40 What Structure In The Diagram Is The Only Place On A Long Bone Not Covered By The Periosteum?
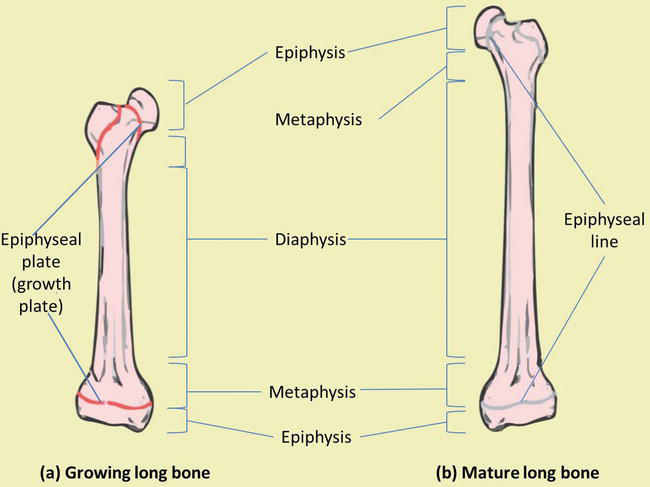
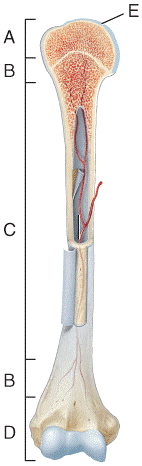
What structure in the diagram is the only place on a long bone NOT covered by the periosteum? a) A b) B c) C d) D e) E 34) What structure in the diagram is the only place on a long bone NOT covered by the periosteum? a) A b) B c) C d) D e) E Answer: e Difficulty: Easy Study Objective 1: SO 6.2 Describe the structure and functions of each part of a long bone. Section Reference 1: Sec 6.2 Structure of Bone
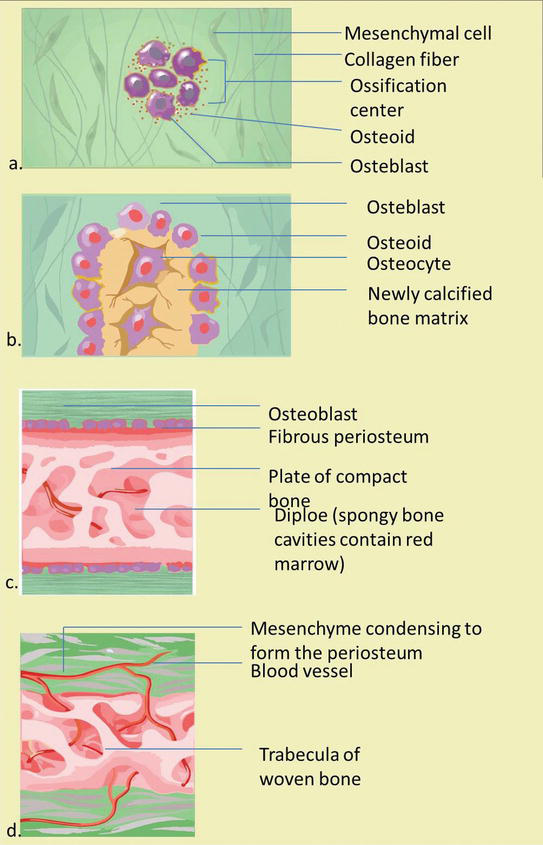
Draw a long bone and label each of the following parts: diaphysis, epiphysis, periosteum, Sharpy's (perforating) Fibers, articular cartilage, epiphyseal line, epiphyseal plate, yellow bone marrow, red bone marrow and medullary canal.. Phase 1- Hyaline cartilage model is completely covered with a bone matrix by osteoblasts (bone forming cells...

What structure in the diagram is the only place on a long bone not covered by the periosteum?
