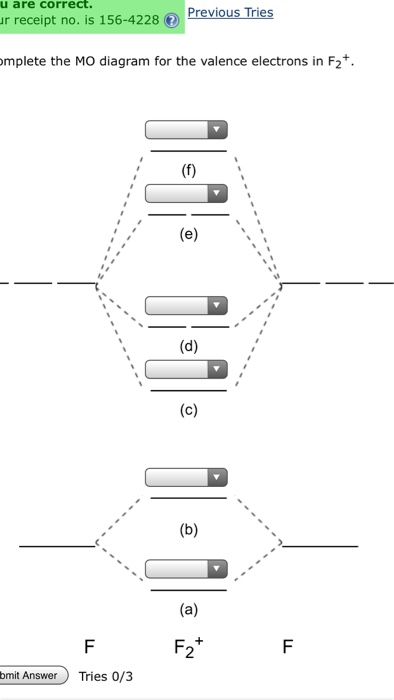
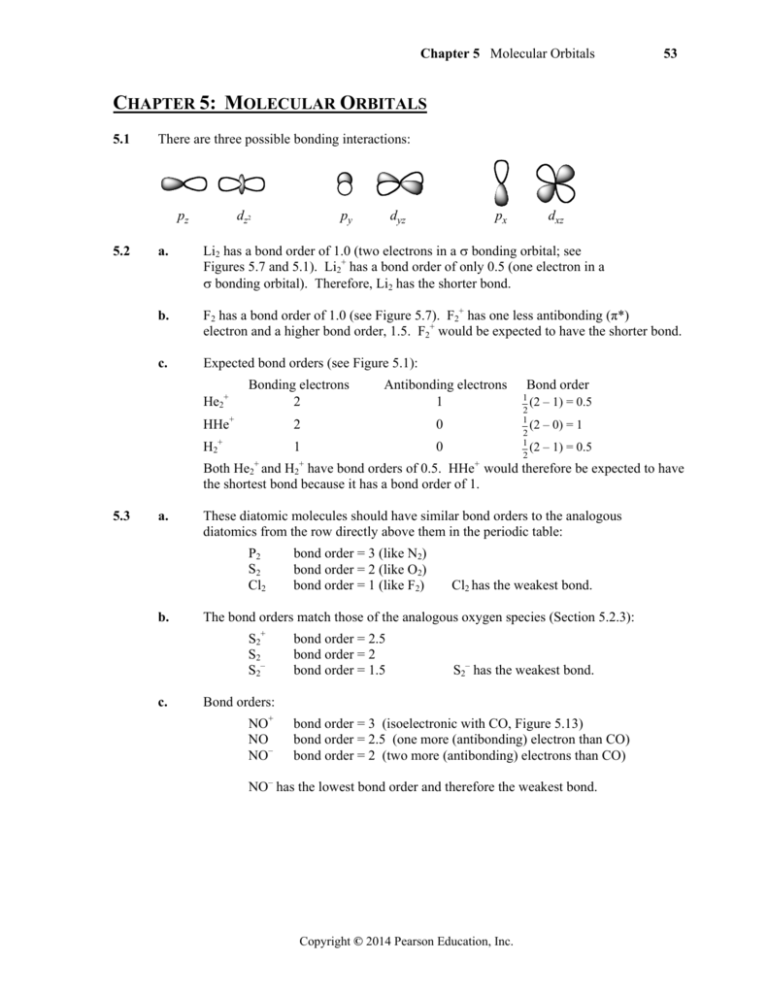
39 F2+ Molecular Orbital Diagram
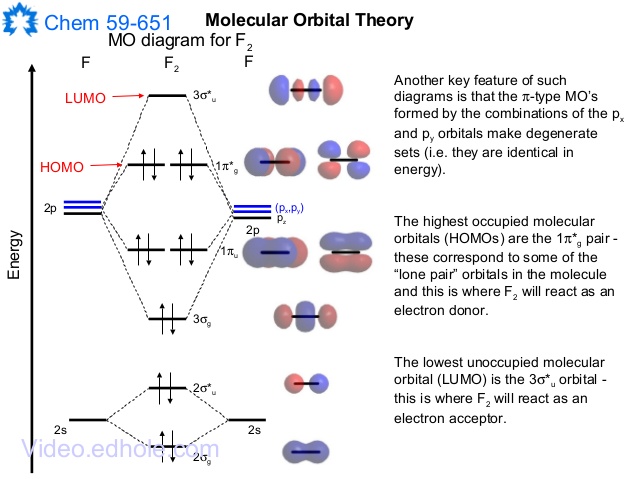
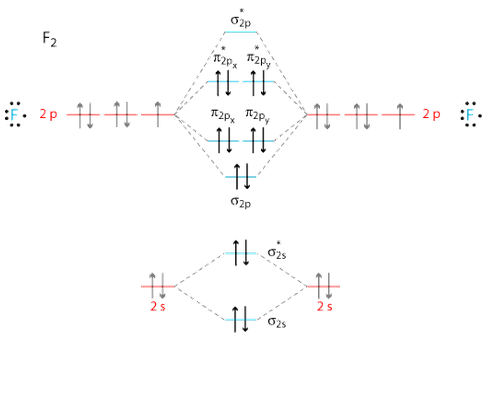
Molecular orbital diagram for f2. A fundamental principle of these theories is that as atoms bond to form molecules a certain number of atomic orbitals combine to form the same number of. C would this ion exist. To further demonstrate the consistency of the lewis structures with mo. For the ion f2. The case of F2 is a simple one because of the symmetry and diatomicity of the molecule. In more complex molecules (polyatomic and asymmetric), the extent of mixing and thus the contribution of individual atomic orbitals to form a particular molecular orbital depends on the relative energy alignment of the atomic orbitals. F2 Polarity
Molecular Orbital Diagram For F2 - A Mechanistic Study Graphene Based Nonvolatile Reram Devices. molecular orbitals of diatomic molecules molecular orbitals of li 2 be 2 to f 2 skills to develop explain how the energy levels of atomic orbitals vary for h li be b c n and o draw relative energy levels diagrams for homonuclear diatomic molecules.
F2+ molecular orbital diagram
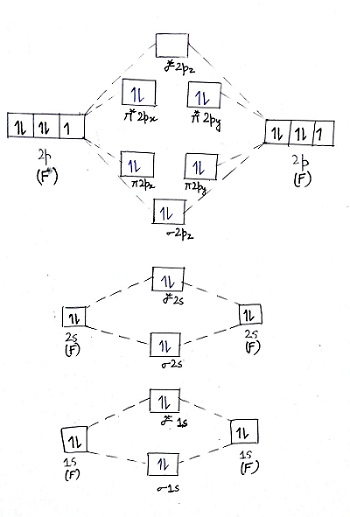
In picture 1 we show the molecular orbital structure of F2. In picture 2 we show the overlapping p orbitals, which form the bond between the two fl uorine atoms, in red and green gradients. The dashed lines show the remaining p orbitals which do not take part in the bonding. σ z y x σ* x y z Construct the molecular orbital diagram for. Relationship between electronic configuration and Molecular behaviour. 