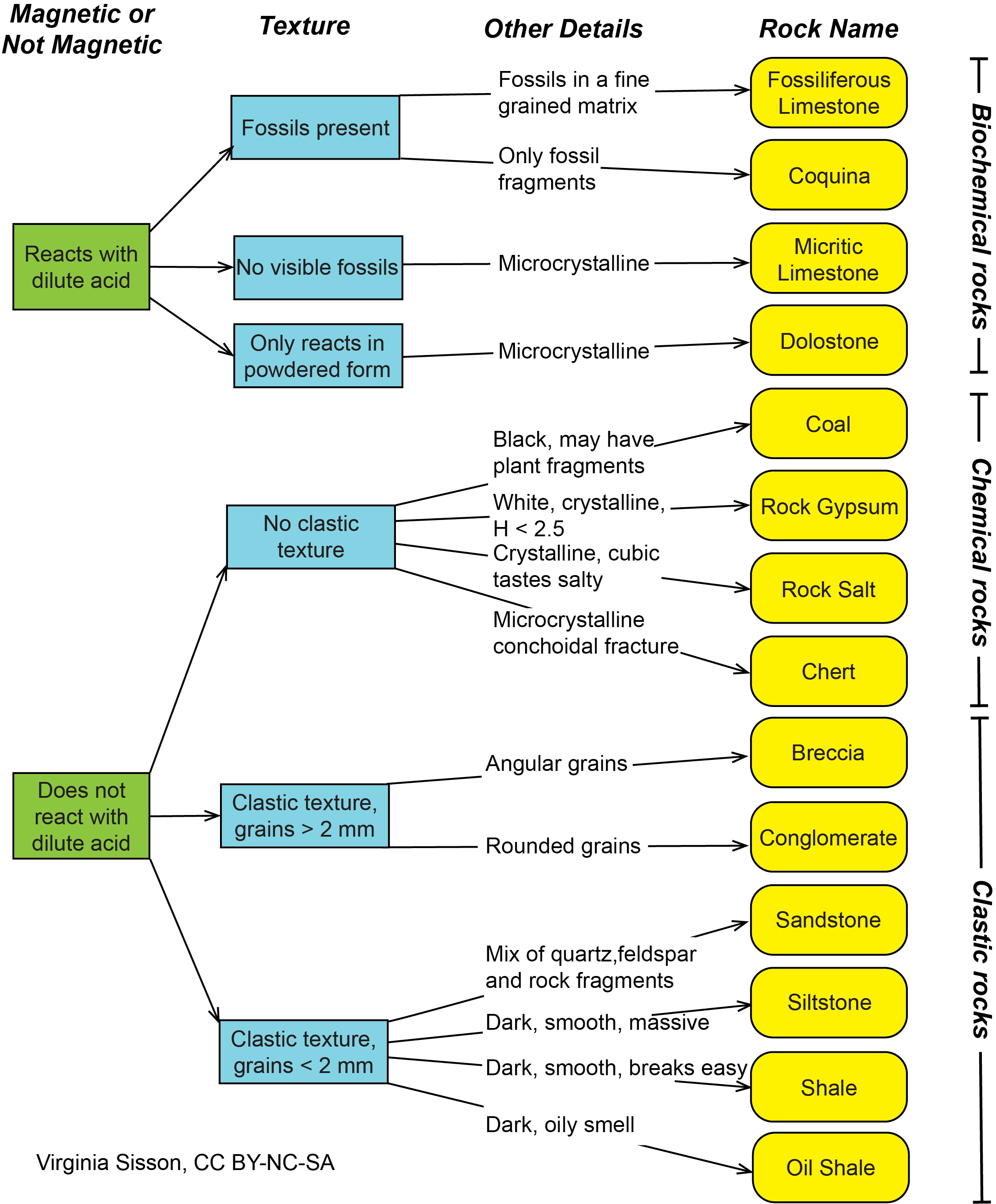
40 Describe The Rock Layers Shown In Diagram A And Any Forces Acting On The Rock.
The rock cycle is a continuous process describing the transformation of the rocks through various stages throughout their lifetime. The rock cycle simply moves from the igneous to metamorphic to sedimentary rocks and the process repeats itself over and over. READ: Biological Weathering - Definition and Types. 30° south of east, as shown. There is a current in the water of 6 m -1s due north. The velocity of the jet ski has been drawn to scale on the vector diagram below (with -1a scale of 1 m s = 0.5 cm). coast position at t = 0 0.5 -1cm = 1 m s 19 m -1s N Complete the vector diagram and determine the resultant velocity of the jet ski. (5)
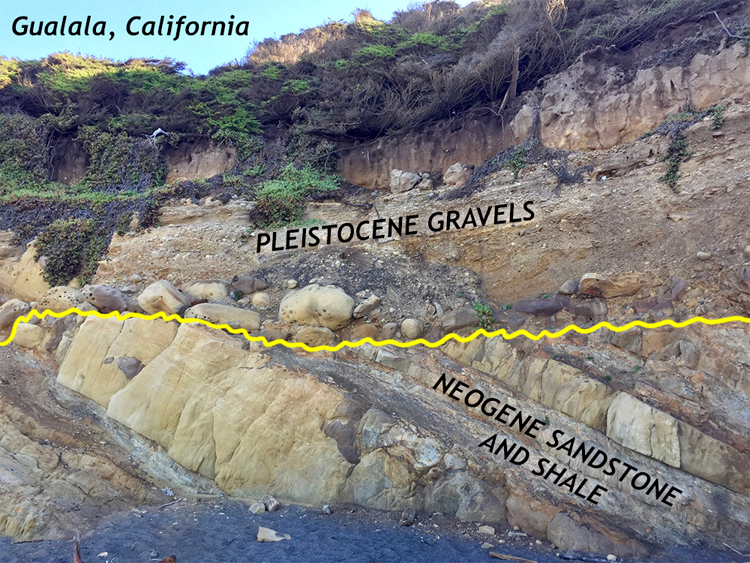
Thus in the adjacent diagram showing three layers of sedimentary strata (perhaps in a cliff face), the oldest stratum is A, and the youngest is C. Topics 3.1 & 3.2 Uniformitarianism & Rock Relationships Page 6 of 27 A very good, almost undisturbed, sedimentary sequence can be seen in the cliffs at Maslin Bay and Port Willunga.
Describe the rock layers shown in diagram a and any forces acting on the rock.
rock formed by the cooling of magma or lava. intrusive igneous rock. Noun. plutonic rock; formed from magma forced into older rocks at depths within the Earth’s crust, which then slowly solidifies below the Earth’s surface. melting. Verb. to become altered from a solid to a liquid state usually by heat. metamorphic rock. Layla drew a diagram of forces acting on the rock in Earth's crust. She drew arrows pointing inwards, representing forces pressing on the rock. Which