39 Fatty Acid Structure Diagram
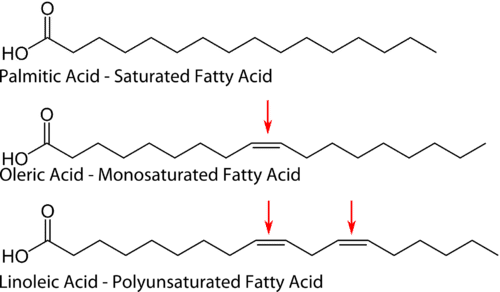
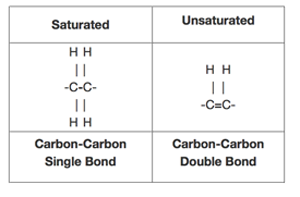
One system of fatty acid classification is based on the number of double bonds. 0 double bonds: saturated fatty acids. Stearic acid is a typical long chain saturated fatty acid. 1 double bond: monounsaturated fatty acids. Oleic acid is a typical monounsaturated fatty acid. 2 or more double bonds: polyunsaturated fatty acids. Oct 09, 2021 · 7SHM Cryo-EM structure of ATP-bound human peroxisomal fatty acid transporter ABCD1. DOI: 10.2210/pdb7SHM/pdb EMDataResource: EMD-25130 Classification: LIPID TRANSPORT.
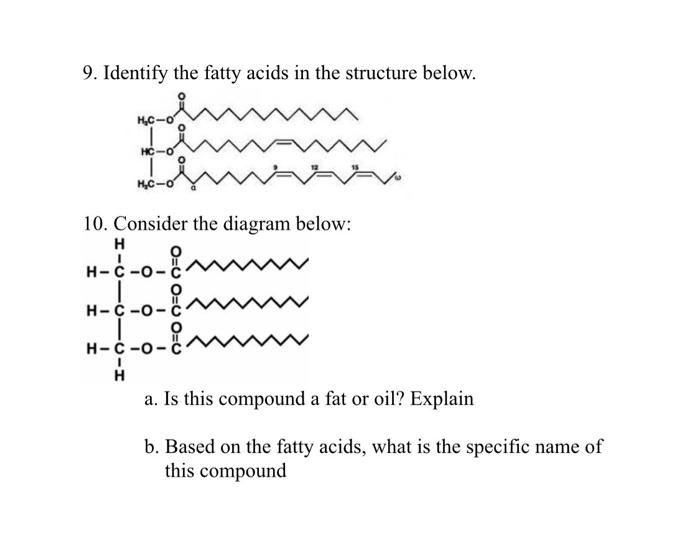
Structure. Triglycerides or triacylglycerols (TAG) are the compounds that are made by esterifying glycerol with three fatty acids. Normally, the fatty acids at carbon 1 and carbon 3 of glycerol are saturated ones while the second carbon of glycerol in triglycerides is esterified to an unsaturated fatty acid. Synthesis.
Fatty acid structure diagram
May 15, 2021 · Cytoskeleton – Definition, Structure, and Functions with Diagram Structure of Cytoskeleton. This is a fibrous network that’s formed from and by different proteins of long chains of amino acids. These proteins are found in the cell cytoplasm of the eukaryotic cells. The diagram shows the general structure of a lipid, which consists of two main parts. The part that is circled is the fatty acid carboxyl group. -Lipids is one of the four important biomolecules, others being, nucleic acid, carbohydrates, and proteins. -Lipids are made of glycerol and fatty acids. Fatty acids consist of a carboxylic acid (-C=O. The following diagram shows the structures of some of these components. Clicking on the diagram will change it to display structures for two representative phospholipids. Note that the fatty acid components (R & R') may be saturated or unsaturated. To see a model of a phospholipid Click Here.