1) Stability of molecules in terms of bonding and antibonding electrons. Number of electrons present in the bonding orbitals is represented by N b and the number of electrons present in antibonding orbitals by Na.. 1) If N b > Na,the molecule is stable because greater number of bonding orbitals are occupied than. molecular orbitals in the diagram suggest a double bond. c. The 2s, 2s *, 2p, and 2p * orbitals exhibit C v symmetry, with the NF bond axis the infinite-fold rotation axis. The 2p and 2p * orbitals exhibit Cs symmetry. The latter do not possess C2 rotation axes coincident to the
F2+ molecular orbital diagram. Relationship between electronic configuration and Molecular behaviour. 1) Stability of molecules in terms of bonding and antibonding electrons. Number of electrons present in the bonding orbitals is represented by N b and the number of electrons present in antibonding orbitals by Na.. 1) If N b > Na,the molecule is stable because greater number of bonding orbitals are occupied than. Here is a video that discusses over the Molecular Orbital Diagram for F2+ and F2+. Then compare their bond length, strength, bond order etc. And explaining a... Click here👆to get an answer to your question ️ 37. Draw molecular orbital diagram for F2 molecule. Also, give its electronic configuration, bond order and magnetic property. 138. Solve the following: Molecular Orbital Diagram - Cl2, Br2, I2 3s & 3p and higher atomic orbitals are not so widely separated in energy and allow significant mixing (hybridization) to occur. This mixing causes the inversion of the σσand πmolecular orbitals' energy. σσσ ππ σ* π* 3,4,5 p 3, 4,5 s σ* σ 3,4,5 s 3,4,5 p Interhalogens Br Br F F Br F F F F.
