39 Bef2 Molecular Orbital Diagram
Sigma pi bond formation Orbital overlap concept ncert Molecular Orbital Diagram. Molecular Orbital Theory is slightly different from VBT and orbital hybridization. Here, AOs from different atoms inside the molecule can come together to form molecular orbitals or MOs. Therefore, valence electrons are shared inside the molecule. The electronic configuration of both C and N are as follows: Carbon.
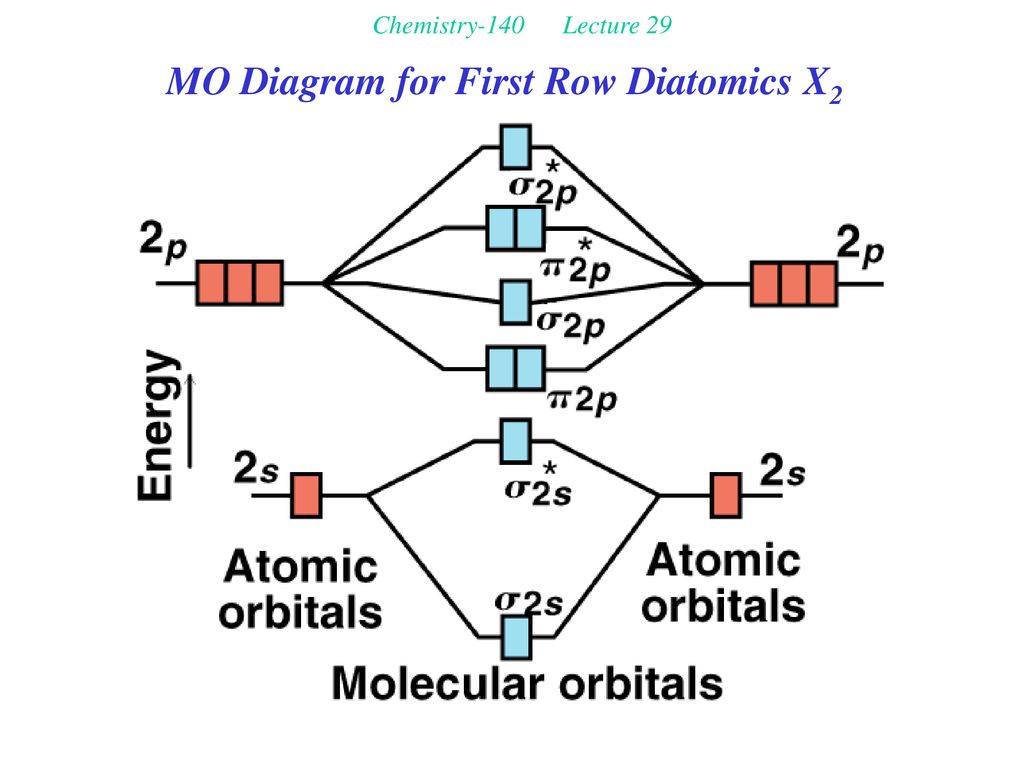
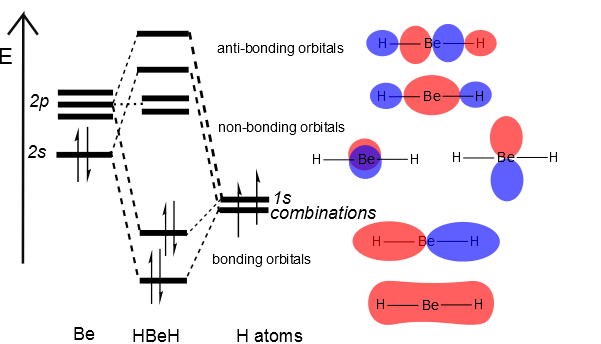
valence orbitals is larger than that between the valence orbitals of C and H, and both the 2s and 2p orbitals of Be are higher in energy than the 1s orbital of H. The result is greater bond polarity in BeH2. 5.16 BeF2 uses s and p orbitals on all three atoms, and is isoelectronic with CO2. The energy level
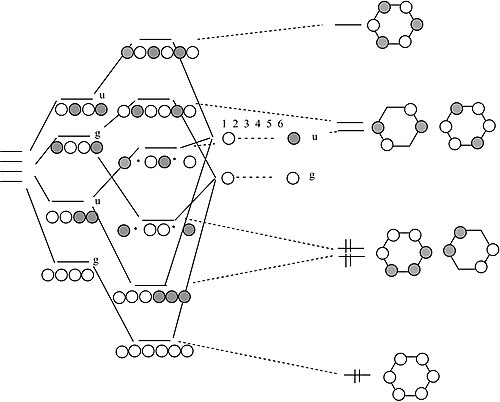
Bef2 molecular orbital diagram
Answer (1 of 2): Hybridisation is no. Of atomic orbitals that are integrated to give molecular orbits hybridisation of bef2 will be as following 1 s orbital and 1 p orbital will be contributed by be in molecule formation thus its hybridisation is sp fe each will contribute s orbital Summary MO Theory • LCAO-MO Theory is a simple method for predicting the approximate electronic structure of molecules. • Atomic orbitals must have the proper symmetry and energy to interact and form molecular orbitals. • Photoelectron spectroscopy provides useful information on the energies of atomic orbitals. • Next we'll see that symmetry will help us treat larger molecules in Molecular Orbital Diagrams simplified. Megan Lim. Oct 26, 2016 · 3 min read. Drawing molecular orbital diagrams is one of the trickier concepts in chemistry. The first major step is understanding.
Bef2 molecular orbital diagram. hybridization and molecular orbital mo theory molecular shapes based on valence electrons lewis dot structures and electron repulsions •molecular orbital theory mo - a molecule is formed by the overlap of atomic orbitals to form molecular orbitals electrons are then distributed into mos a molecule is a collection of nuclei with the orbitals. The three hybridized sp 2 orbitals are usually arranged in a triangular shape. BF 3 molecule is formed by bonding