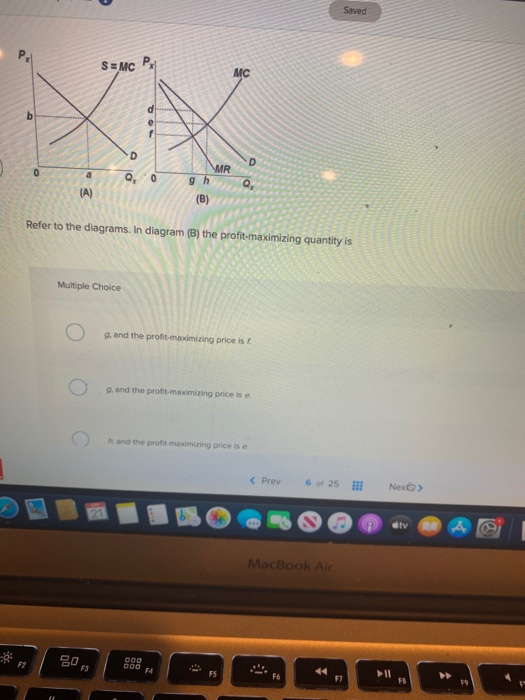
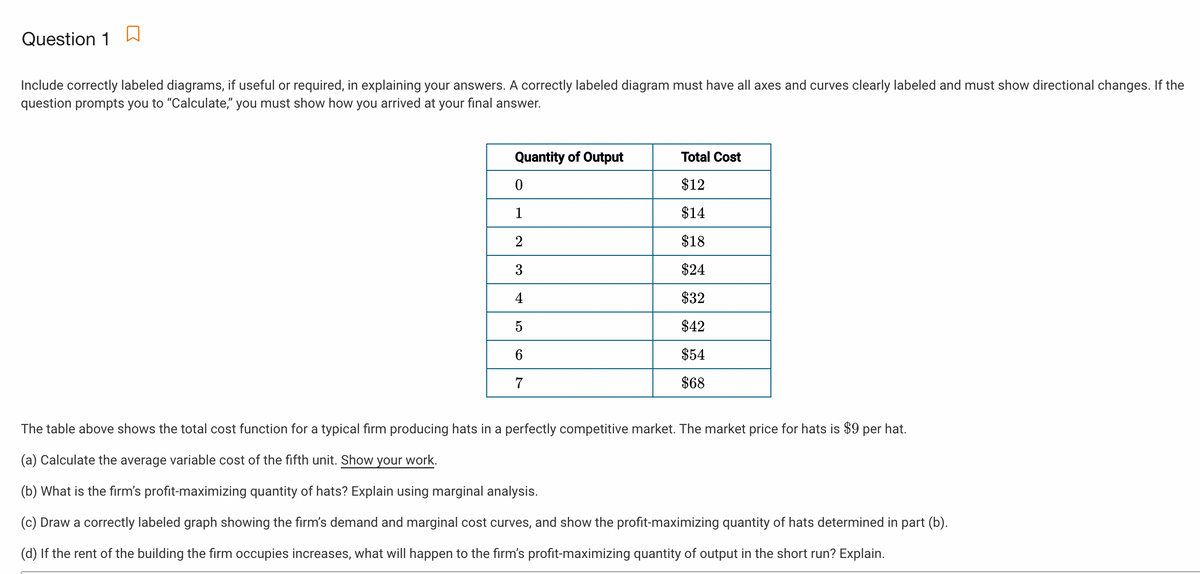
39 Refer To The Diagrams. In Diagram (b) The Profit-maximizing Quantity Is
Refer to the diagrams. In diagram b the profit maximizing quantity is. B output will be the same as in diagram a. Refer to the above diagram for a noncollusive oligopolist. G and the profit maximizing price is f. C b price equals marginal cost resulting in allocative efficiency. G and the profit maximizing price is d. B output will be the same. In diagram (B) the profit maximizing quantity is Multiple Choice and the profit maximizing price ist and the profit maximizing price is e and the profit maximizing price is e < Prev 6 of 2518 Nexo> MacBook Air Refer to the diagrams. In diagram (B) the profit-maximizing quantity is Multiple Choice o 9. and the profit-maximizing price is f 0 g.
