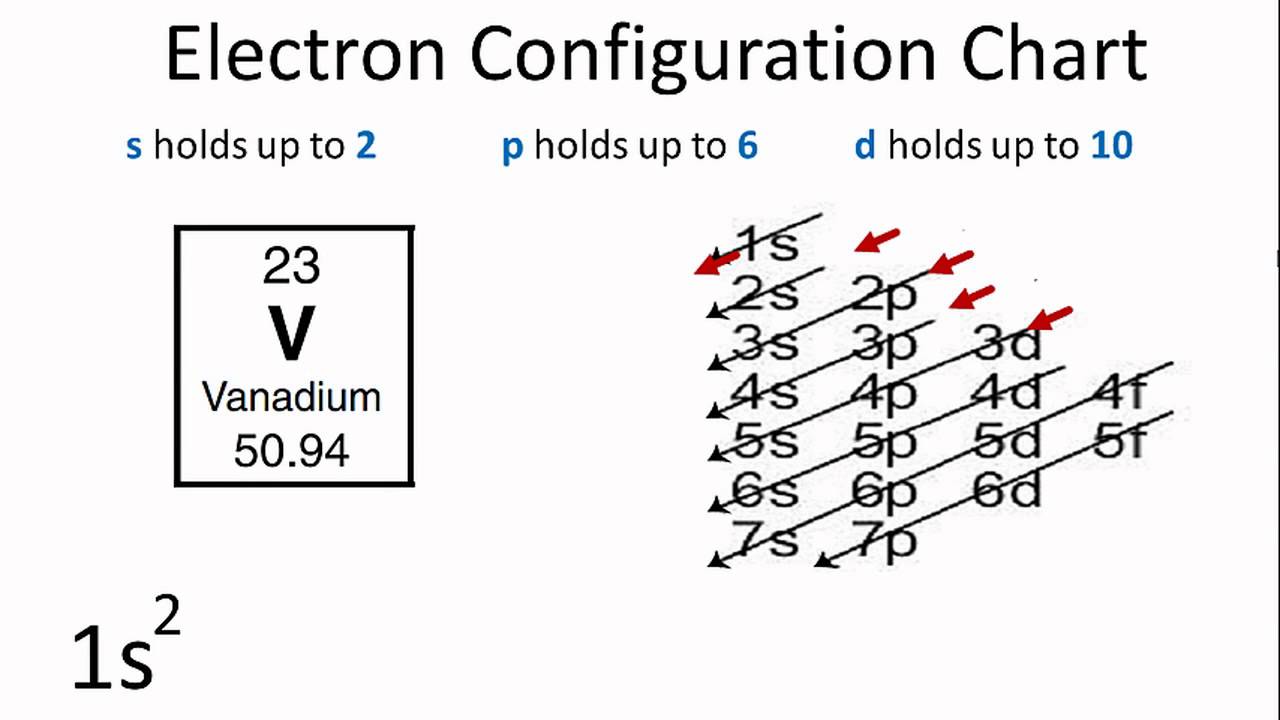
40 Fe2+ Orbital Diagram
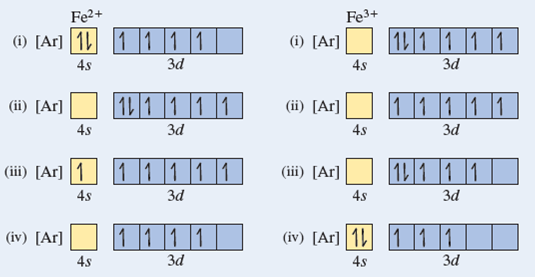
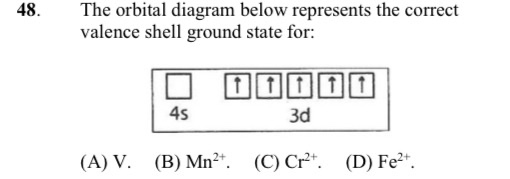
Due to its plus two charge, the electron configuration for Fe2+ contains two fewer electrons than the electron configuration for Fe, which is 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 3d6 4s2. The Fe2+ ion does not contain any electrons in the 4s-orbital, instead ending after completely filling the 3d-orbital. According to UC Davis ChemWiki, the first. Fe, or iron, has the atomic number of 26. Its full orbital diagram is 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d6.
