41 Action Potential Diagram Labeled
Neurotoxins aimed at the ion channels. channels involved in action potentials. The ion channels of insects are sufficiently different from their human counterparts that there are few side effects in humans.... Image of two Purkinje cells (labeled as A) drawn by Santiago Ramón ... April 25, 2013 - Most cells in the body make use of charged particles, ions, to build up a charge across the cell membrane. Previously, this was shown to be a part of ho...
Create a labeled diagram explaining how cardiac muscle fiber excitation (depolarization from action potentials) is coupled to cardiac muscle contraction. Integrate a cardiac muscle fiber, a cardiac action potential trace and the steps of cross-bridge cycling in your diagram. Write a caption for your diagram. 5.
Action potential diagram labeled
Expert Answer. 100% (1 rating) Action Potential: When impulse is initiated by stimulation of sensory nerve ending, movement of ions across the cell membrane indicate action potential. Polarised membrane: The nerve in the resting st view the full answer. Previous question Next question. August 14, 2020 - Action potential is a brief reversal of membrane potential where the membrane potential changes from -70mV to +30mV. When the membrane potential of the axon hillock of a neuron reaches threshold, a rapid change in membrane potential occurs in the form of an action potential. Intended for elementary and secondary school students and teachers who are interested in learning about the nervous system and brain with hands on activities, experiments and information.
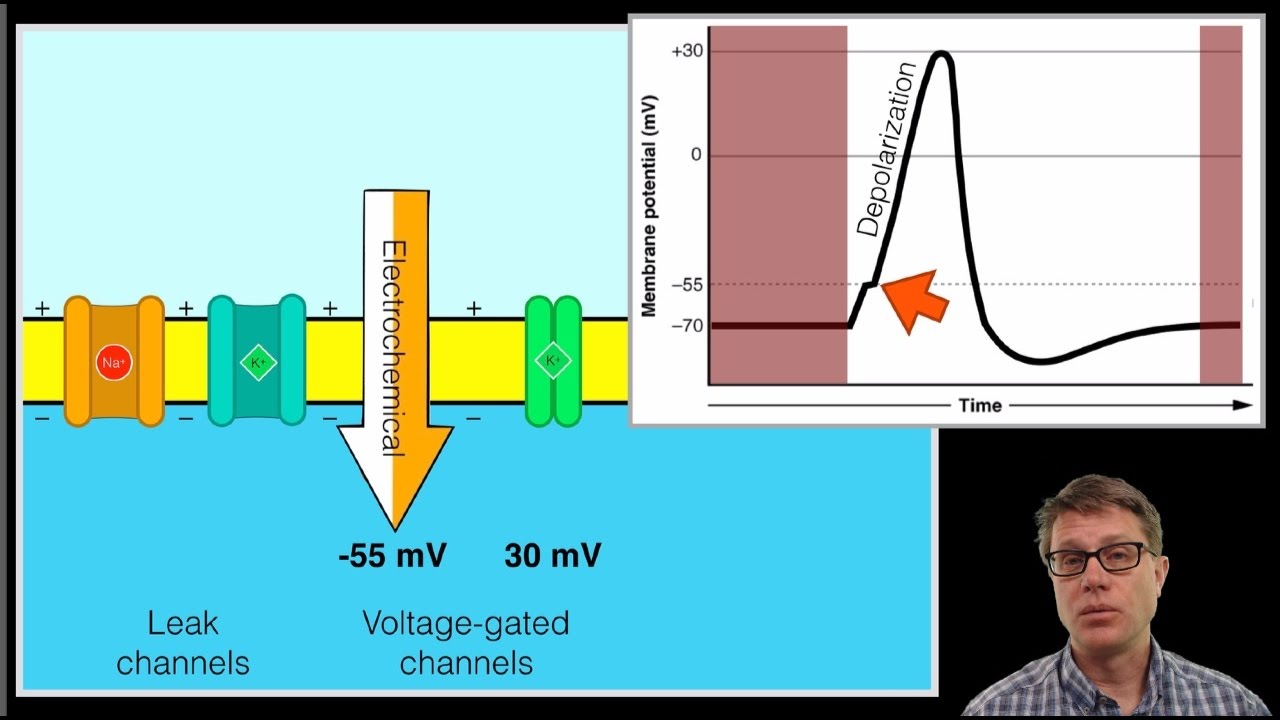