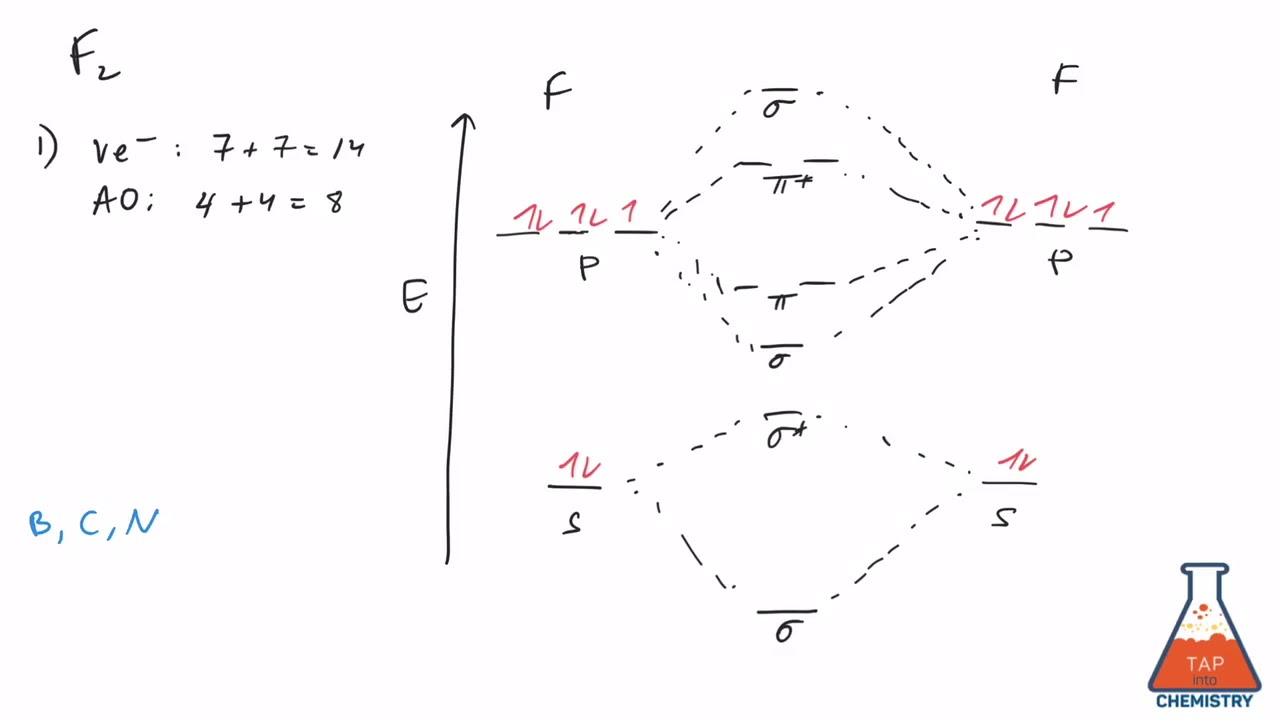
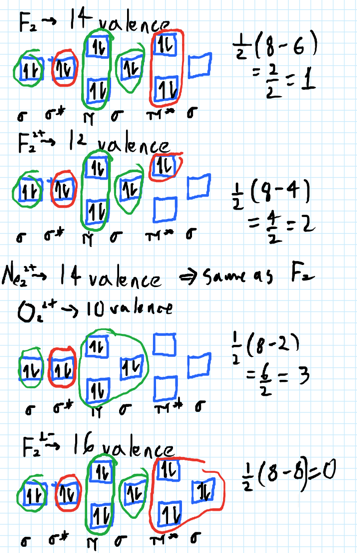
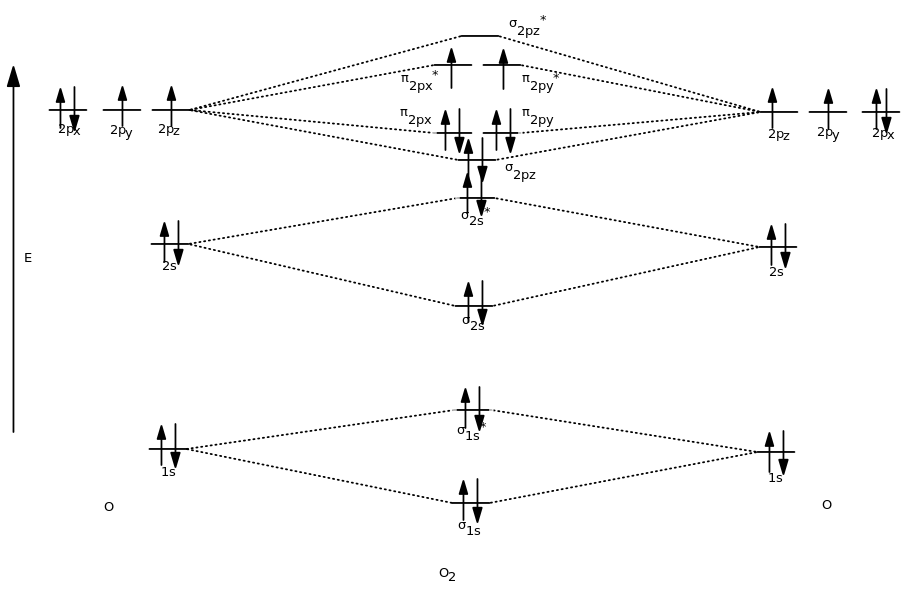
15 F2 Molecular Orbital Diagram. We assume that the electrons would fill the molecular orbitals of molecules like electrons fill atomic we will use this diagram to describe o2, f2, ne2, co, and no. The lowest energy unoccupied molecular orbital is 2p_ (sigma), so that is where the extra electron will be added. When two fluorine atoms bond, the sigma(2p) bonding molecular orbitals are lower in energy than the pi(2p) bonding orbitals.F2(2+) has a bond order of 2, so. Transcribed image text: Molecular Orbitals of a Period 2 Diatomic lon (Molecular Orbital Theory) Practice Exercise 27 Place the following molecular ions in order from smallest to largest bond order: C22+, N, 02, and F2- (a) C22+ <N<0, <F2 (b) F; <0, <N; <C22+ (c)0,- <C22+ <F> <N2 (d) C22+ <F2 <0, <N, (e)F2 <C22+ <0, <N2 Practice Exercise 28 Predict the magnetic properties and bond orders of (a. About Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy & Safety How YouTube works Test new features Press Copyright Contact us Creators.
