38 Life Cycle Of A Fern Diagram
Life cycle of a chicken diagram worksheet pdf. Print here >>> Fly life cycle.. Life cycle of a fern pdf. Worksheet on the life cycle of a fern. Print here >>>... Frogs have an interesting life cycle; they go from eggs to looking like fish and later to frogs as we know them. Check out this test sheet to see if your students master the ... The life cycle of the fern Ceratopteris richardii In order to understand plant life cycles, it is beneficial to some relevant terminology before proceeding. Diploid - A full set of genetic material, consisting of homologous (paired) chromosomes.
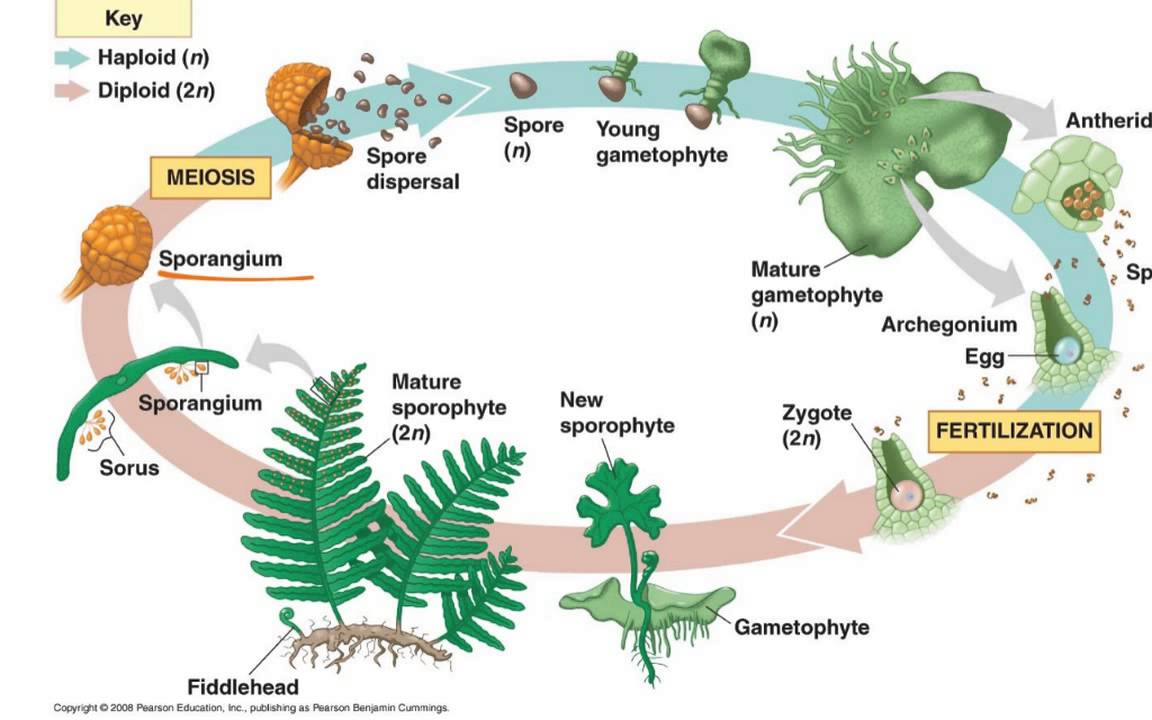
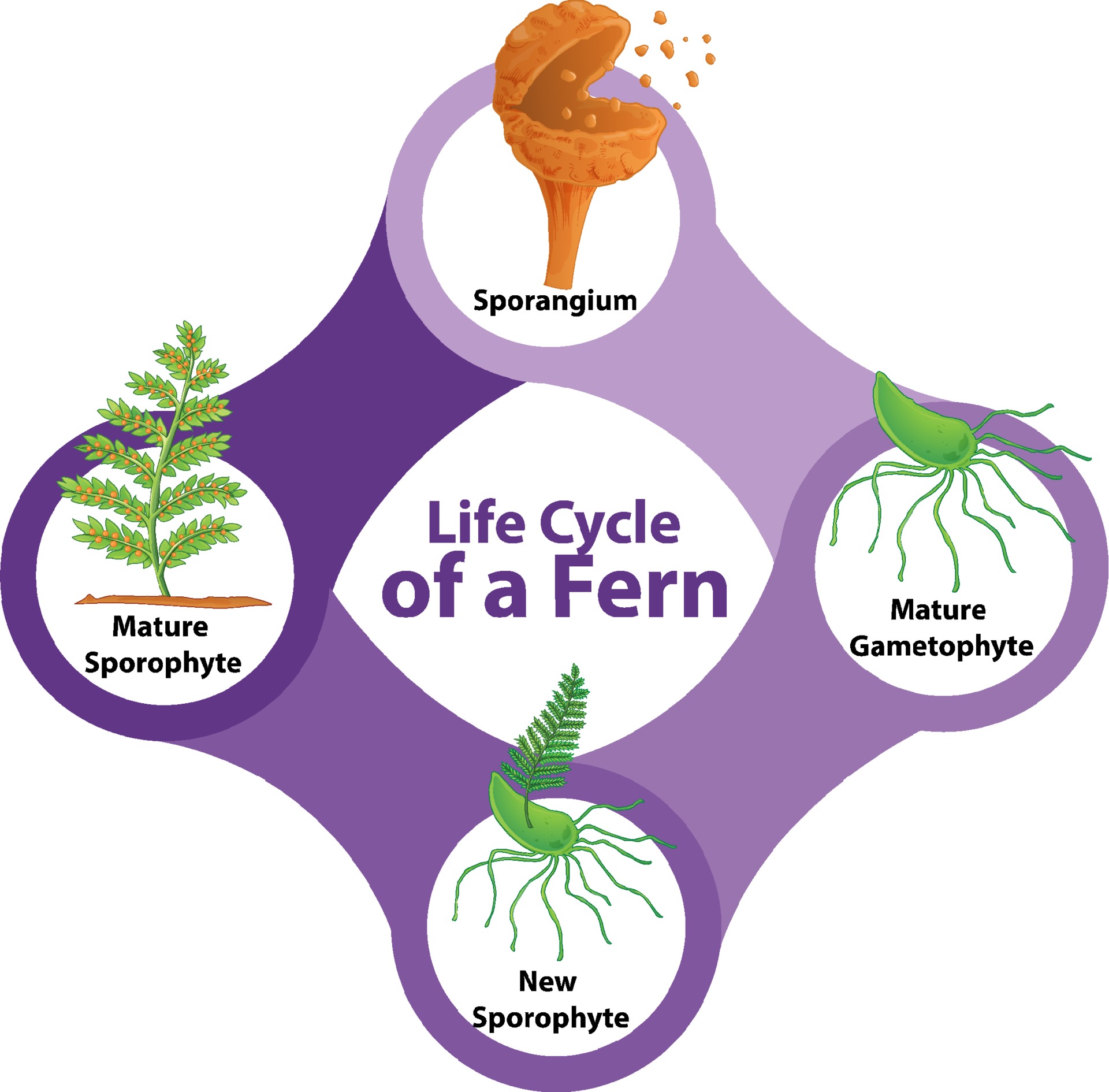
The dominant part of the life cycle, i.e., the plant that is recognized as a fern, represents the sporophyte generation. The gametophyte generation includes the phase of the life cycle between the formation of spores by meiosis and fertilization and formation of the zygote.
