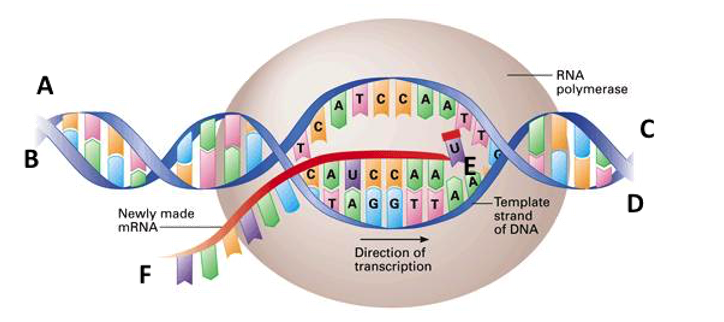
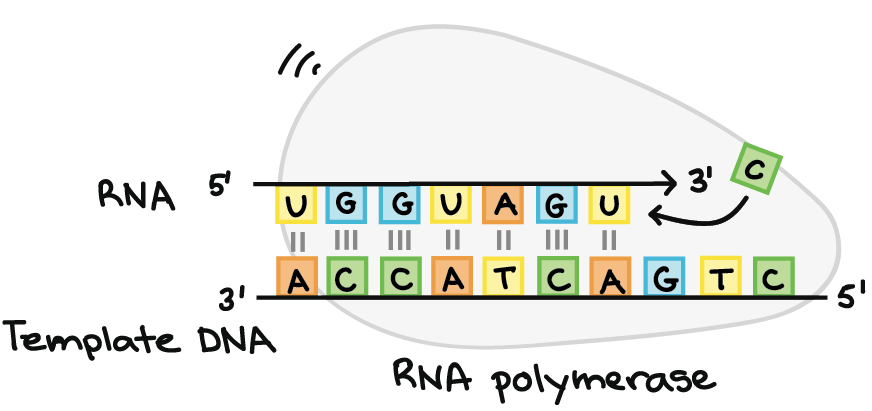
38 What Is The Direction Of Transcription In This Diagram?
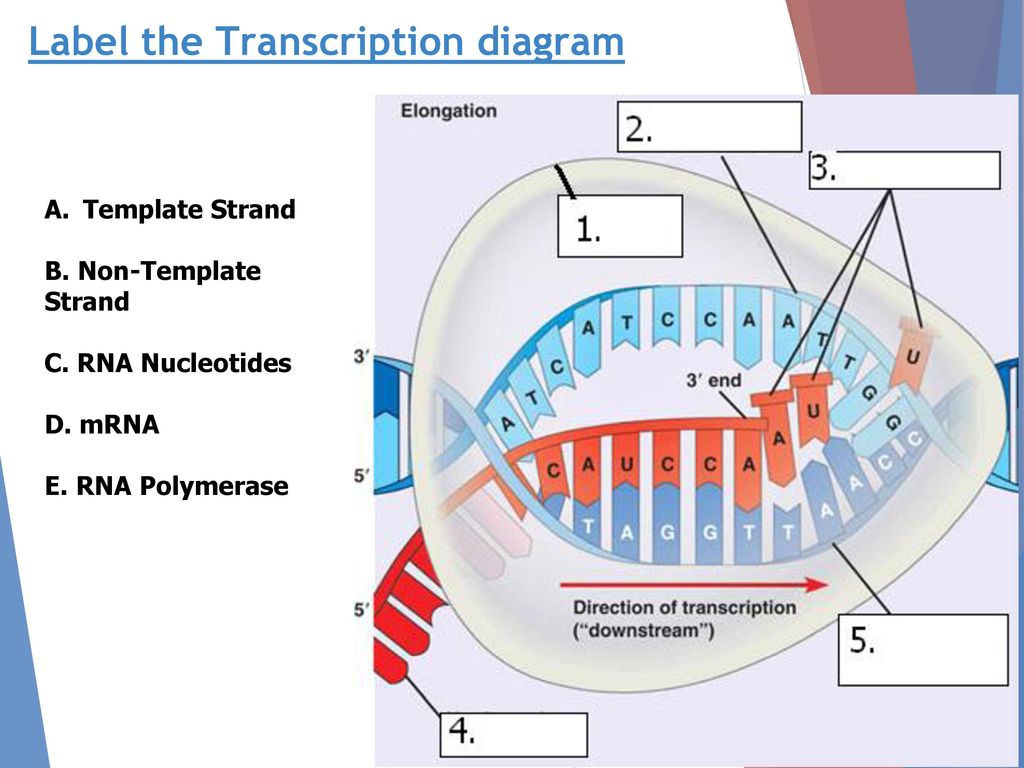
Problem: Part A. Identify the following elements on a diagram of a transcription bubble. Drag the labels to their appropriate locations in the diagram. Labels may be used more than once.Part B. What is the direction of transcription in this diagram?A) From right to leftB) Unable to be determinedC) From left to rightPart C. Transcription. Transcription is the name given to the process where the information in a gene in a DNA strand is transferred to an RNA molecule. The coding strand and the template strand of DNA. The important thing to realise is that the genetic information is carried on only one of the two strands of the DNA. This is known as the coding strand.
