43 Diagram Of Spinal Stenosis
Amit Jain, M.D., Johns Hopkins spine surgeon, explains what spinal stenosis is, the symptoms, how it is diagnosed, the treatment options and prognosis. Dr. J... Spine Surgery Diagram Templates. Edit this example. Structures of Spine. Edit this example. Spinal Stenosis. Edit this example. Examples of Disc Problems. Edit this example. Herniated Disk.
762 spinal stenosis stock photos, vectors, and illustrations are available royalty-free. See spinal stenosis stock video clips. of 8. stenosis spinal nerves veterbrae back disk back pain stenosis spine nerve compression lumbar stenosis lumbar spinal stenosis degenerative diseases of the spine. Try these curated collections.
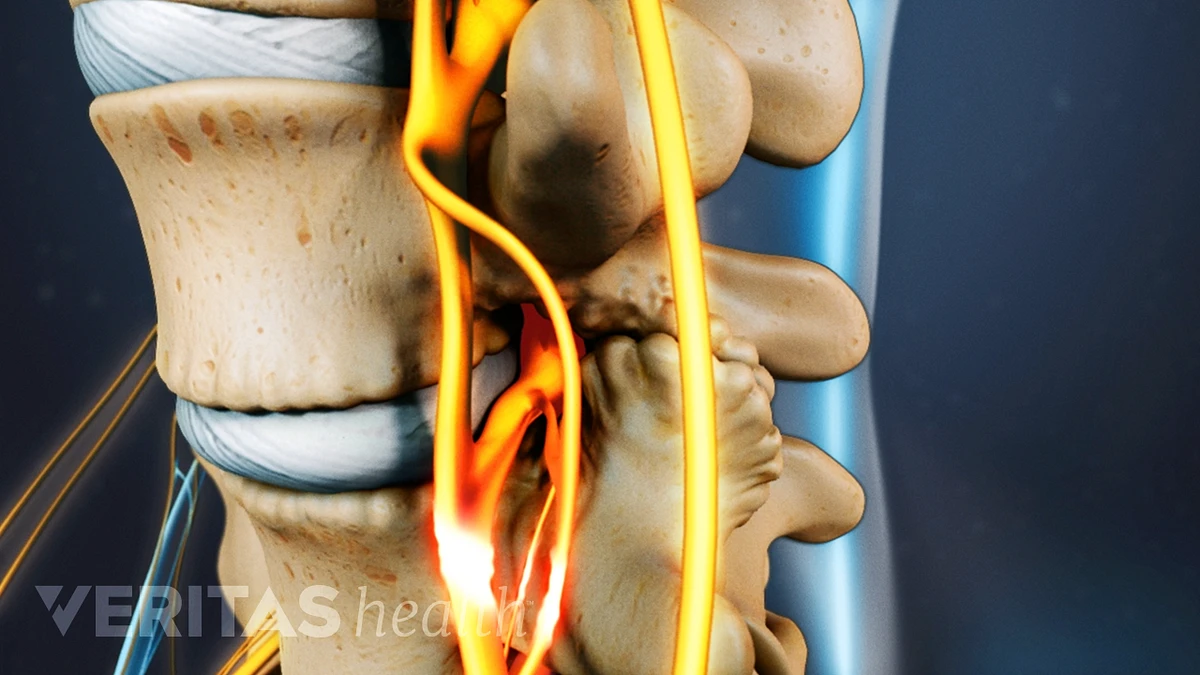
Diagram of spinal stenosis
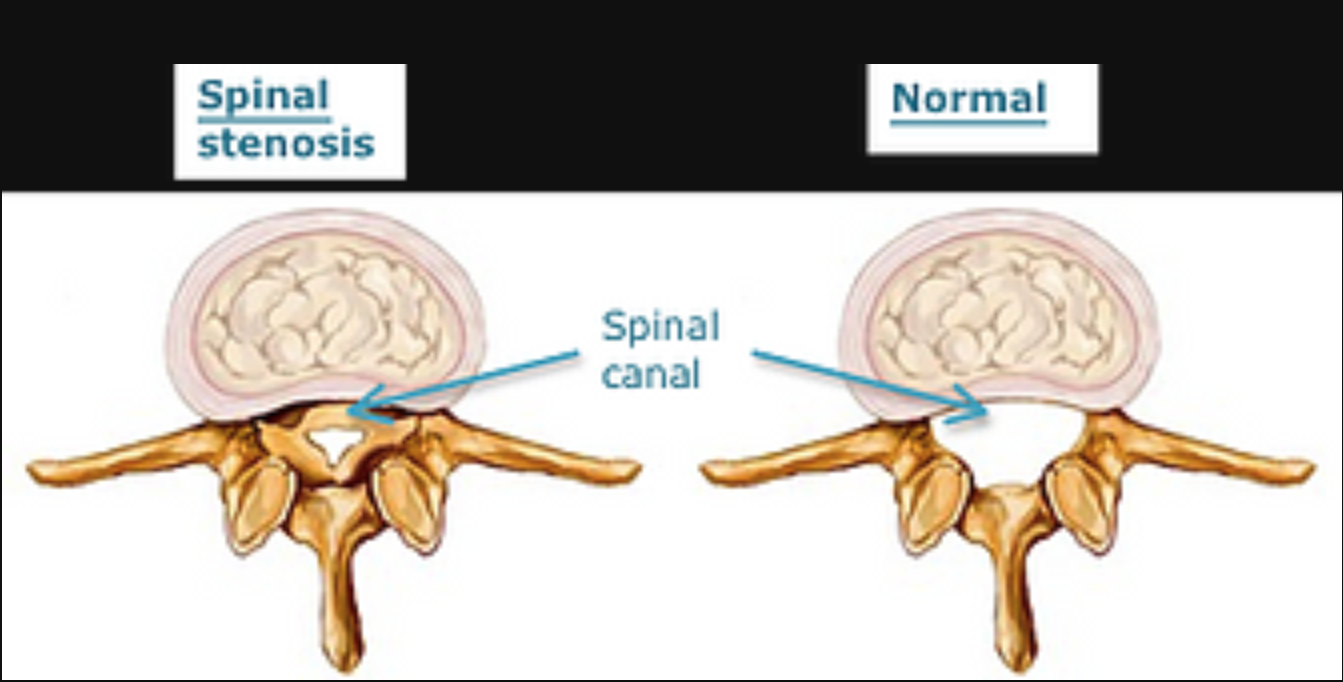