Action potential diagram labeled. Neuron action potentials: The creation of a brain signal. Your body has nerves that connect your brain to the rest of your organs and muscles, just like telephone wires connect homes all around the world. When you want your hand to move, your brain sends signals through your nerves to your hand telling the muscles to contract. September 17, 2021 - Na+ ions entering the cell make the membrane potential less negative. More Na+ channels open as result and a cycle of depolarization develops. Discover the anatomy of the nervous system with these interactive quizzes and labeled diagrams. Hyperpolarization is when the membrane potential becomes more negative at a particular spot on the neuron's membrane, while depolarization is when the membrane potential becomes less negative (more positive). Depolarization and hyperpolarization occur when ion channels in the membrane open or close, altering the ability of particular types of. Label the membrane, the voltage-gated sodium channel, the potassium leak channel, the voltage-gated potassium. Set up an axonal membrane as shown in the diagram below and to the left. Remember to set up... membrane, an action potential cannot be generated there. The inward current that
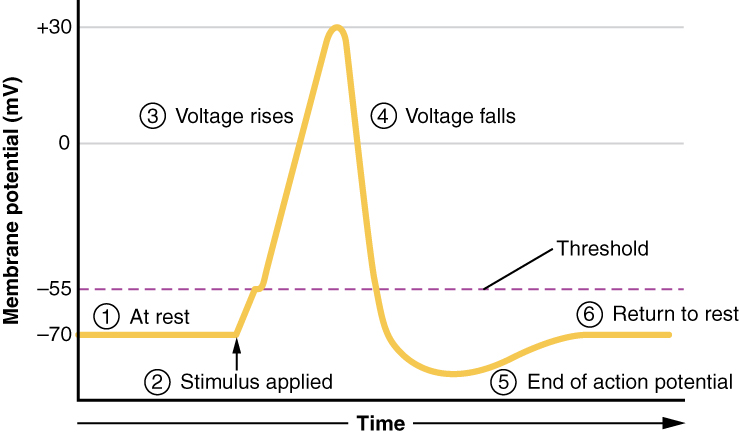
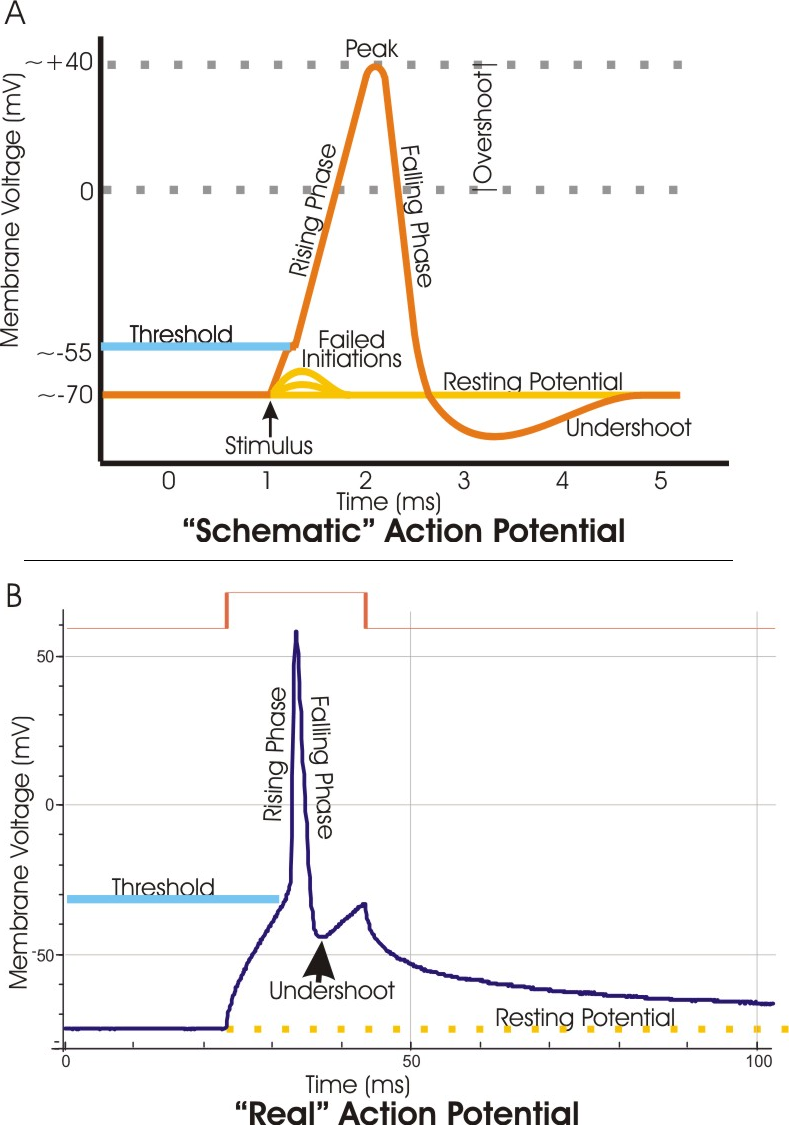
The basis of this communication is the action potential, which demonstrates how changes in the membrane can constitute a signal. Looking at the way these signals work in more variable circumstances involves a look at graded potentials, which will be covered in the next section. External Website. Watch this video to learn about the release of a neurotransmitter. The action potential reaches the end of the axon, called the axon terminal, and a chemical signal is released to tell the target cell to do something—either to initiate a new action potential, or to suppress that activity. An action potential is a rapid rise and subsequent fall in voltage or membrane potential across a cellular membrane with a characteristic pattern. Sufficient current is required to initiate a voltage response in a cell membrane; if