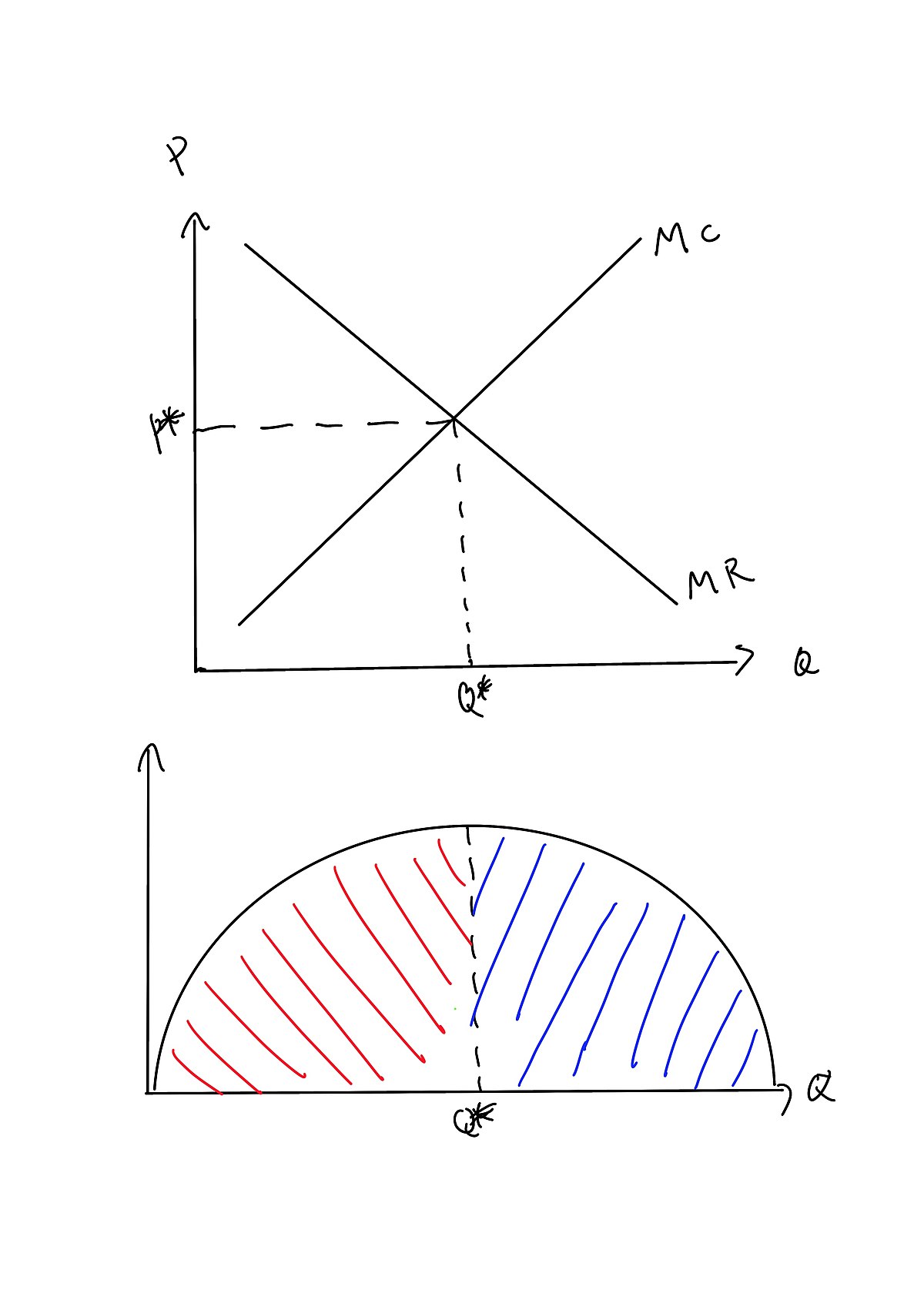
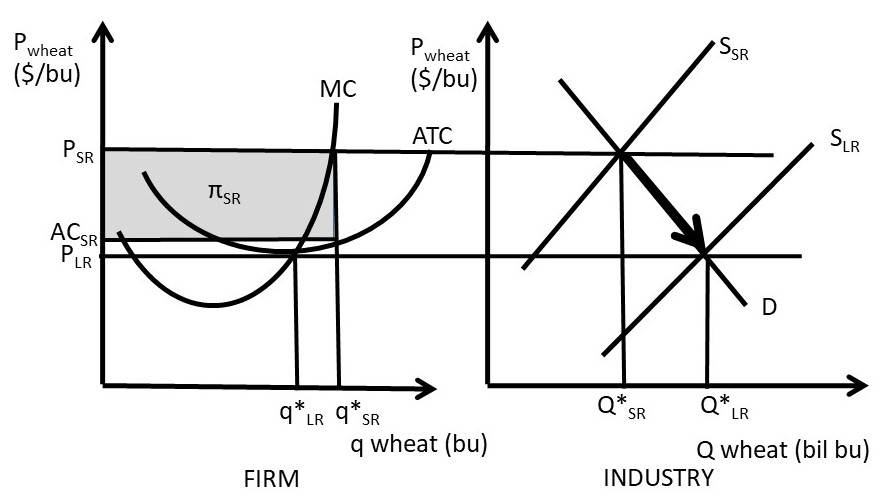
In diagram (B) the profit-maximizing quantity is: g and the profit-maximizing price is d. Refer to the above diagrams. With the industry structure represented by diagram: (A) there will be only a normal profit in the long run, while in (B) an economic profit can persist.
