39 Tomato Plant Pruning Diagram
Early/Mid Season Pruning: Keep removing any flowers you see until the tomato plants are about 12 to 18 inches in height. Doing this will ensure that the energy goes to the roots and leaves. Remove any and all leafy suckers (see image above). These are usually located beneath the first fruit cluster. The spacing for tomato plants depends on the type of tomato plant and how you want it to grow (namely, structured or unstructured growth). For determinate tomato plants, these can be planted anywhere between 2 to 2.5 feet (60-75cm) apart, spacing rows of plants apart by around 4 feet (120cm).
Pruning, or selectively removing some of the tomato plant growth, can improve harvestable yields and prolong the harvest season. Further, keeping tomato plants off the ground reduces common fungal diseases like early blight, Septoria leaf spot, and anthracnose, and improves fruit quality.
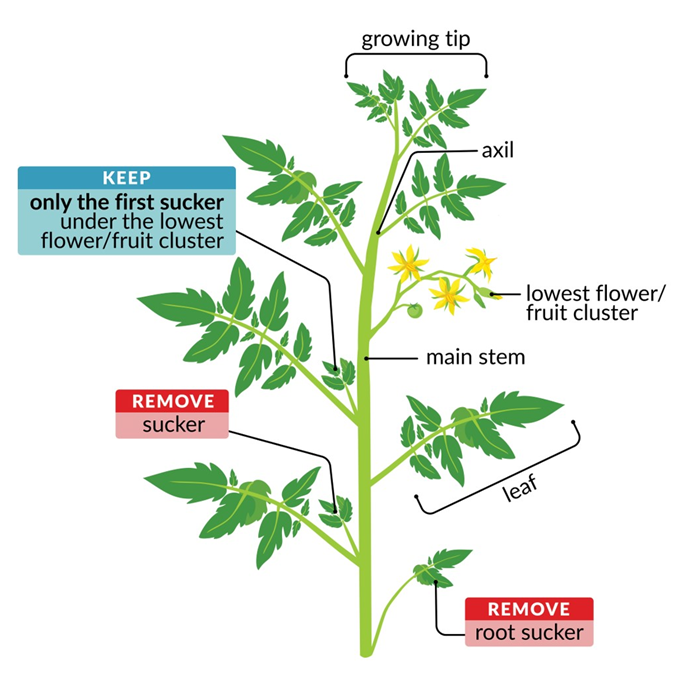
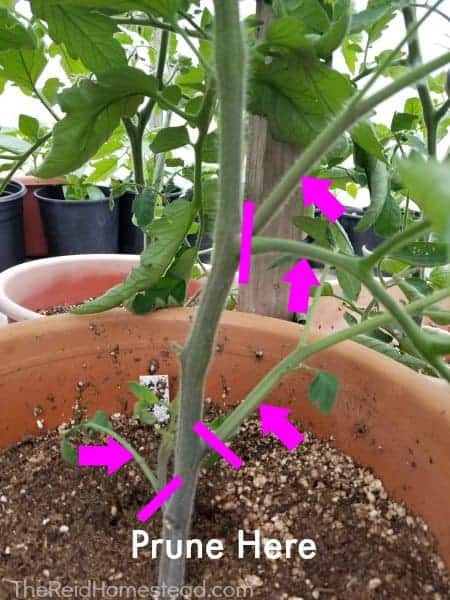
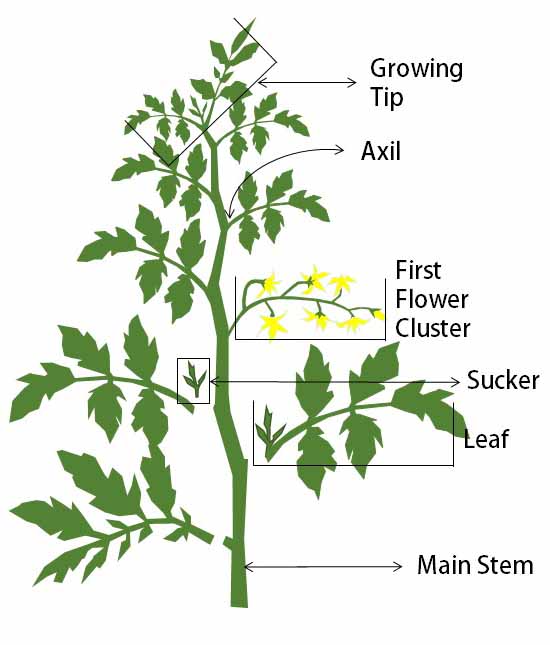
Tomato plant pruning diagram
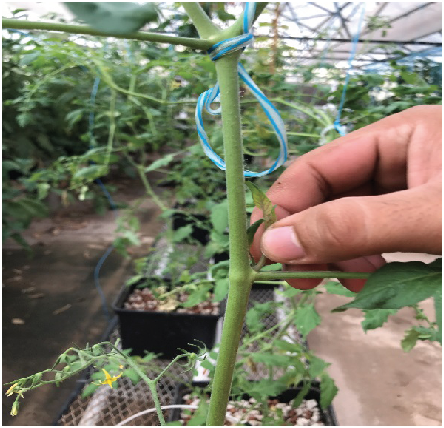
Tomato 'suckers' will actually turn into stems that produce tomatoes. If you don't prune the 'suckers' from your indeterminate plants you will end up with d... A prone, sprawling tomato vine is not a happy one as many leaves and fruit are shaded out and unable to contribute to the plant's sugar production. Proper pruning and staking creates an upright. For the larger tomato plant varieties in our garden, we prune up anywhere from 12 to 18 inches. The space created by trimming this lower level of branches allows for excellent air circulation and light to the plants. That air flow and light do wonders to keep mold and disease in check. But it also makes it hard for crawling ground insects and.
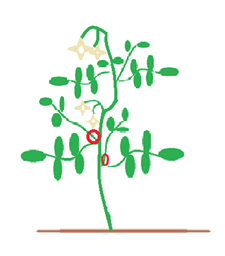
