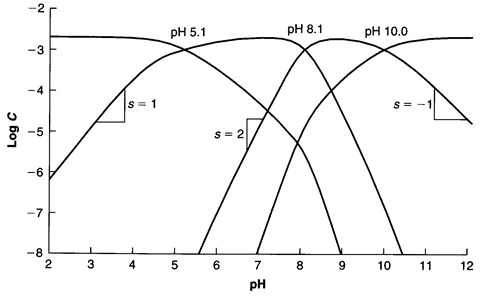
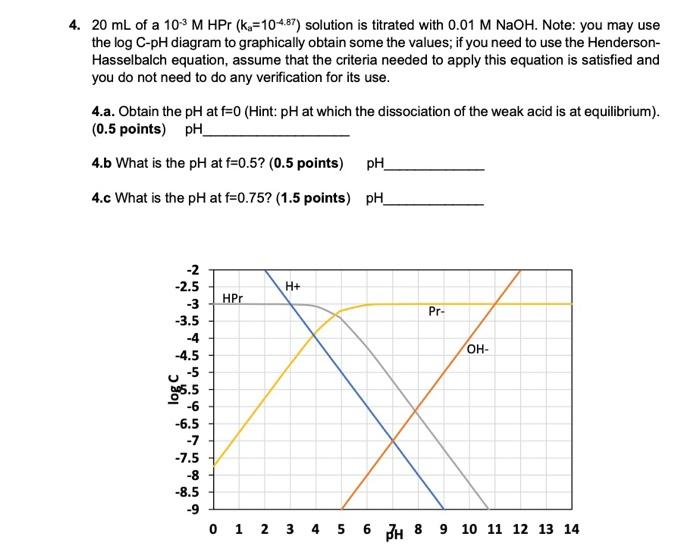
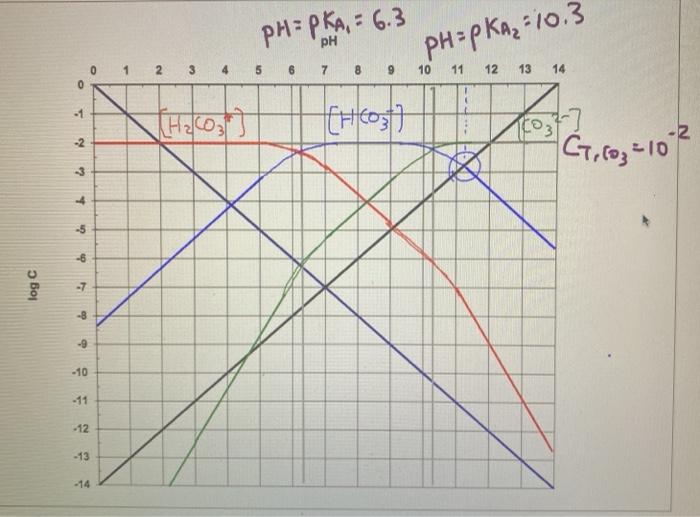
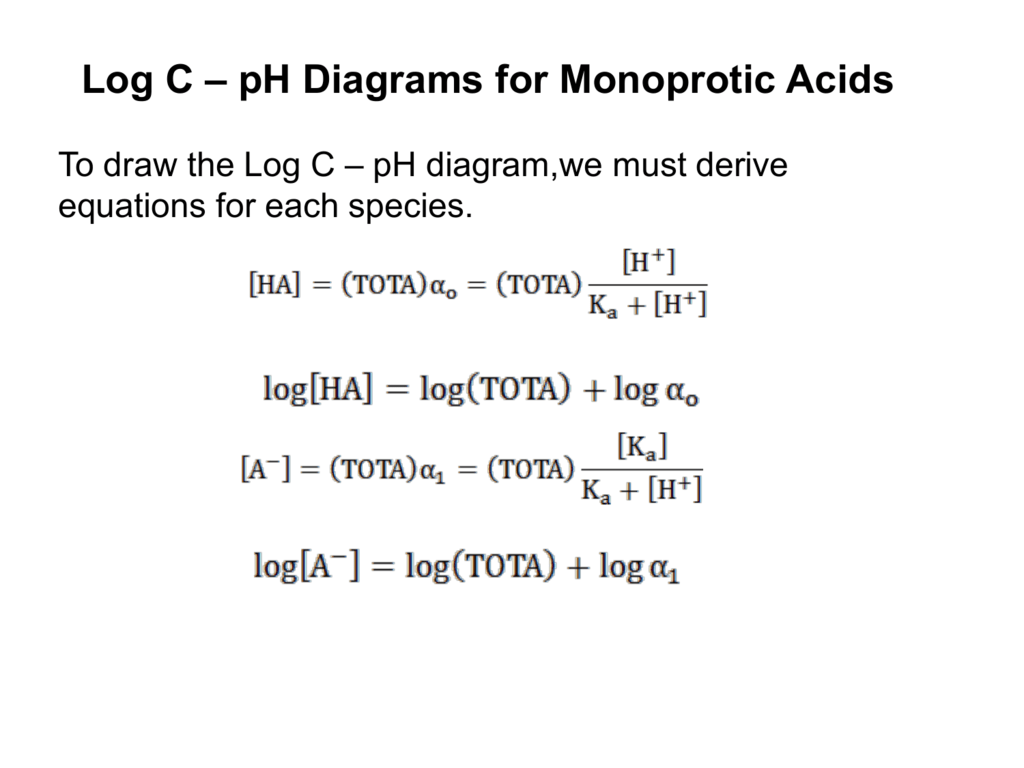
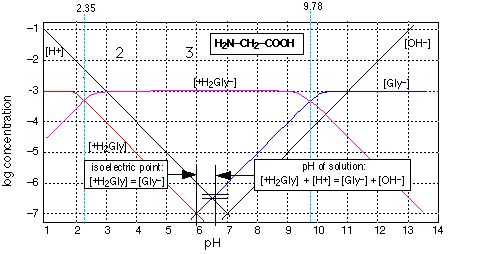
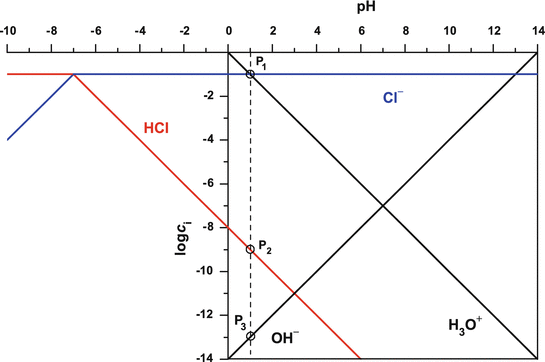
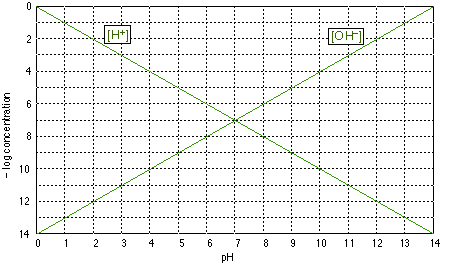
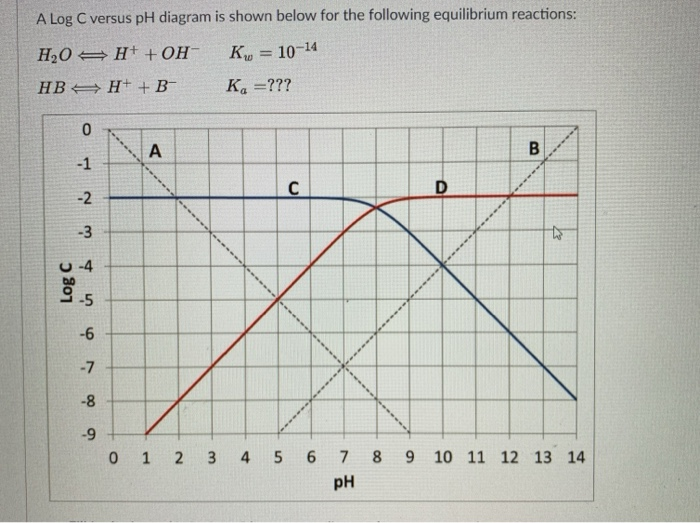
Log c ph diagram. The pH of any polyprotic weak and strong acid (or base) can be calculated employing the logarithmic concentration diagram. The aim of this text is to introduce a joint approach of algebraic, as used in textbook, and graphical method. The logarithmic diagrams provide an easy insight into the acid-base systems. The mathematical complexities are overtaken using a Computer Algebra System program. 3. A log C-pH diagram for an acid/base system containing 1027 M TOTA is shown below. The fully protonated form of the acid is H4A. The s values indicate the slope of the curve in the given region, and the pH values indicate the intersection points of the various curves. using pC pC-pH diagram pH diagram Find pH (or pOH) where the proton condition or charge balance is satisfied. 0 0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 C pH [H +] [OH-] Example 4-17 2 4 ation, pC [HCN] [CN-] Example 4-17 10-3 M NaCN Proton condition: 6 8 10 oncentra [HCN] + [H +] = [OH-] 10 12 14 ‐ log C ACEE 219 Spring 2010 HDP 13 10.1 (equilibrium pH) H+ ∼ c H+. The pH of the electrolyte is defined as the negative of the natural log of the H+ ion concentration in the electrolyte: pH = −log 10c. H + (3) Under room temperature, water as the most common solvant by self-ionization will give pH = 7 which is the neutral pH. For an acidic solution pH < 7, for basic pH > 7. 2.1.