Transcription Regulators Promoters in Bacteria:. Promoter in bacteria is the common feature of DNA transcription regulators in their ability to recognizes the particular DNA pattern to modulate gene expression. The upstream regulation of the region of bacterial coding consists of a promoter, which is the DNA sequence that determines the particular recognition by the RNAP holoenzyme.
What is the direction of transcription in this diagram?
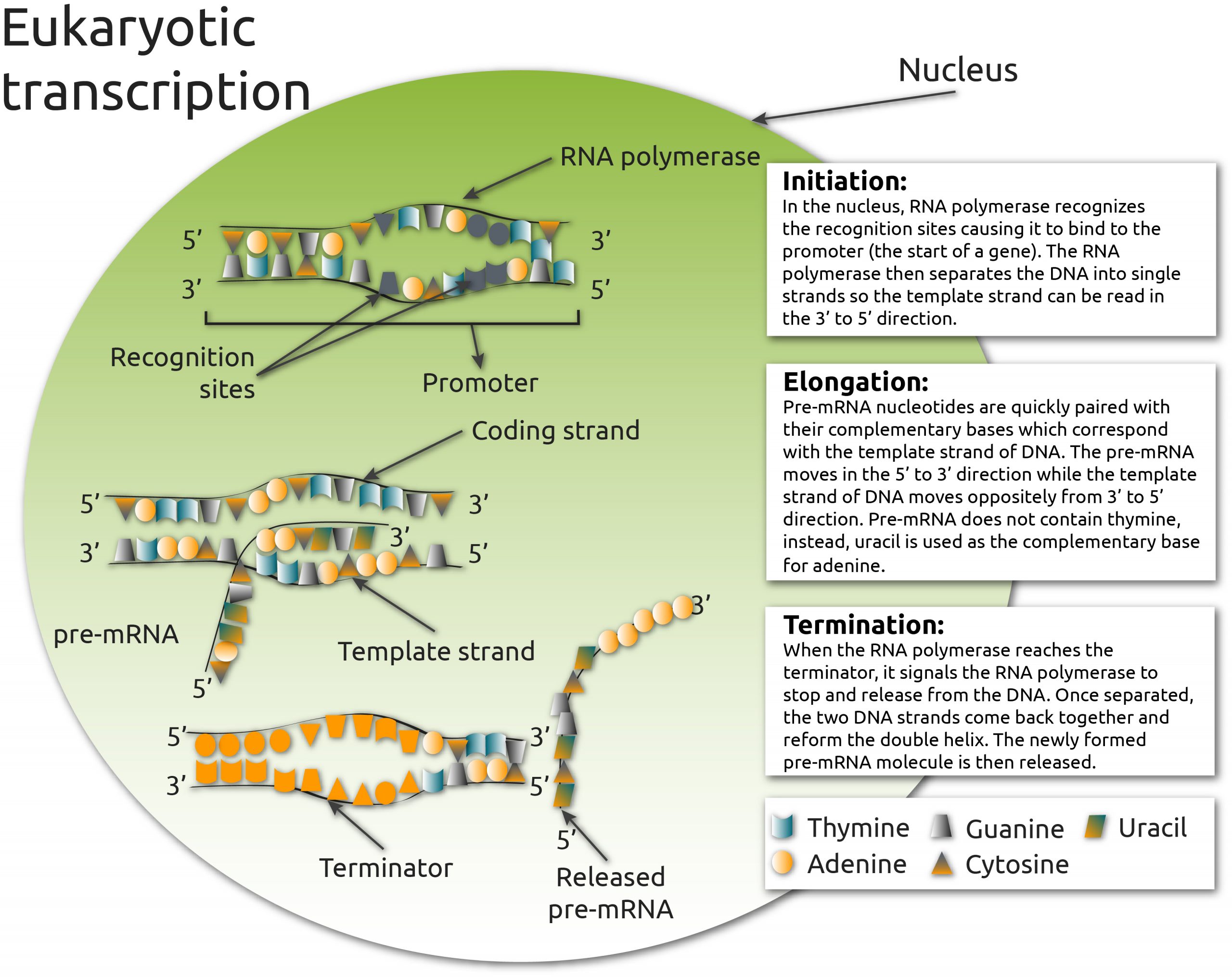
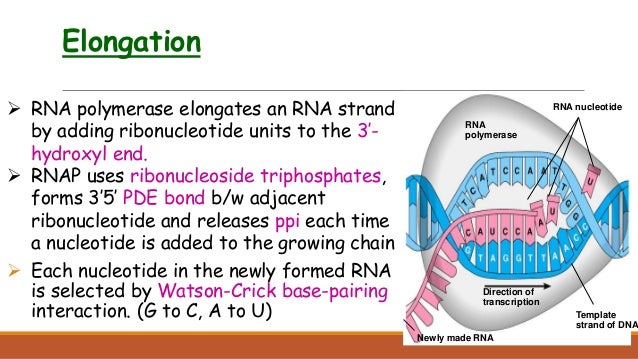
The RNA polymerase is the main enzyme involved in transcription. It uses single-strand DNA to synthesize a complementary RNA strand. The DNA-dependent RNA polymerase binds to the promoter and catalyses the polymerization in the 5’ to 3’ direction on the template strand. Once it reaches the terminator sequence, the process terminates and the. Transcription: Elongation The mRNA is synthesized. RNA polymerase moves downstream breaking the hydrogen bonds between the DNA base pairs exposing 10‐20 DNA nucleotides at a time. Messenger RNA is assembled in the 5' 3' direction using the template DNA strand (diagram 2). Transcription is the process of copying a segment of DNA into RNA. The segments of DNA transcribed into RNA molecules that can encode proteins are said to produce messenger RNA (mRNA). Other segments of DNA are copied into RNA molecules called non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs). Averaged over multiple cell types in a given tissue, the quantity of mRNA is more than 10 times the quantity of ncRNA (though.
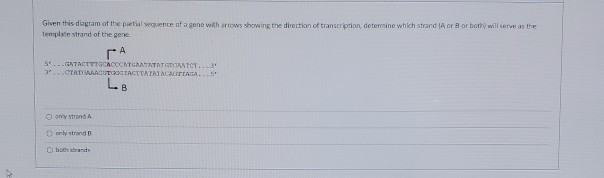
What is the direction of transcription in this diagram?. The transcription occur from 5' to 3' direc.. View the full answer. Transcribed image text: What is the direction of transcription in this diagram? unable to be determined from right to left from left to right Where would you expect to find the promoter for this gene? unable to be determined left side right side. Previous question Next question. • Transcription –DNA message is converted into mRNA format • Translation –mRNA message is converted into