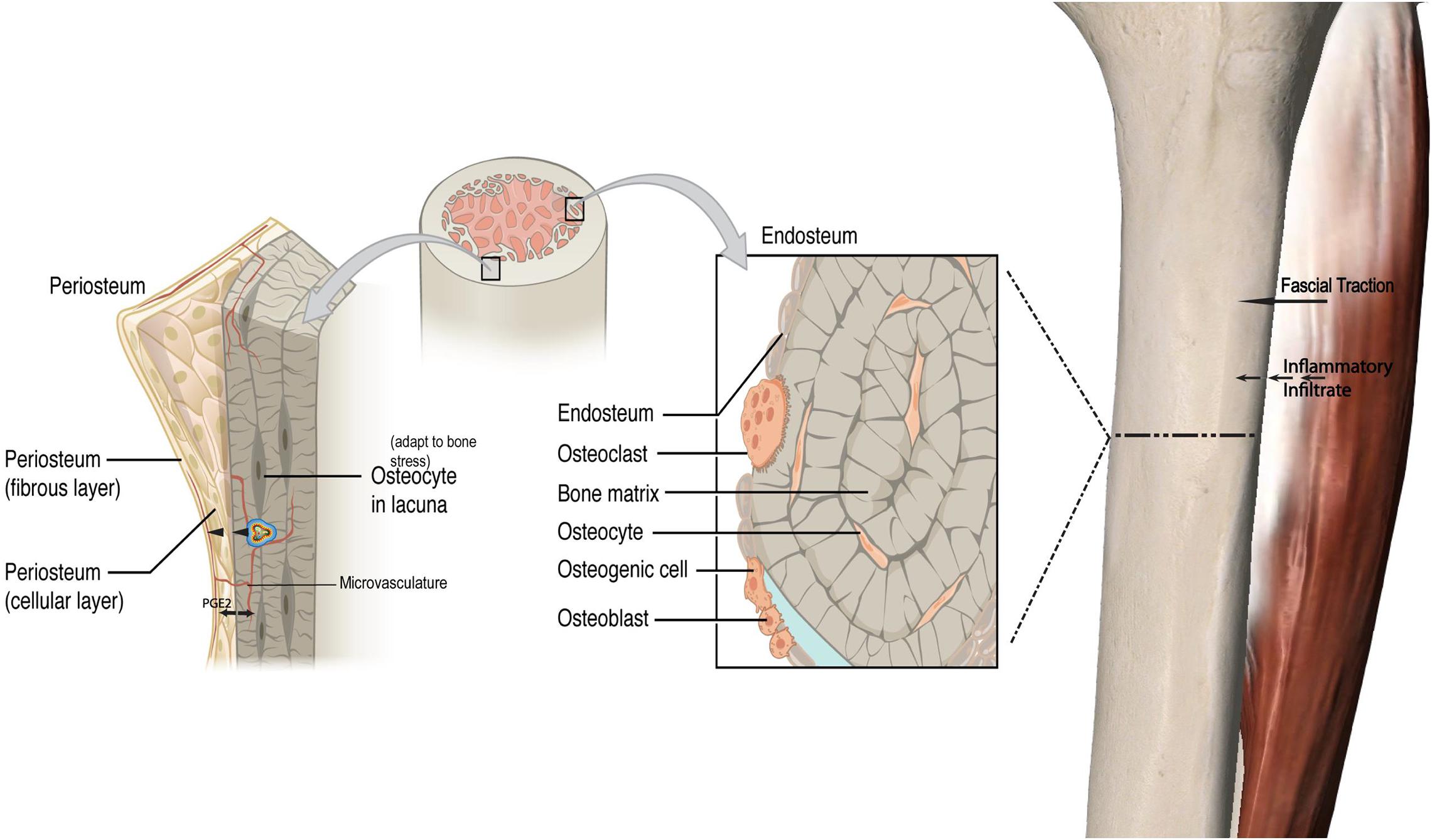
Periosteal Reaction. The periosteum is a membrane several cell layers thick that covers almost all of every bone. About the only parts not covered by this membrane are the parts covered by cartilage. Besides covering the bone and sharing some of its blood supply with the bone, it also produces bone when it is stimulated appropriately. 1. 1) Which of the following is NOT a major function of the skeletal system? 2. 2) Which region of a long bone articulates with other bones? 3. ) What is another name for the shaft of a long bone? 4. Which a layer of hyaline cartilage reduces friction between bones involved in a joint? 5. The periosteum is a membranous tissue that covers the surfaces of your bones. The only areas it doesn't cover are those surrounded by cartilage and where tendons and ligaments attach to bone.
What structure in the diagram is the only place on a long bone not covered by the periosteum?. What structure in the diagram is the only place on a long bone NOT covered by the periosteum? E Which of the following tissues could be found on or within a bone, such as the humerus? 1. This is a structure of a long bone that stores energy. 2. This is the region of a long bone that articulates with other bones. 3. This is the shaft of a logn bone. 4. This is a lyaer of hyaline cartilage that reduces friction between bones involved in the joint. 5. The shaft of a long bone, which is the direction at which the bone can withstand the most stress. Metaphysis. The metaphysis is the place where the diaphysis meets the epiphysis. This is where major bone growth occurs, as well as where blood enters the bone. Periosteum. A thin membrane that covers the outside of the bone, where tendons and. The periosteum is a membranous tissue that covers the surfaces of your bones. The only areas it doesn't cover are those surrounded by cartilage and where tendons and ligaments attach to bone.