between three sp 2 orbitals of B and p of 3 F atoms. All the bonds in BF 3 are sigma bonds. BF 3 Molecular Geometry and Bond Angles. Normally, boron forms monomeric covalent halides which have a planar triangular geometry. Steps to form OF2 Lewis Structure Diagram. Step 1: Find the Total number of Valence Electrons. The first and foremost step is to calculate the total number of valence electrons in an OF2 molecule. Oxygen belongs to group 16, the chalcogen family, and has a valency of 6. Fluorine belongs to the family of halogen in group 17 and has a valency of 7. (a) bonding molecular orbitals possess less energy than atomic orbitals from which they are formed (b) bonding molecular orbitals have low electron density between the two nuclei (c) every electron in the bonding molecular orbitals contributes to the attraction between atoms (d) bonding molecular orbitals are formed when the electron
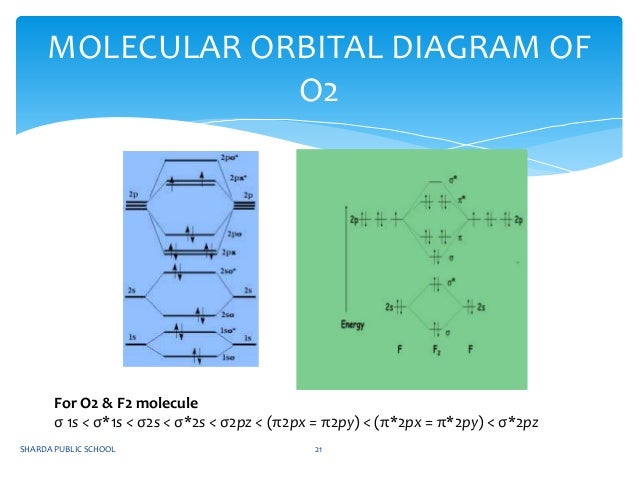
Answer (1 of 2): Hybridisation is no. Of atomic orbitals that are integrated to give molecular orbits hybridisation of bef2 will be as following 1 s orbital and 1 p orbital will be contributed by be in molecule formation thus its hybridisation is sp fe each will contribute s orbital BeF2 uses s and p orbitals on all three atoms, and is isoelectronic with CO2. The energy level. Be able to construct molecular orbital diagrams for homonuclear diatomic, heteronuclear diatomic, homonuclear triatomic, and heteronuclear triatomic molecules. Determine whether the following molecular orbitals are bonding or antibonding. Electronic structure of oxygen atom is Leaving out the 4 electrons in the 1s orbitals of two oxygen atoms constituting the molecule (represented as KK), the molecular orbital energy diagram for remaining 12 electrons of oxygen as molecule is shown: (i) Electronic configuration: (ii) Bond order: Here N b = 8; N a = 4 The two oxygen atoms in a molecule of oxygen are united through two covalent. How to explain the structure of HNO3 with a Molecular Orbital diagram? 7. What does the molecular orbital scheme of beryllium chloride and hydride look like? 2. Confused about identifying delocalized electron pairs in Isoniazid. 10. How is Bent's rule consistent with LCAO MO theory? 3.
