43 Draw A Rough Diagram Of The Rock Cycle
the Rock Cycle! F i r s t , r ead about the Rock Cycle: "Rocks are hard and can be difficult to break. For that reason, many people think of rocks as being permanent. However, rocks break down and change over time. They change because of a process called the rock cycle. That means one type of rock can be changed into a different type of rock. 3. Copy the diagram into your science notebook; you do not have to make your sketch look three-dimensional. Sample answer: Lesson 10 3. Using the lithology key, label the correct names of the rock types on the page and place it in your science journal. Lesson 11 2. Read the information below, and then complete one of the following activities: a.
Draw a diagram for the Rock Cycle. Color - Although color is often used to describe a mineral, it sometimes isn't the best way to tell one mineral from another as one type of mineral can come in several different colors.
Draw a rough diagram of the rock cycle
Rock Cycle Worksheet and Answers This product on the Rock Cycle includes two different Rock Cycle Worksheet and Answers. Both worksheets include a word bank for students to choose words from to fill in the parts of the rock cycle. The processes involved in the rock cycle often take place over millions of years. So on the scale of a human lifetime, rocks appear to be "rock solid" and unchanging, but in the longer term, change is always taking place. In the rock cycle the three main rock types are igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic. Essay #1: Show your understanding of the ROCK CYCLE. Draw and explain the steps of the rock cycle starting with an Igneous Rock. Explain each step or process that could change the rock into the other two types of rock and back into an igneous rock by following only the outer loop of the diagram. You should have at least five sentences.