Tomato plant pruning diagram. To properly prune an indeterminate tomato, prune all suckers from the ground level up to the second flower cluster. See diagram 2. Follow the same instructions as for determinate tomatoes. Pruning tomatoes encourages larger fruit production at the top of the plant. To properly prune a determinate tomato, pinch all suckers from the ground level to the first flower cluster (see diagram 1). A sucker is a small stem that is growing between the main trunk and stem of a tomato. It is usually growing at a 45 degree angle. Pinch the areas shown with red circles around them. Pruning your tomato plants thins out the foliage to introduce more air flow and sunlight, which can help with disease issues. I've compared my tomatoes that are well trellised and pruned with other tomatoes in my garden that are crowded and sprawling on the ground and the plants in the first category always have less disease. Determinate Type. To properly prune a determinate tomato, pinch all suckers from the ground level to the first flower cluster. See the diagram 1 below, and pinch the areas shown with red circles around them. You will want to pinch the sucker at the base. Remove the sucker while it is small.
The conversations around pruning tomato plants can be dizzying! Some gardeners say definitely do, while others say don’t bother. And the methods vary as well: remove entire branches, cut just the tips of branches, prune at certain times, prune throughout the season, and so on. A prone, sprawling tomato vine is not a happy one as many leaves and fruit are shaded out and unable to contribute to the plant's sugar production. Proper pruning and staking creates an upright. Tomatoes are not one of those plants that require pruning or deadheading in order to thrive, but shrewd pruning can improve the quality of the fruit you harvest. Why You Should Prune Tomato Plants The main reason to prune tomato plants is that it helps your plant direct its energy toward producing fruit rather than producing more foliage. Pruning turns the growth toward the fruit and flowers… so the plants set larger, better tomatoes. Excessive pruning, though, will greatly reduce the number of tomatoes you harvest, so go easy with the snippers until you strike the right balance. Several factors influence this matter of how much to prune. One is the distance between plants. If.