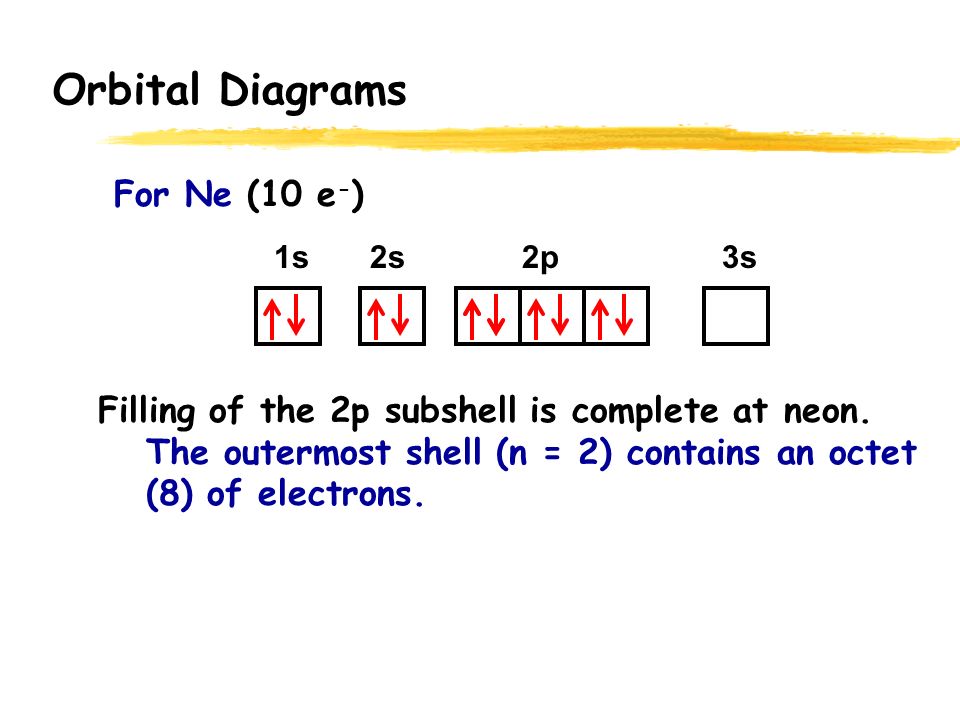
Orbital Diagram 1s ↿⇂ 2s ↿⇂ 2p ↿⇂ ↿⇂ ↿⇂ 3s ↿⇂ 3p ↿⇂ ↿⇂ ↿⇂ 3d ↿⇂ ↿ ↿ ↿ ↿ 4s ↿⇂ 4p 4d 4f: What is electron configuration of Fe?. Fe2+ is easy to oxidize to Fe3+ because removing the electron results in a half filled d subshell. Fe2+ is easy to oxidize to Fe3+ because ions with an odd charge...

Fe2+ orbital diagram
After the 4s is full we put the remaining six electrons in the 3d orbital and end with 3d6. Therefore the Iron electron configuration will be 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p 6 4s 2 3d 6. Note that when writing the electron configuration for an atom like Fe, the 3d is usually written before the 4s. Both of the configurations have the correct numbers of. A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) molecular orbital method in particular.electron configuration for Fe2+ - CHEMISTRY COMMUNITYMolecular orbital diagram - Wikipedia. Postby Chem_Mod » Sat Nov 18, 2017 3:46 am. Hello! So the electron configuration for Fe is [Ar] 3d^6 4s^2. Fe^2+ means that 2 electrons are taken away. You start removing e- from the outermost shell. The outermost shell, in this case, is the 4s orbital. So removing 2 electrons would leave you with the electron configuration of [Ar] 3d^6.