Draw a rough diagram of the rock cycle. The rock cycle shows the continuous changing of rock from one form to another. A. Draw a rough diagram of the rock cycle. (3 points) B. Which types of rocks are formed underground? (2 points) Metamorphic C. Which types of rocks are formed above ground? (1 point) Igneous 7. Fossils can not be found everywhere. (c) Draw a neat well labelled diagram of the Rock Cycle. [3] (d) Give a reason for each of the following: (i) Igneous rocks are also called Primary rocks. (ii) Fossils are present in Sedimentary rocks. (iii) The core of the Earth is in a semi-solid state. [3] Question 5 (a) Name any two types of volcanoes giving one example of each type. [2] A key is provided at the end of this lab document for you to check your work. For each diagram, draw in the geological contacts on each side of the block. Add strike and dip symbols, and other symbols to document geologic features (like direction of movement on faults). Also write the name of the geological feature next to each diagram. You may use a soft pencil for any diagrams, graphs or rough working. Do not use staples, paper clips, highlighters, glue or correction fluid.. 2 Fig.2.1 shows a rock that is falling from the top of a cliff into the river below.... draw a labelled diagram of an everyday situation in which a
Pour the crushed sugar into the foil boat. What part of the rock cycle does this movement represent? Explain in words and draw a labeled diagram below. _____ 4. Carefully put the boat over the candle flame. Observe as the sugar begins to melt. What part o f the rock cycle does this represent? Explain in words and draw a labeled diagram below. Draw a horizon line coming out from the left and the right side of the rock. This shows the boundary between the earth and the sky. To decorate your rock, you should draw hatch marks to show grass below the lines for ground. You could add a circle above the rock, or emerging out of your rock to show the sun. The diagram of the rock cycle is a great way to get a quick view of what the