End of a long bone, "E-piphysis" and "E-nd" begin with e. Periosteum A dense fibrous membrane covering the surface of bones (except at their extremities) and serving as an attachment for tendons and muscles. This is a structure of a long bone that stores energy. a. Diaphysis b. Epiphysis c. Metaphysis d. Periosteum e. Marrow. e. 2. This is the region of a long bone that articulates with other bones. a. Diaphysis. Where in the diagram is the only place not to have a periosteum? a. A b. B c. C d. D e. E. d. This is a structure of a long bone that stores energy. back 1. Marrow. front 2. This is the region of a long bone that articulates with other bones. back 2. Epiphysis. front 3. This is the shaft of a long bone. back 3.. Where in the diagram is the only place not to have a periosteum? back 15. 1. D. 2. C. 3. A and B. 4. B. 5. E. Structure. The gums are part of the soft tissue lining of the mouth. They surround the teeth and provide a seal around them. Unlike the soft tissue linings of the lips and cheeks, most of the gums are tightly bound to the underlying bone which helps resist the friction of food passing over them.
Oct 11, 2021 · Musculoskeletal system. The musculoskeletal system (locomotor system) is a human body system that provides our body with movement, stability, shape, and support.It is subdivided into two broad systems: Muscular system, which includes all types of muscles in the body.Skeletal muscles, in particular, are the ones that act on the body joints to produce movements. What structure in the diagram is the only place on a long bone NOT covered by the periosteum? E.. calcification begins. In stage 3, trabeculae begin to form. Finally, in stage 4, the periosteum develops. In the diagram, where is the zone of hypertrophic cartilage?... Which of the labeled structures in the diagram are fragments of older ... Learning Objective 1: 6.2 Describe the structur e and functions of each part of a long b one. Section Reference 1: 6.2 Structure of Bone 2) This is the region of a long bone that articulates with other bones. a) calcium and chlorine. b) magnesium and sulfur. c) calcium and phosphorous. d) manganese and sulfur. e) potassium and phosphorous. back 15. c. front 16. Which of the following correctly lists the order of the four zones of cartilage found within the growth plate starting at the epiphysis and extending to the diaphysis?
Anatomically, periosteum covers the majority of the bony structures with the exception of their intra-articular surfaces and sesamoid bones. To understand this it is helpful to review the embryology and formation of the long bones and the development of joints. Bone formation occurs by two processes, membranous or endochondral ossification.
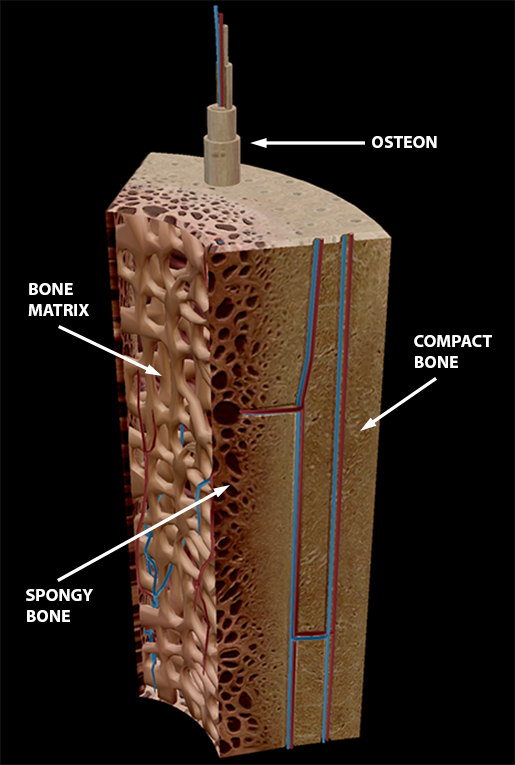
M. While a long bone is growing in length, it is also growing in width. New layers are being added to the outside of the shaft at the same time bone is dissolved away from the inside of the shaft. 1. Shaft of bone becomes wider but not thicker 2. Bone formed from the periosteum and endosteum accounts for the outer and inner circumferential.
A hinge joint (ginglymus) is formed when the cylindrical end of a bone fits into a trough-shaped surface of another bone, like that of an elbow joint (between the humerus and the ulna). These joints act as a hinge, allowing flexion and extension in just one plane. In a pivot joint, the rounded end of the bone fits into a sleeve or ring of bone.