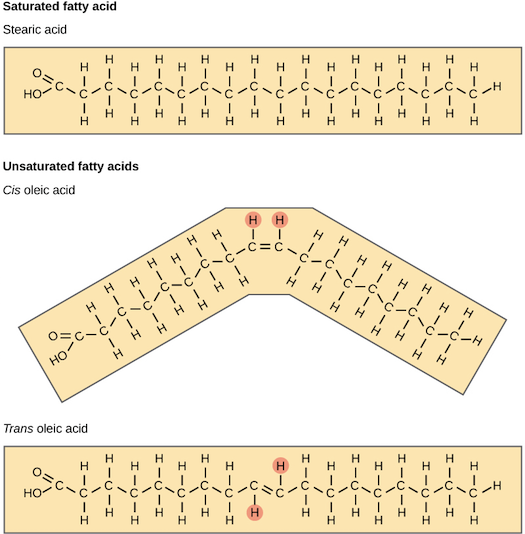
Fatty acid structure diagram. Glycerol and Fatty Acids. One major class of lipids is called glycerolipids. Glycerolipids are composed of glycerol and fatty acids. Glycerol, whose structural formula is shown at right, has three carbon atoms, each of which has a hydroxyl (-OH) group bound to it.. Fatty acids are fairly long linear hydrocarbon chains with a carboxylic acid group at one end. Unsaturated fatty acids most commonly have their double bonds in cis configuration; the other, less common configuration is trans. Cis bond causes a bend in the fatty acid chain, whereas the geometry of trans bond straightens the fatty acid chain, imparting a structure more similar to that of saturated fatty acids. CONTENTS (ii) The student found two graphs about the structure of lipids and their melting points. Chain length / number of carbon atoms in Melting point / fatty acid chain ° C Melting point / ° C Number of double bonds between carbon atoms 75 50 25 0 –25 –50 –75 5 10 15 20 Key saturated fatty acid unsaturated fatty acid 20 10 0 –10 –20. Fatty acids are classified in many ways: by length, by saturation vs unsaturation, by even vs odd carbon content, and by linear vs branched. Length of fatty acids. Short-chain fatty acids (SCFA) are fatty acids with aliphatic tails of five or fewer carbons (e.g. butyric acid).; Medium-chain fatty acids (MCFA) are fatty acids with aliphatic tails of 6 to 12 carbons, which can form medium-chain.
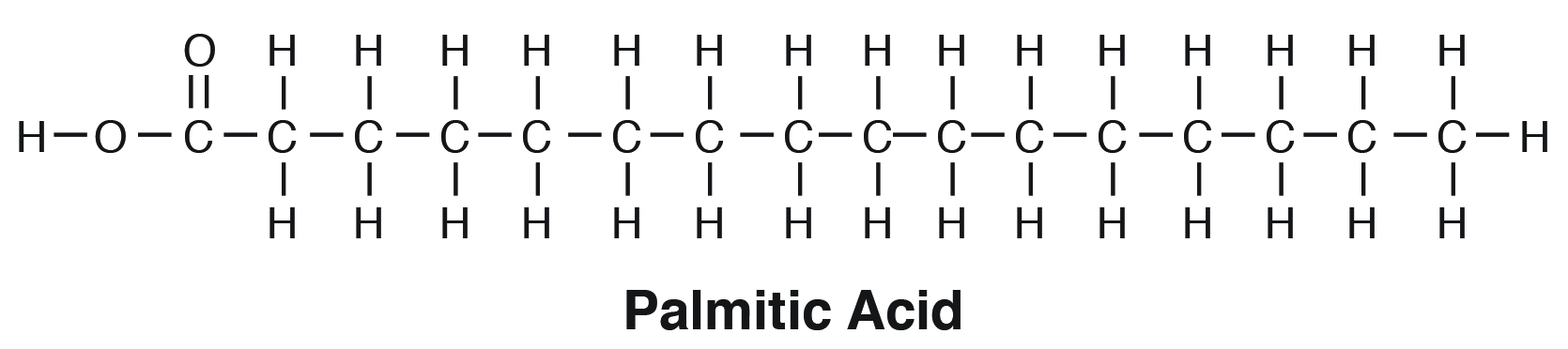
Oct 29, 2021 · Transesterification of fatty acid ethoxylates in supercritical methanol, then gas chromatography-mass spectrometric determination of the derived methyl esters, for identification of the initiators Fresenius’ J. Anal. Chem. , 371 ( 3 ) ( 2001 ) , pp. 369 - 375 May 15, 2021 · Cytoskeleton – Definition, Structure, and Functions with Diagram Structure of Cytoskeleton. This is a fibrous network that’s formed from and by different proteins of long chains of amino acids. These proteins are found in the cell cytoplasm of the eukaryotic cells. Fatty Acid Structure. Fatty acids are composed of carbon chains containing a methyl group at one end and a carboxyl group at the other. The methyl group is termed the omega (ω) and the carbon atom situated next to the carboxyl group is termed the "α" carbon, followed by the "β" carbon, etc. Fatty acid molecules also have two. Fatty acids are composed of long hydrocarbon chains terminated by carboxylic acid groups. Fatty acids are basically the primary derivative of lipids. Chain length from 4 to usually 24C atoms. They contain even number of C atoms majority of fatty acids are those containing 16 and 18 C atoms. Fatty Acid Structure Described Below.