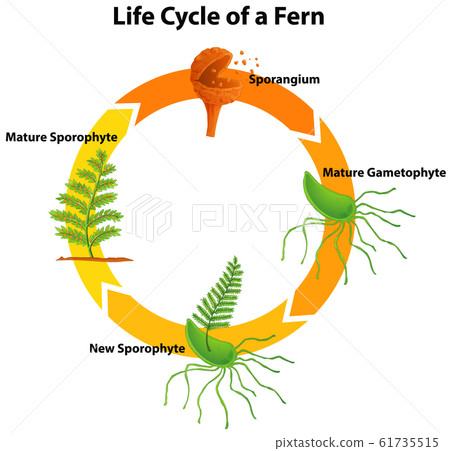
Life cycle of a fern diagram
Nostoc is a genus of cyanobacteria (blue-green algae). They are found mainly in freshwater as free-living colonies or attached to rocks, tree trunks or at the bottom of lakes. They are also found in symbiotic association with plants such as water fern and Anthoceros. Diagram of the fern life cycle The fern begins with the haploid stage as a spore. The spore will undergo mitosis in order to create many identical haploid cells. This is a post titled Fern Plant Diagram, we will share many pictures for you that relate to "Fern Plant Diagram". Hopefully the picture gallery below will be useful for you. May 17, 2018 · Alternation of generations is a type of life cycle found in terrestrial plants and some algae in which subsequent generations of individuals alternate between haploid and diploid organisms. This can be contrasted to sexual reproduction in animals, in which both haploid and diploid cells are found in.