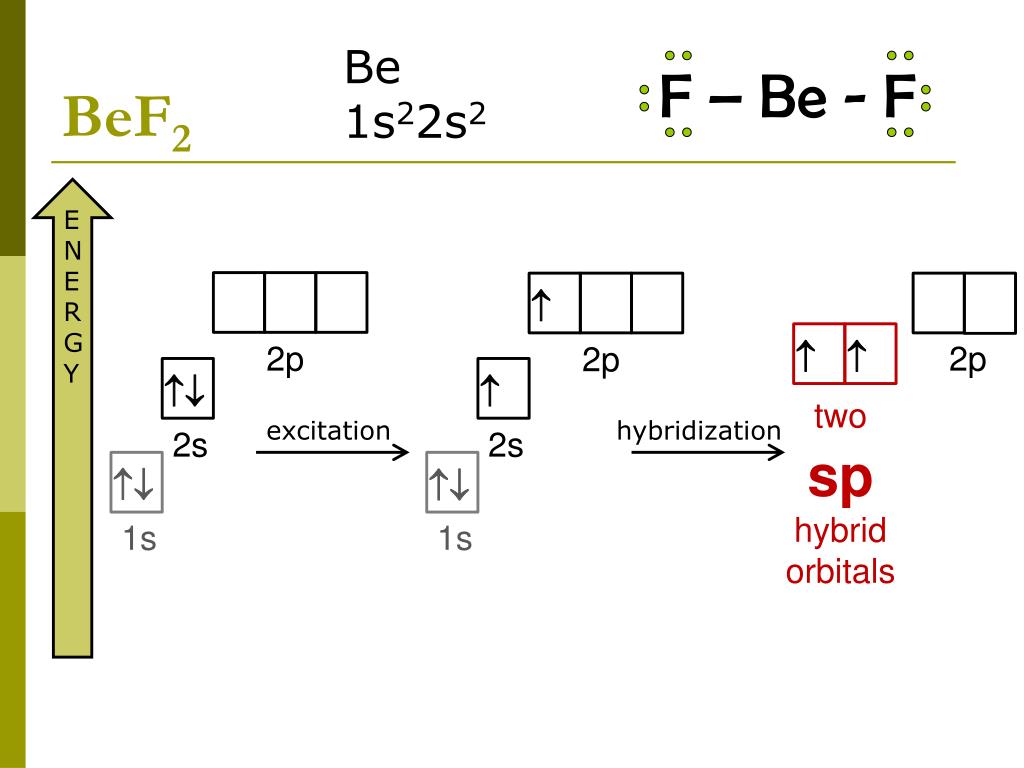
1. Using the point group D2h (as we did for our other linear triatomic molecules), construct a molecular orbital diagram for linear BeF2. Although it is tempting to think of Be as a metal that does not engage in covalent bonding, BeF2 molecules are know to exist in the gas phase. If you need help, follow these steps: a. (i) Orbital structure of BeF2 :To form BeF2 molecule, an electron gets promoted from filled 2s orbital to vacant 2p orbital. Therefore, the excited configuration of Be atom isIn BeF2, Be atom is sp hybridised i.e. two hybrid orbitals are directed along a straight line with a bond angle equal to 180°. Each sp hybrid orbital overlaps axially with 2p half-filled orbital of F atom to form sigma. Hybrid Atomic Orbitals. It is difficult to explain the shapes of even the simplest molecules with atomic orbitals. A solution to this problem was proposed by Linus Pauling, who argued that the valence orbitals on an atom could be combined to form hybrid atomic orbitals.. The geometry of a BeF 2 molecule can be explained, for example, by mixing the 2s orbital on the beryllium atom with one of. Step by step video for producing the MO diagram for BeF2. Captioned within the video but no audio.