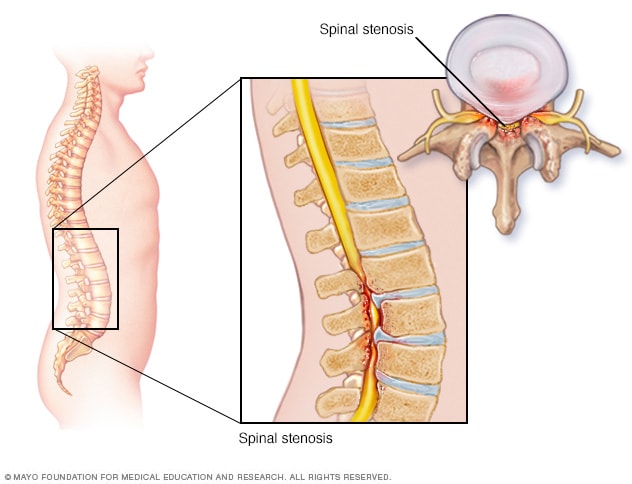
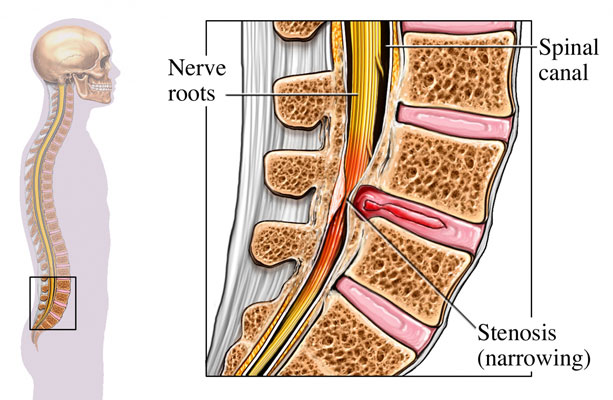
When spinal canal stenosis is severe, the patient may experience numbness, loss of feeling, paralysis or muscle atrophy. The compressed nerve may be permanently damaged or dead, in which case it cannot stimulate muscles. Emergency cases of stenosis, such as cauda equina syndrome, may disrupt bladder and bowel function — if you experience this. Diagram 1: Picture of Narrowing of the Spinal Canal What Causes Lumbar Spinal Stenosis? Lumbar Spinal stenosis can be caused in 2 ways: Acquired Spinal Stenosis - This is a narrowing of the spinal canal due to disc protrusions or bony changes often due to age that take place over time in the low back. The muscles of the lower back help stabilize, rotate, flex, and extend the spinal column, which is a bony tower of 24 vertebrae that gives the body structure and houses the spinal cord.