Answer (1 of 6): Here is the solution, > * For O2 molecule, > * For F2 molecule, Thanks for reading. Molecular Orbitals of the Second Energy Level. The 2s orbitals on one atom combine with the 2s orbitals on another to form a 2s bonding and a 2s * antibonding molecular orbital, just like the 1s and 1s * orbitals formed from the 1s atomic orbitals. If we arbitrarily define the Z axis of the coordinate system for the O 2 molecule as the axis along which the bond forms, the 2p z orbitals on the. Summary MO Theory • LCAO-MO Theory is a simple method for predicting the approximate electronic structure of molecules. • Atomic orbitals must have the proper symmetry and energy to interact and form molecular orbitals. • Photoelectron spectroscopy provides useful information on the energies of atomic orbitals. • Next we'll see that symmetry will help us treat larger molecules in Molecular Orbital Diagram Ne2 28.12.2018 28.12.2018 7 Comments on Molecular Orbital Diagram Ne2 Even rather simple molecular orbital (MO) theory can be used to predict from the bottom of the diagram because this is how MO diagrams are constructed, from N2, O2, F2, Ne2 the complexity of the molecular orbitals develop in two ways.
Figure A partial molecular orbital energy-level diagram for the HF molecule. This interaction introduces an element of s-p mixing, or hybridization, into the molecular orbital theory. The result is a slight change in the relative energies of the molecular orbitals, to give the diagram shown in the figure below.