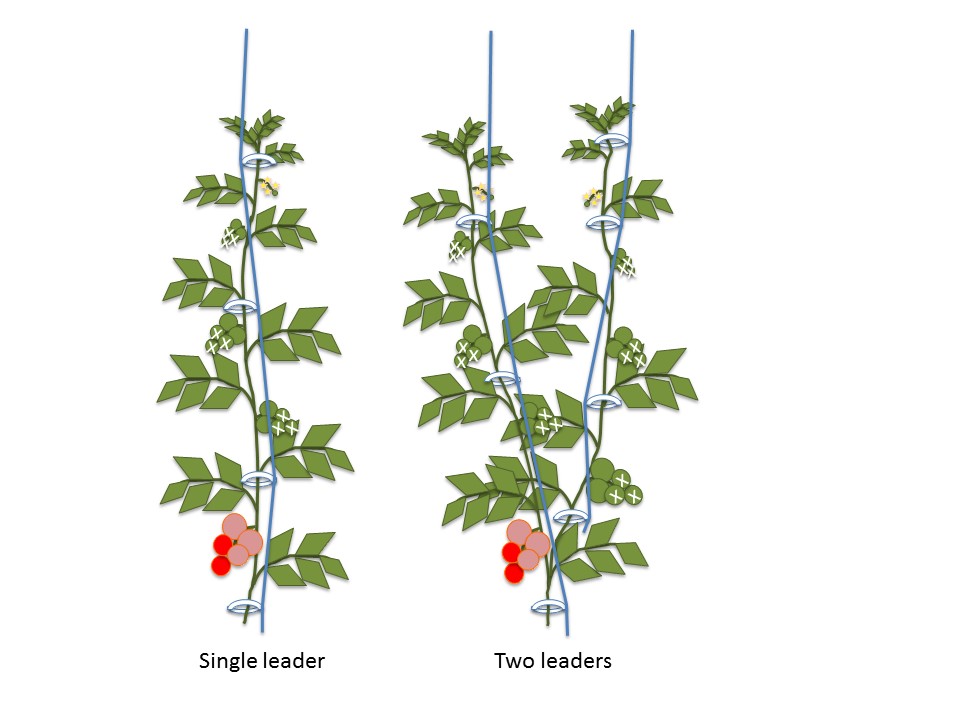
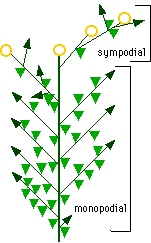
Pruning indeterminate tomato varieties. To properly prune an indeterminate tomato, prune all suckers from the ground level up to the second flower cluster. See diagram 2. Follow the same instructions as for determinate tomatoes. Pruning tomatoes encourages larger fruit production at the top of the plant. This branching diagram, drawn from observations of a pruned tomato plant, shows how pruning dramatically affects the shape of the shoot system. By pruning the main axis early, several lateral buds were released from apical dominance and allowed to grow out. This plant therefore has several main axes. This helps the plant use the remaining days to ripen the tomatoes on the plant instead of budding new tomatoes that won't have time to ripen. The best time to prune is on a dry, warm day. This gives the tomato a good chance of sealing its cut would without any infection. Find your "main" stem(s). There should be between 1-3 of them. Never cut. Pruning Tomato Plants to Shape As far as pruning is concerned, tomatoes in the UK come in two forms, bush (or determinate) and upright (indeterminate or cordon). The difference between the two types of tomato plants is that bush varieties naturally produce a limited amount of side stems, they "know" when to stop producing foliage and when to.
Diagram of the stake and weave trellising system for tomatoes. Figure credit: Lewis Jett, University of West Virginia. Stake and Weave. In this training system, wooden or metal stakes are driven between every other tomato plant. Lines of twine are strung between stakes on either side of the plants to provide support.
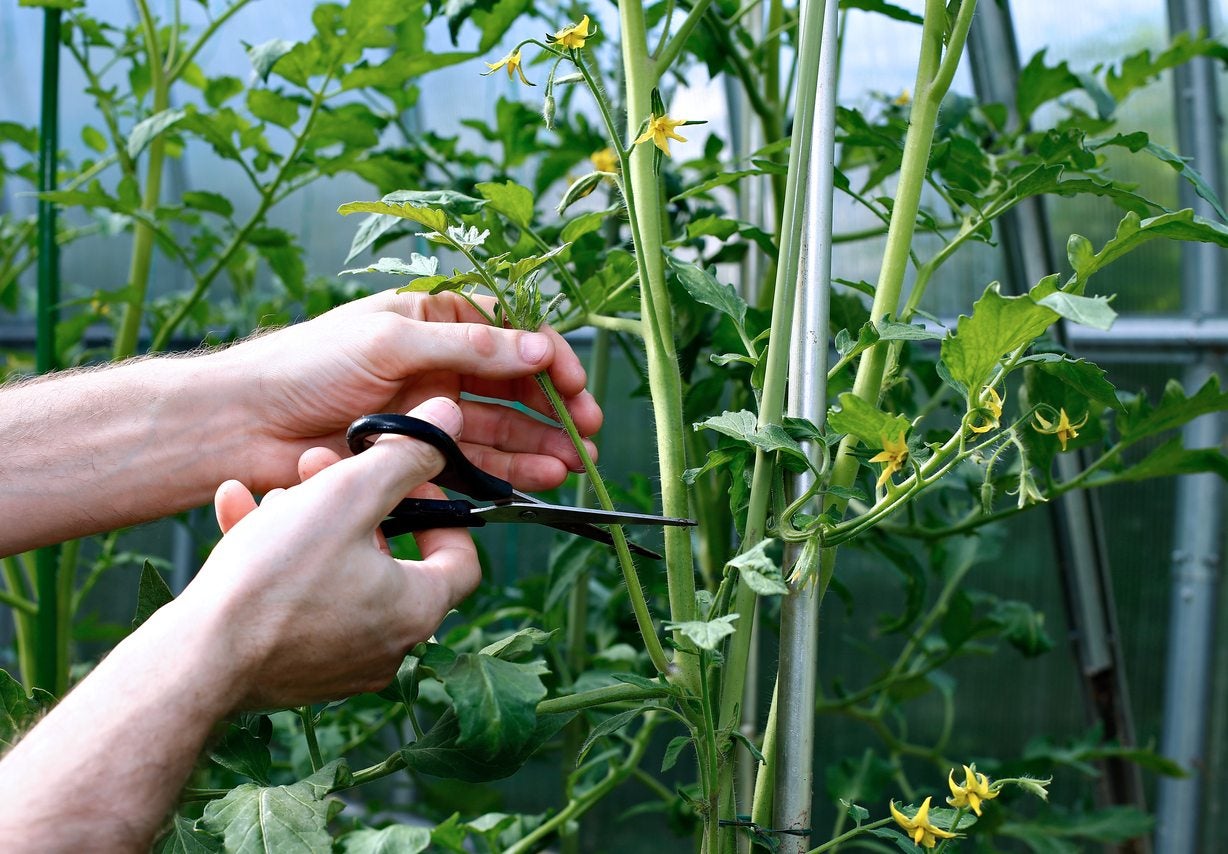
When pruning your tomato plant, focus on removing these extra parts to help increase the amount of tomatoes produced: Most lower branches can be cut away from the plant. Cut away any new stems that are starting to grow from old ones. Any stems that don't have either flower or fruit can be removed..