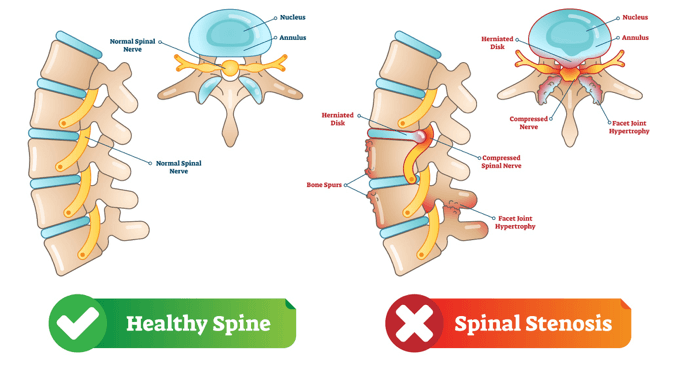
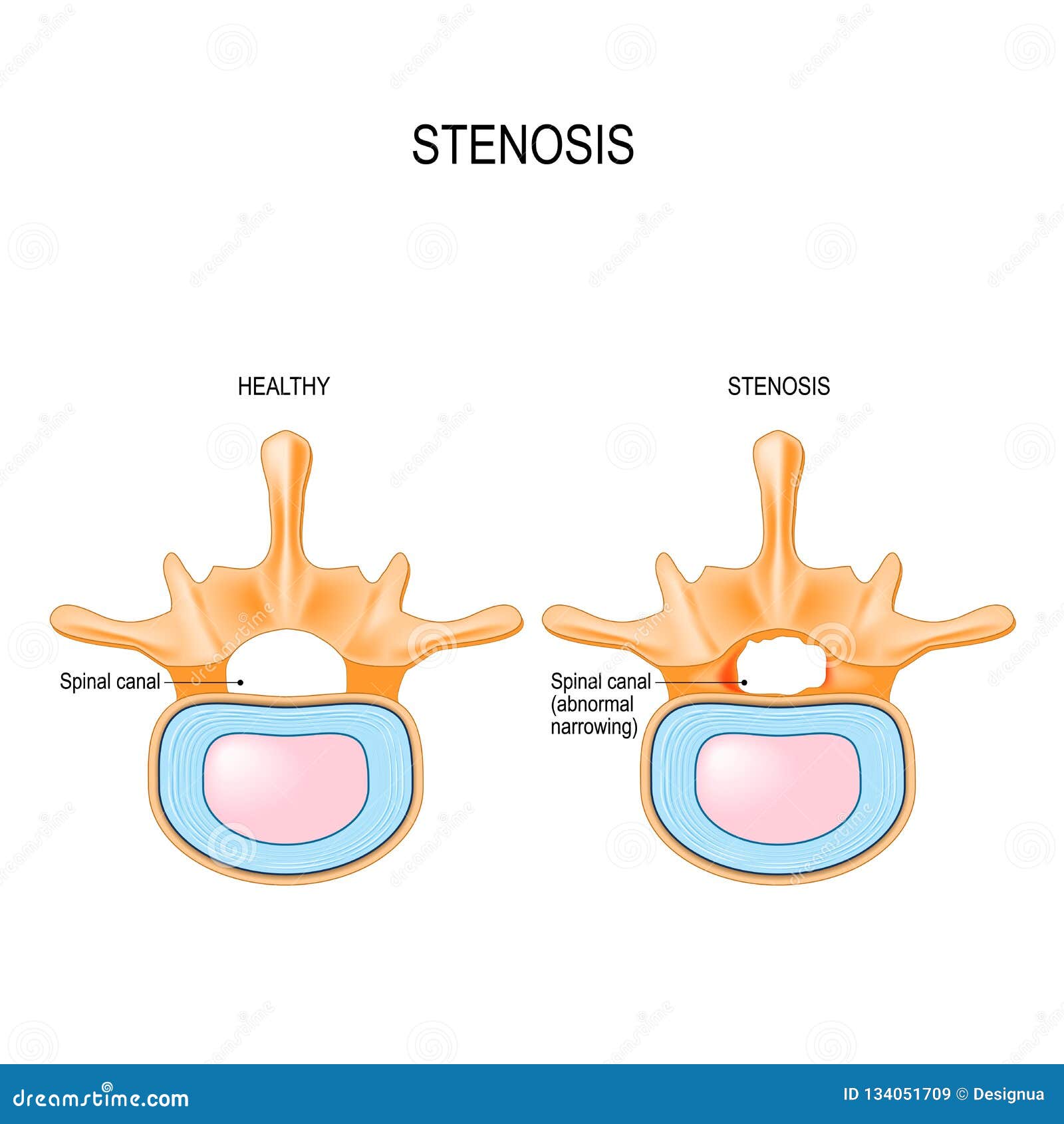
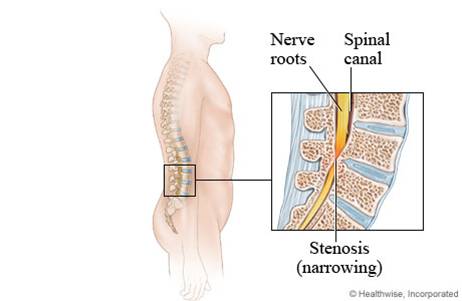
Diagram of spinal stenosis. What is Lumbar Spinal Stenosis? Low back pain affects people of all ages and gender. Lumbar spinal stenosis a common cause of low back pain. It is the narrowing of the spinal canal and the space between the vertebrate that are occupied by the spinal nerves or spinal cord. In lumbar spinal stenosis, the nerve roots in the low back become. The L5-S1 spinal motion segment, also called the lumbosacral joint, is the transition region between the lumbar spine and sacral spine in the lower back. In this region, the curvature of the spine changes from lumbar lordosis (forward curve) to sacral kyphosis (backward curve). L5-S1 helps transfer loads from the spine into the pelvis and legs. Spinal stenosis is a narrowing of spaces in the spine (backbone) that results in pressure on the spinal cord and/or nerve roots. This disorder usually involves the narrowing of one or more of three areas of the spine: (3) the openings between vertebrae (bones of the spine) through which nerves leave the spine and go to other parts of the body. Cervical stenosis occurs when the spinal canal narrows and compresses the spinal cord and is most frequently caused by aging. The discs in the spine that separate and cushion vertebrae may dry out and herniate.As a result, the space between the vertebrae shrinks, and the discs lose their ability to act as shock absorbers.