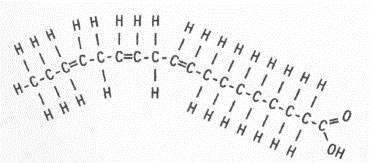
Omega−3 fatty acids, also called Omega-3 oils, ω−3 fatty acids or n−3 fatty acids, are polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) characterized by the presence of a double bond, three atoms away from the terminal methyl group in their chemical structure. They are widely distributed in nature, being important constituents of animal lipid metabolism, and they play an important role in the human. Lipid Structure Diagram. Molecular Structure of Lipids (With Diagram). Further reading and references The structure of the fatty acids influences the structure of the lipid. Lipids serve many important biological roles. They also play a role in diseases. Lipid Phospholipid Structure Diagram - Diagramaica. Saturated fatty acids do not contain double bonds C-C (only single bonds), whereas unsaturated fatty acids contain one or more double bonds C=C. The chain length of most common fatty acids is of 16-18 number of carbon. The triglyceride is considered as the common and simple type of fat, having three fatty acids and glyceride. fatty acid structure. saturated fatty acid have. all the available bonds in a saturated…. unsaturated fatty acids have. the double bonds makes the. a single bond between carbons in the hydrocarbon chain. are saturated with hydrogen. double bonds between carbon atoms in the hydrocarbon chain. molecule bends which means they cannot pack.
fatty acid, important component of lipids (fat-soluble components of living cells) in plants, animals, and microorganisms. Generally, a fatty acid consists of a straight chain of an even number of carbon atoms, with hydrogen atoms along the length of the chain and at one end of the chain and a carboxyl group (―COOH) at the other end. It is that carboxyl group that makes it an acid.
Fatty acid ethoxylates. Fatty acid ethoxylates are a class of very versatile surfactants, which combine in a single molecule the characteristic of a weakly anionic, pH-responsive head group with the presence of stabilizing and temperature responsive ethyleneoxide units. Special ethoxylated fatty esters and oils Ethoxylated amines and/or fatty.
1 Triglycerides are synthesised from glycerol and fatty acids. (a) The diagrams below show the structures of three fatty acids and their melting temperatures. (i) Using the diagrams above, describe the structure of oleic acid. (2)..... (ii) Using the information in the diagrams, explain why these fatty acids have different melting temperatures. (3)
Notes on Fatty Acids (With Diagram) The fatty acids are an important and also abundant group of lipids. In cells, the fatty acids only sparingly occur freely; instead, they are esterified to other components and form the saponifiable lipids. A fatty acid molecule may be either saturated or unsaturated. The saturated fatty acids consist of.
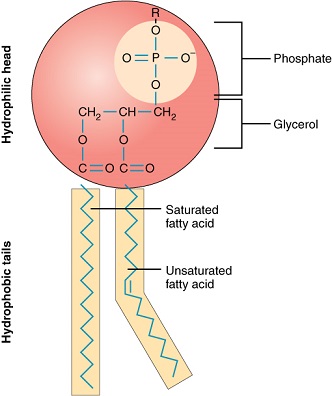
Jul 05, 2021 · The most abundant lipid which is present in the cell membrane is a phospholipid which contains a polar head group attached to two hydrophobic fatty acid tails. The embedded proteins act as channels for the transfer of particles across the cell with some proteins acting as receptors for the binding of various components.
Omega-3 fatty acids are also associated with protection from heart disease, arthritis and cancer. The following figure shows how omega-3 and other fatty acids are taken in and used by the bodies of animals including humans. Use the information in the figure to explain two ways in which fatty acids are important in the formation of new cells.
The structure of a triglyceride is often depicted as a simplified drawing of the glycerol backbone and three fatty acids. There are different types of fatty acids, and triglycerides can contain a mixture of them. Fatty acids are classified by their carbon chain length and degree of saturation. Foods contain different proportions of fatty acid.