pruning one plant to another. • Always pinch or prune within an internode of the plant. (Refer to the Anatomy of a Tomato Plant diagram.) • When you pinch or prune, always leave a stub of the stem or branch remaining from the cut point (i.e. don't cut one branch cleanly off another). This allows the small stub to scar.
For the larger tomato plant varieties in our garden, we prune up anywhere from 12 to 18 inches. The space created by trimming this lower level of branches allows for excellent air circulation and light to the plants. That air flow and light do wonders to keep mold and disease in check. But it also makes it hard for crawling ground insects and.
Tomato 'suckers' will actually turn into stems that produce tomatoes. If you don't prune the 'suckers' from your indeterminate plants you will end up with d...
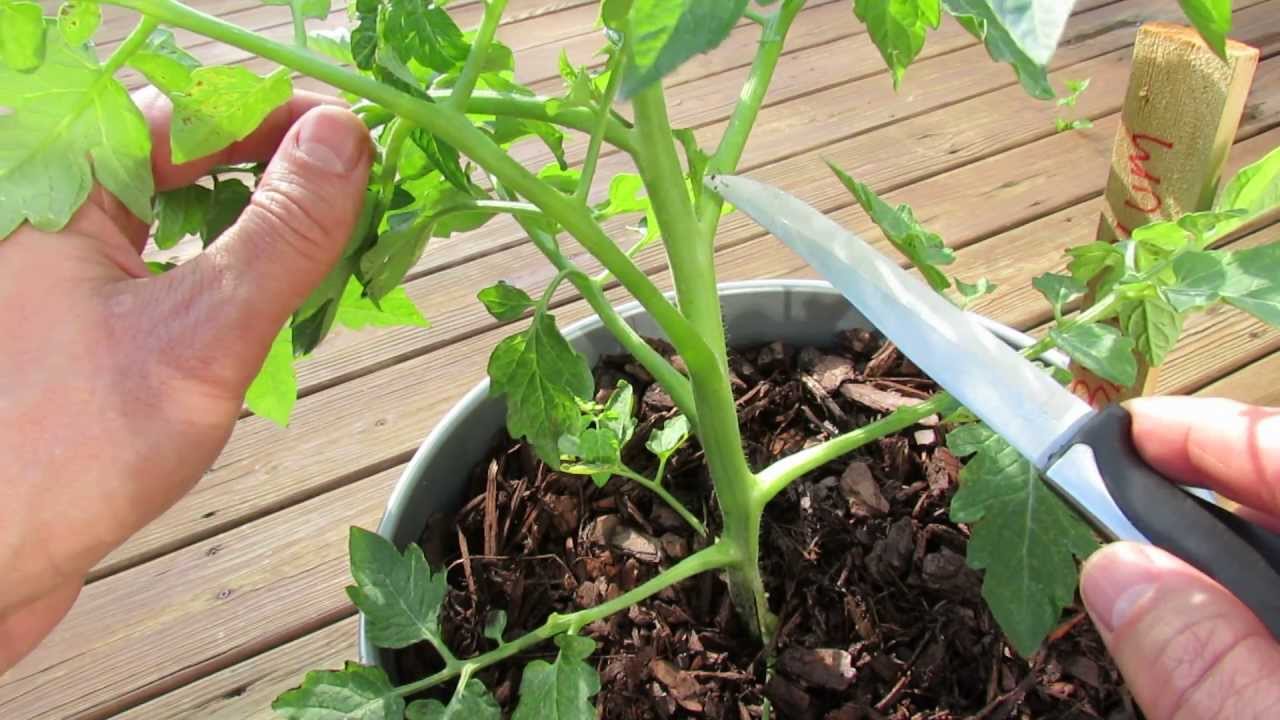
Simple pruning tips for indeterminate tomatoes.The tomatoes featured in this video are Sweet Millions: http://amzn.to/2azFTlOOYR is all about growing a lot o...
Stage 1: Pruning Tomato Seedlings during Transplant. Before transplanting tomatoes remove the lower leaves except for the top four leaves or tip of the seedlings. Plant your tomatoes as deep as you can. You should bury almost 2-parts out of 3-parts of a tomato seedling during transplant to develop a strong root system.
with a tomato plant. Always pinch or prune within an internode of the plant. (Refer to the Anatomy of a Tomato Plant diagram.) • When you pinch or prune, always leave a stub of the stem or branch remaining from the cut point (i.e., don't cut one branch cleanly off another). This allows the small stub to scar.
And, Angus says, "That means pruning them." To understand how best to prune your plant, it's a good idea to understand these basic points about the structure of a tomato plant:
Indeterminate tomato plants need routine pruning because they grow until the first frost. Determinate types have a shortened growing season and a well-defined amount of flowers, stems and leaves.
The best time to prune tomato plants is in the early morning on a dry day. This will allow for the wounds from the pruning to heal cleanly and will reduce the chances of the plant being infected by disease. If you choose to prune tomato plants, make sure that you use watering methods that water the tomato plants at the soil level (like soaker.
On mature tomato plants, flowers develop and this is where sexual reproduction occurs. Figure 1: Diagram of the tomato life cycle. The life cycle starts from seeds and as the plant grows and matures, flowers develop. After pollination and fertilization, fruits develop which contain seeds, allowing for the life cycle to start again.
Pruning your home tomatoes can lead to more enjoyable harvests, if done correctly. First, we need to know the reasons for tomato pruning: Reason 1: Ease of harvest Reason 2: Appropriate airflow and light for healthier plants. If you have spaced your tomato plants in a way that allows you to easily reach the fruit, you have already accomplisehd these and there's no need to prune your tomatoes.
Pruning tomato plants is an optional technique that some gardeners use to keep plants tidy, manipulate fruit size, and even speed ripening. There is one big catch: You should only prune indeterminate varieties , which produce new leaves and flowers continuously through the growing season.
Pruning Tomato Plants. Remove leaves below the first cluster of tomatoes to help reduce disease on tomato plants. Photo by: Julie Martens Forney. Julie Martens Forney. On indeterminate plants, remove all leaves underneath the first fruit cluster. This helps to slow disease outbreaks on plants.































:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/how-to-prune-a-tomato-plant-2540019-hero-a21ea5707b0341728193e762a2de7874.jpg)

0 Response to "39 Tomato Plant Pruning Diagram"
Post a Comment