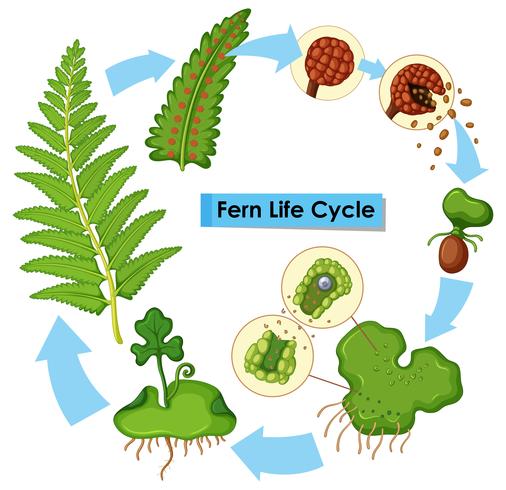
Life cycle of a fern diagram. The life cycle of a plant describes the different stages of the plant from the beginning of its life until the end, which is from seed to mature plant. However, not all plants produce seed. Some plants such as fern or mosses produce different kinds of cells called “ Spores ”. Diagram of the fern life cycle The fern begins with the haploid stage as a spore. The conspicuous part of a fern plant is a _____. The mature fern plant consists of three major parts the rhizome the fronds and the sporangia. Ferns produce spores but they dont have seeds or blossoms making them seedless vascular plants. Moss has stems and leaves. Diagram of the fern life cycle The fern begins with the haploid stage as a spore. The spore will undergo mitosis in order to create many identical haploid cells. Ferns are seedless vascular plants.Most of them are terrestrial where as some are epiphytes, xerophytes or hydrophytes. Some of the members are Salvinia, Azolla, Adiantum etc.. There is a regular alternation of generation between the sporophytic phase and gametophytic phase in the life cycle of ferns. The sporophytic generation is the prominent one.. Sporophytic phase may produce spores on.
The life cycle of most mosses begins with the release of spores from a capsule, which opens when a small, lidlike structure, called the operculum, degenerates. A single spore germinates to form a branched, filamentous protonema, from which a leafy gametophyte develops. The gametophyte bears organs for sexual reproduction. Sperm, which are released by the mature antheridium (the male. The life cycle of ferns has two forms. The beautiful plant body that we see is called the "Sporophyte" which means Spore bearing plant and is the dominant part of the cycle. There is another form called as the "Gametophyte" or the plant body bearing gametes which is very less-lived when compared to the sporophyte. The life cycle of fern completes in (2 stage), the sporophyte (2n) and the gametophyte (n). The two stages occur one after the other to complete the life cycle. This process is known as alternation of generation. Alternation of generation in a diagram. Draw the labelled diagram of archegonium. May 17, 2018 · Alternation of generations is a type of life cycle found in terrestrial plants and some algae in which subsequent generations of individuals alternate between haploid and diploid organisms. This can be contrasted to sexual reproduction in animals, in which both haploid and diploid cells are found in.
Hornwort life cycle diagram In ferns and their allies, including clubmosses and horsetails , the conspicuous plant observed in the field is the diploid sporophyte. The haploid spores develop in sori on the underside of the fronds and are dispersed by the wind (or in some cases, by floating on water). The diagram below illustrates the life cycle of Dictyostelium, a cellular slime mold. Label the diagram to indicate the processes that are occurring as well as whether each cell type is haploid or diploid. The zygote eventually develops into a mature sporophyte, full of diploid cells, initiating the life cycle once more, as shown in stage (E) of the diagram. Having reviewed the life cycle of a typical fern plant, we can answer this question correctly. The stage in the diagram that corresponds to reproduction by spores is (B). Consider the characteristics of moss and fern life cycles. Which of the following sets of statements is true? In mosses, the gametophyte is the dominant stage of the life cycle; in ferns, the sporophyte is the dominant stage of the life cycle. In both mosses and ferns, moisture is required for sperm to.
Nostoc is a genus of cyanobacteria (blue-green algae). They are found mainly in freshwater as free-living colonies or attached to rocks, tree trunks or at the bottom of lakes. They are also found in symbiotic association with plants such as water fern and Anthoceros.