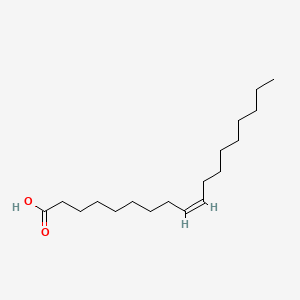
Structure and classification of unsaturated fatty acids. Unsaturated fatty acids contain one or more double/triple carbon-carbon bonds in the carbon chain. On this basis they can be divided into three classes: monounsaturated fatty acids (MUFAs), if only one double bond is present; polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs), if at least two double.
The influence of a fatty acid's structure on its melting point is such that branched chains and cis double bonds will lower the melting point compared with that of equiv-alent saturated chains. In addition, the melting point of a fatty acid depends on whether the chain is even- or odd-numbered; the latter have higher melting points.
Unit 7, Lesson 2 Lipids and Carbohydrates 3 Triglycerides are a commonly occurring lipid. When one glycerol molecule bonds covalently to three fatty acids through dehy-dration synthesis, the product is a triglyceride (Figure 1), a lipid commonly referred to as fat.
Based on the chemical structure of the fatty acid chain, there are two types of fatty acids present in the body; namely, saturated and unsaturated fatty acids. Simple fats are mainly composed of glyceride and fatty acids. The most common simple fat is the triglyceride, made up of glyceride and three fatty acids..
acids. Amino acids all have the general structure: The R in the diagram represents a functional group that varies depending on the specific amino acid in question. For example, R can be simply an H atom, as in the amino acid glycine, or a more complex organic group. When 2 amino acids bond together, the two ends of nearby amino acids are
The following diagram shows the structures of some of these components. Clicking on the diagram will change it to display structures for two representative phospholipids. Note that the fatty acid components (R & R') may be saturated or unsaturated. To see a model of a phospholipid Click Here.
Fatty acids have 3 parts to their structure: '-COOH' carboxyl group, '-CH3' methyl group (or omega group) and the hydrocarbon chain in the middle.Saturated V...
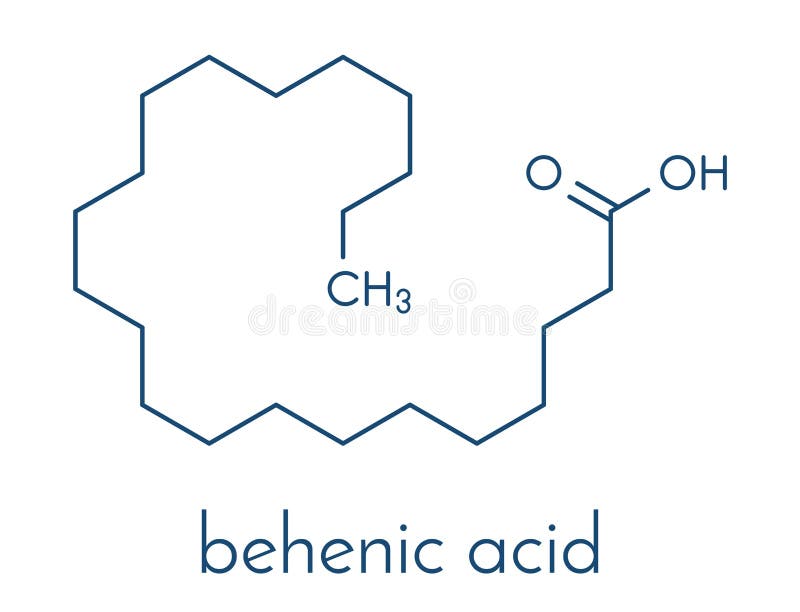
Overview. The elements of fatty acid structure are quite simple. There are two essential features: The chain length ranges from 4 to 30 carbons; 12-24 is most common. The chain is typically linear, and usually contains an even number of carbons. The many fatty acids which occur naturally arise primarily through variation of chain length and.
The structure of a triglyceride and the formation of ester- bond are shown in Fig. 8.18: It is important to note that the hydrophobic nature of fats and oils is due to the long-chain fatty- acids which are highly insoluble in water and are strongly hydrophobic, though glycerol itself is a hydrophilic compound.