rock cycle is. The rock cycle process consists of sedimentary, metamorphic, and igneous rock cycles within. The diagram is helpful but does not go into great detail of all possible directional steps that can happen due to the effects of our earth. Draw a diagram to show how water from the ocean can fall as rain on land. Q12 Which is NOT a fossil fuel? a. Coal b. Oil. rough and jagged. The mountains in Picture B are smooth and rounded.... like the water cycle and the rock cycle. How does the water cycle influence the rock cycle in an area like the
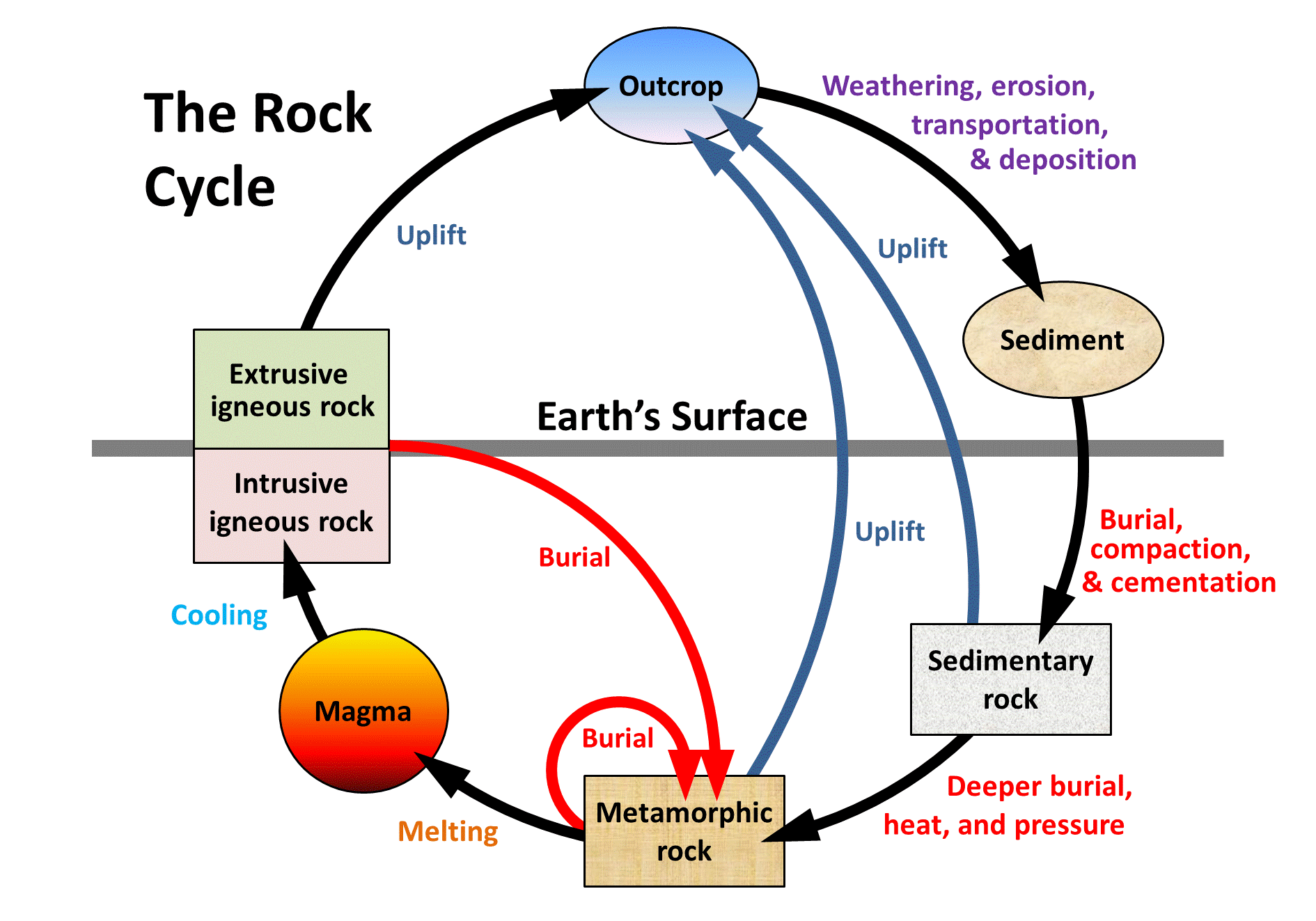
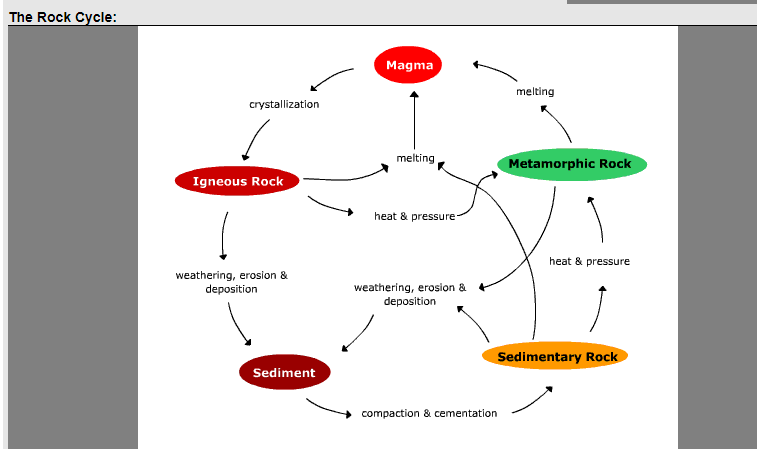
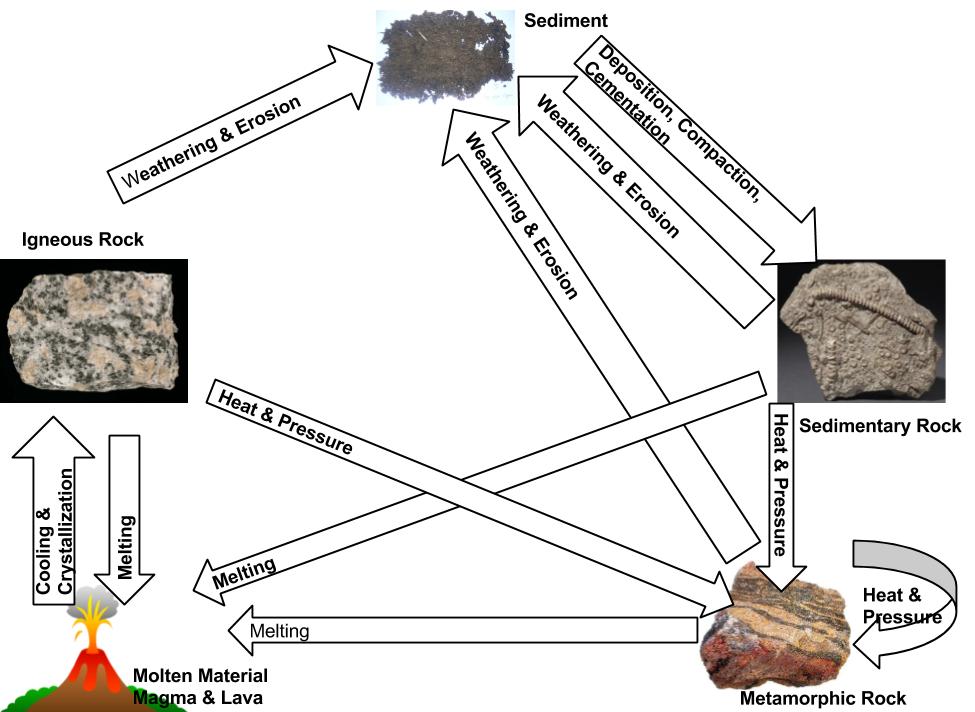
Draw the free-body diagram for the rod. G is the center of gravity of the rod. Draw the vectors starting at the black dots. The location and orientation of the vectors will be graded. Explanation of the Rock CycleThanks to http://www.cotf.edu/ete/modules/msese/earthsysflr/rock.html for the image Draw a picture of the rocks you find and then draw a diagram of the rock cycle steps. Keep reading to see how you can experience the rock cycle process for yourself! Gemstones. Wind and water and blowing sand can, over time, rub away the rough edges of rocks, leaving smooth stones. In nature, this is called 'weathering.' A useful way to illustrate how the three main types of rock are related to one another and how changes to rocks happen in a recurring sequence is the rock cycle. It can be presented in a diagram like the one below. The concept of the rock cycle is attributed to James Hutton (1726–1797), the 18th-century founder of modern geology.
Weathering of Rocks (With Diagram) | Geography. This article throws light upon the two types of weathering of rocks. The types are: 1. Chemical Weathering 2. Physical or Mechanical Weathering. Type # 1. Chemical Weathering: Chemical weathering is the basic process by which denudation proceeds. It is the extremely slow and gradual decomposition.