The spinal nerves and their corresponding dermatomes are as follows: (Cervical) C2 - forehead, and temple. C3 - neck, posterior cheek. C4 - shoulders, clavicle, upper shoulder blade. C5 - deltoids, anterior arm (facing forward) down to the base of the thumb. C6 - anterior arm as well as the radial side of the hand. Spinal Stenosis Spinal stenosis is a term used to describe a narrowing of the spinal canal. The narrowing may not cause any symptoms. However, the narrowing may progress to cause squeezing (compression) of the spinal nerves. Spinal stenosis can cause back pain and/or leg pain. Most often it occurs when you walk. Spinal stenosis is a narrowing of the spinal canal. It occurs when the bony openings within the spine (foramina) begin to narrow, placing pressure on the nerves traveling throughout the spine. This reduced nerve space can occur within the spinal cord or where the spinal nerves exit the spinal canal. Spinal stenosis occurs when the spinal cord and nerves, which travel through the lower back into the legs, are compressed due to spinal canal narrowing; the disorder emerges either at the level of the neck (cervical spinal stenosis) or at the level of the lower back (lumbar spinal stenosis), while rare cases affect the middle section of the back (thoracic spinal stenosis).
Diagram 1: Picture of Narrowing of the Spinal Canal What Causes Lumbar Spinal Stenosis? Lumbar Spinal stenosis can be caused in 2 ways: Acquired Spinal Stenosis - This is a narrowing of the spinal canal due to disc protrusions or bony changes often due to age that take place over time in the low back. Spine Diagram Labeled. Spine Diagram Labeled. On him we rely and use it to move. Among these is the birth defect spina bifida, which is the incomplete development of the central nervous system, including the spine. This spinal column provides the main support for your body, allowing you to stand upright, bend, and twist, while protecting the. The muscles of the lower back help stabilize, rotate, flex, and extend the spinal column, which is a bony tower of 24 vertebrae that gives the body structure and houses the spinal cord. To start your spinal stenosis lumbar flexion exercise progression, perform the flexion in lying exercise. To do this: Lay on your back with your knees bent. Slowly bring your knees up to your chest, and grab onto them with your hands. Hold this balled-up position for 2 seconds.
Spivak, JM "Degenerative Lumbar Spinal Stenosis" in JBJS, Vol 80, No. 7, July, 1998, p 1060. 5. Simotas, AC " Nonoperative Treatment of Lumbar Spinal Stenosis". Clin Ortho 384, March, 2001,p155-156. 6. Sengupta DK, Herkowitz HN. "Lumbar Spinal Stenosis- Treatment Strategies and Indications for Surgery" Ortho. Clin N Am 34(2003), p282.
Diagram of "house" analogy. What causes lumbar spinal stenosis? Trauma to the spine can cause stenosis, but more commonly, narrowing within the lumbar spine results from a herniated disc, the development of arthritis, or the formation of bone spurs.
Spinal stenosis leads to pain in the lower back, buttock, lower extremities, and feet, which can decrease daily function. Typically, pain will increase when going from sitting to standing, walking, and performing back extension as well as waking in the morning. You can have one or several of these symptoms with spinal stenosis.
15 Spinal Stenosis Exercises You Can Do Anywhere - Pain Doctor. Skip to content.
Lumbar spinal stenosis is a narrowing of the spinal canal, compressing the nerves traveling through the lower back into the legs. While it may affect younger patients, due to developmental causes, it is more often a degenerative condition that affects people who are typically age 60 and older.
Spinal stenosis usually affects the cervical (neck) and lumbar (low back) spinal regions. Occurrence in the thoracic (upper/mid back) spine is rare. The purpose of this article is to help you understand the basic anatomy associated with spinal stenosis, a condition known to cause narrowing of the spinal canal and/or nerve passageways that leads.
Spinal stenosis is a narrowing of the spaces within your spine, which can put pressure on the nerves that travel through the spine. Spinal stenosis occurs most often in the lower back and the neck. Some people with spinal stenosis may not have symptoms. Others may experience pain, tingling, numbness and muscle weakness.
