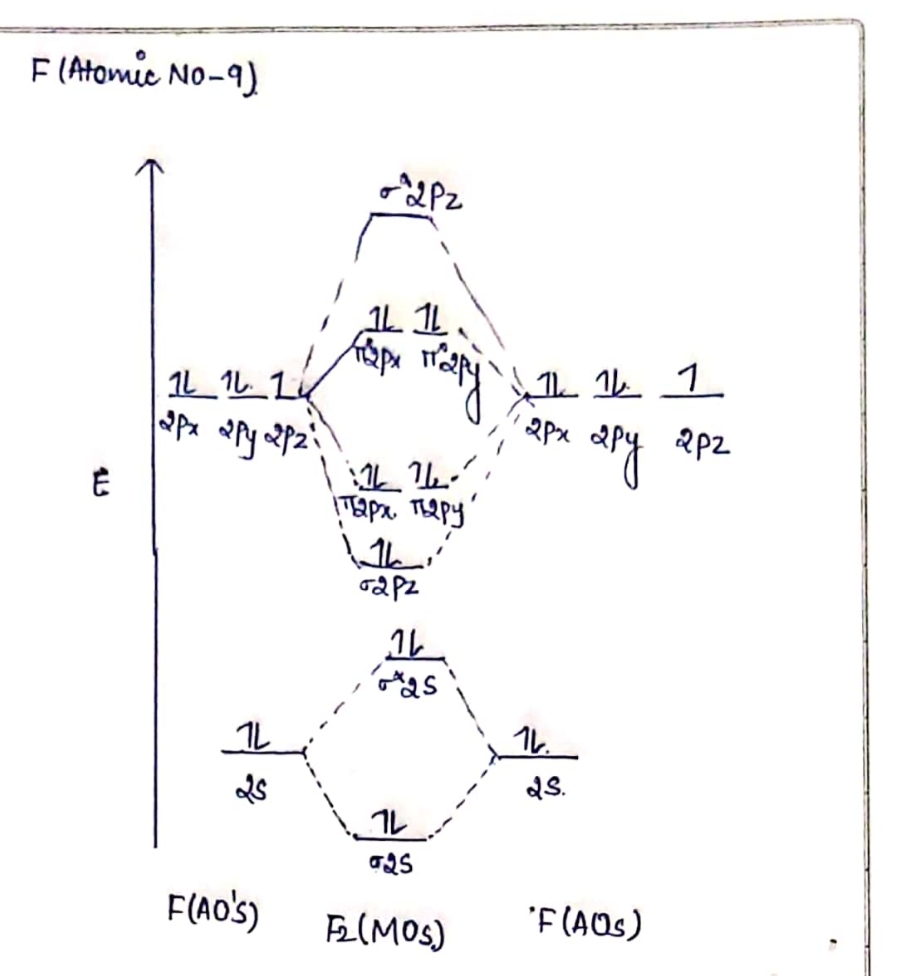
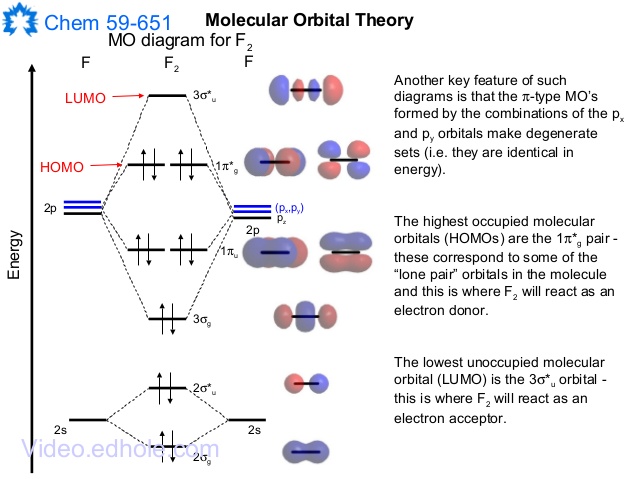
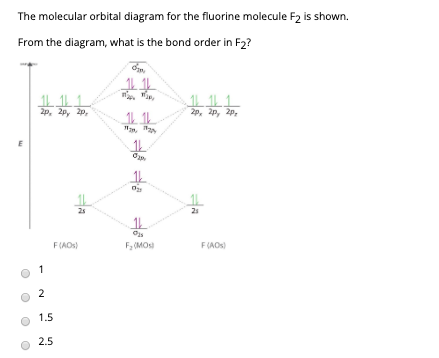
41 Molecular Orbital Diagram For F2
This video is about MO Diagram #2 - F2 It is common to omit the core electrons from molecular orbital diagrams and configurations and include only the valence electrons. Figure 8. This is the molecular orbital diagram for the homonuclear diatomic Be 2 +, showing the molecular orbitals of the valence shell only. The molecular orbitals are filled in the same manner as atomic orbitals.