the current is insufficient to depolarize the membrane to the threshold level, an action potential will not fire. August 14, 2020 - Action potential is a brief reversal of membrane potential where the membrane potential changes from -70mV to +30mV. When the membrane potential of the axon hillock of a neuron reaches threshold, a rapid change in membrane potential occurs in the form of an action potential.
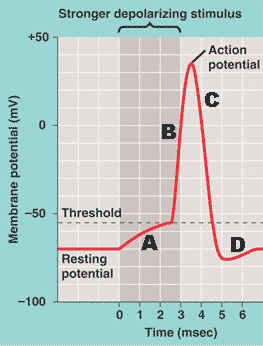
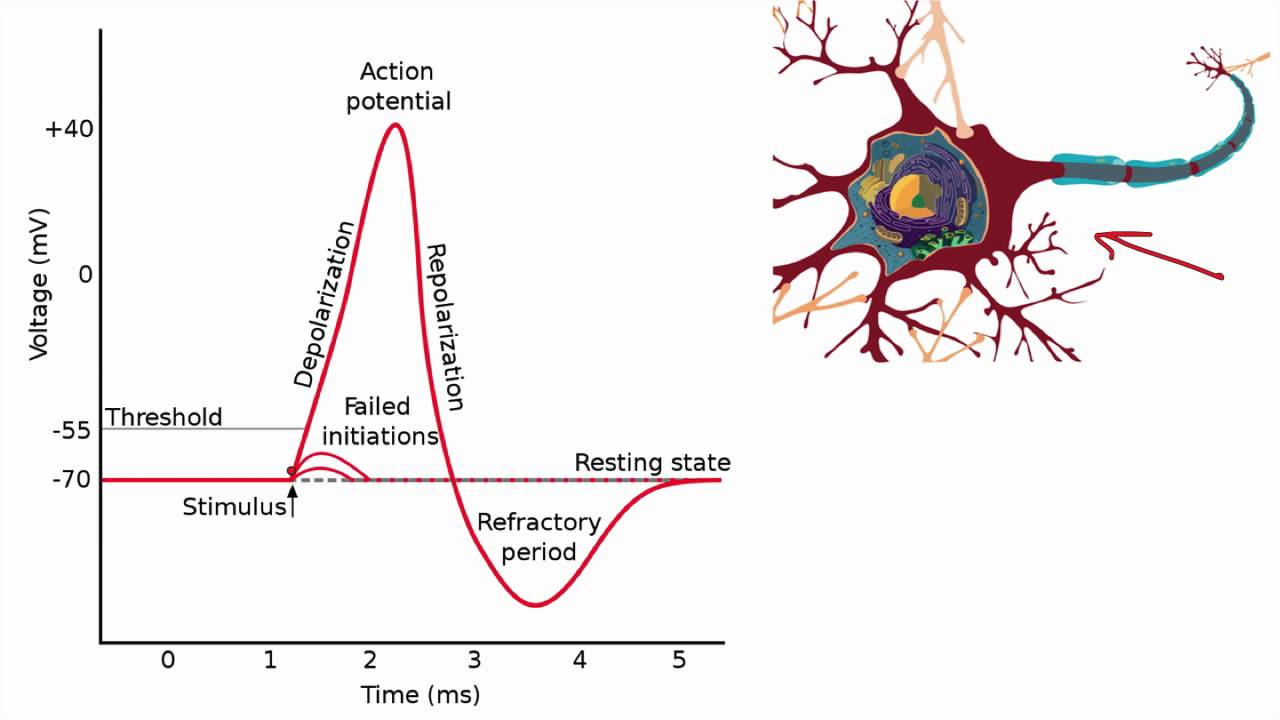
The Action Potential. Resting membrane potential describes the steady state of the cell, which is a dynamic process that is balanced by ion leakage and ion pumping. Without any outside influence, it will not change. To get an electrical signal started, the membrane potential has to change. • Initiation of action potential in autorhythmic cells: 1. Pacemaker Potential due to influx of sodium and reduced efflux of potassium. 2. Depolarization and reversal of the membrane potential due to influx of calcium. 3. Repolarization due to efflux of potassium. • Initiation of action potential in contractile cells: 1. Label the components of the action potential depicted in this diagram 1 A = Threshold 2. B = Depolarizing 3. C = Repolarizing 4. D = Hyperpolarization 2. Label the components of the action potential depicted in this diagram 1. A = Threshold 2. B = Depolarizing 3. C = Repolarizing 4. D = Hyperpolarization 3. Voltage-gated Na+ channels can be in Action potential curve and phases (diagram) Hypopolarization is the initial increase of the membrane potential to the value of the threshold potential.The threshold potential opens voltage-gated sodium channels and causes a large influx of sodium ions.
In my 2-Minute Neuroscience videos I explain neuroscience topics in 2 minutes or less. In this video, I discuss the action potential. The term "action potent...