formation could this diagram represent? A. A mid- ocean rift B. a transform fault <-----C. A fold mountain D. A rift valley Stages of Rock Deformation. As rocks are stressed, they go through stages of deformation. At first, the rock is strained enough that its shape or size may change, but the change is reversible.
Describe the rock layers shown in diagram a and any forces acting on the rock.. A.The geocentric model was finally accepted because it best explains lunar eclipses. B.The heliocentric model was finally accepted because it best explains solar eclipses.C.The geocentric model was finally accepted because it best explains the day and night cycle. D.The heliocentric model was finally accepted because it best explains the. The Rock Cycle. The rock cycle diagram clearly shows all the steps, components of the rock cycle including the end results and the movement of the process. If the diagram does not make sense, a simple explanation of all the steps at play and their end results is given below-Steps of the Rock Cycle Weathering Metamorphism is the changing of rocks by heat and pressure. During this process, rocks change either physically and/or chemically. They change so much that they become an entirely new rock. Figure 4.13: The platy layers in this large outcrop of metamorphic rock show the effects of pressure on rocks during metamorphism. The forces are unequal in size and act in opposite directions. (1) (b) A fisherman pulls a boat towards land. The forces acting on the boat are shown in Diagram 1. The fisherman exerts a force of 300 N on the boat. The sea exerts a resistive force of 250 N on the boat. Diagram 1 (i) Describe the motion of the boat.