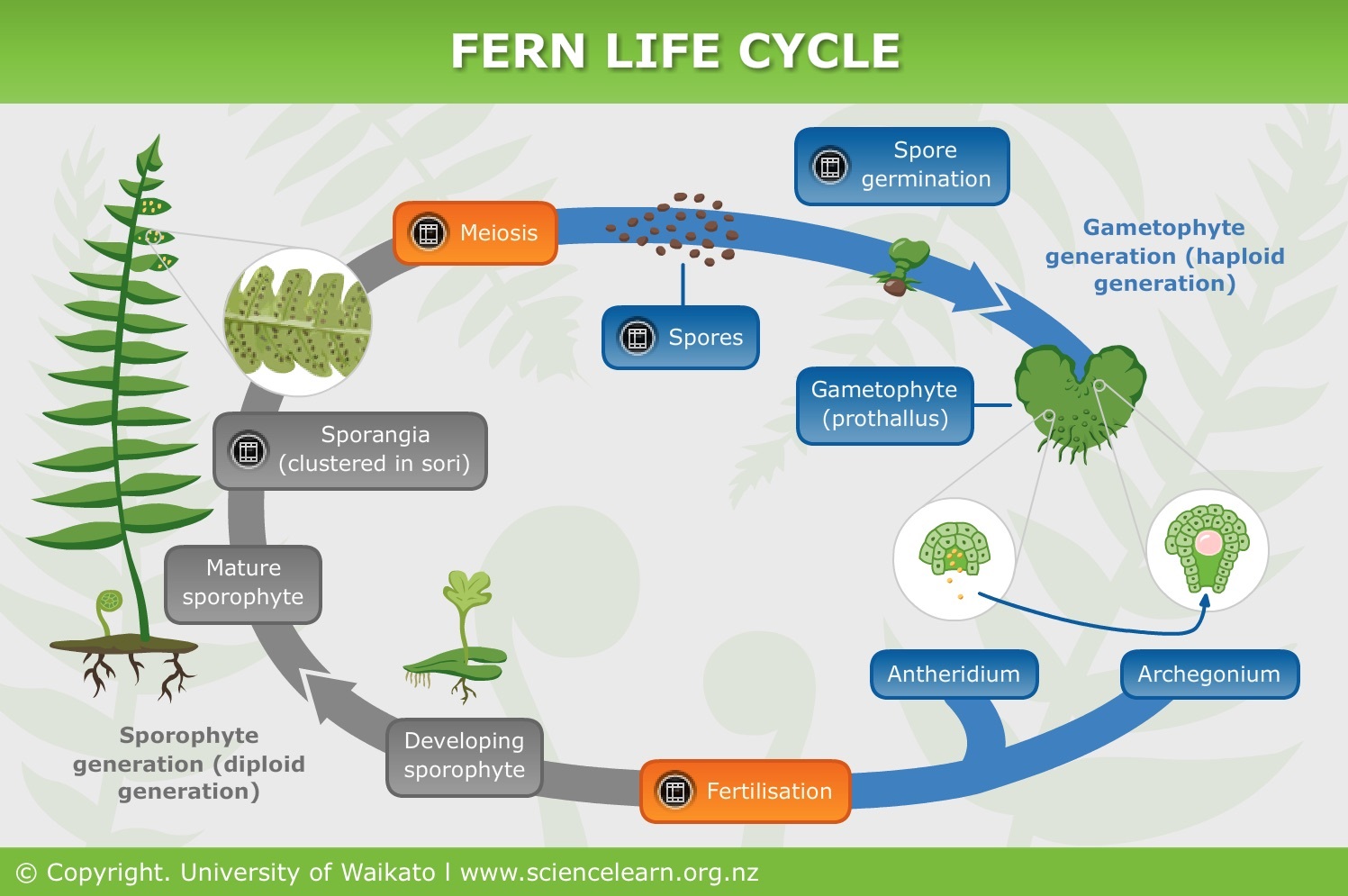
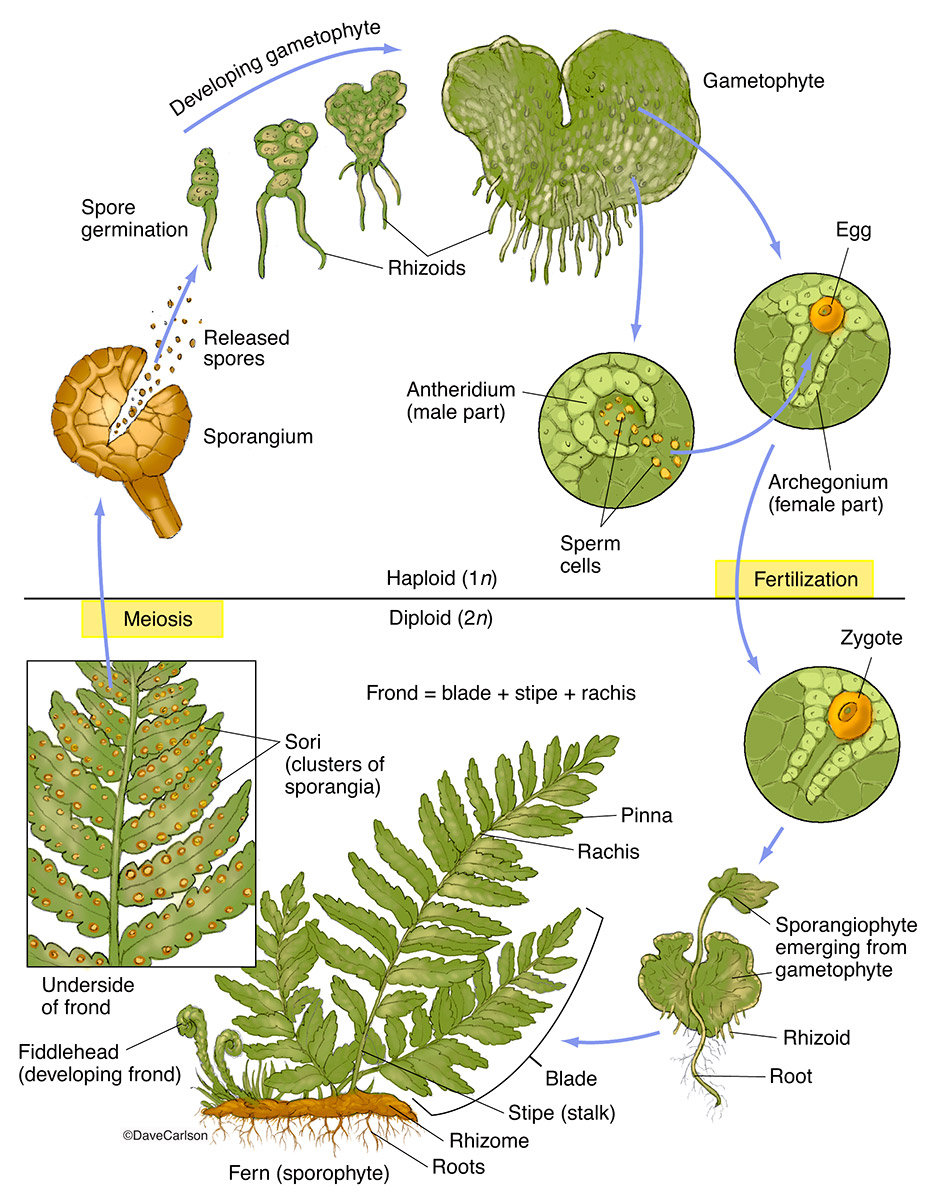
FERN LIFE CYCLE A DIFFERENT WAY OF REPRODUCING. This basic life cycle is found in all non-seed producing plants including... Starting on the lower left of the diagram, the regular fern plant is the sporophyte with fronds. The arrow above shows a leaf segment or pinna with spore clusters or sori underneath. The next arrow points to a single
The Alternation of Generations and what it means in a fern's life cycle The haploid stage and corresponding terminology The diploid Stage and corresponding terminology; Practice Exams.
The life cycle of ferns is different from other land plants as both the gametophyte and the sporophyte phases are free living. This interactive.Diagram of the fern life cycle The fern begins with the haploid stage as a spore. The spore will undergo mitosis in order to create many identical haploid cells. Start studying Fern Life Cycle.
Features of the fern life cycle. Whether a fern actually blooms or is it a delusion, a person has been interested in since ancient times. To clarify the issue, you should trace the cause-and-effect relationship. As you know, the flower of a plant, after wilting, forms a testis. That is, if a certain culture is grown from seeds, then initially.
Fern Life Cycle. Ferns belong to the Division Pterophyta characterized by vascular plants with leaves (fronds) arising from subterranean, creeping rhizomes. In tree ferns, the leaves are produced on a definite woody trunk. The dominant (conspicuous) part of the life cycle is the diploid, leaf-bearing sporophyte.
The fern life cycle requires two generations of plants to complete itself. This is called alternation of generations. One generation is diploid, meaning it carries two identical sets of chromosomes in each cell or the full genetic complement (like a human cell). The leafy fern with spores is part of the diploid generation, called the sporophyte.
Diagram of the fern life cycle The fern begins with the haploid stage as a spore. The spore will undergo mitosis in order to create many identical haploid cells. This is a post titled Fern Plant Diagram, we will share many pictures for you that relate to "Fern Plant Diagram". Hopefully the picture gallery below will be useful for you.
Life Cycle of Equisetum | Pteridophyta | Botany. Equisetum, commonly known as 'horsetail' is found with about 25 species all over the world excepting Australia and New Zealand, and is mostly an inhabitant of the cool and temperate regions. It is usually found in hills, especially in dark and marshy places, wet fields, gravelly or loamy soil.
Each leaf on label a chart/model showing a fern life cycle How can microscopic protists and fungi be Read and Color the "Life Cycle of a Moss" Tracheophytes (aka Vascular Plants) Division Pterophyta: Ferns Read and color the "Life Cycle of a Fern" Online quiz answers should be emailed to the teacher. structures and life cycle development f.
Start studying Life Cycle of a Fern. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools.