The fatty acids present in various lipid molecules are the moieties of great nutritional interest. Fatty acids. The most abundant fatty acids have straight-chains of an even number of carbon atoms. There is a wide spectrum of chain-lengths, ranging from a four-carbon fatty acid in milk to thirty-carbon fatty acids in some fish oils.
Saturated fatty acids are a type of dietary fat derived from animal products and plant oils. Explore the structure and formula of saturated fatty acids, then review examples of the foods that.
Chemical structure. Δx. C:D. n−x. Myristoleic acid. CH3(CH2)3CH=CH(CH2)7COOH. cis-Δ9. 14:1. n−5. Palmitoleic acid. CH3(CH2)5CH=CH(CH2)7COOH. cis-Δ9. 16:1. n−7. Sapienic acid. CH3(CH2)8CH=CH(CH2)4COOH. cis-Δ6. 16:1. n−10. Oleic acid. CH3(CH2)7CH=CH(CH2)7COOH. cis-Δ9. 18:1. n−9. Elaidic acid. CH3(CH2)7CH=CH(CH2)7COOH. trans-Δ9. 18.
Fatty Acid Biosynthesis 4 Fatty Acid Synthase (FAS) • FAS is a polypeptide chain with multiple domains, each with distinct enzyme activities required for fatty acid biosynthesis. •ACP: Recall that CoA is used as an activator for β-oxidation. For fatty acid biosynthesis, the activator is a protein called the acyl carrier protein (ACP).
Structure. The main molecule that starts the structure of a triglyceride is glycerol. Glycerol is a three-carbon molecule with three hydroxyl groups on them. These hydroxyl groups are the site of an ester reaction with three fatty acid molecules. The fatty acids can be different types, and the fatty acid structure defines the type of triglyceride.
Polyunsaturated fatty acids are hydrocarbon chains containing two or more double bonds. The characterisation of PUFAs as either an n-3 PUFA or n-6 PUFA refers to the position of the first double bond relative to the methyl end of the fatty acid.
The diagram shows the general structure of a lipid, which consists of two main parts. The part that is circled is the fatty acid carboxyl group. -Lipids is one of the four important biomolecules, others being, nucleic acid, carbohydrates, and proteins. -Lipids are made of glycerol and fatty acids. Fatty acids consist of a carboxylic acid (-C=O.














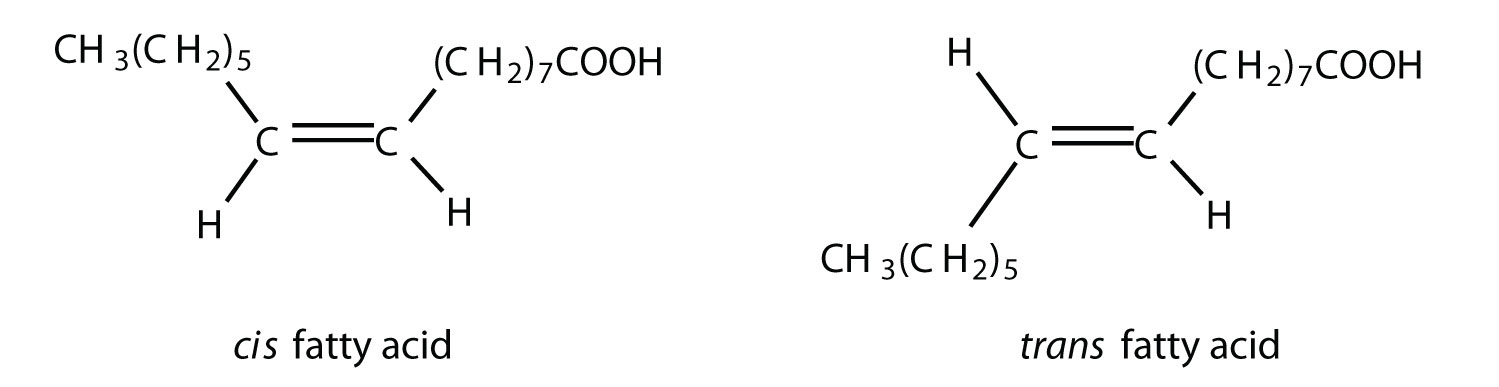








0 Response to "39 Fatty Acid Structure Diagram"
Post a Comment