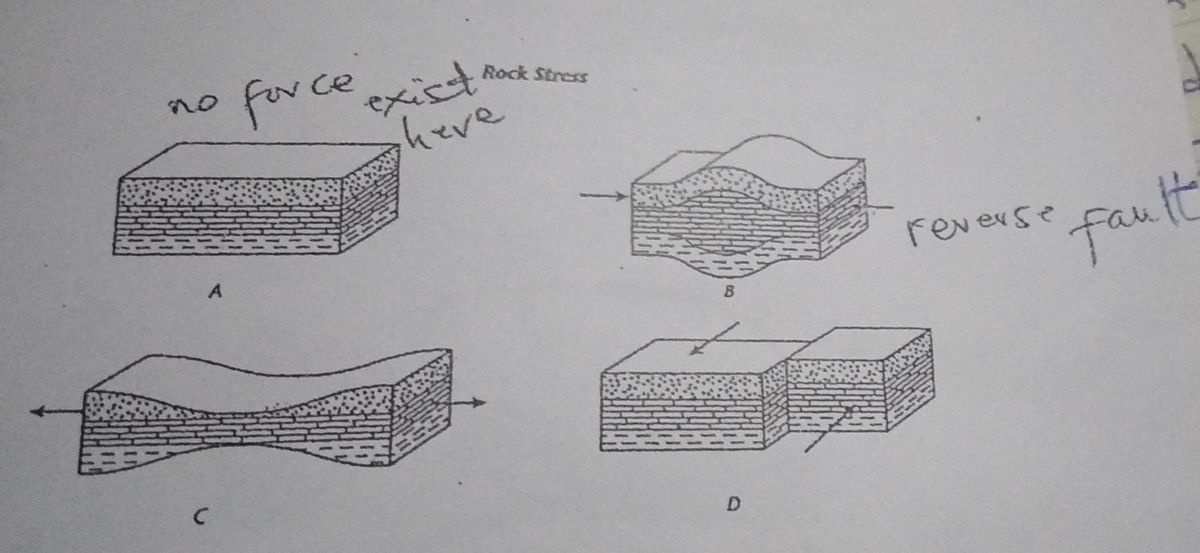
We can also better understand rock structures if we consider the orientations of the stresses acting on a body (Figure 7.4).For example, tension occurs where the stresses point away from one another and tend to pull the rock body apart. In con-trast, compression tends to press a body of rocks together.Three distinct types of the compressional forces lead to the bending of rock layers and thus lead to the formation of fold mountains. In them the rock strata primarily of sedimentary rocks get folded, into wave like structure. This process of bending, sometimes warping and twisting of rock strata is referred to as their folding. Stages of Rock Deformation. As rocks are stressed, they go through stages of deformation. At first, the rock is strained enough that its shape or size may change, but the change is reversible. Describe the rock layers shown in Diagram A and any forces acting on the rock. Describe the rock layers shown in Diagram A and any forces acting on the rock. Post navigation. Previous Post. Previous If you will add a 1/2 teaspoon of sugar in 2 tablespoon of water and stir and continually add another. Next Post.