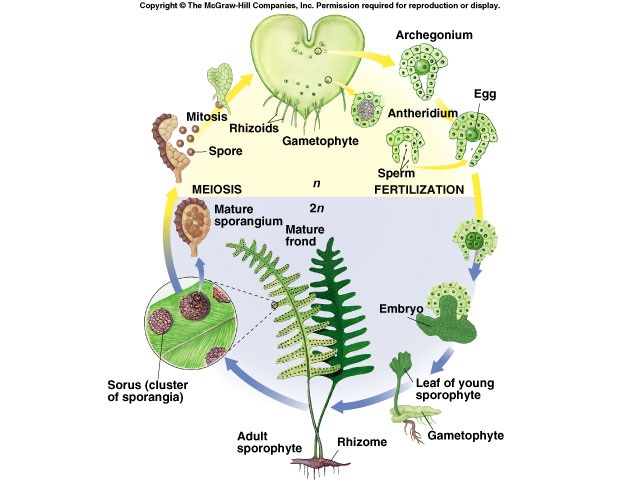
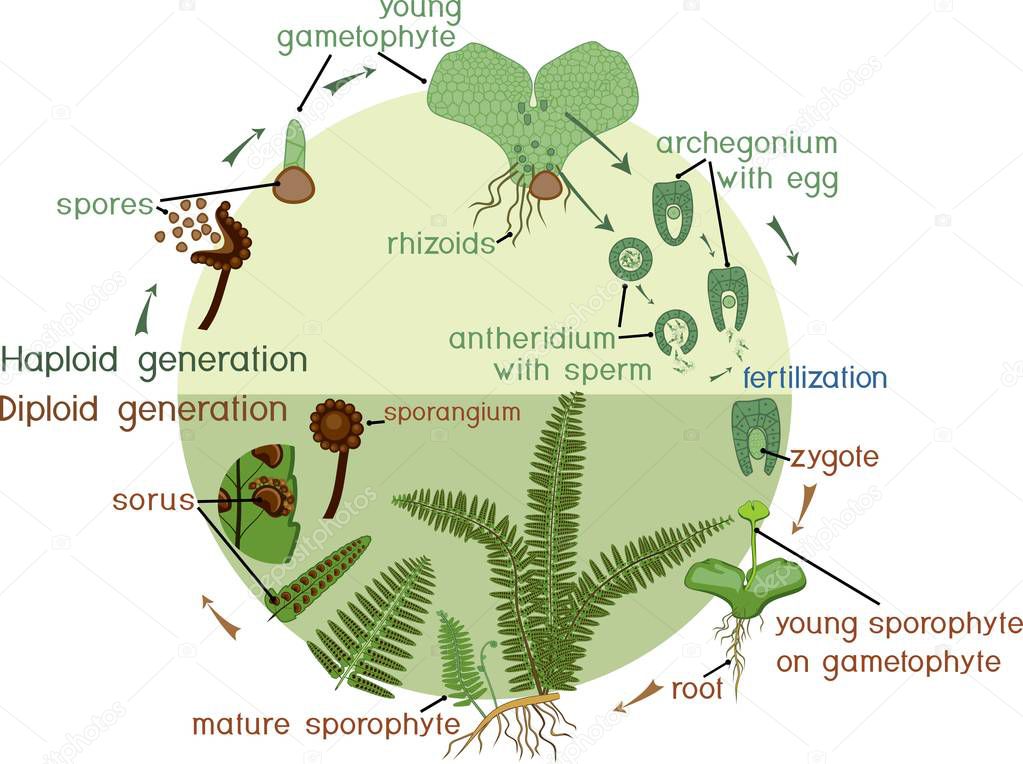
By repeated cell division oospore gives rise to the multicellular embryo, which develops into a new fern plant, thus completing the life-history. Life-Cycle of Ferns : The above life-history shows that it has two distinct parts, the plant itself reproducing asexually by spores and the pro-thallus reproducing sexually by gametes.
Jul 14, 2018 · Life Cycle of Pteridophyta. Pteridophytes show alternation of generations. Their life cycle is similar to seed-bearing plants, however, the pteridophytes differ from mosses and seed plants as both haploid gametophyte and diploid sporophyte generations are independent and free-living.
Fern life cycle. Araucaria angustifolia ( Brazilian pine), Brazil. Diagram showing bean life cycle. Diagram showing moss life cycle. Moss life cycle. Diagram of a life cycle of a Common haircap moss. Diagram showing bean plant life cycle. Green fern frond with sori. More similar stock illustrations.
