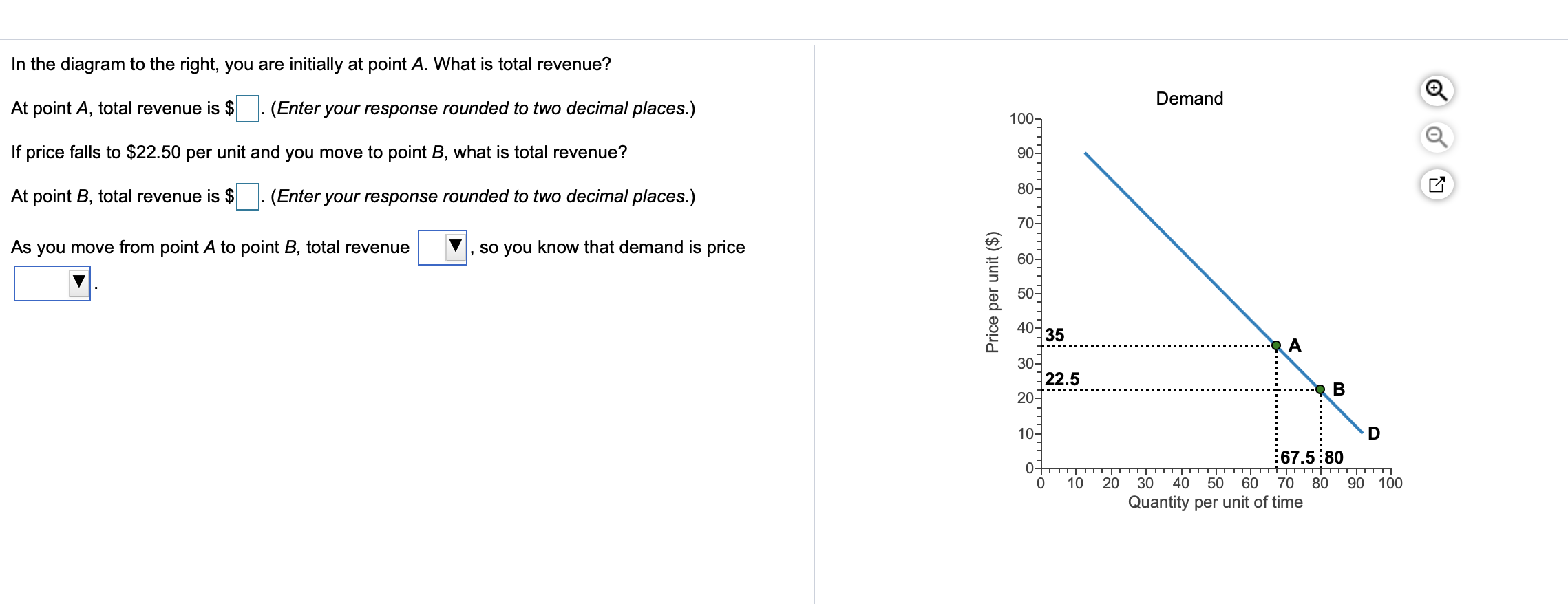
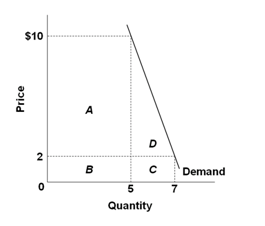
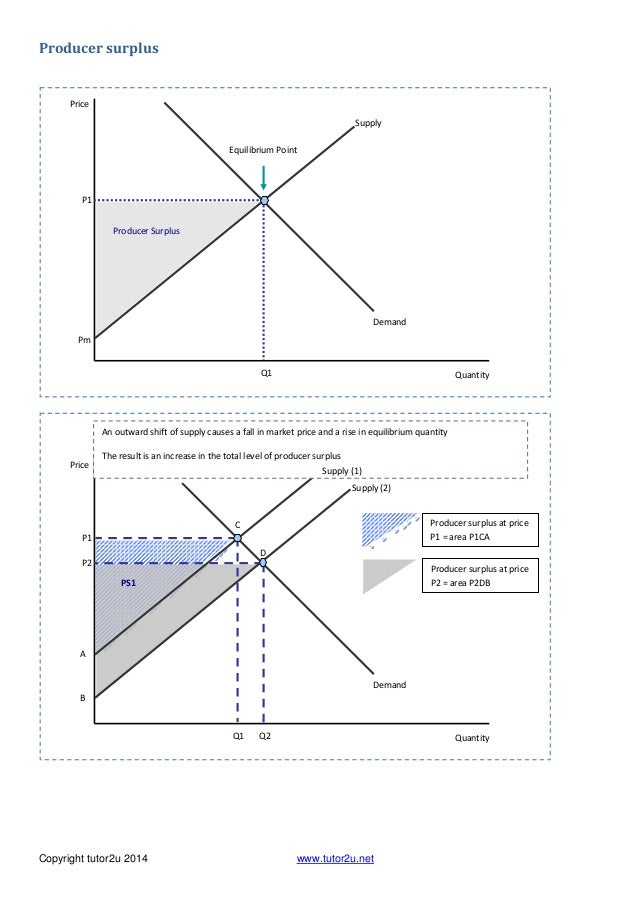
38 Refer To The Diagram. If Price Falls From P1 To P2, Total Revenue Will Become Area(s)
c. Suppose the firm now charges three prices: the initial price it charged as a single price monopolist, P1, and P2. Calculate the firm's TR under this pricing scheme. Calculate the firm's TC given this pricing arrangement (don't forget those fixed costs!). Then, calculate the firm's profits. Refer to Figure 7-4. When the price rises from P1 to P2, which area represents the increase in producer surplus to existing producers? a. BCE b. ACF c. DEF d. ABED Figure 7-5. On the graph below, Q represents the quantity of the good and P represents the good's price. ____ 17. Refer to Figure 7-5. If the price of the good is $8.50, then.
b. Consider the market for college education in the U.S. and assume that this market is initially in equilibrium at P1 and Q1. Suppose that there is an increase in the number of foreign-born students seeking a college education in the U.S. Illustrate this market's initial equilibrium as well as its new equilibrium (Q2, P2) in a well labeled.

Refer to the diagram. if price falls from p1 to p2, total revenue will become area(s)
Refer to the above diagram. If price falls from P1 to P2, total revenue will become area(s): B + D. Refer to the above diagram. The decline in price from P1 to P2 will: increase total revenue by D - A. Refer to the above diagram. In the P1 to P2 price range, we can say: Refer to the above diagram. If price falls from P1 to P2, total revenue will become area(s): A. B+D. Refer to the above diagram. The decline in price from P1 to P2 will: D. increase total revenue by D-A. Refer to the above diagram. In the P1 to P2 price range, we can say: Refer to the diagram. If price falls from P1 to P2, total revenue will become area(s) Question: 16. Refer to the diagram. If price falls from P1 to P2, total revenue will become area(s) This problem has been solved! See the answer See the answer See the answer done loading. 16. Refer to the diagram.
Refer to the diagram. if price falls from p1 to p2, total revenue will become area(s). Refer the to above diagram. If price falls from P1 to P2 total revenue will become area(s): B + D. The demand schedules for such products as eggs, bread, and electricity tend to be: relatively price inelastic. 3. The price elasticity of toll calls within the 510 area code, for which Pacific Bell is the only supplier, is estimated to be about -1.1. If rate for these calls is raised, Pacific Bell earns (a) more revenue (b) less revenue (c) same revenue (d) need more information 4. The amount of capital (K) a firm is willing to trade for a unit of labor. Become Our Regulars We put decades of writing experience to work for you and are passionate about helping you succeed. Let the figures tell our story!. Total price: $ 0.00. We can help you reach your academic goals hassle-free. We can help you reach your academic goals hassle-free. Power up Your Academic Success with the Total price: $ 26. free inquiry. Features. fill. Filling the forms involves giving instructions to your assignment. The information needed include: topic, subject area, number of pages, spacing, urgency, academic level, number of sources, style, and preferred language style.... This writers are also assigned a skilled mentor who guides them ...