A key structural characteristic for a synovial joint that is not seen at fibrous or cartilaginous joints is the presence of a joint cavity. This fluid-filled space is the site at which the articulating surfaces of the bones contact each other. At synovial joints, the articular surfaces of bones are covered with smooth articular cartilage.
chondrocytes, are located within lacunae. Bone is a highly vascularized tissue and, unlike cartilage, bone tissue can recover from injuries in a relatively short time. The structure of bone will be considered further in Lesson 6. Fluid Connective Tissue. Lymph and blood are the fluid connective tissues.
The game Bones is available in the following languagesHumerus bone quiz for anatomy and physiology! When you are taking anatomy and physiology you will be required to know the anatomical structure locations of the humerus bone. Ribs: The ribs are long curved bones which form a cage that protects the organs found in the chest.
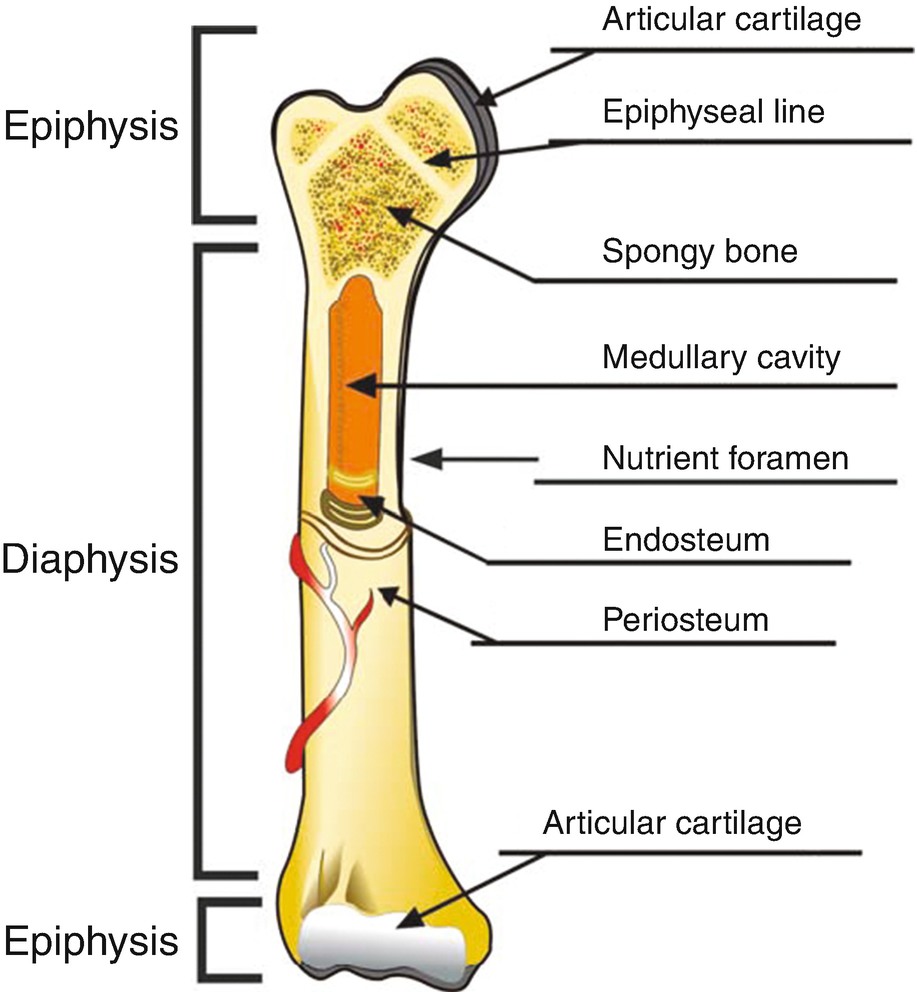
Gross Anatomy of Bone. The structure of a long bone allows for the best visualization of all of the parts of a bone ( Figure 6.7 ). A long bone has two parts: the diaphysis and the epiphysis. The diaphysis is the tubular shaft that runs between the proximal and distal ends of the bone.
Periosteal Reaction. The periosteum is a membrane several cell layers thick that covers almost all of every bone. About the only parts not covered by this membrane are the parts covered by cartilage. Besides covering the bone and sharing some of its blood supply with the bone, it also produces bone when it is stimulated appropriately.
1. 1) Which of the following is NOT a major function of the skeletal system? 2. 2) Which region of a long bone articulates with other bones? 3. ) What is another name for the shaft of a long bone? 4. Which a layer of hyaline cartilage reduces friction between bones involved in a joint? 5.