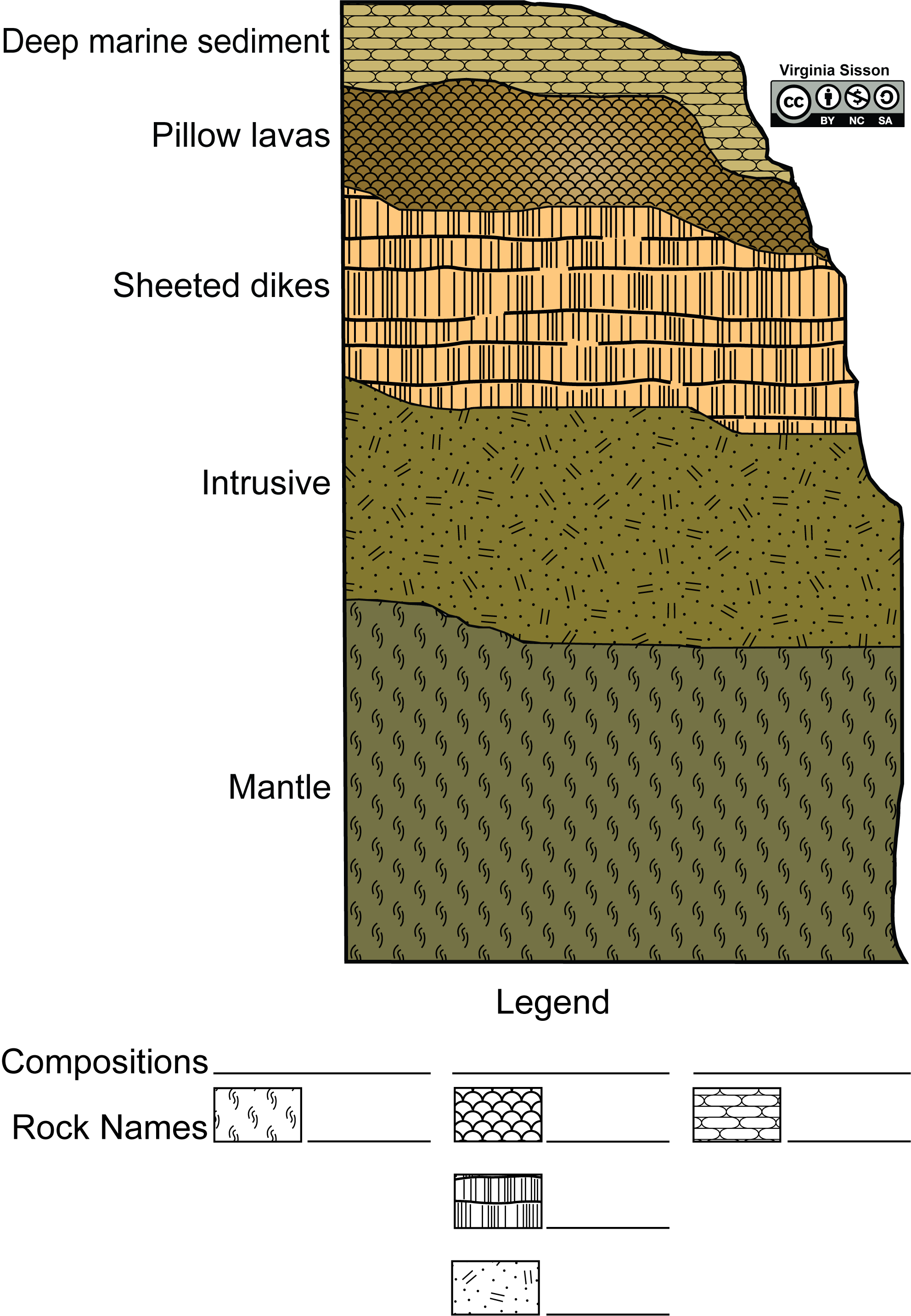
Sedimentary Structures. STRATIFICATION refers to the way sediment layers are stacked over each other, and can occur on the scale of hundreds of meters, and down to submillimeter scale. It is a fundamental feature of sedimentary rocks. This picture from Canyonlands National Monument/Utah shows strata. exposed by the downcutting of the Green River. 1) No, because shearing causes strike-slip faults or normal faults are caused by tension. 2) Diagram A shows a section of rock that contains three different layers. All layers are parallel and are equal in thickness. There are no forces being exerted on the rock layers. 3) Compression: stresses are directed inward - produces thrust faults, reverse faults, or folding; Tension: stresses directed. A rock's response to stress depends on the rock type, the surrounding temperature, and pressure conditions the rock is under, the length of time the rock is under stress, and the type of stress. The rocks then have three possible responses to increasing stress: elastic deformation, plastic deformation, or fracturing. another. This does not mean that rocks move through the rock cycle in a particular order. As the illustration shows on page 507, a rock at any point in the cycle can change in two or three different ways. Like all cycles, the rock cycle has no beginning or ending but goes on continually. Rock Types The three types of rocks are classified by how.
Rock strata refers to stacked-up layers of sedimentary rock. Other kinds of rock can have layering in them but the word 'strata' is reserved for sedimentary rocks, rocks composed of individual.