MO Diagram for HF The AO energies suggest that the 1s orbital of hydrogen interacts mostly with a 2p orbital of fluorine. The F 2s is nonbonding. H-F nb σ σ* Energy H -13.6 eV 1s F -18.6 eV -40.2 eV 2s 2p So H-F has one σ bond and three lone electron pairs on fluorine
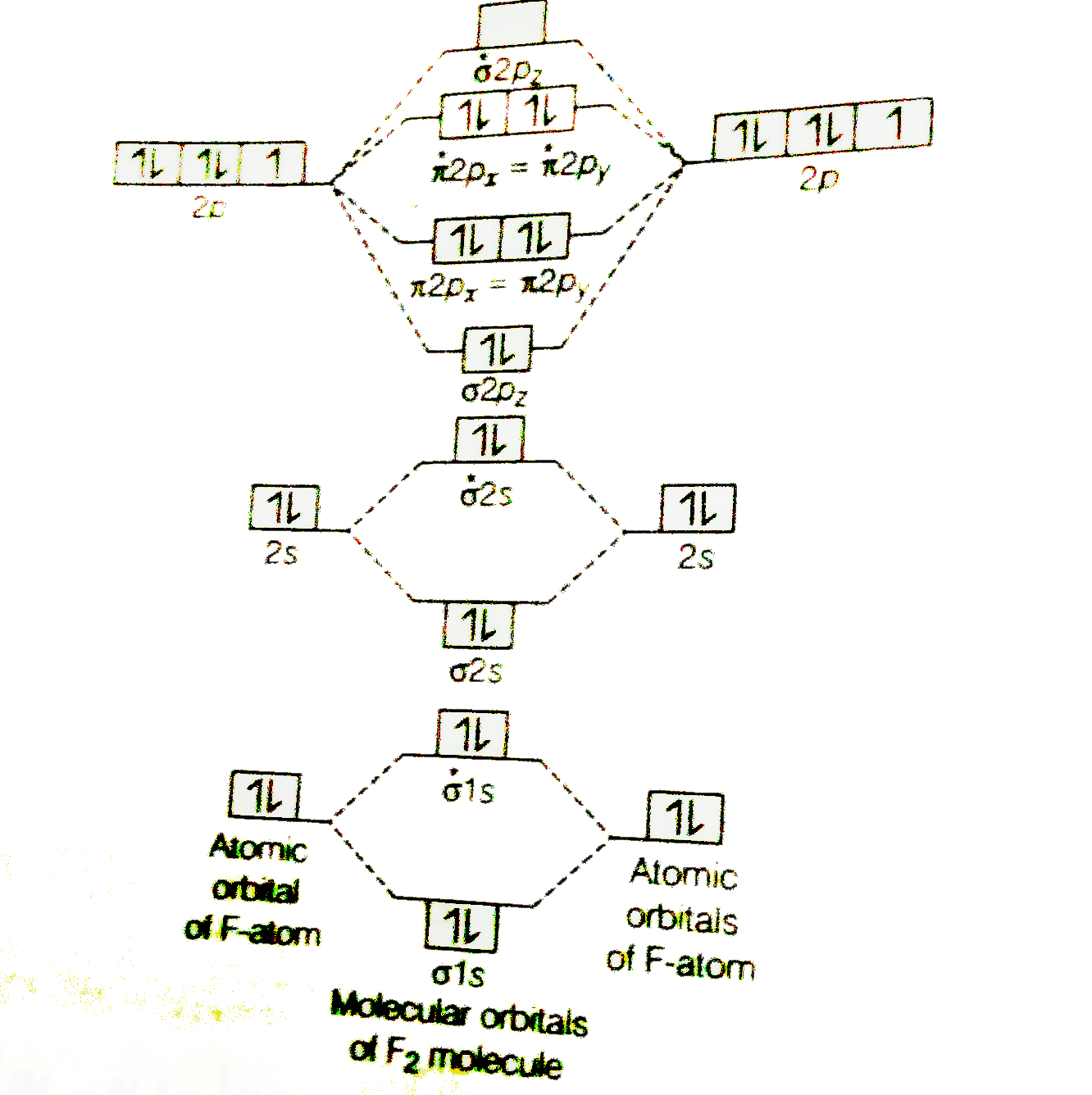
Molecular orbital diagram for f2
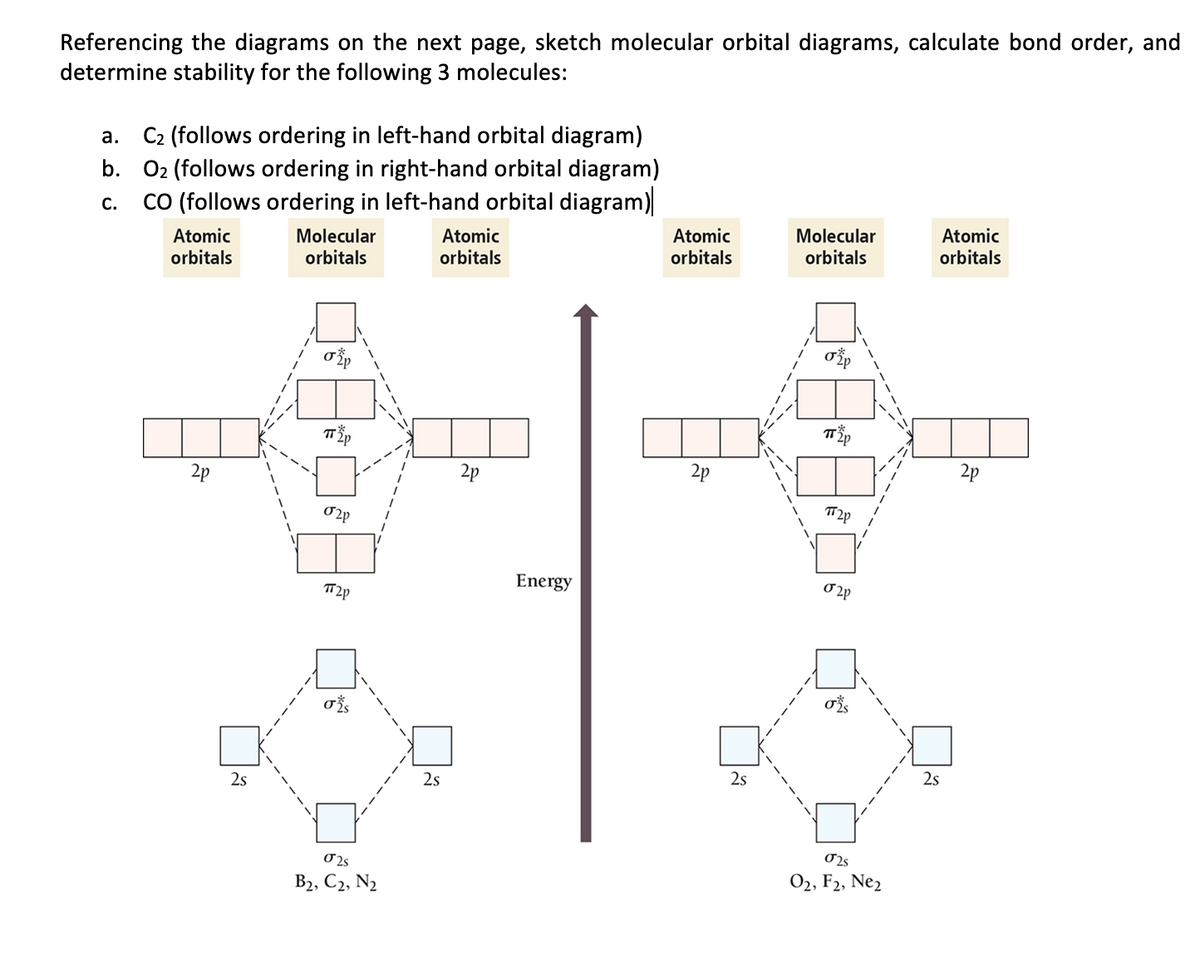
Experts are tested by Chegg as specialists in their subject area. We review their content and use your feedback to keep the quality high. 100% (13 ratings) Transcribed image text: Fill in the Molecular Orbital Energy Diagram for the diatomic molecule F2 MO's fluorinep fluorineA 2p ー2p 2p In this case σ2pch2p * σ2s 1s Ơİs. together to produce a sigma molecular orbital [σ = (1sa + 1sb)]. Since the electrons in this orbital are more stable than on the individual atoms, this is referred to as a bonding molecular orbital. A second molecular orbital is also created, which we simplistically show as a subtraction of the two atomic 1s orbitals [σ* = (1sa - 1sb)]. This. Transcribed image text: Question 6 10 marks Please draw the molecular orbital diagrams of the following molecules, calculate the bond order, and give the details for each MO diagram based on the following table requirement. a) boron nitride (BN) b) HBO c) F2 d) NO Marks will be awarded for: Marks (1) Correct MOs diagram (ii) Identifying the number of valence electrons in the molecular ion (iii.