A) F2; B) F2^2+ C) Ne2^2+ D) O2^2+ E) F2^2-2) Use molecular orbital diagrams to determine which of the following are paramagnetic. A) O2^2-B) Ne2^2+ C) O2^2+ D) F2^2+ E) None of the above are paramagnetic; 3) Draw the molecular orbital diagram needed, and determine which of the following is paramagnetic.
This video is about MO Diagram #2 - F2
molecular orbitals in the diagram suggest a double bond. c. The 2s, 2s *, 2p, and 2p * orbitals exhibit C v symmetry, with the NF bond axis the infinite-fold rotation axis. The 2p and 2p * orbitals exhibit Cs symmetry. The latter do not possess C2 rotation axes coincident to the
Now, let us draw the molecular orbital diagram of ${N_2}$. Now, first let us understand what magnetic behavior and bond order means. - Magnetic behavior: As we know the electron has an electron magnetic dipole moment, which is generally generated by the electron's spin property, which induces an electric charge into motion. As we can see the.
Solved question 1 by drawing molecular orbital diagrams solved look at the mo diagrams of corresponding neutral diatom when doing molecular orbitals the pi bonds come before sigma for b2 what is the energy level diagram of n2 and f2 brainly in. Information from the mo diagram justify o2s stability and show that its bonding order is 2.
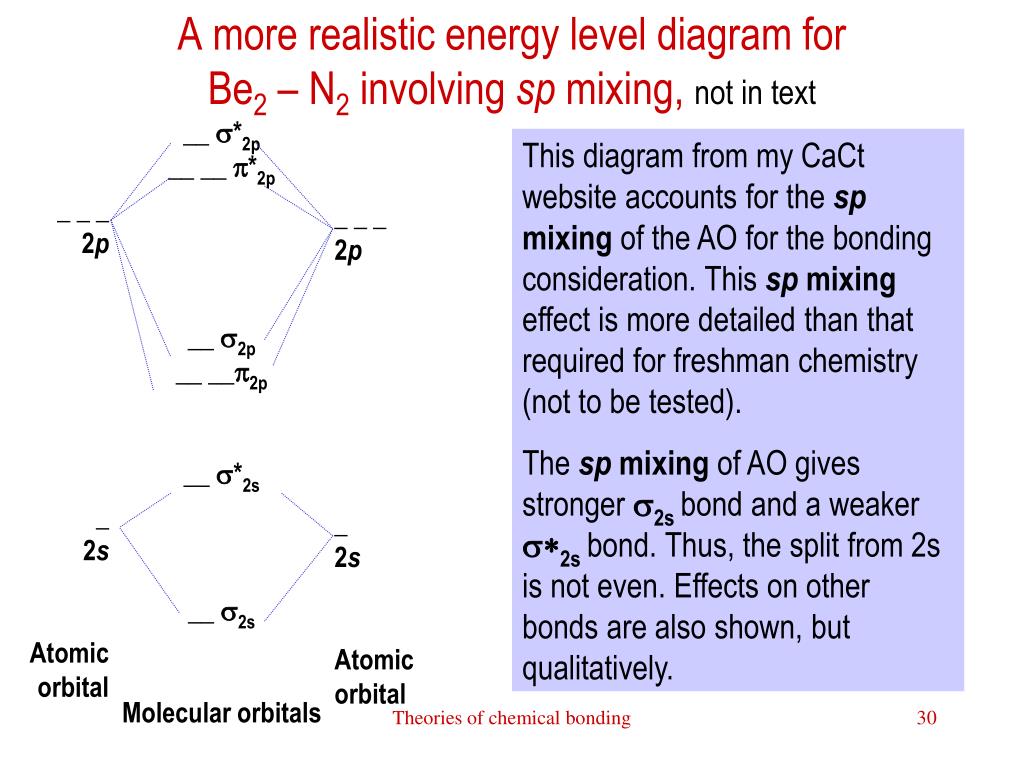
Since F2 is after N2 in the second row of the periodic table (where these effects are not present), the orbital energy ordering is "normal". In general, the molecular orbital energies follow these rules: The relative atomic orbital energy differences approximate the relative σ/σ orbital energy differences.