protein • DNA is the informational molecule which specifies the structure of proteins using RNA. gene occurs in the _____ direction. • A) 3’ to 5’ What is transcription? Transcription occurs in a 5' to 3' direction During transcription, an RNA is transcribed in the 5'-to-3' direction. The template strand is read in a 3'-to-5' direction. Transcription is the first step of gene expression, in which a particular segment of DNA This is called coupled transcription and translation. Transcription, translation and degradation of mRNA all occur in the same 5′ → 3′ direction. Transcription in Eukaryotes: The basic features of transcription and structure of mRNA in eukaryotes are similar to those of bacteria.
The RNA polymerase is the main enzyme involved in transcription. It uses single-strand DNA to synthesize a complementary RNA strand. The DNA-dependent RNA polymerase binds to the promoter and catalyses the polymerization in the 5’ to 3’ direction on the template strand. Once it reaches the terminator sequence, the process terminates and the. DNA transcription is the process by which the genetic information contained within DNA is re-written into messenger RNA (mRNA) by RNA polymerase. This mRNA then exits the nucleus, where it acts as the basis for the translation of DNA. By controlling the production of mRNA within the nucleus, the cell regulates the rate of gene expression.In this article we will look at the process of DNA. Translation is the process by which the genetic code contained within a messenger RNA (mRNA) molecule is decoded to produce a specific sequence of amino acids in a polypeptide chain.It occurs in the cytoplasm following DNA transcription and, like transcription, has three stages: initiation, elongation and termination. In this article we will discuss the components and stages of DNA translation. Biology questions and answers. Part B What is the direction of transcription in this diagram? A) From right to left B) Unable to be determined C) From left to right Part C Where would you expect to find the promoter for this gene? A) Right Side B) Left Side C) Unable to be determined.