Stenosis in the spine is the narrow-ing of the bony canal that surrounds the nerves. It may result from trauma or as a normal part of aging. When the narrowing happens in the lower part of your back, it is called lumbar stenosis. This may put pressure on the nerves and can cause pain, numbness, or weakness in your buttocks, legs, or feet.
Spinal stenosis is a narrowing of the space surrounding your spinal cord and nerve roots, so these exercises are designed to open that space. These 3 gentle stretches promote strength, flexibility, and range of motion throughout your low back—this trifecta helps relieve pressure on your lumbar spinal nerves.
Browse 1,343 lumbar spine anatomy stock photos and images available, or search for spinal cord to find more great stock photos and pictures. Anatomical diagrams illustrate the human nervous system, especially the brain and spinal cord. lumbar spine, illustration - lumbar spine anatomy stock illustrations.
Spinal stenosis is the narrowing of the spaces within the spine, which eventually results in pressure on the spinal cord or nerve roots. Symptoms of spinal stenosis vary widely from person to person and range from no symptoms to pain in the back or neck and numbness, tingling and weakness in the arms and/or legs.
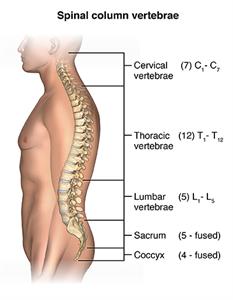
Cervical Spine Diagram. The Cervical Spine Diagram shown below is a lateral view which means you are looking at the spine from its side. Cervical spine is the spine in the neck area. On the diagram you could see the 7 cervical vertebrae; C1 down to C7. In between the vertebrae the space for the disc material is seen too.
Introduction. Degenerative lumbar spinal stenosis (DLSS) is a leading cause of pain, disability, and loss of independence in older adults. 1 The prevalence and economic burden of DLSS is growing exponentially due to the aging population. It is a chronic disease caused by age related degenerative narrowing (stenosis) of the spinal canal that can lead to compression and ischemia of the spinal.