Draw molecular orbital diagram for F2 molecule Also gives its electronic configuration bond order and magnetic property. Claim your FREE Seat in Vedantu Master Classes!. -MOT uses a linear combination of atomic orbitals strategy to represent molecular orbitals resulting from bonds between atoms. These are bonding, anti-bonding and non-bonding.
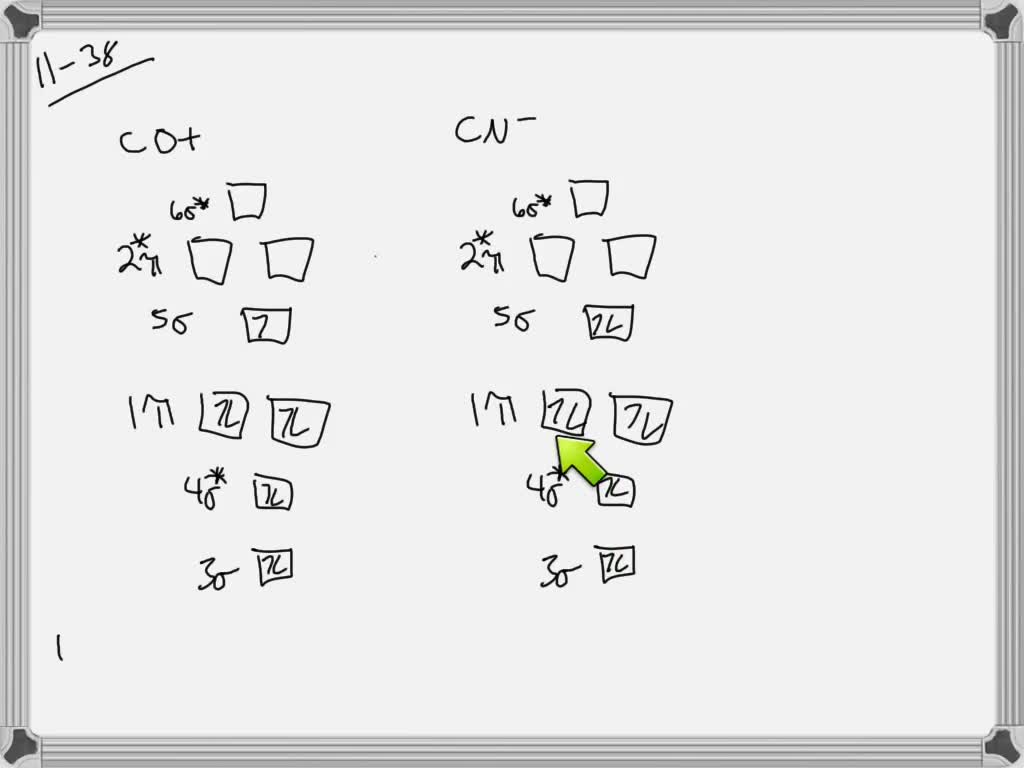
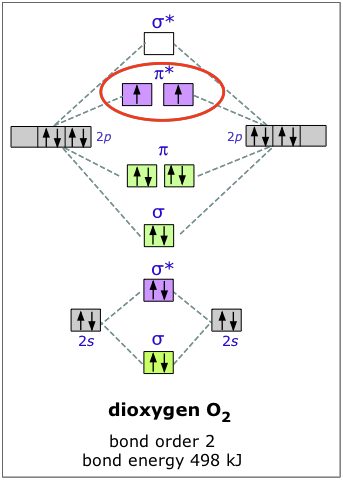
In O2 and F2, the 𝜋2𝑝 orbitals are higher in energy than the 𝜎2𝑝 orbital as shown in diagram B. The number of valence electrons per atom of an element is related to the group number in the periodic table.. Fill in the molecular orbitals in the molecular orbital diagram for CO.