A look at the fern's life cycle. View more lessons: http://www.educreations /yt/645144/?ref=ytd
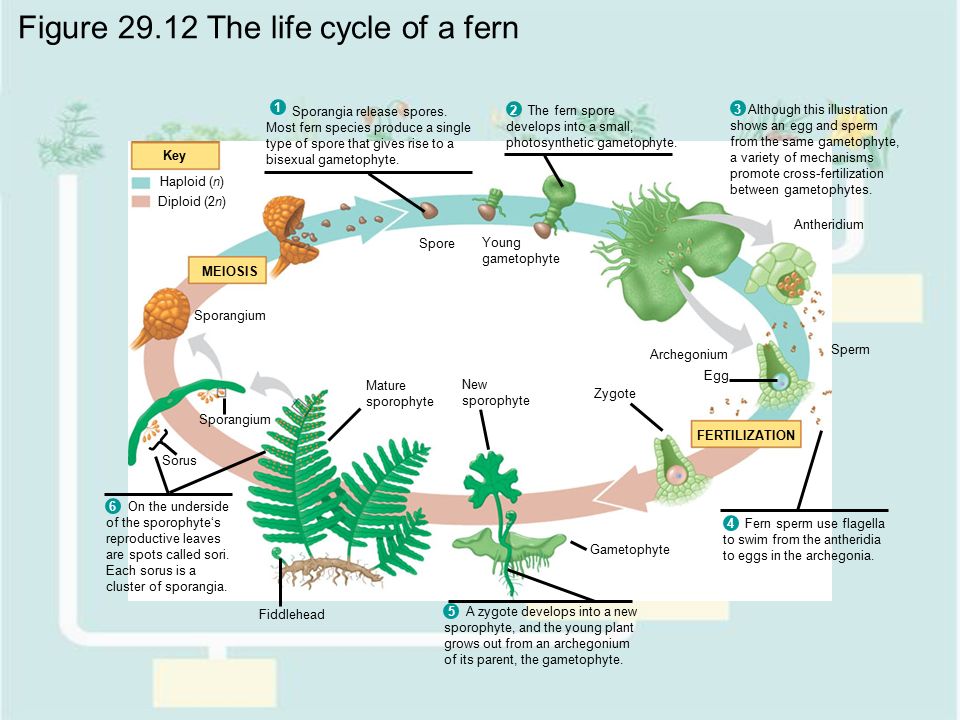
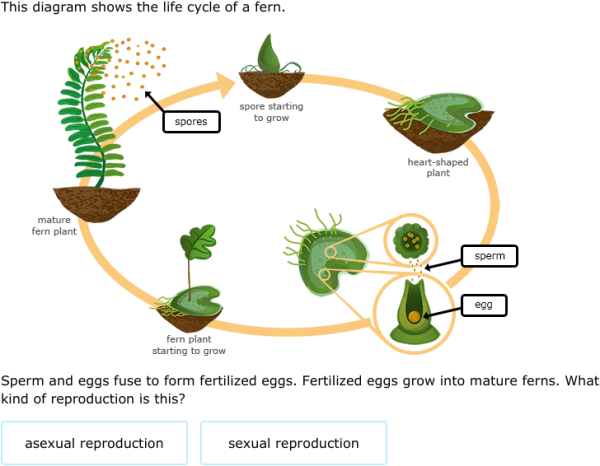
Answers: 3 on a question: Use the diagram to identify the correct order of steps in the life cycle of a fern. SCI5A_03_02_QC A. spore production, fertilized egg, heart-shaped plant, sex cells, new plant B. spore production, heart-shaped plant, sex cells, fertilized egg, new plant C. fertilized egg, spore production, sex cells, heart-shaped plant, new plant D. fertilized egg, sex cells, heart.
The Fern Life Cycle Another example of the alternation of generations in plants: Student Tutorial - Click on this link to learn more about the life cycle of the fern.See pictures and diagrams of the organs associated with the gametophyte and sporophyte generations.