heart; blood. sarcoplasmic reticulum is more extensive in smooth muscle fibers than in skeletal muscle fibers. false. the sinoatrial (sa) node, or the ______________, sets the rate of the hearts contractions by sending action potentials through the specialized conduction fibers to the atria and ventricle. pacemaker.
READ MORE BELOW!In this video, we discuss the events of the cardiac muscle action potential by viewing the action potential graph/diagram.INSTAGRAM | @thecat...
An action potential (AP) is the mode through which a neuron transports electrical signals. It is defined as a brief change in the voltage across the membrane due to the flow of certain ions into and out of the neuron. In this article we will discuss how an action potential is generated and how conduction of an action potential occurs.
Potential Energy Diagrams · A potential energy diagram plots the change in potential energy that occurs during a chemical reaction. This first video takes you through all the basic parts of the PE diagram
Easily learn the conduction system of the heart using this step-by-step labeled diagram. The cardiac conduction system is the electrical pathway of the heart that includes, in order, the SA node, AV node, bundle of His, bundle branches, and Purkinje fibers. Learn about pacemaker cells and cardiac ac
The action potential thus moves along the axon as a wave of depolarization traveling away from the cell body. • Label where the action potential is in these two diagrams: Page 17. Conduction Velocity Depends on Diameter and Myelination of the Axon • Conduction velocity is the speed with which an action potential is propagated.
The basis of this communication is the action potential, which demonstrates how changes in the membrane can constitute a signal. Looking at the way these signals work in more variable circumstances involves a look at graded potentials, which will be covered in the next section.