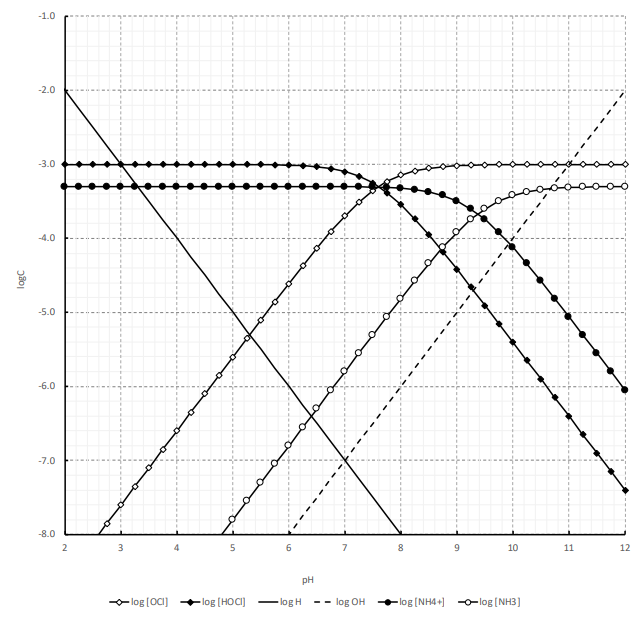
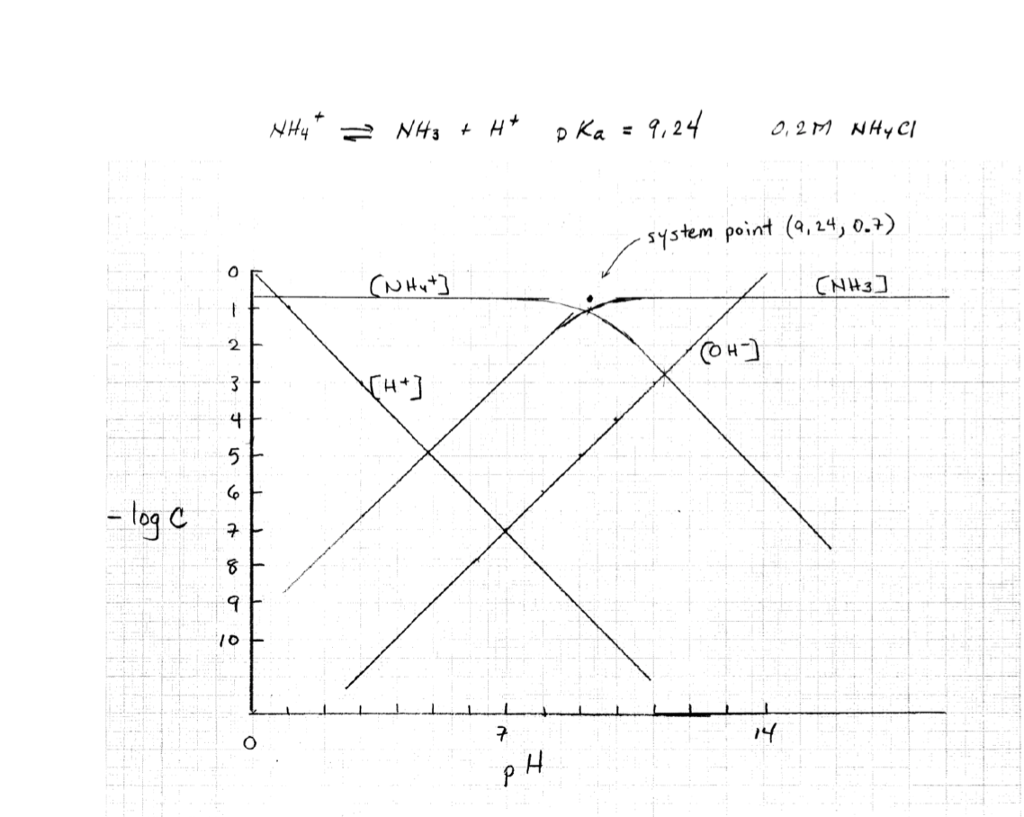
c nþ ð17Þ We can now calculate the pH-dependence of the solu-bility of M(OH) n when we substitute c Mnþ in Eq. 12 by the expression K sol;MOHðÞn cn OH from Eq. (11). This gives: S MOHðÞ n ¼ K sol;MOHðÞ n cn OH ð18Þ Substituting in this equation the term c OH by K w c H 3Oþ, i.e., taking into account the autoprotolysis constant of. The pH is a measure of the concentration of hydrogen ions in an aqueous solution. pKa (acid dissociation constant) and pH are related, but pKa is more specific in that it helps you predict what a molecule will do at a specific pH.Essentially, pKa tells you what the pH needs to be in order for a chemical species to donate or accept a proton. Transcribed image text: 2-2 Determine the pH of 1 mM NaOCI+0.5mM NH3 water solution using the pH-log C diagram method. (Show the excel table, proton balance equation and the pH-logC diagram). (10 marks). * prepare a Log C vs pH diagram, but working backwards * known CT, and known pH, find pKa * PBE suggests that pH lies at intersection of urate (Ur-) line and the H+ line * draw line with +1 slope passing through H+ line at pH=3.2 * where it intersects CT is the pKa (about 3.8) * then write PBE for base addition (i.e., NaUr) and solve Log C vs.