Fe2+ orbital diagram. Transcribed image text: Draw an orbital diagram for the Zn2+, Cu2+, Co2+, Fe2+, Fe3+, and Cr3+ ions in the presence of solvent molecules. Use up and down arrows to represent the spin of electrons. Only two electrons can occupy a single box. Fill the lower three boxes before filling the upper two and make sure to follow Hund's rule as you fill the orbitals with electrons. Au3 Xe 4f14 5d7 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 3d10 4s2 4p6. The outermost shell in this case is the 4s orbital. Sketch an atomic orbital diagram for Fe2 in its ground state. A normal Fe atom has an electron arrangement of. Paramagnetic With One Unpaired Electronb. The Ground State Electron Configuration Of Fe2 Ion Is 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 3d6 Therefore Fe2 Is. Answer (1 of 4): Use the online periodic table below to look up the electron configuration of any element. Dynamic Periodic Table Here's what you would see for iodine. orbital diagram. Solution: 8 O= 1s2 2s2 2p4. 24. Nickel atom can lose two electrons to form Ni2+ ion. The atomic number of nickel is 28. From which orbital will nickel lose two electrons. Solution: One Ni atom has 28 electrons and its electronic configuration is : [Ar] 4s2 3d8
Academia.edu is a platform for academics to share research papers. Transcribed image text: Choose the correct d-orbital splitting diagrams for the octahedral complex ions of Fe2+ (high and low spin). (Select all that apply.) 4 4 4 + + 47 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 + 1 4 4 4 + 4 Previous Nov 06, 2021 · Electron configuration escape room level 4 [email protected] Answer to: Draw orbital box diagrams for Fe^2+, Fe^3+, Zn, and Zn^2+. Tell which is paramagnetic. [Paramagnetic means that it has unpaired...
After the 4s is full we put the remaining six electrons in the 3d orbital and end with 3d6. Therefore the Iron electron configuration will be 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p 6 4s 2 3d 6. Note that when writing the electron configuration for an atom like Fe, the 3d is usually written before the 4s. Both of the configurations have the correct numbers of. Fig.2. Molecular orbital diagram for the Fe3*Mn2*O,o clus-ter in the (a) ferromagnetic and (b) antiferromagnetic configu-rations. Orbitals indicated with a dashed line are unoccupied. Note that the orbital energies correspond to "orbital electronega-tivities" (Slater, 1974). The energy differences between orbitals Draw a molecular orbital diagram for Fe2 (Fe-Fe) Use the diagram to predict the bond order and magnetism of Fe2. Might such a molecule exist (exist if bond order is not 0)? If it exists, what is its magnetism; Question: Draw a molecular orbital diagram for Fe2 (Fe-Fe) Use the diagram to predict the bond order and magnetism of Fe2. Might such a. an crystal field splitting diagrams to show orbital occupancies in both weak and strong octahedral fields, and (ii) indicate the number of unpaired electrons in each case. Label. the diagrams (iii) weak or strong field, (iv) high spin or low spin (as appropriate), (v) with the names of the d-orbitals, and (vi) with the appropriate orbital sets.
What is the correct orbital diagram for Fe2+? Re: electron configuration for Fe2+ So the electron configuration for Fe is [Ar] 3d^6 4s^2. Fe^2+ means that 2 electrons are taken away. You start removing e- from the outermost shell. The outermost shell, in this case, is the 4s orbital.
Answer (1 of 9): Transition metals, when losing electrons, first lose s electrons and then d electrons. Here are electron configurations of Co, Co+, Co2+ and Co3+: Co [Ar] 3d7 4s2 Co+ [Ar] 3d7 4s1 Co2+ [Ar] 3d7 Co3+ [Ar] 3d6 <--- answer to your question
electrons into the same orbital •Πeis a stabilizing energy for electron exchange associated with two degenerate electrons having parallel spin total 3 e 0 c eg* t2g d4HS eg* t2g d8 eg* t2g d6LS total 7 e 3 c total 6 e 3 c LFSE 3 0.4 O 10.6 O 0.6 O LFSE 6 0.4 O 20.6 O
When two fluorine atoms bond, the sigma(2p) bonding molecular orbitals are lower in energy than the pi(2p) bonding orbitals.F2(2+) has a bond order of 2, so.