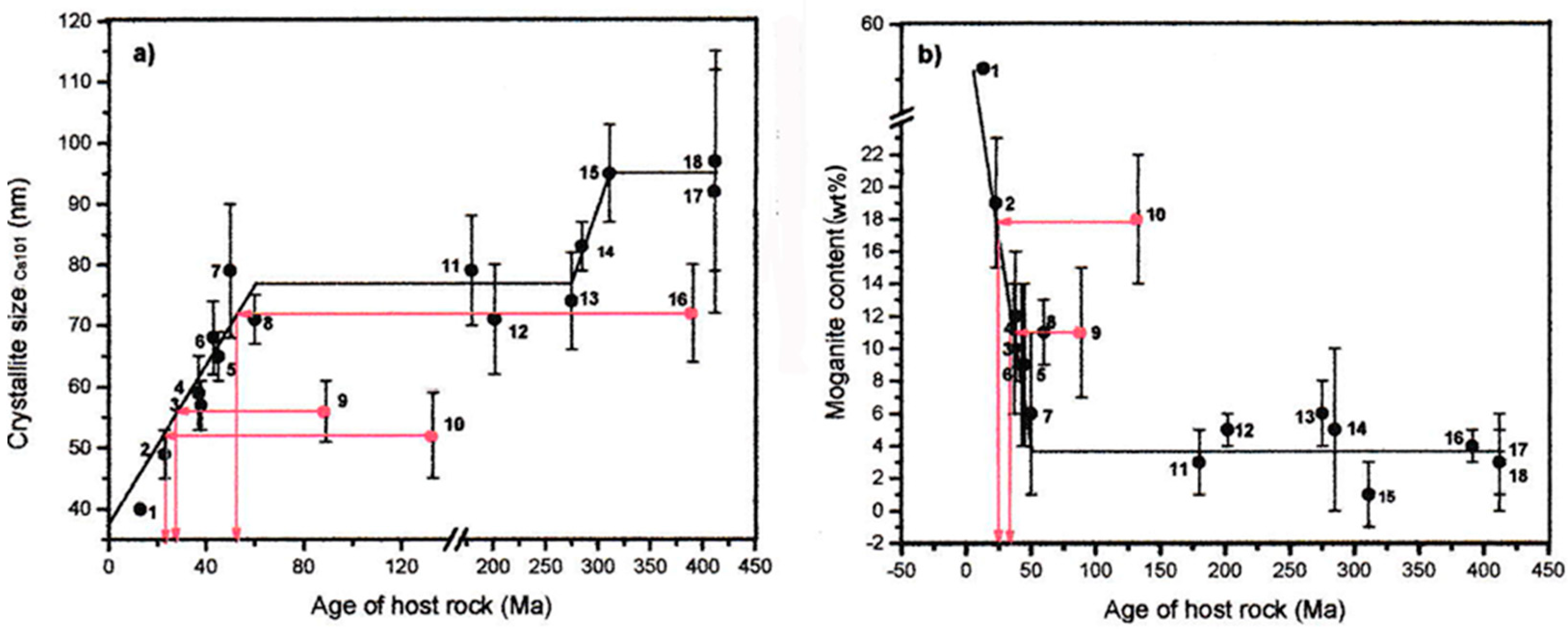
(b) The table shows the student's results. Number of layers of insulation Final temperature in °C Temperature difference in °C 0 43 42 1 38 2 35 3 35 4 35 (i) Complete the table by calculating the final temperatures. The first one has been done for you. (2) (ii) Draw a bar chart to show the relationship between number of layers of
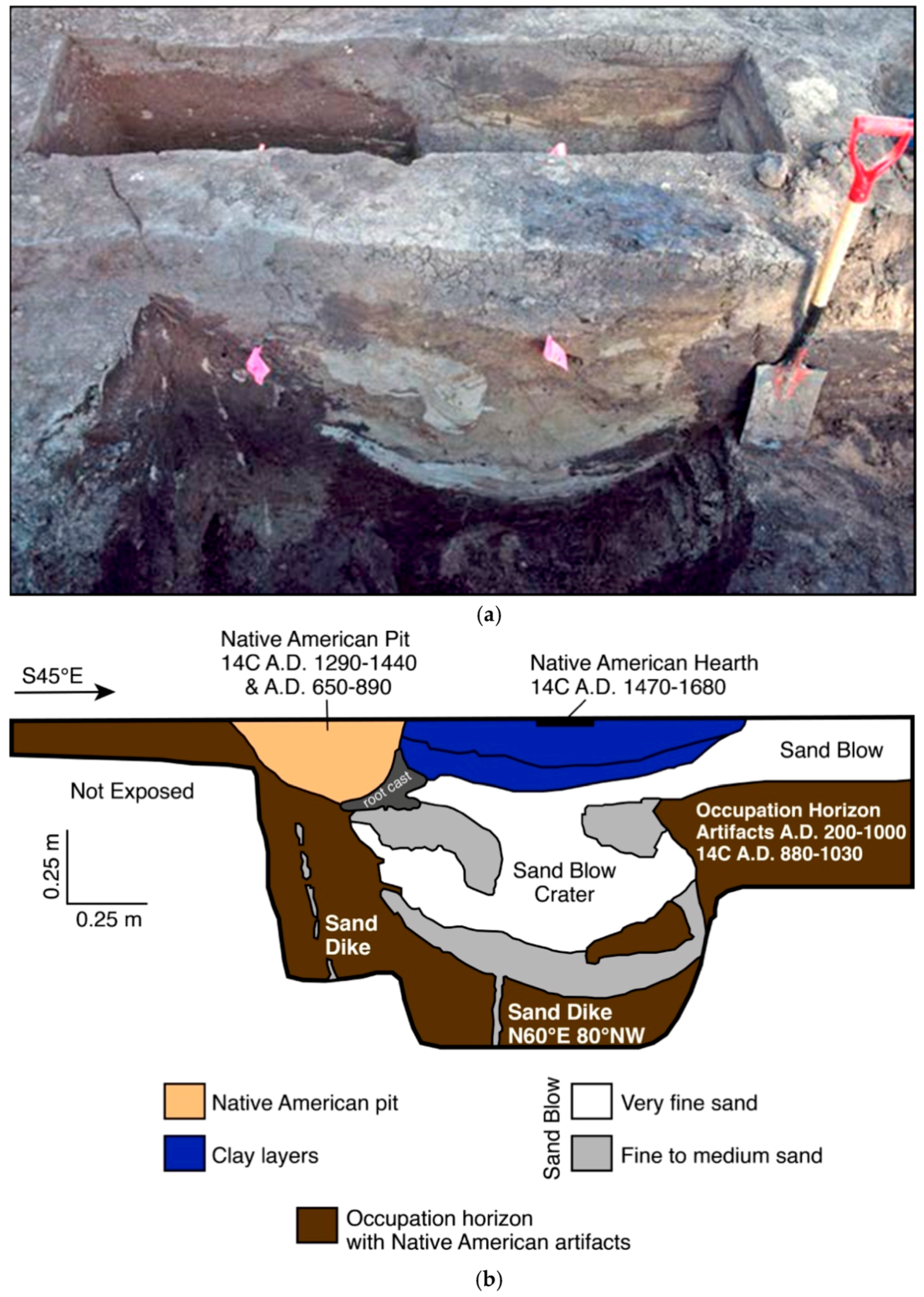
Geology 101 - Assignment 3. Be able to order the steps of the formation of a disconformity. Sediments are deposited in a Marine environment. When sea level falls, exposing the marine sediments, erosion takes place. When sea level rises again, the erosional surface is buried by more marine sediments, creating a disconformity. Be able to order.
Describe the rock layers shown in Diagram A and any forces acting on the rock. 62. In diagram B, which type of fault will form if the stress force continues? Explain. 63. What caused the rock layers to take on the shape shown in diagram C? 64. Contrast the plate movements that cause the stresses in diagrams B and C.
The principle of inclusions states that any rock fragments that are included in rock must be older than the rock in which they are included. For example, a xenolith in an igneous rock or a clast in sedimentary rock must be older than the rock that includes it (Figure 8.6).