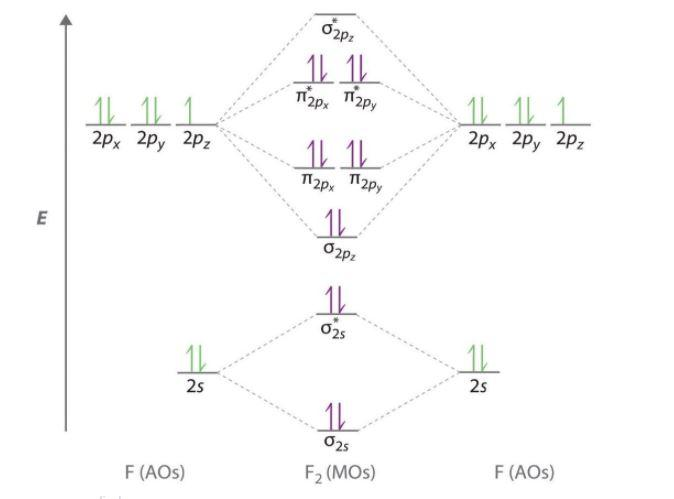
Molecular orbital diagram for f2. Draw molecular orbital diagram for F 2 molecule. Also, gives its electronic configuration, bond order and magnetic property. Hint: The Molecular Orbital Theory (MOT) explains the formation of the molecule in a better way than Valence Bond Theory (VBT). The bond order calculations are feasible using MOT and so is the description of electronic. Molecular orbital diagram for f2. A fundamental principle of these theories is that as atoms bond to form molecules a certain number of atomic orbitals combine to form the same number of. C would this ion exist. To further demonstrate the consistency of the lewis structures with mo. For the ion f2. Draw the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which of the following is paramagnetic B2 Place the following in order of decreasing X-A-X bond angle, where A represents the central atom and X represents the outer atoms in each molecule. About Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy & Safety How YouTube works Test new features Press Copyright Contact us Creators.
Aug 08, 2015 · The short answer is: we could not tell it using the primitive molecular orbital theory introduced in the general chemistry courses. In exact same way we could not tell why $\mathrm{\sigma_{2p_{z}}}$ MO becomes lower in energy than $\mathrm{\sigma_{2p_{z}}}$ MO to the left of $\ce{N2}$ and not to the left of, say, $\ce{C2}$. A) F2; B) F2^2+ C) Ne2^2+ D) O2^2+ E) F2^2-2) Use molecular orbital diagrams to determine which of the following are paramagnetic. A) O2^2-B) Ne2^2+ C) O2^2+ D) F2^2+ E) None of the above are paramagnetic; 3) Draw the molecular orbital diagram needed, and determine which of the following is paramagnetic. Energy level diagram for Molecular orbitals.. If N b = Na,the molecule is again unstable because influence of electrons in the antibonding molecular orbital is greater than the bond influence of electron in the bonding molecular orbitals. 2) Stability of molecules in terms of bond order. Here is a video that discusses over the Molecular Orbital Diagram for F2+ and F2+. Then compare their bond length, strength, bond order etc. And explaining a...
Transcribed image text: Question 6 10 marks Please draw the molecular orbital diagrams of the following molecules, calculate the bond order, and give the details for each MO diagram based on the following table requirement. a) boron nitride (BN) b) HBO c) F2 d) NO Marks will be awarded for: Marks (1) Correct MOs diagram (ii) Identifying the number of valence electrons in the molecular ion (iii. Answer (1 of 4): The atomic number of fluorine is 9, so a (neutral) F2 molecule has a total of 18 electron, or 14 valence electrons (excluding the four 1s electrons). The (F2)- ion has one more valence electron, or 15. The orbital diagram for a diatomic molecule is To find the bond order, add th... Nov 12, 2021 · F2 Molecular Orbital (MO) Diagram. As per molecular orbital (MO) theory, all the constituent atoms in a molecule contribute to the formation of molecular orbitals. These MOs are a linear combination of the atomic orbitals. Thus, the electrons in a molecule are not individually assigned to atomic orbitals but to molecular orbitals. Let us have a. Nov 02, 2021 · Molecular orbital energy diagram of b2. Sep 29, 2017 · By drawing molecular orbital diagrams for b2 c2 n2 o2 and f2 predict which of these homonuclear diatomic molecules are magnetic. Even rather simple molecular orbital (MO) theory can be used to predict which we start reading from the bottom of the diagram because this is how MO diagrams are.
A) The total number of molecular orbitals formed doesn't always equal the number of atomic orbitals in the set. B) A bond order of 0 represents a stable chemical bond. C) When two atomic orbitals come together to form two molecular orbitals, one molecular orbital will be lower in energy than the two separate atomic orbitals and one molecular.