The difference between molecules on the questions 1 and 2 are introduced somewhat at the beginning of the topic It basically is the mixing between orbitals use the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which use the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which of the following is most stable a f22 b ne2… get the answers you need now
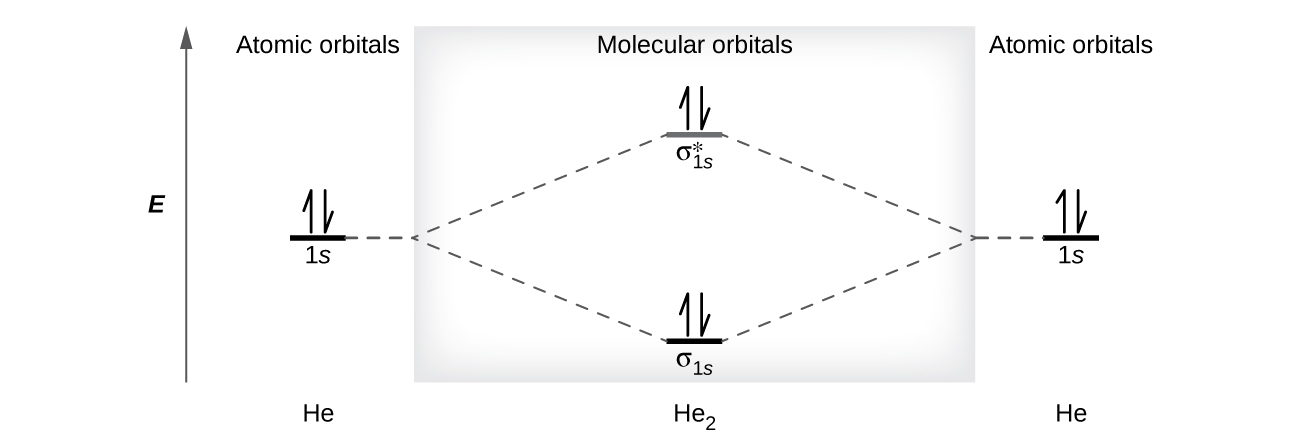
of the molecular orbitals compared to the original atomic orbitals. • Because the energy of the two electrons is lower than the energy of the individual atoms, the molecule is stable. Figure 9.26: (a) The molecular orbital energy-level diagram for the H2 molecule. (b) The shapes of the molecular orbitals are obtained by squaring the wave
The molecular orbital diagram for an o 2 molecule would therefore ignore the 1s electrons on both oxygen atoms and concentrate on the interactions between the 2s and 2p valence orbitals. F2 molecular orbital diagram. Atomic oxygen stock alamy. Organic chemistry lone pairs bonding pi molecular orbitals. F2 molecular orbital theory.
In picture 1 we show the molecular orbital structure of F2. In picture 2 we show the overlapping p orbitals, which form the bond between the two fl uorine atoms, in red and green gradients. The dashed lines show the remaining p orbitals which do not take part in the bonding. σ z y x σ* x y z Construct the molecular orbital diagram for.
Molecular orbital diagram for f2. In o 2 and f 2 there is a crossover of the sigma and the pi ortbials. Molecular orbitals mo are constructed from atomic orbitals. The relative energies of the sigma orbitals drop below that of the pi orbitals. The size of the effect depends on the 2s 2p energy difference. It is called a sigma molecular orbital.
Molecular Orbital Energy Diagram For F2 Energy Etfs How To Draw Molecular Orbital Diagram 142452 Paramagnetism And What Is The Molecular Orbital Diagram Of O2 And F2 Quora Mo Diagram 2 F2 Youtube Molecular Orbital Theory C2 Molecule Doubly Or Quadruply Bonded Mapping Ignorance Quiz 3 Molecular Orbitals Che 331 Molecular Science Ii Studocu.
A bare molecular orbital diagram is presented and you must drag the correct orbitals and labels onto the diagram. Molecular orbital diagram for f2. The other molecular orbital produced s h h shows a decrease in electron density between the nuclei reaching a value of zero at the midpoint between the nuclei where there is a nodal plane.
Chemistry questions and answers. Complete the molecular orbital diagram of F2 and F2-. What type of orbital contains the highest energy electron (s) in F2? pi, antibonding sigma, bonding sigma, antibonding pi, bonding Which atom is larger in size (radius), Cr or Cr3+? Question: Complete the molecular orbital diagram of F2 and F2-.

















0 Response to "39 F2+ Molecular Orbital Diagram"
Post a Comment