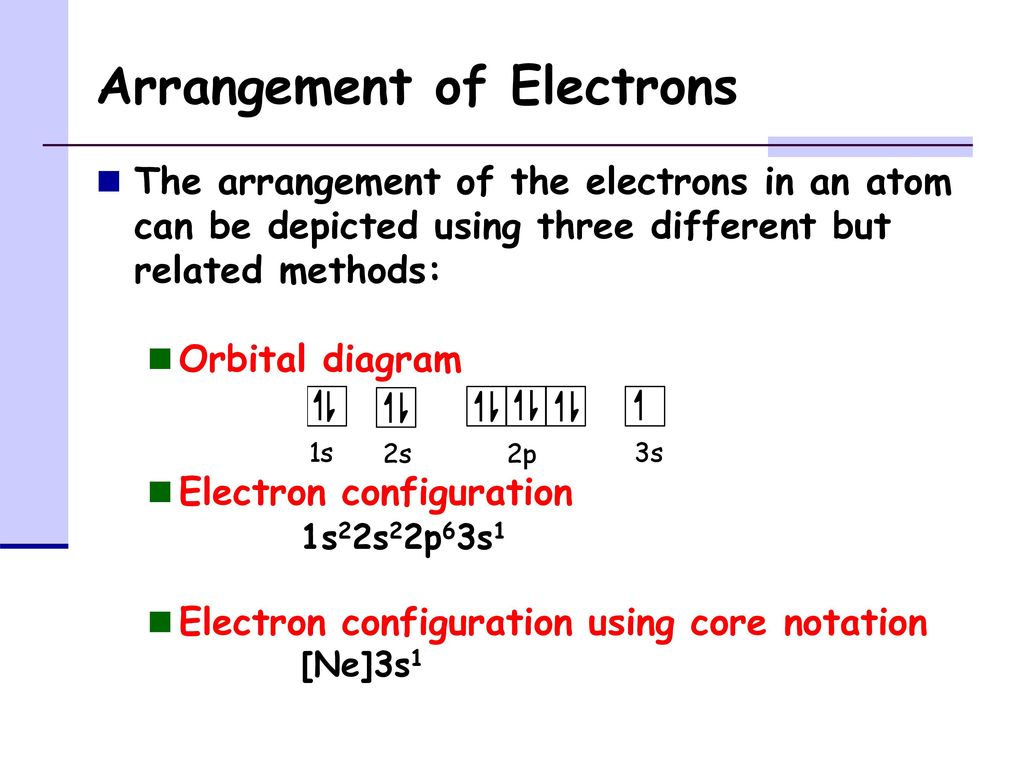
Electron orbital diagrams and written configurations tell you which orbitals are filled and which are partially filled for any atom. The number of valence electrons impacts on their chemical properties, and the specific ordering and properties of the orbitals are important in physics, so many students have to get to grips with the basics.
A solid solution describes a family of materials which have a range of compositions (e.g. A x B 1−x) and a single crystal structure.Many examples can be found in metallurgy, geology, and solid-state chemistry.The word "solution" is used to describe the intimate mixing of components at the atomic level and distinguishes these homogeneous materials from physical mixtures of components.
A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) molecular orbital method in particular.electron configuration for Fe2+ - CHEMISTRY COMMUNITYMolecular orbital diagram - Wikipedia.
Fe orbital Diagram. what is the orbital diagram for fe answers fe or iron has the atomic number of 26 its full orbital diagramis 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d6 electron configuration orbital diagram iron electron configuration orbital diagram iron how to write electron configurations and orbital diagrams duration fe fe2 & fe3
Transition Fe3+ ions and draw the orbital box diagrams for both ions. Using this. There for 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 3d5 is the electronic configration for Fe3+. half of electrons (there must be one electron in each orbital, and d has 5 orbitals). That's for filling up orbitals for ground state atoms.