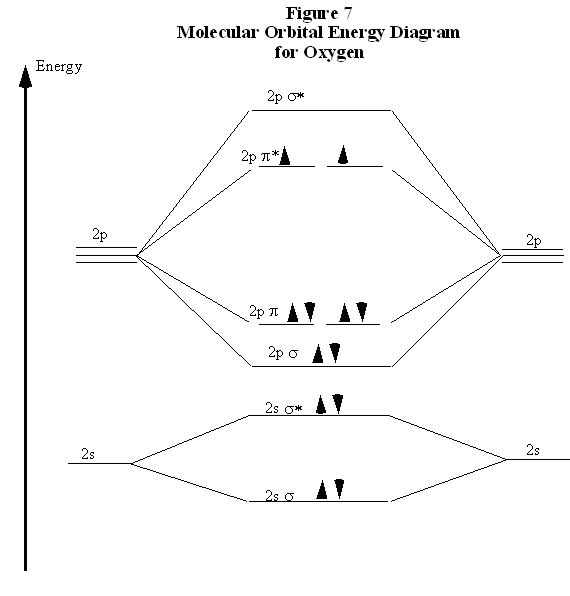
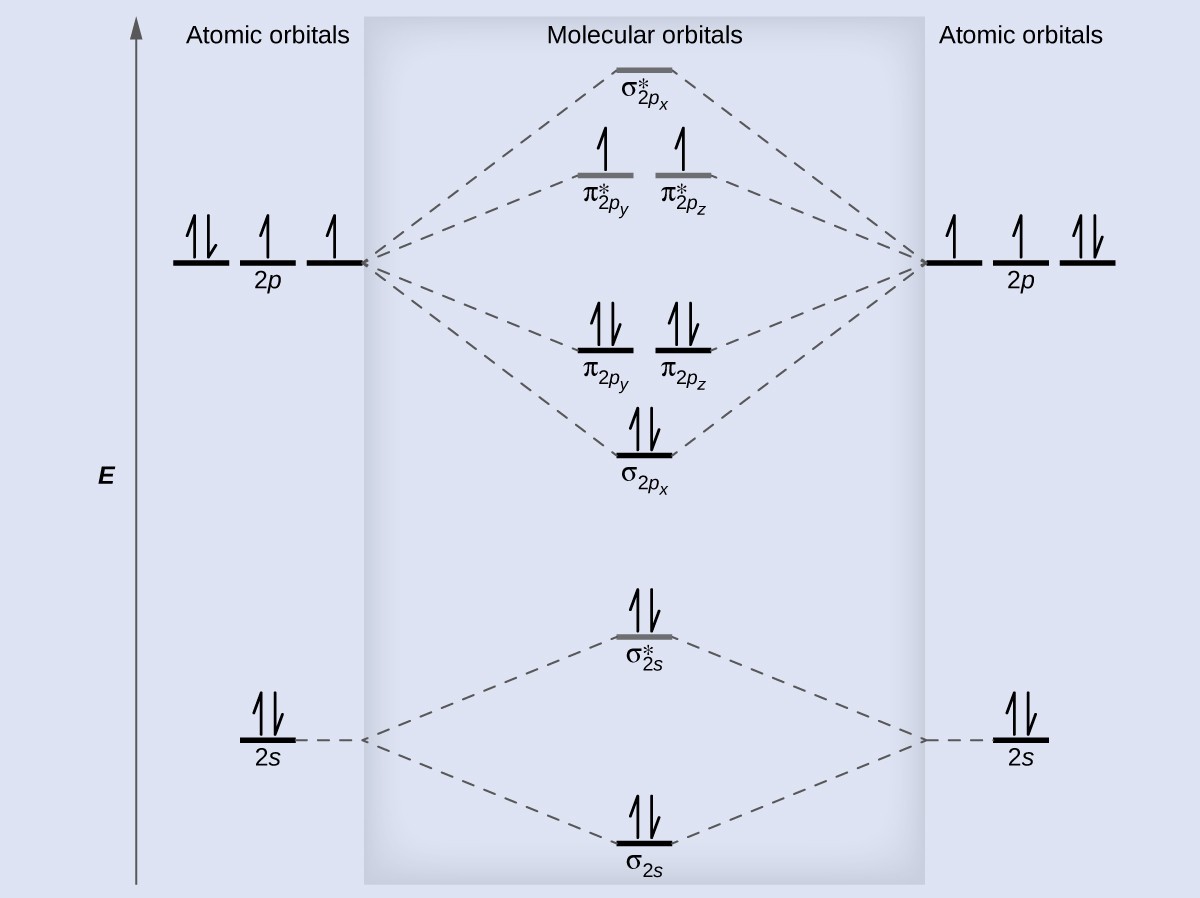
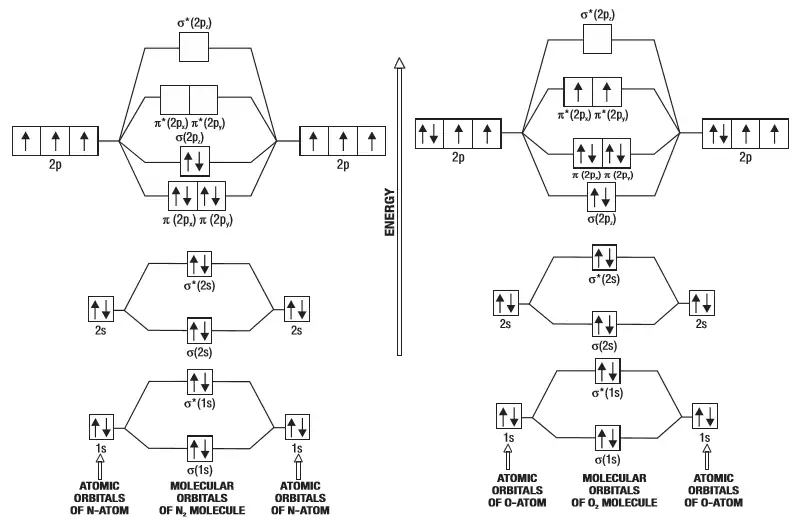
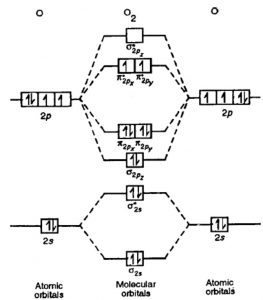
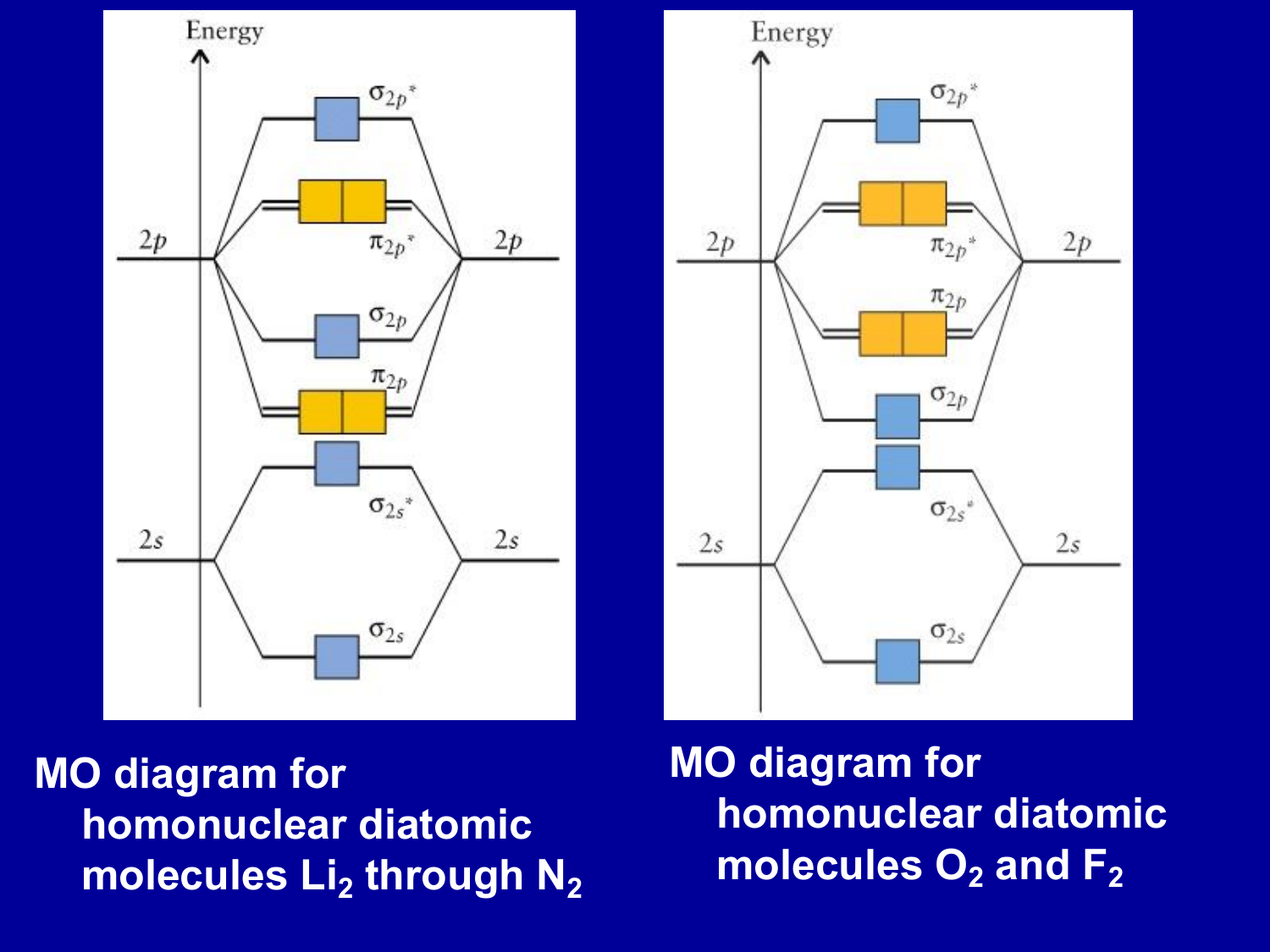
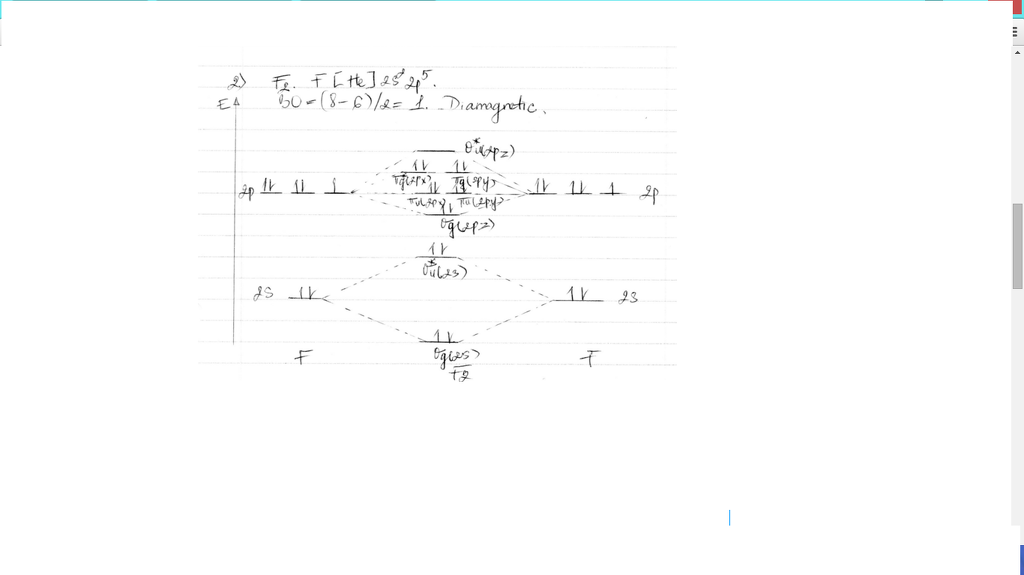
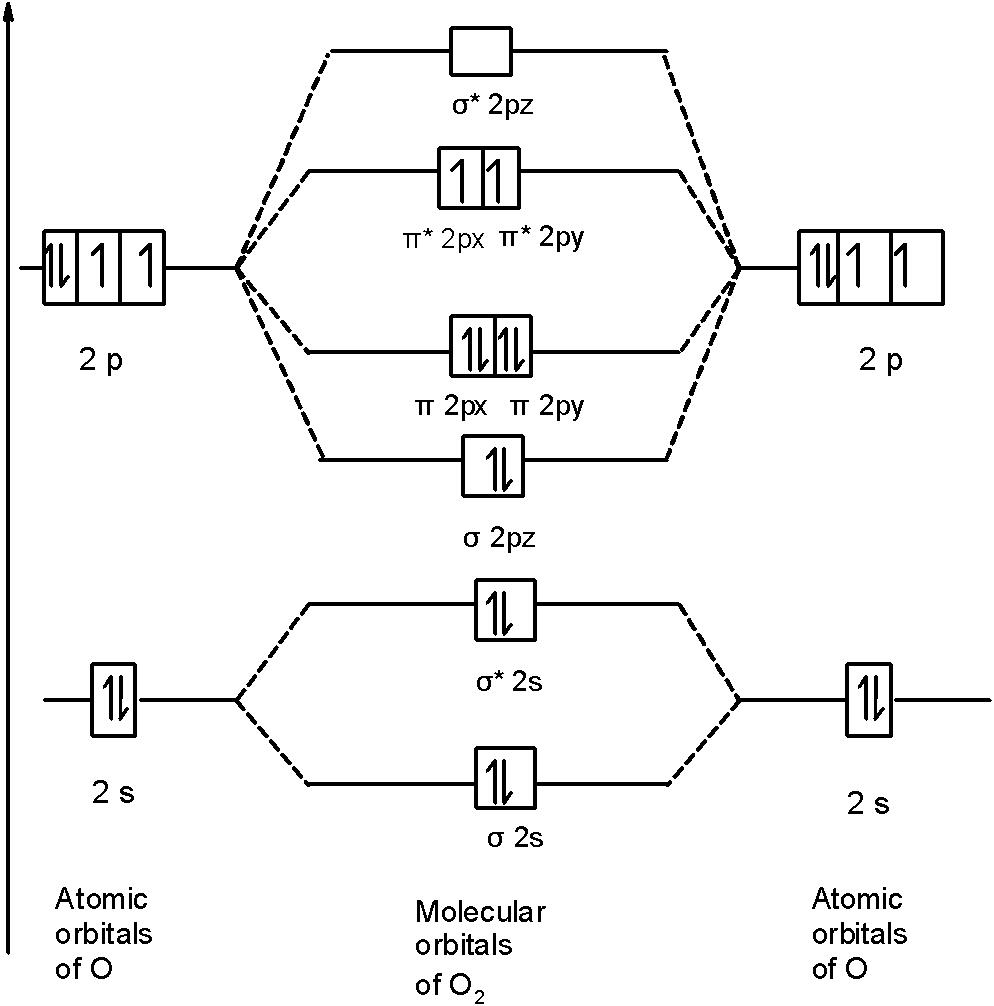
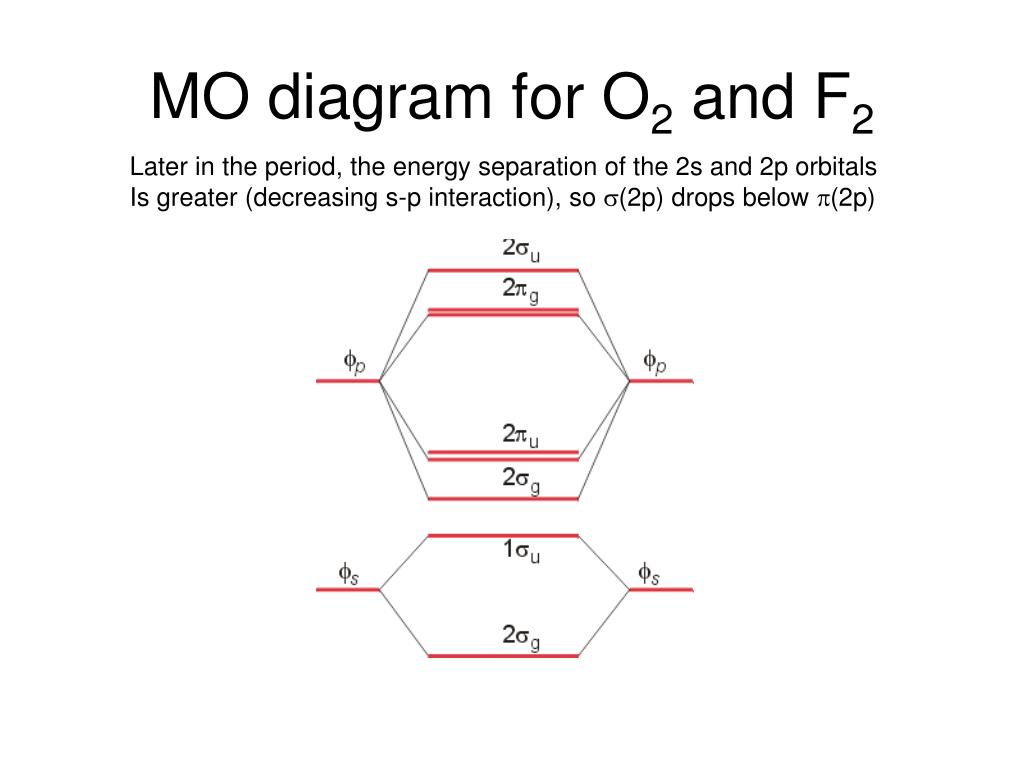
this diagram explains the observed paramagnetism of B2. Figure 9.39: The molecular orbital energy-level diagrams, bond orders, bond energies, and bond lengths for the diatomic molecules B 2 through F2.Note that for O2 and F2 the σ2p orbital is lower in energy than the π2p orbitals. 3.O2 has 12 valence electrons. Its MO configuration is:
Arrange the following in order of decreasing stability. a blank molecular orbital diagram (part a 1 figure) has been provided to you. rank the fluorine species from most to least stable. to rank items as equivalent, overlap them. f2, f2+, f2-
A blank molecular orbital diagram (Figure 1) has been provided to help you. Rank the fluorine species from highest to lowest bond energy. To rank items as equilvalent, overlap them. View Available Hint(s) Reset Help F2 F2 Lowest bond energy Highest bond energy The correct ranking cannot be determined.