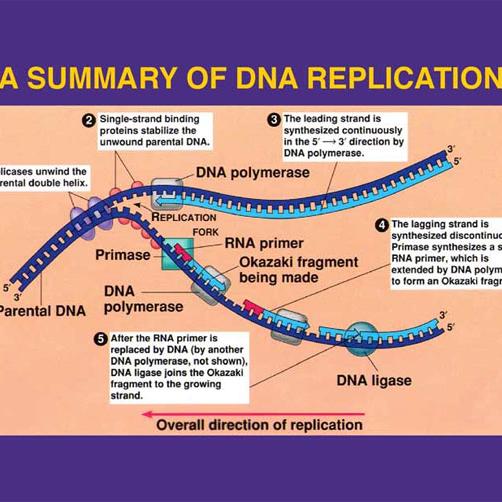
What is the direction of transcription in this diagram? from left to right The RNA polymerase reads the template strand from the 3' to 5' direction, and synthesizes RNA from 5' to 3'. The template strand is the DNA strand that is based paired to RNA as transcription proceeds. In this example, the RNA is paired with the bottom strand. Either DNA strand may be used as a template by RNA polymerase, but a single DNA strand oriented in the 3'-5' direction is used as a template each time transcription occurs. Gene transcription occurs from left to right for gene A and gene B, whereas transcription occurs from right to left for gene C, as in the diagram. RNA is synthesized in the 5' -> 3' direction (as seen from the growing RNA transcript). There are some proofreading mechanisms for transcription, but not as many as for DNA replication. Sometimes coding errors occur. Differences in Transcription. There are significant differences in the process of transcription in prokaryotes versus eukaryotes. Replication is the process in which a cell makes an exact copy of its own DNA (copy DNA -> DNA). Replication occurs in the S-fase in preparation to cell division during which the genetic information for the synthesis of proteins is transfered from the mothercell to the daughtercell. Whether this cell division will eventually be a mitosis or a.