34.Identify the only skull bone, which is not fused or locked in place, and name the joint at which it moves. 35.Describe the structure, location and function of the hyoid bone. 36List the 4 major curvatures of the vertebral column and 5 regions of the vertebral column and identify the number of vertebrae in each.
Looking at a bone in cross section, there are several distinct layered regions that make up a bone. The outside of a bone is covered in a thin layer of dense irregular connective tissue called the periosteum. The periosteum contains many strong collagen fibers that are used to firmly anchor tendons and muscles to the bone for movement.
After about the fifth year the red bone marrow is gradually replaced in the long bones by yellow bone marrow. By 20 to 25 years the red bone marrow persists only in the vertebrae, sternum, ribs, clavicles, scapulae, pelvis, cranial bones and in the proximal ends of femora (pi. of femur) and humeri (pi. of humerus).
Bone is found in the shafts of long bone and consists of various cylindrical units named as haversian system 47. Circle the correct underlined figure 9.1 external anatomy of the right lateral aspect of the skull. What structure in the diagram is the only place on a long bone not covered by the periosteum?
34) What structure in the diagram is the only place on a long bone NOT covered by the periosteum? a) A b) B c) C d) D e) E Answer: e Difficulty: Easy Study Objective 1: SO 6.2 Describe the structure and functions of each part of a long bone. Section Reference 1: Sec 6.2 Structure of Bone
Which of the labeled structures in the diagram are fragments of older osteons that have. What structure in the diagram is the only place on a long bone NOT covered by the periosteum?
Where in the diagram is the distal epiphysis? D In which region of the diagram would you find the medullary cavity? C Where in the diagram can you find red bone marrow in an adult? A & B Where in the diagram is the metaphysis? B What structure in the diagram is the only place on a long bone NOT covered by the periosteum? E What type of bone cell starts forming the bone matrix?
The tongue is unique in that it is the only muscle that isn't connected to bone at both ends. It is connected on one end to the hyoid bone, which is also unique as it is the only bone not.
periosteum, dense fibrous membrane covering the surfaces of bones, consisting of an outer fibrous layer and an inner cellular layer (cambium).The outer layer is composed mostly of collagen and contains nerve fibres that cause pain when the tissue is damaged. It also contains many blood vessels, branches of which penetrate the bone to supply the osteocytes, or bone cells.
What structure in the diagram is the only place on a long bone NOT covered by the periosteum? a) A b) B c) C d) D e) E 20. What type of bone cell starts forming the bone matrix?
The external auditory canal is a curved tube about 2.5 cm (1 in.) long that lies in the temporal bone and leads to the eardrum. The tympanic membrane or ear drum is a thin, semitransparent partition between the external auditory canal and middle ear. The tympanic membrane is covered by epidermis and lined by simple cuboidal epithelium.
osteocyte, a cell that lies within the substance of fully formed bone.It occupies a small chamber called a lacuna, which is contained in the calcified matrix of bone. Osteocytes derive from osteoblasts, or bone-forming cells, and are essentially osteoblasts surrounded by the products they secreted.Cytoplasmic processes of the osteocyte extend away from the cell toward other osteocytes in small.
In anatomy, the mandible, lower jaw or jawbone is the largest, strongest and lowest bone in the human facial skeleton. It forms the lower jaw and holds the lower teeth in place. The mandible sits beneath the maxilla.It is the only movable bone of the skull (discounting the ossicles of the middle ear). It is connected to the temporal bones by the temporomandibular joints.
Bone increases in diameter via appositional growth as new bone matrix is laid down by osteoblasts in the periosteum. Briefly describe the processes by which bone increases in length and diameter. after the break in the bone occurs, blood vessels in that area are damaged and blood surrounds the fracture.
These cells are part of the outer double layered structure called the periosteum (peri- = "around" or "surrounding"). The cellular layer is adjacent to the cortical bone and is covered by an outer fibrous layer of dense irregular connective tissue (see Figure 6.3.4a). The periosteum also contains blood vessels, nerves, and lymphatic.
What is the only place on a long bone NOT covered by the periosteum? E.. Which of the following labeled structures in the diagram are concentric lamellae? C.... cells of the periosteum differentiating into osteoblasts. An elderly woman trips and falls. She puts out her hand to try to stop her fall, and ends up with a fracture of the lower arm.




























0 Response to "40 What Structure In The Diagram Is The Only Place On A Long Bone Not Covered By The Periosteum?"
Post a Comment