So, we may calculate total revenue from each market for different price-quantity combinations and then the corresponding MR. So, when the firm sells 600 units in market I, at a price of Rs. 40 per unit and 800 units in market 2 at a price of Rs. 50, MR 1 = MR 2 and total revenue is Rs. 24,000 + Rs. 40,000 = Rs. 64,000 which is maximum. Choose the Writer’s Samples option – study 3 randomly-provided pages from orders that have been written by the assigned writer. Request a specific writer – choose an academic writer from the dropdown list in the order’s form (optional for returning customers). Refer to the above diagram. If price falls from P1 to P2, total revenue will become area(s): A. B + D. B. C + D. C. A + C. D. C. 8. Refer to the above diagram. The decline in price from P1 to P2 will: A. increase total revenue by D. B. increase total revenue by B + D. C. decrease total revenue by A. D. increase total revenue by D - A. 9. At Q1, AR > AC and the difference between average revenue and average cost is the distance AB. This is the profit per unit. To find the total super normal profit, we must multiply the profit per unit by the number of outputs. In the diagram, this is the area ABCP1 (the green box). MC SHORT-RUN INDUSTRY EQUILIBRIUM The given price is P2.
Refer to the diagram and assume a single good. If the price of the good increased from $5.70 to $6.30 along D1, the price elasticity of demand along this portion of the demand curve would be:. Refer to the diagram. If price falls from P1 to P2, total revenue will become area(s): B + D.... demand will become less price elastic. If the ... Refer to the above diagram. If price falls from P1 to P2, total revenue will become area(s): A. B+D. Refer to the above diagram. The decline in price from P1 to P2 will: D. increase total revenue by D-A. Refer to the above diagram. In the P1 to P2 price range, we can say: Refer to the diagram. If price falls from P1 to P2, total revenue will become area(s) Question: 16. Refer to the diagram. If price falls from P1 to P2, total revenue will become area(s) This problem has been solved! See the answer See the answer See the answer done loading. 16. Refer to the diagram. We give anonymity and confidentiality a first priority when it comes to dealing with client’s personal information. The following are some of the ways we employ to ensure customer confidentiality. We have encrypted all our databases; All our client’s personal information is stored safely; We have servers that operate 99.9% of the time
Cheap essay writing sercice. If you need professional help with completing any kind of homework, Solution Essays is the right place to get it. Whether you are looking for essay, coursework, research, or term paper help, or with any other assignments, it is no problem for us.
We guarantee a perfect price-quality balance to all students. The more pages you order, the less you pay. We can also offer you a custom pricing if you feel that our pricing doesn't really feel meet your needs. Proceed To Order. Writing. Fine-crafting custom academic essays for each individual’s success -.
Economics Q&A Library Figure 3-16 Price P2 :B P1 Q1 Q2 Quantity Refer to Figure 3-16. When the price falls from P2 to P1, producer surplus decreases by an amount equal to C. decreases by an amount equal to A + B. decreases by an amount equal to A + C. increases by an amount equal to A + B.
While the consumer is now paying price (P1) the producer only receives price (P2) after paying the tax. Due to the tax, the area of consumer surplus is reduced to area A and producer surplus is reduced to area B. The tax revenue is equal to the tax per unit multiplied by the units sold.
If price falls from P1 to P2, total revenue will become area(s):-A + C.-C + D.-B + D.-C.-B+D. Refer to the diagram and assume a single good. If the price of the good increased from $5.70 to $6.30 along D1, the price elasticity of demand along this portion of the demand curve would be:. Refer to the diagram. If price falls from $10 to $2...
Quick Quizzes. 1. When a competitive firm doubles the amount it sells, the price remains the same, so its total revenue doubles. 2. The price faced by a profit-maximizing firm is equal to its marginal cost because if price were above marginal cost, the firm could increase profits by increasing output, while if price were below marginal cost, the firm could increase profits by decreasing output.