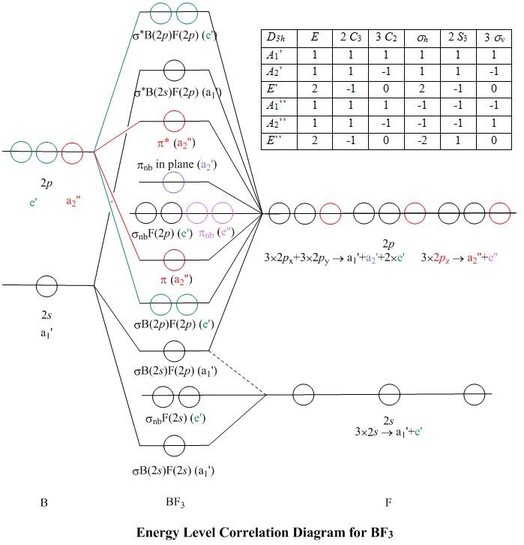
Show activity on this post. I'm trying to build a molecular orbital diagram for BF 3 and I'm running into problems with irreducible representations on the F side. 2s for B has an irreducible representation of A1. 2p for B has an irreducible representation of E' and A''2. 2s for F considered non bonding. 2p (along the bond axis) for F has an.
RE: a thank you to entice the C-N molecular orbital diagram for the sigma bond in HCN? Label each and every molecular orbital with its call. Create a molecular orbital diagram of the linear BeF2 molecule. For Be use a basis set that consists of the 2s, 2px, 2py, 2pz atomic orbitals. Unlike in question 4.
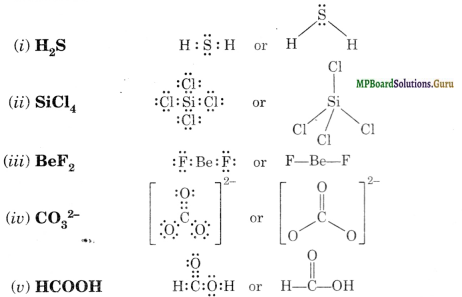
Best lewis structure for BeF2. Lewis structure for BeF2. Best Lewis structure for CH2Cl2. Most stable? OCN- , ONC- , NOC.. Orbital diagram of N (neutral charge) Neutral electron configuration of Se [Ar] 4s2,3d10,4p4... Trigonal planar molecular geometry. 2 bonding groups 1 lone pairs. Trigonal planar electron geometry
Determine whether the following molecular orbitals are bonding or antibonding. ( c. 8 pts.) An incomplete MO diagram for NO+ is provided. a. (6 pts.) The point group for BeF2 is D∞h, but when determining the symmetry of the group orbitals.The linear combination of atomic orbitals always gives back the same number of molecular orbitals.
BeF2 is a nonpolar molecule because of symmetrical geometry that causes the uniform distribution of charge in the molecule that leads to its net dipole moment zero. In the BeF2 Lewis dot structure, a total of 6 lone pairs and 2 bonded pairs are present. The molecular geometry of BeF2 is linear and its electron geometry is also linear in nature.
Molecular geometry is the name of the geometry used to describe the shape of a molecule. Sulfur promotes two electrons into two of the 3d orbitals (one from 3s and one from 3p x). Molecular Geometries:Simple chemical bonding concepts allow us to predict the shapes of most molecules. Expert's Answer. the molecular shape of bef2 is: f.
Molecular Orbital Diagrams simplified. Megan Lim. Oct 26, 2016 · 3 min read. Drawing molecular orbital diagrams is one of the trickier concepts in chemistry. The first major step is understanding.