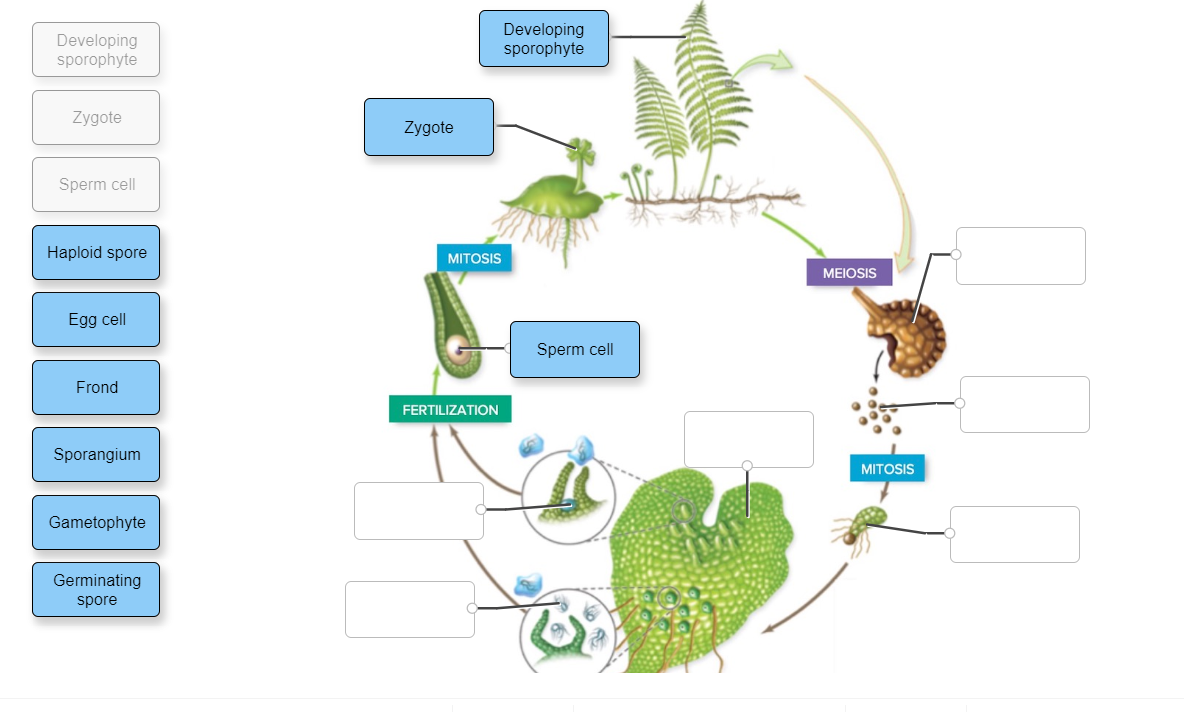
Transcribed image text: Complete the following diagram to describe the life cycle of a fern. The sporophyte is dominant in ferns. As the sporophyte becomes visible, it develops a rhizome from which fronds emerge. Sporophyte Flagellated sperm swim from the antheridia to the archegonium. - leaflet sporangium indusium Sorus Meiosis occurs and spores are produced and released. fiddlehead rhizome.
It grows using mitosis and develops into a young fern plant. Acknowledgement: George Shepherd. Mature sporophyte. The mature fern plant consists of three major parts – the rhizome, the fronds and the sporangia. The mature fern plant is the sporophyte structure that produces spores, which are released from sporangia. Acknowledgement: Steve Attwood
This allows self-fertilization, which is more successful in dry conditions since the distance to travel by the sperm cells is less. The fertilization produces a new sporophyte on the gametophyte. The typical life cycle of a fern is shown in figure 2. Similarities Between Mosses and Ferns. Mosses and ferns are primitive plants.
False; Club mosses are vascular plants, not nonvascular just like real mosses are. Term. Match the following words to where they are found: whisk ferns, horsetails, ferns. a. grow in wetland areas and along streams and rivers. b. grow from undergound stems called rhizomes. c. grow mostly in the tropics and subtropics. Definition. whisk ferns - c.
The diagram shows the life cycle of a fern. HELP ASAP!!!! What does stage 3 show? A) A mature spore-producing fern plant has fonds and produces spores. B) A spore grows into a mature gamete-producing plant. C) A zygote forms when a sperm fertilizes an egg cell D) A gamete-producing fern plant is flat and shaped like a heart.
Life Cycle of Pteridophytes: There is alternation of generation in the lifespan of pteridophytes. This is known as metagenesis. Just like in the seed bearing plants and mosses there is a diploid generation alternating with a haploid generation. The diploid generation is the sporophyte which produces the spores.
Life Cycle of a Fern. The life cycle of the fern has two different stages; sporophyte, which releases spores, and gametophyte, which releases gametes. Gametophyte plants are haploid, sporophyte plants diploid. This type of life cycle is called alternation of generations. To follow the life cycle of the fern, begin at number one below.
The life cycle of a typical fern proceeds as follows: A diploid sporophyte phase produces haploid spores by meiosis (a process of cell division which reduces the number of chromosomes by a half). A spore grows into a free-living haploid gametophyte by mitosis (a process of cell division which maintains the number of chromosomes).
Drag and drop each label into the correct location within the diagram showing the life cycle of a fern. start bottom left go up. Select all of the following that are true about the fern gametophyte. site of pollen production invisible to the naked eye.
Draw and label the life cycle of a fern (Pterydophyta). Draw and label the two phases of the life cycle. Include on the life cycle the events that must occur to switch from one phase to the other. Be sure to indicate which portions of the life cycle are haploid and/or diploid. Include and label any spore and/or gamete producing structures or organs












/GettyImages-521606980-5a7b3f7cc064710037c365fd.jpg)






0 Response to "38 Life Cycle Of A Fern Diagram"
Post a Comment