Refer to the above diagram. If price falls from P1 to P2, total revenue will become area(s): A. B+D. Refer to the above diagram. The decline in price from P1 to P2 will: D. increase total revenue by D-A. Refer to the above diagram. In the P1 to P2 price range, we can say:
Total revenue is maximized. C) Marginal revenue is zero. D). That can alter the market price of the good(s) it produces. D)... diagram "a" presents the cost curves that are relevant to a firm's production decision, and diagram "b" shows the market demand and supply curves for the market.
If the price of bread falls by 10 percent, the quantity demanded will increase by: 2 percent and total expenditures on bread will fall. Refer to the above diagram which is a rectangular hyperbola, that is, a curve such that each rectangle drawn from any point on the curve will be of identical area.
23. Refer to the above diagram. If price falls from P1 to P2, total revenue will become area (s): A. B + D. B. C + D. C. A + C. D. C. 24. Refer to the above diagram. The decline in price from P1 to P2 will: A. increase total revenue by D. B. increase total revenue by B + D. C. decrease total revenue by A. D. increase total revenue by D - A.
refer to the diagram if price Falls from P1 to P2 total revenue will become areas b + d refer to the diagram and assume that price increases from $2 to $10 the coefficient of the price elasticity of supply midpoint formula relating to this price range is about
Refer the to above diagram. If price falls from P1 to P2 total revenue will become area(s): B + D. The demand schedules for such products as eggs, bread, and electricity tend to be: relatively price inelastic. The elasticity of demand for a product is likely to be greater:
With no trade, the price of suits is 3 ounces of gold, consumer surplus is area A, producer surplus is area B + C, and total surplus is area A + B + C. When trade is allowed, the price falls to 2 ounces of gold, consumer surplus rises to A + B + D (an increase of B + D), producer surplus falls to C (a decline of B), so total surplus rises to A.
Refer to the above diagram. If price falls from P1 to P2, total revenue will become area(s): B + D. Refer to the above diagram. The decline in price from P1 to P2 will: increase total revenue by D - A. Refer to the above diagram. In the P1 to P2 price range, we can say:
70. Refer to the above diagram. If price falls from P1 to P2, total revenue will become area(s): A) B + D B) C + D C) A + C D) C Answer: A. Type: G Topic: 2 E: 360 MI: 116 71. Refer to the above diagram. The decline in price from P1 to P2 will: A) increase total revenue by D. C) decrease total revenue by A.
Refer to the diagram. Total revenue at price P1 is indicated by area(s): A) A + C. B) C + D.. The decline in price from P1 to P2 will: A) increase total revenue by D - A. B) decrease total revenue by A. C) increase total revenue by B + D. D) increase total revenue by D.... Suppose that as the price of Y falls from $2.00 to $1.90, the ...
Total revenue at price P1 is indicated by area(s): B. A+B. Refer to the above diagram. If price falls from P1 to P2, total revenue will become area(s): A. B+D. Refer to the above diagram. The decline in price from P1 to P2 will: D. increase total revenue by D-A. Refer to the above diagram. In the P1 to P2 price range, we can say:
If, at the output where marginal cost equals marginal revenue, both a pure competitor's and a monopolist's marginal revenue is $5.00: A) both sellers' profit-maximizing price will be $5.00. B)) bot...
If price falls from P1 to P2, total revenue will become area(s) B + D.. In which of the following instances will total revenues decline? price rises and Ed equals 2.47. Refer to the diagram. In the P3P4 price range, demand is. relatively inelastic.... Total revenue falls as the price of a good is raised, if the demand for the good is.
The table gives the demand schedule for peanuts When the price of peanuts falls from $1.60 to $1.20, what is the change in total revenue? Over the price range if $1.20 and $1.60, the demand for pe.










/law_of_demand_chart2-5a33e7fc7c394604977f540064b8e404.png)


:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/law_of_demand_chart2-5a33e7fc7c394604977f540064b8e404.png)




0 Response to "38 Refer To The Diagram. If Price Falls From P1 To P2, Total Revenue Will Become Area(s)"
Post a Comment