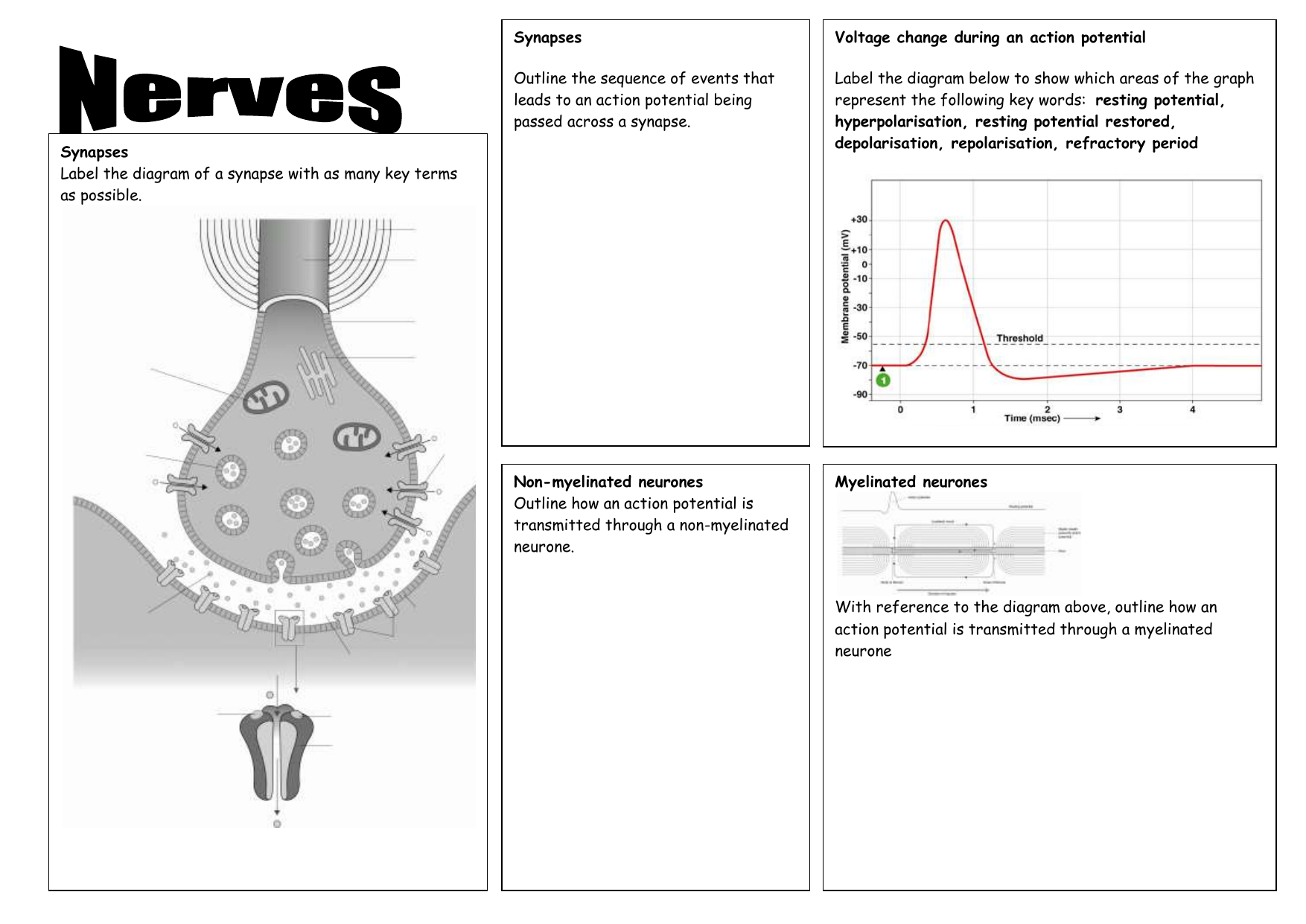
Draw a labeled diagram or series of labeled diagrams to explain: resting, action potential and refractory period of a neuron. Be sure to illustrate the relative charge inside and outside of the neuron, the types of ions present, and the movement of ions across the cellular membrane. Describe what factors stimulate an action potential to occur.
The basis of this communication is the action potential, which demonstrates how changes in the membrane can constitute a signal. Looking at the way these signals work in more variable circumstances involves a look at graded potentials, which will be covered in the next section.
When a stimulus reaches a resting neuron, the neuron transmits the signal as an impulse called an action potential. During an action potential, ions cross back and forth across the neuron's membrane, causing electrical changes that transmit the nerve impulse: The stimulus causes sodium channels in the neuron's membrane to open, allowing the.