View Transcription Week 3.pdf from BIOLOGY 136 at University of California, San Diego. 5. The diagram below shows RNA polymerase in the elongation phase of transcription. On the diagram, label the
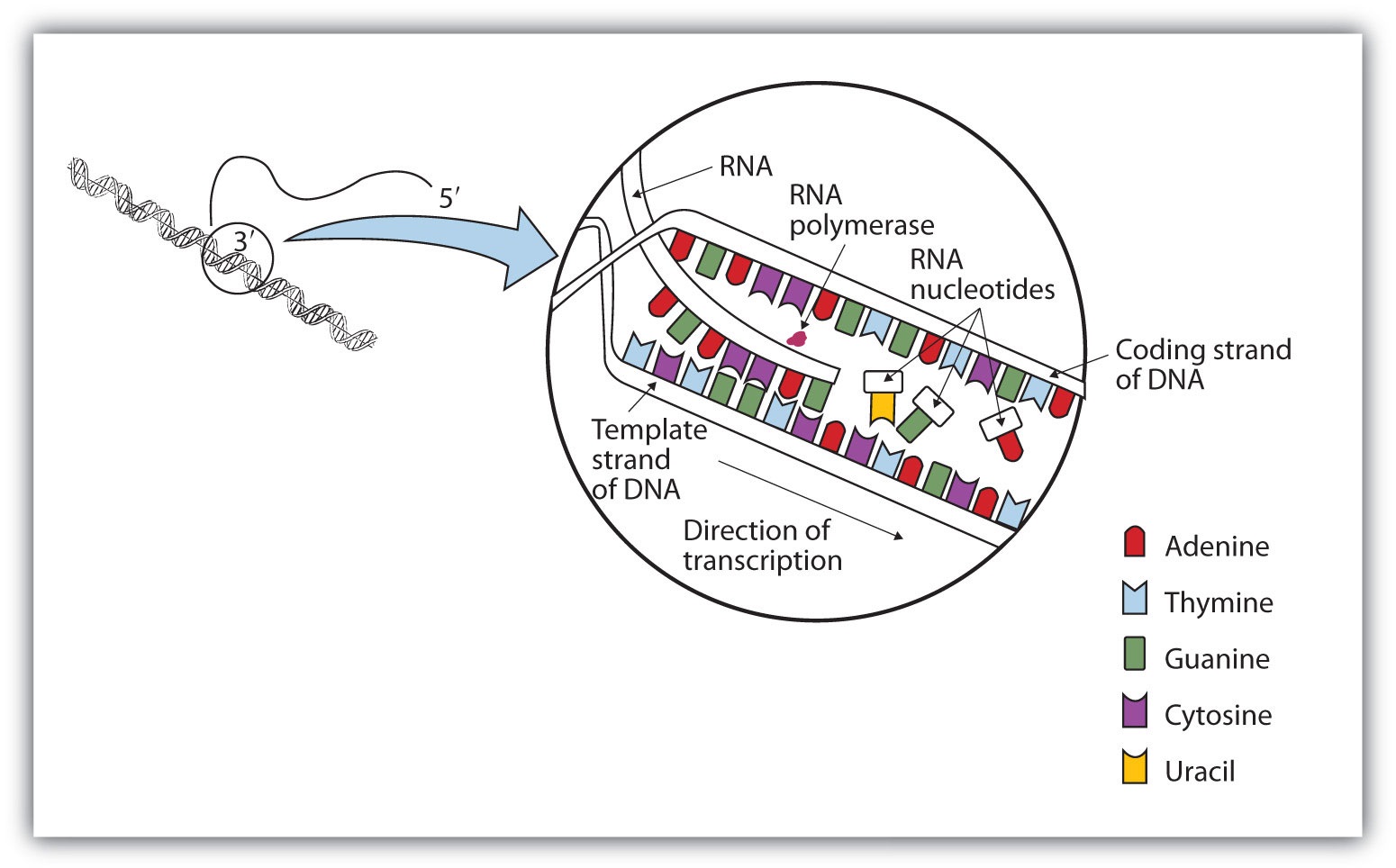
During transcription, the enzyme RNA polymerase (green) uses DNA as a template to produce a pre-mRNA transcript (pink). The pre-mRNA is processed to form a mature mRNA molecule that can be.
DNA Transcription Diagram. Create Biology Diagram examples like this template called DNA Transcription Diagram that you can easily edit and customize in minutes. 6/20 EXAMPLES. EDIT THIS EXAMPLE. CLICK TO EDIT THIS EXAMPLE. Text in this Example: DNA anti-codon Strand DNA coding strand mRNA Free Floating Nucleotides RNA Polymerase.
Genetic transcription unit. a segment of DNA that codes for an RNA. molecule and the sequences necessary for its transcription. includes: nontemplate and template strands, promoter, RNA coding region with a transcription start site and termination sequence. transcription starts at the ____ nucleotide. +1.
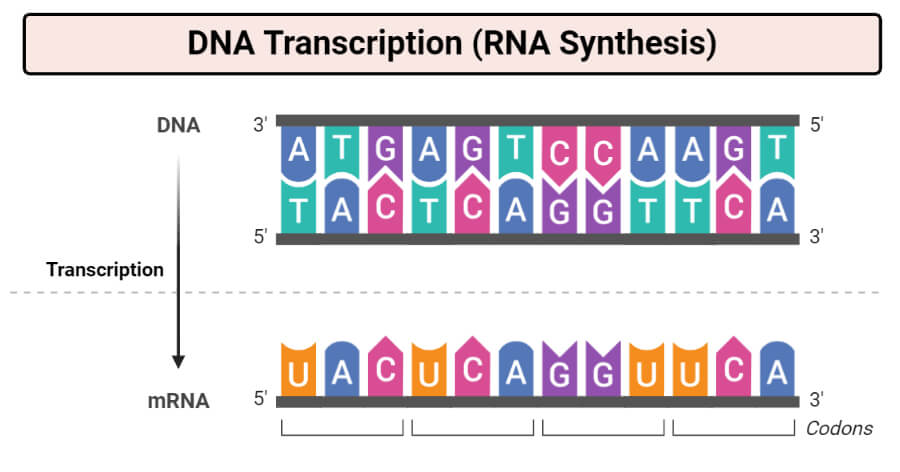
DNA transcription, also known as RNA synthesis is the process by which genetic information that is contained in DNA is re-written into messenger RNA (mRNA) by an RNA polymerase enzyme. The synthesized mRNA is transported out of the cell nucleus where it will later on aid in the synthesis of proteins by the mechanism of translation.