pE-pH Diagrams pE-pH stability field diagramsshow in a comprehensive way how protons (pH) and electrons (pE) simultaneously shift equilibria of reactions under various conditions These diagrams also indicate which species predominate. pH = -log{H+} Set limit: {H 2} = 1. The precise definition of pH is "the negative common logarithm of the activity of hydrogen ion in solution". For practical purposes, the activity is approximated as concentration in moles/L: pH = - log 10 ( [H+]). The lower case letter p before upper case letters (X), such as H, OH, or K stands for. "- log 10 (X)". solution will not be 7.0. For example, at a pressure of 93 kbar and 527 C, K w = 10 −3.05, the pH of pure water would be 1.5. Such conditions might conceivably apply to deposits of water in geological formations and in undersea vents. Problem Example 1 At 60 C, the ion product of water is 9.6E-14. What is the pH of a neutral solution at this. Use the attached phosphoric acid log C-pH diagram | Chegg . Science. Chemistry. Chemistry questions and answers. Use the attached phosphoric acid log C-pH diagram obtain equilibrium composition for the following aqueous solutions: 10-4 M H3PO4 10-4 M Na3PO4 10-4M Na2HPO4 5 Times 10-5 M NaH2PO4 + 5 Times 10-5 M H3PO4.
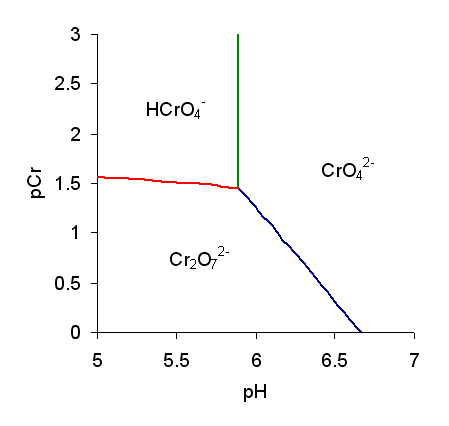
1 A log C - pe diagram for a pH 5 system containing 1.1x10−3 M TOTCr and 3x10−3 M TOTFe is shown below.Based on the information in the diagram, answer the following questions. a. What is peo for the H 2CrO4/Cr 3+ redox couple? b.
Environmental Chemistry,Prof. Bhanu Prakash Vellanki,Civil Engg. Dept.IIT RoorkeeIn this video, different aspects in developing the logC-pH diagram for monop...
Fe III species and the revised potential - pH diagram of Fe - H 2 O system at 25º C, 1 bar and a [Fe] = 10 - 6 mol l - 1 are plotted. Aqueous chemistry of iron is studied very widely.