Fe2+ Orbital Diagram. For midterm question Q5C, why the electron configuration for Fe2+ is not [Ar]3d^5 4S^1? The outermost shell, in this case, is the 4s orbital. You're removing 2 electrons from it to generate the Fe2+ ion, which are removed from the 4s orbital first (this is always the case in transition chemistry - as far as.
MO Diagram for HF The AO energies suggest that the 1s orbital of hydrogen interacts mostly with a 2p orbital of fluorine. The F 2s is nonbonding. H-F nb σ σ* Energy H -13.6 eV 1s F -18.6 eV -40.2 eV 2s 2p So H-F has one σ bond and three lone electron pairs on fluorine
Postby Chem_Mod » Sat Nov 18, 2017 3:46 am. Hello! So the electron configuration for Fe is [Ar] 3d^6 4s^2. Fe^2+ means that 2 electrons are taken away. You start removing e- from the outermost shell. The outermost shell, in this case, is the 4s orbital. So removing 2 electrons would leave you with the electron configuration of [Ar] 3d^6.
The 4s orbital lies lower in energy than the 3d orbital for Cu and Fe2 An element M reacts with chlorine to form MCl2, with oxygen to form MO, and with nitrogen to.
The electron configuration for Fe2+ is 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 3d6The electron configuration for Fe3+ is 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 3d5Ask me questions: http://www.chem...
Answer (1 of 8): The configuration of neutral Fe atom is: 1s² 2s² 2p⁶ 3s² 3p⁶ 3d⁶ 4s² where 4s electrons are the most energetic ones, therefore they are the first ones to be removed when atom is ionized. Thus, configuration of Fe⁺ cation is: 1s² 2s² 2p⁶ 3s² 3p⁶ 3d⁶ 4s¹ and of Fe²⁺ cation is:...
An orbital diagram, or orbital box diagram, is a way of representing the electron configuration of an atom. Arrows (or half arrows) are used to represent the electrons occupying the orbitals. What is more reactive Fe2+ or Fe3+?
We assume that orbital order is the same as that for N2. The bond order is Figure The molecular orbital energy-level diagram for both the NO+ and CN-ions. Figure A partial molecular orbital energy-level diagram for the HF molecule. This interaction introduces an element of s-p mixing, or hybridization, into the molecular orbital theory.
After the 4s is full we put the remaining six electrons in the 3d orbital and end with 3d9. Therefore the expected electron configuration for Copper will be 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p 6 4s 2 3d 9. Note that when writing the electron configuration for an atom like Cu, the 3d is usually written before the 4s.
And so for #Hg# we got 80 electrons to distribute according to the Aufbau scheme..... #underbrace(1s^(2)2s^2 2p^6 3s^2 3p^6 3d^10 4s^2 4p^6 4d^10 5s^2 5p^6 4f^14 5d.
The octahedral crystal field splitting diagram for is as followscthe electron configuration of is. 1 draw the octahedral crystal field splitting diagram for each metal ion. Fe2 low spin is broken down into a number of easy to follow steps and 23 words. Answer to draw the octahedral crystal field splitting diagram for each metal ion.
We discuss the low-energy physics of the three-orbital Anderson impurity model with the Coulomb interaction term of the Kanamori form which has orbital SO(3) and spin SU(2) symmetry and describes.
A molecular orbital diagram or MO diagram for short is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the Linear combination of atomic orbitals molecular orbital method (LCAO method) in particular.This tool is very well suited for simple diatomic molecules such as dihydrogen, dioxygen and carbon monoxide but becomes.
Choose the valence orbital diagram that represents the ground state of Sr2+. orbital diagram where the 5s orbital contains 1 pair of electrons. 4d orbitals contain 2 unpaired electrons. orbital diagram where the 4s orbital contains 1 pair of electrons. 4p orbitals contain 3 pairs of electrons.
This book is ideal for who want to use a strong molecular-orbital approach to explain structure and reactivity in inorganic chemistry.. × Close Log In. Log in with Facebook Log in with Google. or. Email. Password. Remember me on this computer. or reset password. Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link..
























0 Response to "40 Fe2+ Orbital Diagram"
Post a Comment