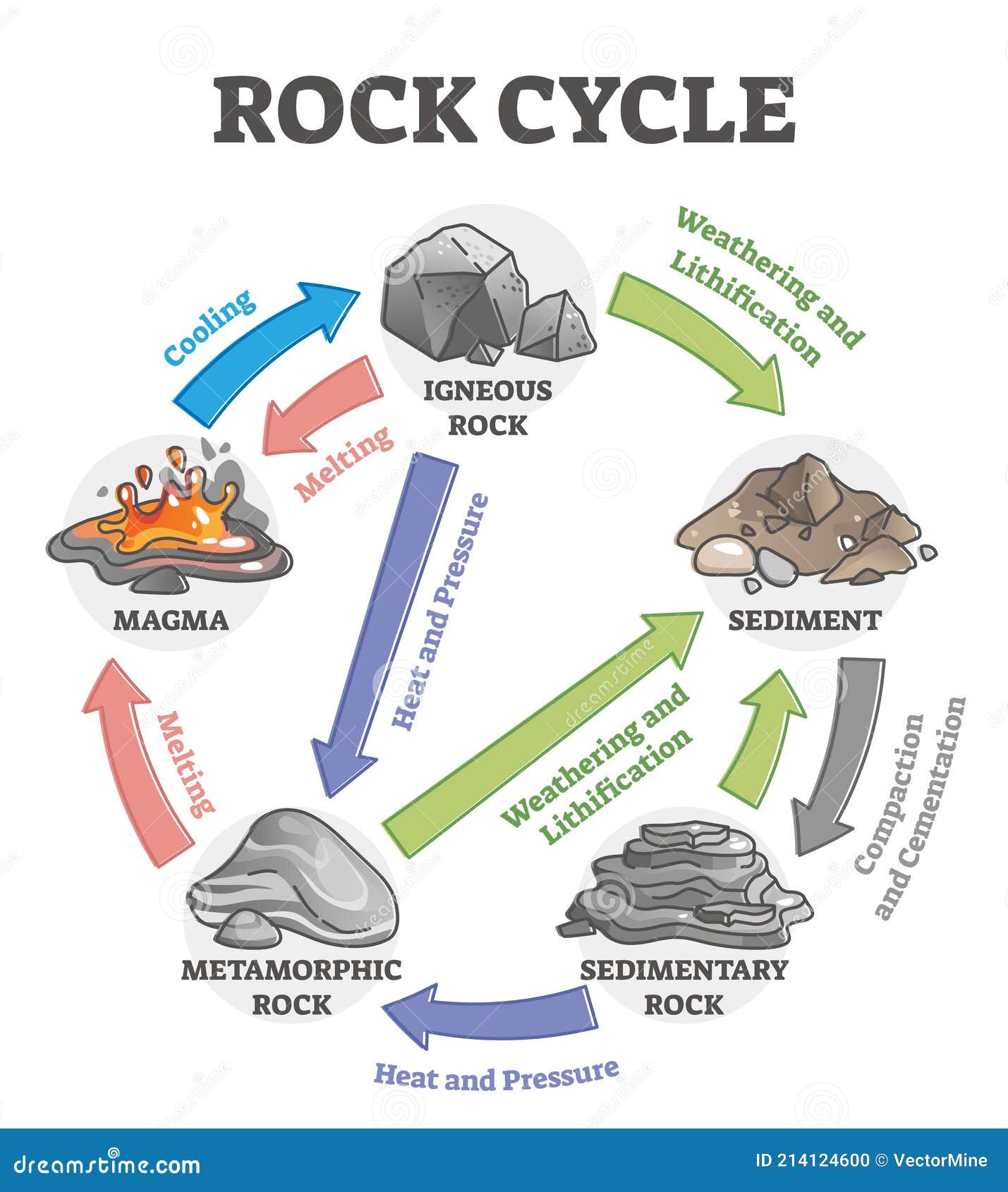
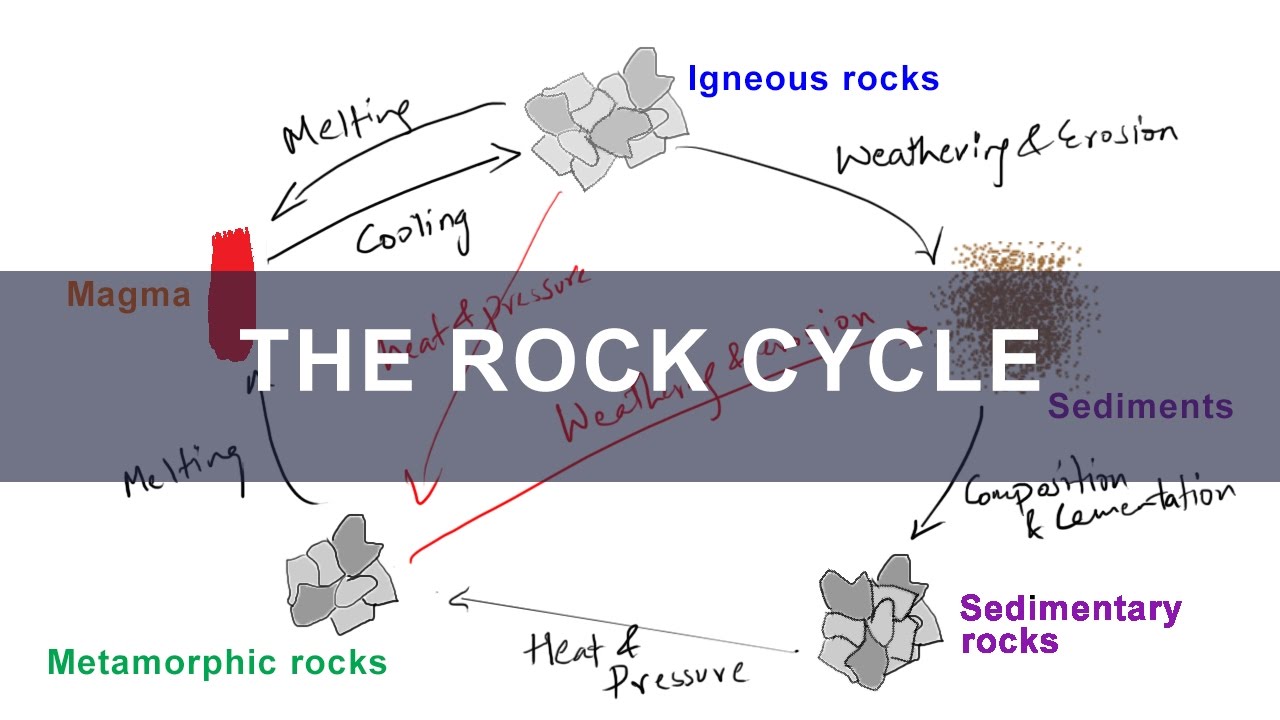
The process of transformation of rocks from one form to the other in a cyclic manner is known as the rock cycle. It includes the following processes: Hot lava cools down to form igneous rocks. Igneous rocks are then broken down into small particles which are transported and then deposited. This results in the formation of sedimentary rocks.
Rock Cycle Diagram. Rocks are broadly classified into three groups: igneous, sedimentary and metamorphic, and the simplest diagram of the "rock cycle" puts these three groups in a circle with arrows pointing from "igneous" to "sedimentary," from "sedimentary" to "metamorphic," and from "metamorphic" to "igneous" again.
The processes involved in the rock cycle often take place over millions of years. So on the scale of a human lifetime, rocks appear to be "rock solid" and unchanging, but in the longer term, change is always taking place. In the rock cycle the three main rock types are igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic.
1. Block diagrams- portrays in three dimensions the shape of the land and the subsurface distributions of rock units 2. Cross section- shows surficial and subsurface features in two dimensions 3. Stratigraphic section- shows the rock units stacked on top of one another 4. Evolutionary diagrams- shows the history of an area as a series of steps
The rock cycle describes the creation, alteration and destruction of the rocks that form from magma. Learn more about the rock cycle, including the three main rock types - igneous (magma that.
On the inside of the foldable, we diagram what the rock cycle looks like in action. We draw a volcano with magma at its center. We draw rain and wind weathering the igneous rock that formed near the volcano. Sediments being carried to a nearby pond where it settles to the bottom and is cemented together to form sedimentary rock.