On the lateral, lumbar, plain radiograph (L3 level), the AP diameters of the vertebral body spinal canal were measured. Methods: The images of these 40 individuals were then randomized and distributed in a blinded fashion to five separate spine surgeons who graded the presence and severity of congenital stenosis utilizing a five-tier scale.
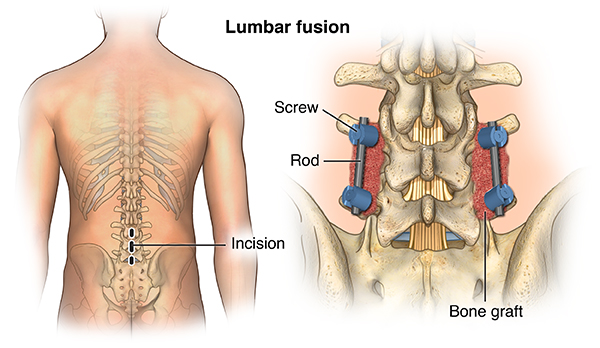
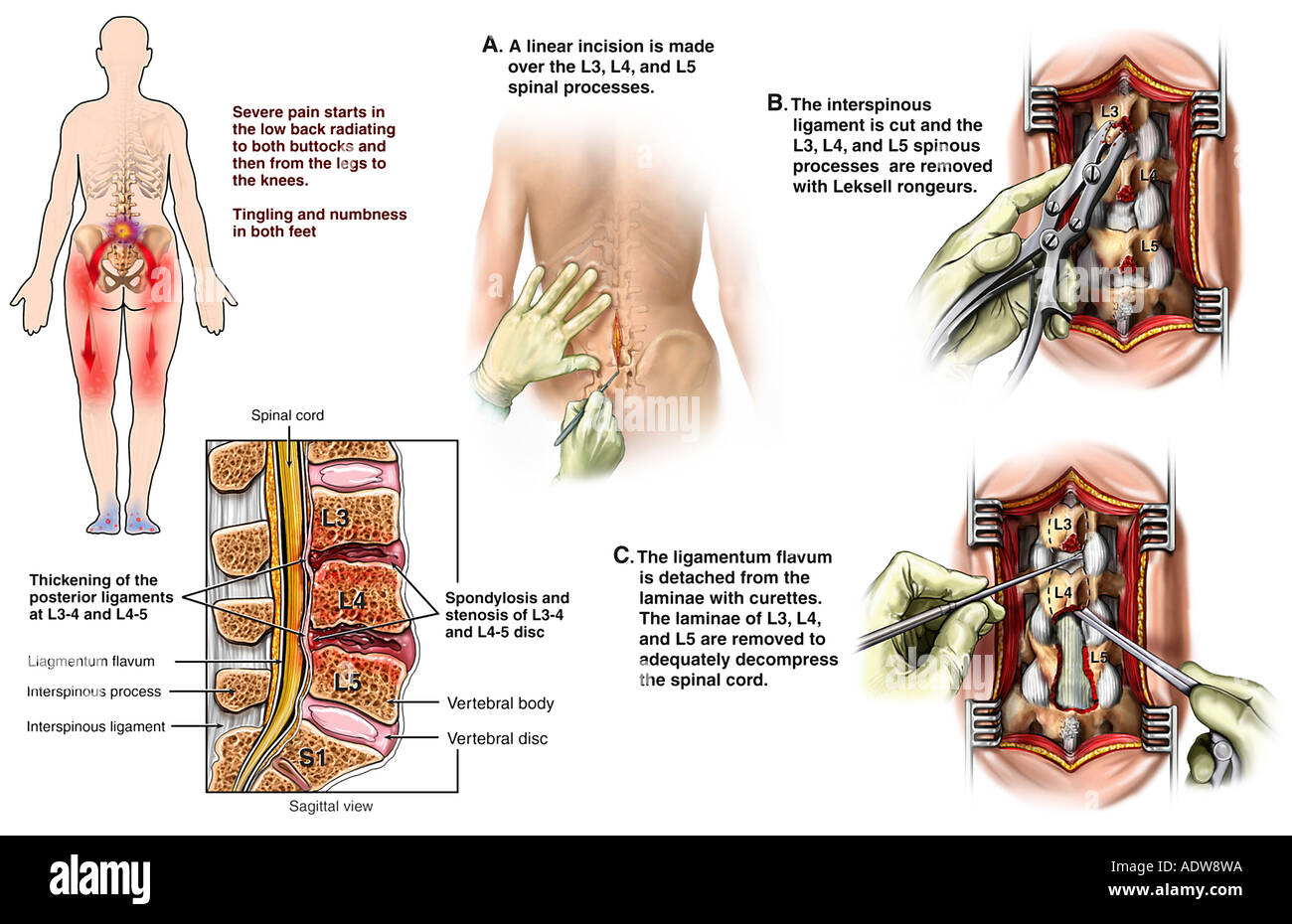
A lumbar laminectomy is an open surgery that is performed to alleviate pain caused by neural impingement due to spinal stenosis. Watch: Lumbar Laminectomy Surgery Video Lumbar laminectomy is typically considered after nonsurgical treatments such as physical therapy, medications, and/or epidural steroid injections have been tried for a period of 8 to 12 weeks without improvement. 1
1. degenerative disc disease at the c2-c3 level to result in mild to moderate spinal canal stenosis at this level. 2.. degenerate changes at the c5-c6 and c6-c7 levels resulting in mild to moderate spinal cana. Could mean 3: The word should you use could describe up to three nerves involved.
When spinal canal stenosis is severe, the patient may experience numbness, loss of feeling, paralysis or muscle atrophy. The compressed nerve may be permanently damaged or dead, in which case it cannot stimulate muscles. Emergency cases of stenosis, such as cauda equina syndrome, may disrupt bladder and bowel function — if you experience this.





























:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/GettyImages-184328981-56a50c7c5f9b58b7d0daa68e.jpg)
0 Response to "43 Diagram Of Spinal Stenosis"
Post a Comment