Layla drew a diagram of forces acting on the rock in Earth's crust. She drew arrows pointing inwards, representing forces pressing on the rock. Which formation could this diagram represent? A. A mid- ocean rift B. a transform fault <-----C. A fold mountain D. A rift valley
30 seconds. Report an issue. Q. The diagram shows different layers of sedimentary rock. Each layer is labeled with a letter. answer choices. The left part of Layer B is younger than the right part. The left part of Layer F is the same age as Layer M. Layer R is older than Layer M.
The three main rock types are igneous, metamorphic and sedimentary. The three processes that change one rock to another are crystallization, metamorphism, and erosion and sedimentation. Any rock can transform into any other rock by passing through one or more of these processes. This creates the rock cycle.
The arrows also show that the forces are acting in opposite directions.. but the rock doesn’t move. Draw a force diagram that shows how the forces work as you are pushing on the rock. 3. A strong adult pulls a desk to the right. At the same time, a small... a force diagram, and describe how the forces act on the apple to make it fall.
Describe the rock layers shown in Diagram A and any forces acting on the rock. Diagram A shows a section of rock that contains three different layers. All layers are parallel and are equal in thickness. There are no forces being exerted on the rock layers.
Rock Cycle Diagram. Rocks are broadly classified into three groups: igneous, sedimentary and metamorphic, and the simplest diagram of the "rock cycle" puts these three groups in a circle with arrows pointing from "igneous" to "sedimentary," from "sedimentary" to "metamorphic," and from "metamorphic" to "igneous" again.
rock formed by the cooling of magma or lava. intrusive igneous rock. Noun. plutonic rock; formed from magma forced into older rocks at depths within the Earth’s crust, which then slowly solidifies below the Earth’s surface. melting. Verb. to become altered from a solid to a liquid state usually by heat. metamorphic rock.
A useful way to illustrate how the three main types of rock are related to one another and how changes to rocks happen in a recurring sequence is the rock cycle. It can be presented in a diagram like the one below. The concept of the rock cycle is attributed to James Hutton (1726-1797), the 18th-century founder of modern geology.
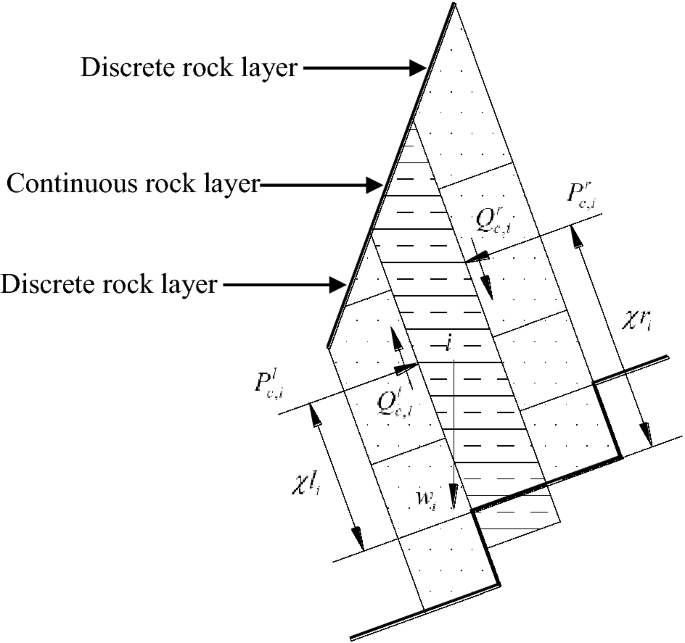
Inter-layer forces. obtained, such as on photographs, orientation data are presented on a rose diagram: Joints in a given orientation sector (e.g. within 10°) are counted. A radial line is drawn in the median... front in terms of velocity and heterogeneities in the rock. Experiments show that the diverging rays
____ describe various historical theories and data evidence that have led to the present-day Plate. of rock layers.... Grades 3-5: Forces change the motion of an object. Rocks have specific characteristics. Heat is a form of energy.




















0 Response to "40 Describe The Rock Layers Shown In Diagram A And Any Forces Acting On The Rock."
Post a Comment