Is BeF2 sp3 hybridized? BeF2 molecule Since there are no unpaired electrons in the valency shell, it cannot form any covalent bond. Thus, 2s-orbital is first unpaired and an electron is shifted to 2p-orbital. Now, there is hybridization between one s-and one p orbital. Two orbitals (hybrid) of same shape and energy come into existence.
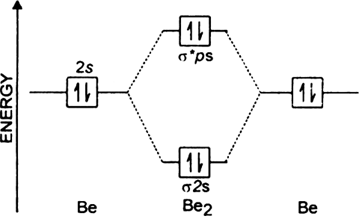
Draw the molecular orbital energy level diagram for each of the following species Be2+, Be2, and Be Indicate theirnumbers of unpaired electron and mention their magnetic diagramweb ate their bond orders, and state which species is moststable% (1). Molecular orbitals of Li 2, Be 2, to F 2 The molecular orbital theory (MO) has been introduced.
Alternate ISBN: 9780133558944, 9780321917799. Inorganic Chemistry (5th Edition) Edit edition Solutions for Chapter 5 Problem 16P: In the gas phase, BeF2 forms linear monomeric molecules. Prepare a molecular orbital energy-level diagram for BeF2, showing clearly which atomic orbitals are involved in bonding and which are nonbonding...
Answer (1 of 2): Shape = Linear Hybridisation = sp Bond angle = 180 Explanation = (1) Be has electron in outer most orbit = 2 (2) No of atom linked with Be = 2 (3) Hybridisation = 2+2/2 = 4/2 = 2 sp F-Be-F Linear and bond angle =180
Summary MO Theory • LCAO-MO Theory is a simple method for predicting the approximate electronic structure of molecules. • Atomic orbitals must have the proper symmetry and energy to interact and form molecular orbitals. • Photoelectron spectroscopy provides useful information on the energies of atomic orbitals. • Next we'll see that symmetry will help us treat larger molecules in
Assignment CM1101. 5% CA. Select one of the molecules from (i) to (iii) below and use either (a) Lewis and VSEPR to. determine the structure (estimating all angles and providing the structure) then apply. either VB theory, (b) combined VB-MO theory (covered in Lecture XVI), or (c) MO. theory to determine the MOs for any of the molecules (i) to.
Interpreting Molecular Orbital Print Outs Molecular Orbital Drawings: First note that the orientation of the molecule is with atom 2, which is a F, along the x-axis. The other F's are also in the x-y plane. In picturing the orbitals, start with orbital 7. Since orbital 7 involves p z-orbitals, it is a π type orbital. Note the form of the
There are two MO diagrams you need to memorize for diatoms (N2, O2, Ne2, etc).One is for the elements up to Nitrogen. The other is for AFTER nitrogen (start...
The new orbitals thus formed are known as hybrid orbitals. More significantly, hybrid orbitals are quite useful in explaining atomic bonding properties and molecular geometry. Let us quickly look at the example of a carbon atom. This atom forms 4 single bonds wherein the valence-shell s orbital mixes with 3 valence-shell p orbitals.