Refer to the diagrams. in diagram (b) the profit-maximizing quantity is
79. Refer to the above diagrams. In diagram (B) the profit-maximizing quantity is: A. g and the profit-maximizing price is e. B. h and the profit-maximizing price is e. C. g and the profit-maximizing price is f. D. g and the profit-maximizing price is d. 134. Refer to the above diagrams. In diagram (B) the profit-maximizing quantity is: A) g and the profit-maximizing price is e. C) g and the profit-maximizing price is f. B) h and the profit-maximizing price is e. D) g and the profit-maximizing price is D View Homework Help - ECONHW13Sols41.pdf from ECON 4103 at University of New South Wales. 117. Award: 1.00 point Refer to the diagrams. In diagram (B) the prot-maximizing quantity is g, and the
Refer to the diagrams. in diagram (b) the profit-maximizing quantity is. 79. Refer to the above diagrams. In diagram (B) the profit-maximizing quantity is: A. g and the profit-maximizing price is e. B. h and the profit-maximizing price is e. C. g and the profit-maximizing price is f. D. g and the profit-maximizing price is d. The profit maximizing quantity is given by: q* 9.7. 100 2q 3 8q 0 dq d (q) 100q q2 420 3q 4q2 = = − − − = Π In a picture, this all looks like: A graph showing a profit curve that has an inverted U-shape and has a peak at the profit maximizing quantity. Profit is maximized at the quantity q* and is lower at all other quantities. The curvature View Homework Help - ECONHW13Sols41.pdf from ECON 4103 at University of New South Wales. 117. Award: 1.00 point Refer to the diagrams. In diagram (B) the prot-maximizing quantity is g, and the Refer to the above diagrams. With the industry structure represented by diagram: A) (A) there will be only a normal profit in the long run, while in (B) an economic profit can persist. B) (A) price exceeds marginal cost, resulting in allocative inefficiency. C) (B) price equals marginal cost, resulting in allocative efficiency.
134. Refer to the above diagrams. In diagram (B) the profit-maximizing quantity is: A) g and the profit-maximizing price is e. C) g and the profit-maximizing price is f. B) h and the profit-maximizing price is e. D) g and the profit-maximizing price is D `refer to the diagram. at the profit maximizing level of output. 0BHE `refer to the diagram. at the profit maximizing level of output total revenue will be. 0AJE `refer to the diagrams. diagram (A) represents. equilibrium price and quantity in a purely competitive industry `Refer to the diagrams. In diagram (B) the profit-maximizing quantity is. Refer to the above diagrams. Diagram (A) represents.. In diagram (B) the profit-maximizing quantity is: g and the profit-maximizing price is d. Refer to the above diagrams. With the industry structure represented by diagram (A) there will be only a normal profit in the long run, while in (B) an economic profit can persist.... 10. Refer to the diagrams. In diagram (B) the profit-maximizing quantity is A. g, and the profit-maximizing price is e. B. h, and the profit-maximizing price is e. C. g, and the profit-maximizing price is f. D. g, and the profit-maximizing price is d.
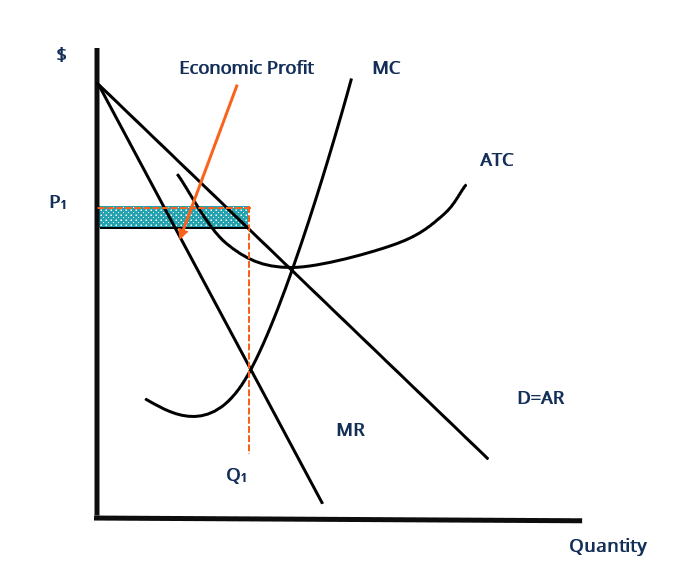
Profit Maximisation Theory: In the neo-classical theory of the firm, the main objective of a business firm is profit maximisation. The firm maximises its profits when it satisfies the two rules. MC = MR and the MC curve cuts the MR curve from below Maximum profits refer to pure profits which are a surplus above the average cost of production.



/law_of_demand_chart2-5a33e7fc7c394604977f540064b8e404.png)












0 Response to "39 Refer To The Diagrams. In Diagram (b) The Profit-maximizing Quantity Is"
Post a Comment