Part a by drawing molecular orbital diagrams for b2, c2, n2, o2, and f2, predict which of these homonuclear diatomic molecules are magnetic. Categories Uncategorized Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Solved question 1 by drawing molecular orbital diagrams solved look at the mo diagrams of corresponding neutral diatom when doing molecular orbitals the pi bonds come before sigma for b2 what is the energy level diagram of n2 and f2 brainly in. Information from the mo diagram justify o2s stability and show that its bonding order is 2.
Click here👆to get an answer to your question ️ 37. Draw molecular orbital diagram for F2 molecule. Also, give its electronic configuration, bond order and magnetic property. 138. Solve the following:
Molecular Orbital Diagram - Cl2, Br2, I2 3s & 3p and higher atomic orbitals are not so widely separated in energy and allow significant mixing (hybridization) to occur. This mixing causes the inversion of the σσand πmolecular orbitals' energy. σσσ ππ σ* π* 3,4,5 p 3, 4,5 s σ* σ 3,4,5 s 3,4,5 p Interhalogens Br Br F F Br F F F F.
Molecular orbital diagram for f2. A bare molecular orbital diagram is presented and you must drag the correct orbitals and labels onto the diagram. How to graph a mo molecular orbital diagram for f2. By drawing molecular orbital diagrams for b2 c2 n2 o2 and f2 predict which of these homonuclear diatomic molecules are magnetic.
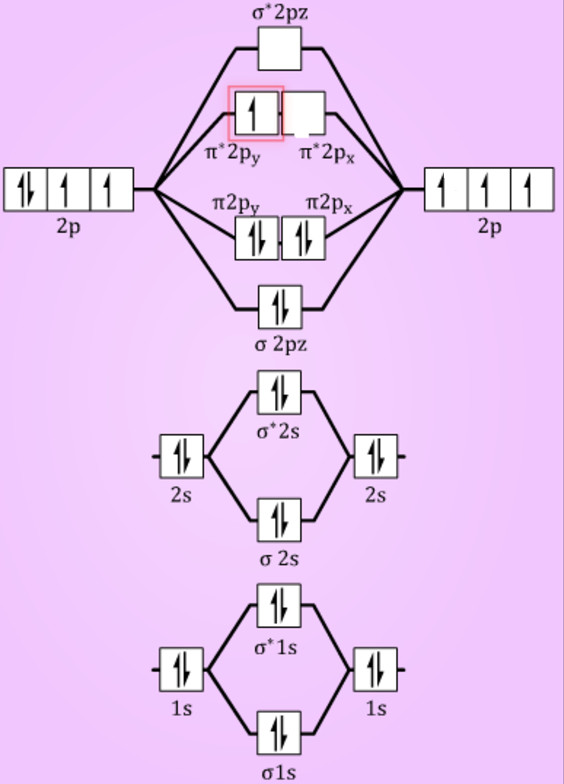
Since F2 is after N2 in the second row of the periodic table (where these effects are not present), the orbital energy ordering is "normal". In general, the molecular orbital energies follow these rules: The relative atomic orbital energy differences approximate the relative σ/σ orbital energy differences.
Molecular Orbital Diagram For F2 - A Mechanistic Study Graphene Based Nonvolatile Reram Devices. molecular orbitals of diatomic molecules molecular orbitals of li 2 be 2 to f 2 skills to develop explain how the energy levels of atomic orbitals vary for h li be b c n and o draw relative energy levels diagrams for homonuclear diatomic molecules.
Before we can draw a molecular orbital diagram for B₂, we must find the in-phase and out-of-phase overlap combinations for boron's atomic orbitals. Then we rank them in order of increasing energy. We can ignore the 1s orbitals, because they do not contain the valence electrons. Each boron atom has one 2s and three 2p valence orbitals. The 2s orbitals will overlap to form 2sσ and 2sσ.
Molecular orbital diagram for ne2 2. Molecular orbital diagram for ne2 2 Molecular orbital diagram for ne2 2.
Solved question 1 by drawing molecular orbital diagrams solved look at the mo diagrams of corresponding neutral diatom when doing molecular orbitals the pi bonds come before sigma for b2 what is the energy level diagram of n2 and f2 brainly in.
Experts are tested by Chegg as specialists in their subject area. We review their content and use your feedback to keep the quality high. 100% (13 ratings) Transcribed image text: Fill in the Molecular Orbital Energy Diagram for the diatomic molecule F2 MO's fluorinep fluorineA 2p ー2p 2p In this case σ2pch2p * σ2s 1s Ơİs.
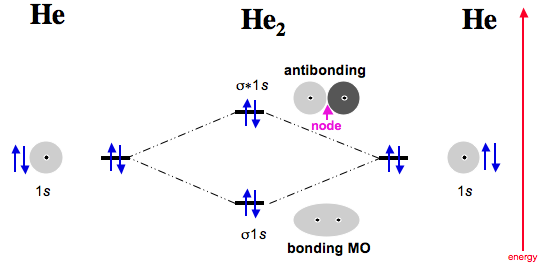
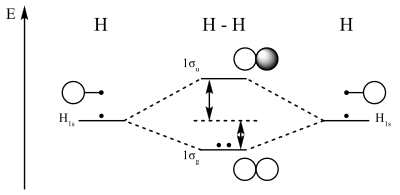
Electrons are added to molecular orbitals, one at a time, starting with the lowest energy molecular orbital. The two electrons associated with a pair of hydrogen atoms are placed in the lowest energy, or bonding, molecular orbital, as shown in the figure below. This diagram suggests that the energy of an H 2 molecule is lower than that of a.
Nov 12, 2021 · The molecular orbital diagram of ethane would be: The molecular orbital is formed from the combination of atomic orbitals, which must have nearly the same energy and are symmetrical about the molecular axis. To understand the MO diagram of ethane, we consider it as a homonuclear diatomic A2 molecule.
26. Define anti-bonding molecular orbital. Ans: This can be defined as the molecular orbital which is formed by the subtraction of atomic orbitals is called anti-bonding molecular orbital. This is represented as: ${{\sigma }^{+}}=\Psi A-\Psi B$ 27. Explain diagrammatically.