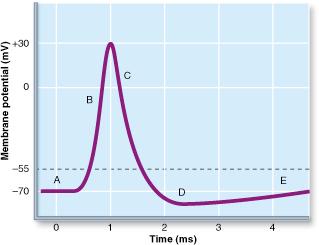
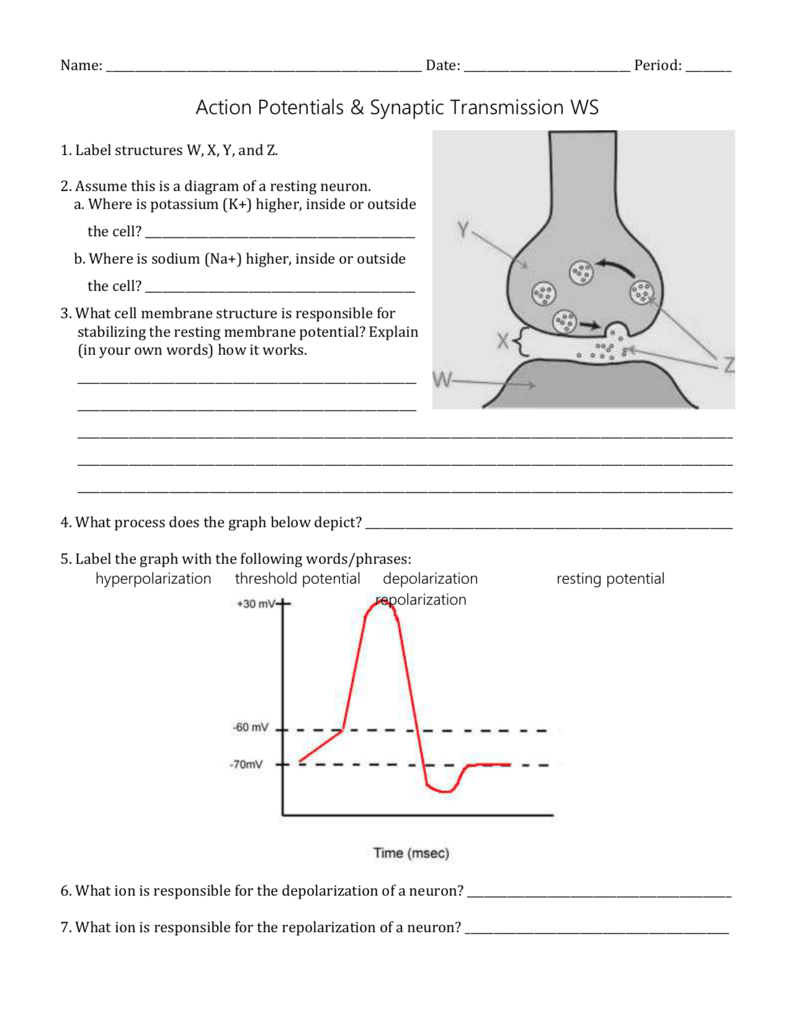
Label and explain steps 1-7 in the action potential diagram below. 0 -55 -70 Time ; Question: 6. Label and explain steps 1-7 in the action potential diagram below. 0 -55 -70 Time. This problem has been solved! See the answer See the answer See the answer done loading. Show transcribed image text
July 9, 2019 -
If depolarization reaches -55 mV, then the action potential continues and runs all the way to +30 mV, at which K + causes repolarization, including the hyperpolarizing overshoot. Also, those changes are the same for every action potential, which means that once the threshold is reached, the exact same thing happens.
Anatomy and Physiology questions and answers. Cellular communication between neurons and other body cells happens through an electrical signal called an action potential. Identify the step of the action potential in the diagram below labeled 4. Plasma membrane of axon Outside of axon Inside of axon Na Na Na" e Select one: a.
E. In the diagram, which labeled structure is the marginal branch of the right coronary artery? B. In the diagram, which labeled structure is the circumflex branch of the left coronary artery? D. Describe what is happening during the phase of the cardiac action potential labeled 2 in the diagram. Phase 2 is the plateau phase which occurs due to.
Print How to Label an Action-Potential Graph Showing Depolarization Worksheet 1. Which of the following segments shows a phase where the neuron will be less likely to fire an action potential?
An action potential is triggered when the cumulative quantity of these signals surpasses a particular threshold, and an electrical signal is delivered down the axon away from the soma.. Draw a labeled diagram of a neuron. (5 marks) Ans. A labeled diagram of a neuron: Ques 10.