Rock Cycle Worksheet and Answers This product on the Rock Cycle includes two different Rock Cycle Worksheet and Answers. Both worksheets include a word bank for students to choose words from to fill in the parts of the rock cycle.
2q \rxu rzq 2q wkh 6,08/$7,21 wde folfn 6wduw djdlq ,q wkh vsdfhv ehorz olvw wkuhh urfn f\fohv <rx fdq vwduw dq\zkhuh exw hdfk f\foh pxvw ehjlq dqg hqg dw wkh vdph srlqw &\foh bb6rlo 6hglphqw 6hglphqwdu\ 5rfn 6rlobbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbb
Transcribed image text: Question 1. Draw and explain the Rock Cycle. Be as complete as you can Question 2. Discuss the relationship between Silica content of a magma and igneous rock compositional category, magma temperature, density, and viscosity Question 3.
Essay #1: Show your understanding of the ROCK CYCLE. Draw and explain the steps of the rock cycle starting with an Igneous Rock. Explain each step or process that could change the rock into the other two types of rock and back into an igneous rock by following only the outer loop of the diagram. You should have at least five sentences.
The duration of the cycle, however, varies from organism to organism and cell to cell. A typical eukaryotic cell cycle is divided into two main phases:-Interphase. Also known as the resting phase of the cell cycle; interphase is the time during which the cell prepares for division by undergoing both cell growth and DNA replication.
331x519 Rock Climbing, Rock Vector, Movement, Sketch Png And Vector For - Rock Climbing Sketch. 960x720 Magmalava Sediments The Rock Cycle. The Rock Cycle Using Your - Rock Cycle Sketch.
Earth's rock cycle. Build Vocabulary Cycle Diagram Have students construct a cycle diagram of the rock cycle. Students should use the terms igneous rock, sedimentary rock, meta-morphic rock, sediments, magma, and lava to indicate the materials involved in the rock cycle. The processes of the rock cycle are shown in Figure 2 on p. 67.
A block of mass m is released from rest at a height R above a horizontal surface. The acceleration due to gravity is g.The block slides along the inside of a frictionless circular hoop of radius R • Which one of the following expressions gives the speed of the mass at
The independent variable is the variable that changes, or the manipulative variable. The dependent variable is the variable that only changes if the independent variable changes, or the responding variable. Nice work! You just studied 68 terms! Now up your study game with Learn mode.
(ii) Give an example of residual mountain and an example of depositional plain. [2] (c) Draw a neat well labelled diagram of the Rock Cycle. [3] (d) Give a reason for each of the following: (i) Igneous rocks are also called Primary rocks. (ii) Fossils are present in Sedimentary rocks. (iii) The core of the Earth is in a semi-solid state. [3.
The Rock Chronicles Directions: Complete each row by drawing pictures and writing captions in the missing spaces. Hi! I am a small piece of rock called sediment. My other sediment friends and I always hang out together, but one day we noticed that things were changing… (What process happens here? How does a piece of sediment become a.
Steps of the Rock Cycle. 1) Formation of Igneous Rock – Melting, Cooling, and Crystallization. Magma, the molten rock present deep inside the earth, solidifies due to cooling and crystallizes to form a type of rock called igneous rocks. Cooling of igneous rocks can occur slowly beneath the surface of the earth or rapidly at its surface.
Name: Date: Period: Rock Cycle Project 1. Set-up your poster according to the diagram below: a. Orient the paper to Landscape, add a two-inch border to the top of the page. i. Write your name and the period in the top left hand corner of the border. ii. Write and decorate the title The Rock Cycle in the two-inch border. b. Add a half-inch border below the Title Border.
H) DIAGRAM: In the space below, draw a diagram of the Rock Cycle. Draw 5 separate boxes to show the individual components of the Rock Cycle. Draw arrows to represent the processes linking each component. Correctly label everything. For Igneous Rocks, include the same degree-of-explanation as was made on the videos.











/rock-cycle-56a368e43df78cf7727d3c3f.gif)












0 Response to "43 Draw A Rough Diagram Of The Rock Cycle"
Post a Comment