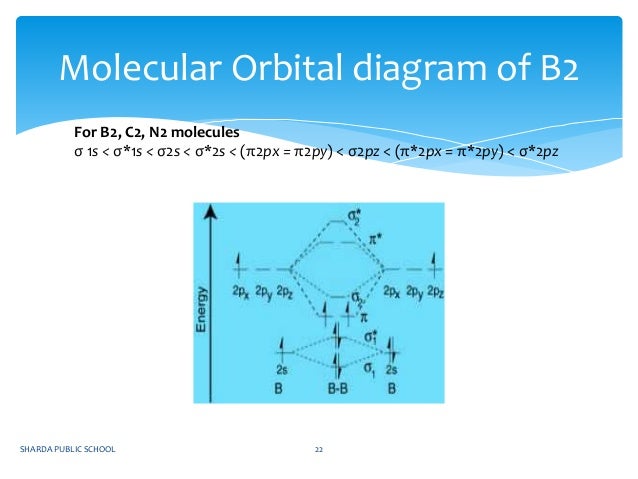
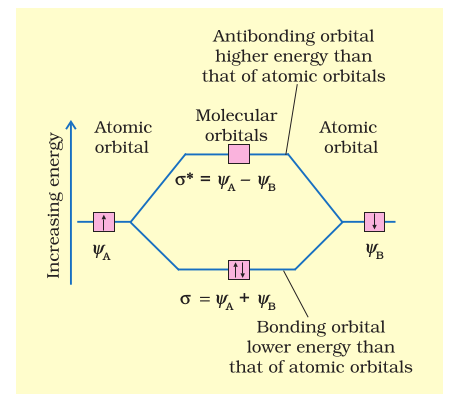
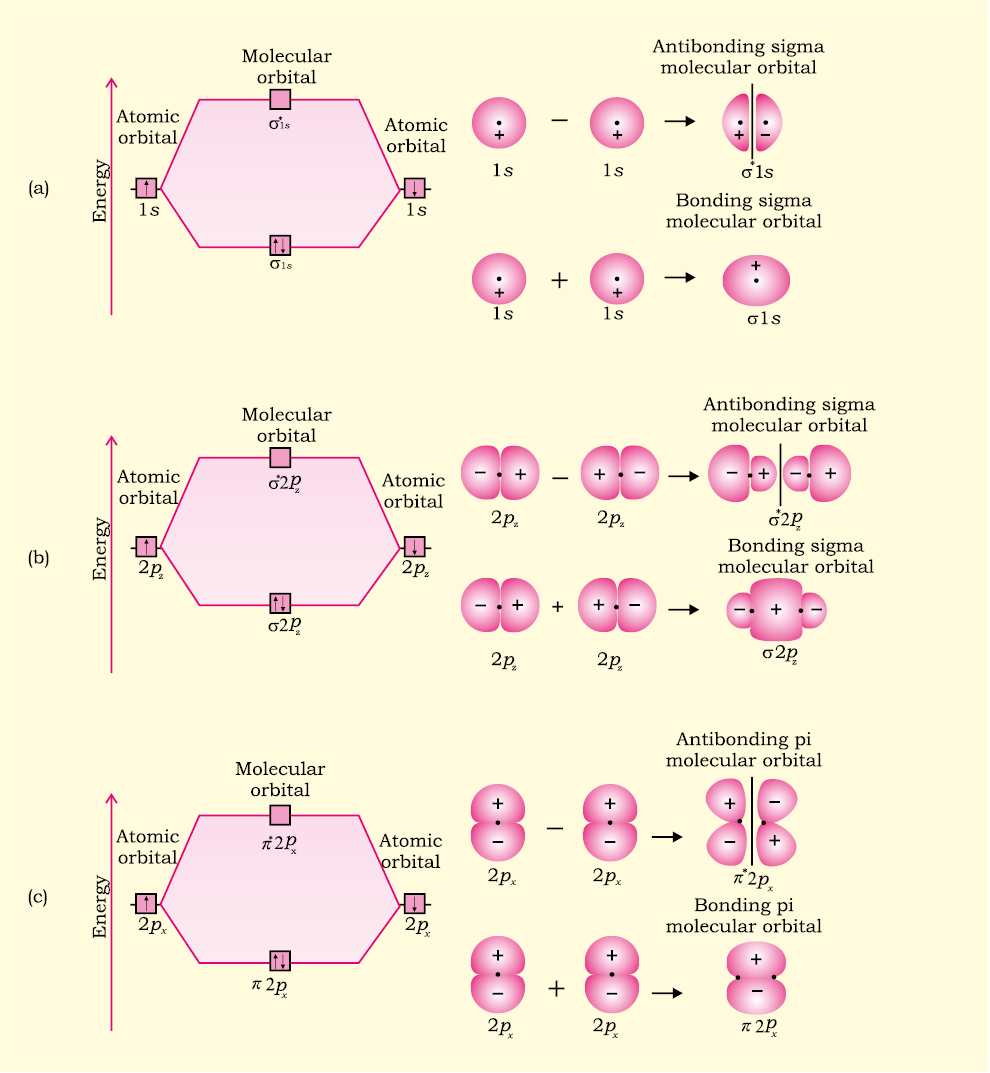












0 Response to "39 Bef2 Molecular Orbital Diagram"
Post a Comment