For log c - pH diagrams, make sure the linear portions of the log c curves "aim" for the correct point at log TOTA, and that they curve (i.e., deviate from linearity) so that they intersect at the correct location. 6. Draw the graph to include all regions that are relevant to the solution of the
View S21_HW_8_Solution.pdf from ENV 4513 at Florida International University. Spring 2021 ENV 4513/5519 S. Laha Homework 8 -5 1 Use the attached 10 M phosphoric acid log C-pH diagram to obtain
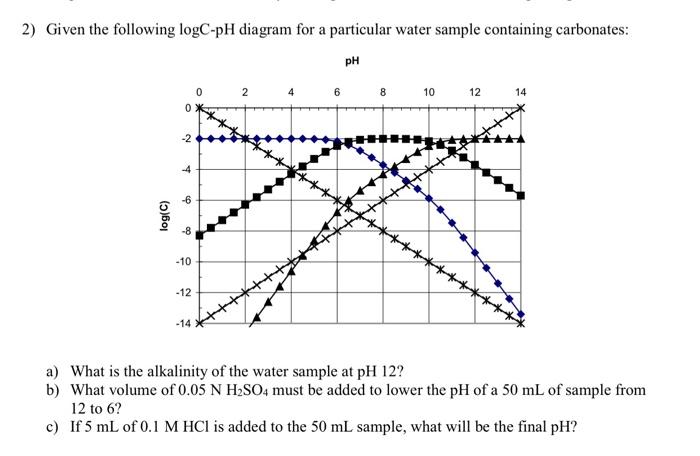
pH 4 6 8 10 12 Log activity of carbonate species-10-8-6-4-2 0 2 P co2 = 1 atm H 2 CO 3 o HCO 3-CO 3 2-Soil Chemistry 5-8 Section 5- Carbonate Chemistry Figure 5.4 Effect of carbon dioxide partial pressure on the solution concentration of carbonate species in the CO 2-water system. - Log P CO 2
•A log C-pH diagram helps visualize the speciation of acids and bases over a wide range of conditions. •We can use these diagrams to determine the pH and the speciation of the whole solution at equilibrium. •Before computers were widely accessible, this was the only way to solve acid/base problems.
About Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy & Safety How YouTube works Test new features Press Copyright Contact us Creators.
(3) Locate system point, pH = pK and HA = A-; note that the cross over is 0.3 log units below the C T line, for the acetic acid above this is at pH 4.7 (4) Draw lines for the species, slope = +1 for [A - ] and slope = -1 for [HA]; remember
the diagram is drawn, the user can point the cursor at a given pH and the concentrations of each ion will be given. Additional discussions of pC-pH diagrams can be found in Langmuir (1997) and Snoeyink and Jenkins (1980). References Langmuir, D. Aqueous Environmental Geochemistry, Prentice Hall, New Jersey, 1997. Snoeyink, V.L. and D. Jenkins.
Carbon Dioxide: Pressure - Enthalpy Diagram Melting Line-40 o -40 C-2 0-2 0. Title: mollier_chart_met.xls Created Date: 11/10/1999 5:42:45 PM
, the pH of a neutral solution will not be 7.0. For example, at a pressure of 93 kbar and 527 ⇥ C, K. w = 10. 3.05, the pH of pure water would be 1.5. Such conditions might conceivably apply to deposits of water in geological formations and in undersea vents. Problem Example 1. At 60 ⇥ C, the ion product of water is 9.6E-14.
pH diagrams, which are practical and useful for understanding geochemical behavior of elements. An Eh-pH diagram depicts the dominant aqueous species and stable solid phases on a plane defined by the Eh and pH axes. In an Eh-pH diagram, the solid stability area is related to the saturation condition,
Engineering; Chemical Engineering; Chemical Engineering questions and answers; 1. Use the attached 10-5 M phosphoric acid log C-pH diagram to obtain equilibrium compositions for the following aqueous solutions: (a) 10 5 M H3PO4 (b) 10-5 M NaH2PO4 (c) 10-5 M Na2HPO4 (d) 10-5 M Na3PO4 (e) 5 x 10-6 M NaH2PO4 + 5 x 10 M H3PO4 (f) 5 x 10-6 MH3PO4 +5 x 10-6 M Na2HPO4 We looked at this in class.
Prepare a solubility diagram (log C vs pH) for a water that is potentially in equilibrium with zinc hydroxide and zinc carbonate. Assume the water has 10 -3 M total carbonates. Show all soluble species along with the Zn T line and indicate where precipitation will occur and the type of precipitate.
2.1 The pressure-enthalpy diagram; 2.2 Basic components; 2.3 The basic cycle in a log Ph diagram; 2.4 The complex cycle in a log Ph diagram; 2.5 Other components; 3. Compressors 4. Expansion valves 5. Refrigerants 6. Evaporators 7. Condensers 8. Practical advice 9. Troubleshooting 10. Systems Appendix
1. Prepare a solubility diagram (log C vs pH) for a water that is potentially in equilibrium with zinc hydroxide and zinc carbonate. Assume the water has 10-2 M total carbonates (i.e., 10 mM C T). Show all soluble species along with the ZnT line and indicate where precipitation will occur and the type of precipitate.


















0 Response to "43 Log C Ph Diagram"
Post a Comment