C. Nucleotides are linked in a 3′ to 5′ direction and the new strands are anti-parallel to the template strands.. There still seems to be some confusion in the topic of transcription as to which is the sense or antisense strand of DNA. The syllabus specifies how this should be treated in 7.3.2.... The diagram shows the cross section of ...
A transcription bubble is a molecular structure formed during DNA transcription when a limited portion of the DNA double strand is unwound. The size of a transcription bubble ranges from 12-14 base pairs. A transcription bubble is formed when the RNA polymerase enzyme binds to a promoter and causes two DNA strands to detach. It presents a region of unpaired DNA, where a short stretch of.
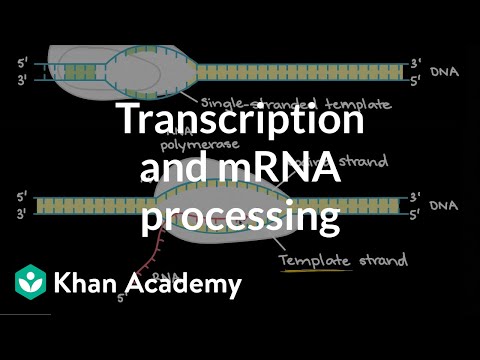
Overview of transcription. Transcription is the first step in gene expression, in which information from a gene is used to construct a functional product such as a protein. The goal of transcription is to make a RNA copy of a gene's DNA sequence. For a protein-coding gene, the RNA copy, or transcript, carries the information needed to build a.
1. Diagram 11 A Reference : - a . The direction of Strike is N-S . N North Strike dined in W E South > Dip Direction S The direction of Dip of beds is towards East. b. Proper Symbol : - The symbol is + Map view C. Proper Symbed on Prespective View :. The symbol is + d. The angle of Dip measured Ipometrically is 50 degrees.
Step 1: Initiation. Initiation is the beginning of transcription. It occurs when the enzyme RNA polymerase binds to a region of a gene called the promoter. This signals the DNA to unwind so the enzyme can ''read'' the bases in one of the DNA strands. The enzyme is now ready to make a strand of mRNA with a complementary sequence of bases.
What is the direction of transcription in this diagram? The RNA polymerase reads the template strand from the 3' to 5' direction, and synthesizes RNA from 5' to 3'.The template strand is the DNA strand that is based paired to RNA as transcription proceeds.
State the direction of transcription and draw a simple diagram to show the addition of an RNA molecule to a growing mRNA strand. Transcription is in 5' - 3' direction. 4.
Part B What is the direction of transcription in this diagram? ANSWER: Correct The RNA polymerase reads the template strand from the 3' to 5' direction, and synthesizes RNA from 5' to 3'. The template strand is the DNA strand that is based paired to RNA as transcription proceeds. In this example, the RNA is paired with the bottom strand.
Reverse transcription is the process of making a double stranded DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) molecule from a single stranded RNA (ribonucleic acid) template. It is called reverse transcription as it acts in the opposite or reverse direction to transcription. This idea was very unpopular at first as it contradicted the central dogma of molecular.
An in-depth looks at how transcription works. Initiation (promoters), elongation, and termination. Google Classroom Facebook Twitter. Email. Transcription. DNA replication and RNA transcription and translation. Transcription and mRNA processing. Molecular structure of RNA.
Transcription is the process of copying a segment of DNA into RNA. The segments of DNA transcribed into RNA molecules that can encode proteins are said to produce messenger RNA (mRNA). Other segments of DNA are copied into RNA molecules called non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs). Averaged over multiple cell types in a given tissue, the quantity of mRNA is more than 10 times the quantity of ncRNA (though.
Transcription: Elongation The mRNA is synthesized. RNA polymerase moves downstream breaking the hydrogen bonds between the DNA base pairs exposing 10‐20 DNA nucleotides at a time. Messenger RNA is assembled in the 5' 3' direction using the template DNA strand (diagram 2).









:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/transcription_elongation-58f91de33df78ca159d34363.jpg)











0 Response to "38 What Is The Direction Of Transcription In This Diagram?"
Post a Comment