A bare molecular orbital diagram is presented and you must drag the correct orbitals and labels onto the diagram. Molecular orbital diagram for f2. The other molecular orbital produced s h h shows a decrease in electron density between the nuclei reaching a value of zero at the midpoint between the nuclei where there is a nodal plane.
Experts are tested by Chegg as specialists in their subject area. We review their content and use your feedback to keep the quality high. 100% (1 rating) Transcribed image text: Draw Molecular Orbital diagram of F2 molecule. Determine ) bond order and (1) magnetic behavior for F2, F2 and F2 molecules Attach File Browse My Computer Browse.
Determining Molecular Shape (VSEPR) Hybridization *Molecular Orbital Theory (Bond Order, Diamagnetism, Paramagnetism) Coordination Compounds and their Biological Importance Naming Shape, Structure, Coordination Number, Ligands Biological Examples Industrial Examples *Stereochemistry *Crystal Field Theory *Molecular Orbital Theory Applied To.
When two fluorine atoms bond, the sigma(2p) bonding molecular orbitals are lower in energy than the pi(2p) bonding orbitals.F2(2+) has a bond order of 2, so.
together to produce a sigma molecular orbital [σ = (1sa + 1sb)]. Since the electrons in this orbital are more stable than on the individual atoms, this is referred to as a bonding molecular orbital. A second molecular orbital is also created, which we simplistically show as a subtraction of the two atomic 1s orbitals [σ* = (1sa - 1sb)]. This.
Molecular orbital diagram for f2. In o 2 and f 2 there is a crossover of the sigma and the pi ortbials. Molecular orbitals mo are constructed from atomic orbitals. The relative energies of the sigma orbitals drop below that of the pi orbitals. The size of the effect depends on the 2s 2p energy difference. It is called a sigma molecular orbital.
Answer (1 of 6): Here is the solution, > * For O2 molecule, > * For F2 molecule, Thanks for reading.
Answer (1 of 7): UNDERSTANDABLE VERSION- See boy... If you are in class 11th then don't look for stuff like this. It hasn't been explained for a good reason. I will explain it to you in very crude terms but not its role in MOT as you wont be able to understand and I am saying this from experience...







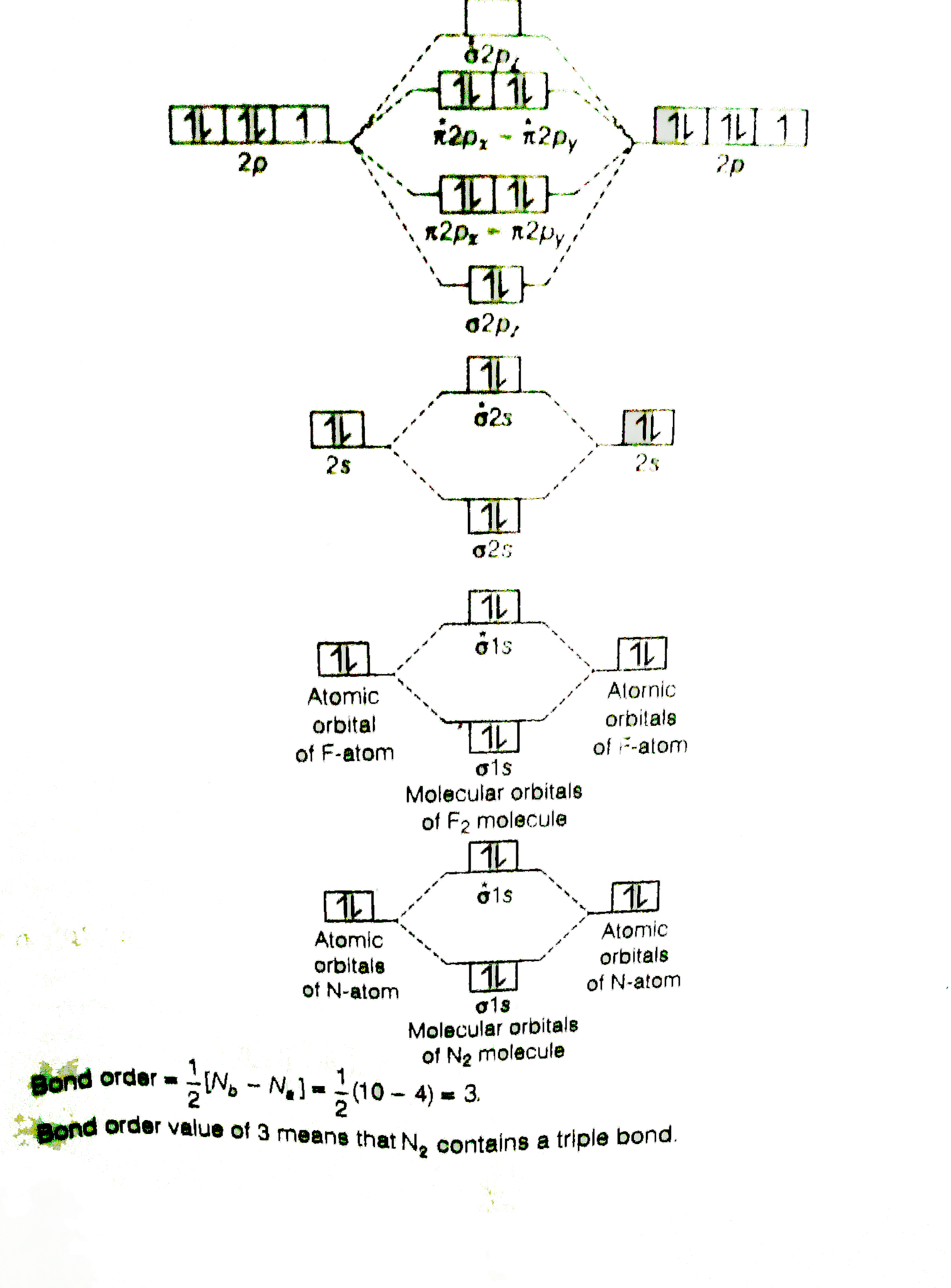







0 Response to "41 Molecular Orbital Diagram For F2"
Post a Comment