EKG or ECG waveform parts are explained clearly to make EKG interpretation easy. Learn the meaning of each component of an EKG wave with this step-by-step labeled diagram of the conduction system of the heart. Provides information on atrial depolarization and the P wave, ventricular depolarization a
Expert Answer. 100% (1 rating) Action Potential: When impulse is initiated by stimulation of sensory nerve ending, movement of ions across the cell membrane indicate action potential. Polarised membrane: The nerve in the resting st view the full answer. Previous question Next question.
Start studying Action Potential Graph. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools.
Labeled Neuron Diagram. Alex Bolano on May 29, 2019 Leave a Comment!. During an action potential event, the cell membrane potential at a specific point on the axon rapidly rises then drops, causing the membrane potential to drop elsewhere along the axon. An action potential event in Neuron A causes the release of neurotransmitters in the...
To understand how neurons are able to communicate, it is necessary to describe the role of an excitable membrane in generating these signals. The basis of this process is the action potential. An action potential is a predictable change in membrane potential that occurs due to the open and.
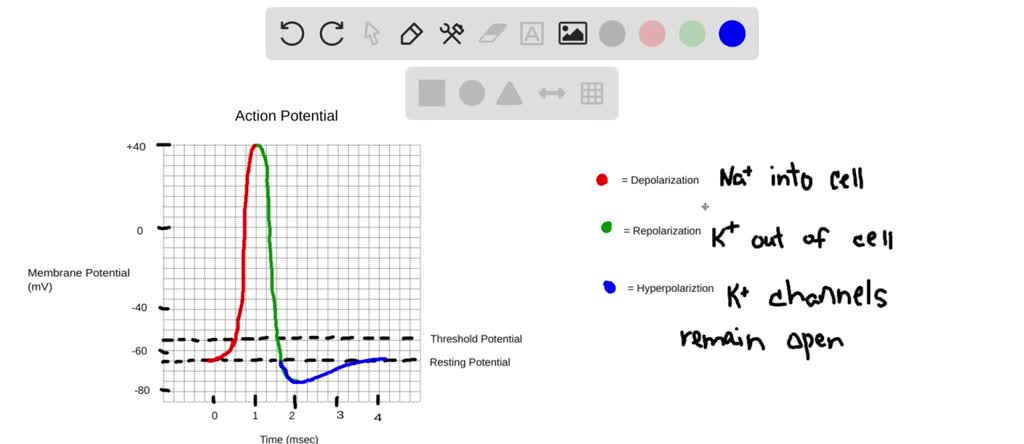
Draw And Label An Action Potential Including Which Ions Are Moving Through The Membrane And In Which Direction They Are Flowing In Each Phase How Does Each Ions Conductance Change With Each 86763
July 9, 2021 - The energy changes that occur during a chemical reaction can be shown in a diagram called a potential energy diagram, or sometimes called a reaction progress curve. A potential energy diagram shows the change in potential energy of a system as reactants are converted into products.
Action Potential. A stimulus from a sensory cell or another neuron causes the target cell to depolarize toward the threshold potential. If the threshold of excitation is reached, all Na + channels open and the membrane depolarizes. At the peak action potential, K + channels open and K + begins to leave the cell.
In this lesson, you'll be reviewing the parts of an action potential: depolarization, resting potential, threshold, and the refractory period. We'll look in detail about how to label these parts.
Intended for elementary and secondary school students and teachers who are interested in learning about the nervous system and brain with hands on activities, experiments and information.
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/11522/Action_potential_curve.png)




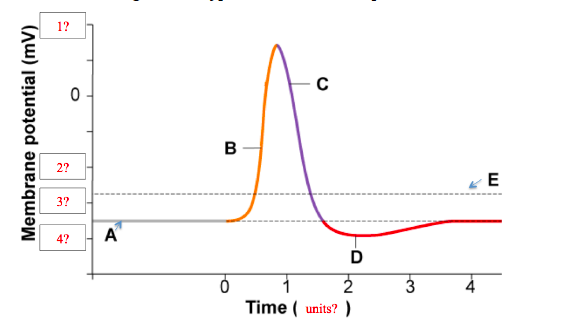



















0 Response to "41 Action Potential Diagram Labeled"
Post a Comment