38 Drag The Labels Onto The Diagram To Identify Aspects Of Gas Transport And Exchange.
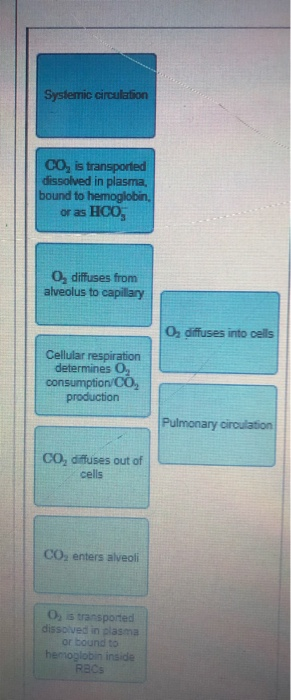
Gas exchange in tissues is a result of tissue surface area, gas partial pressure gradients, and the blood perfusion of those tissues. Key Terms Cellular respiration : The cellular process of producing adenosine triphosphate (ATP), water, and carbon dioxide from glucose and oxygen. Question. : Drag the labels onto the diagram to identify the mechanisms involved in the transport of carbon dioxide in the blood Reset Help 23 percent of CO2 transported bound to hemoglobin CARBON DIOXIDE TRANSPORT dissolved CO2 diffuses out of the plasma Most CO2 in the blood has been converted to bicarbonate ion, HCO VENOUS BLOOD Ht ions.
Drag the labels to their appropriate locations in the figure.. Gas exchange involves the transport of two respiratory gases, oxygen and carbon dioxide. Review how each gas is transported between the atmosphere and the cells of your body by completing this exercise.... Drag the labels onto the diagram to identify the path a secretory protein ...
Drag the labels onto the diagram to identify aspects of gas transport and exchange.
View Homework Help - Ch 18 HW.pdf from BIOL 65 at California State University, Fresno. 4/11/2015 Ch18HW Ch18HW Due:11:59pmonSunday,April5,2015. Transcribed image text: Drag the labels onto the diagram to identify aspects of gas transport and exchange. Art-labeling Activity Figure 18.1 Drag the labels onto the diagram to identify aspects of gas transport and exchange Systemic circulation PULMONARY GAS EXCHANGE AND TRANSPORT 6032 Airways CO, is transported dissolved in plasma bound to hemoglobin or as HCO, Alveoli of lungs O, diffuses. There are three planes commonly referred to in anatomy and medicine, as illustrated in Figure 1.4.3. The sagittal plane divides the body or an organ vertically into right and left sides. If this vertical plane runs directly down the middle of the body, it is called the midsagittal or median plane.
Drag the labels onto the diagram to identify aspects of gas transport and exchange.. Identify which diagram suggests the presence of a catalyst, and determine the activation energy for the catalyzed reaction: Solution A catalyst does not affect the energy of reactant or product, so those aspects of the diagrams can be ignored; they are, as we would expect, identical in that respect. Atoms are made up of subatomic particles such as the proton, electron and neutron. Two or more atoms combine to form a molecule, such as the water molecules, proteins, and sugars found in living things. Molecules are the chemical building blocks of all body structures. A cell is the smallest independently functioning unit of a living organism. Figure 10.2.2 - Muscle Fiber: A skeletal muscle fiber is surrounded by a plasma membrane called the sarcolemma, which contains sarcoplasm, the cytoplasm of muscle cells. A muscle fiber is composed of many myofibrils, which contain sarcomeres with light and dark regions that give the cell its striated appearance. Transcribed image text: Drag the labels onto the diagram to identify aspects of gas transport and exchange. Reset Help Systemic circulation PULMONARY GAS EXCHANGE AND TRANSPORT Airways CO2 is transported dissolved in plasma, bound to hemoglobin or as HCO3 Alveoli of lungs CO₂ O₂ O2 diffuses from alveolus to capillary co, so O2 diffuses into cells Cellular respiration determines 02.
Drag the labels onto the diagram to identify aspects of gas transport and exchange. Human cadaver anatomical models histology cat and fetal pig. Drag the labels onto the flowchart to identify the sequence in which carbon moves through these organisms 1. Glycolysis citric acid cycle and electron transport. Label the mechanisms of carbon dioxide transport. (Refer to the posted image for labeled answers) Drag the labels onto the diagram to identify the mechanisms involved in the transport of carbon dioxide in the blood. Identify the major reservoirs and processes in the carbon cycle by labeling the diagram below. Drag the labels onto this diagram of the carbon cycle. Part a drag the labels onto the diagram to identify aspects of gas transport and exchange. Then drag the pink labels onto the pink targets to identify the processes and reservoirs in the carbon cycle. Key events in gas exchange. Drag the labels onto the diagram to identify the major components of the respiratory system. Part a drag the labels onto the diagram to identify features of cell signaling and receptors. The other major requirement for protein synthesis is the translator molecules that physically read the mrna codons.
Transcribed image text: Drag the labels onto the diagram to identify aspects of gas transport and exchange. Art-labeling Activity Figure 18.1 Drag the labels onto the diagram to identify aspects of gas transport and exchange Systemic circulation PULMONARY GAS EXCHANGE AND TRANSPORT 6032 Airways CO, is transported dissolved in plasma bound to hemoglobin or as HCO, Alveoli of lungs O, diffuses. View Homework Help - Ch 18 HW.pdf from BIOL 65 at California State University, Fresno. 4/11/2015 Ch18HW Ch18HW Due:11:59pmonSunday,April5,2015. The actual sites of gas exchange within the lungs are the.. thick secretions that are difficult to transport.... Drag the labels onto the diagram to identify the major components of the respiratory system. Upper respiratory system (top to bottom): nose, nasal cavity, sinuses, pharynx ... Two important aspects of gas exchange in the lung are ventilation and perfusion. Ventilation is the movement of air into and out of the lungs, and perfusion is the flow of blood in the pulmonary capillaries. For gas exchange to be efficient, the volumes involved in ventilation and perfusion should be compatible.
Terms in this set (33) Drag the labels onto the diagram to identify aspects of gas transport and exchange. the diaphragm and rib muscles contract. Which statement is correct? In the blood, oxygen is bound to hemoglobin, a protein found in red blood cells. it returns to the heart, and is then pumped to body cells.
Identify the different epithelia of the body, and describe the chief function(s) and location(s) of each. An epithelium (ep″ ı˘-the ′le-um; "covering") is a sheet of cells that covers a body surface or lines a body cavity (Figure 4.1). Epithelial tissue occurs in two different forms:
15.3 Hearing Audition (Hearing) Hearing, or audition, is the transduction of sound waves into a neural signal that is made possible by the structures of the ear (Figure 15.3.1).The large, fleshy structure on the lateral aspect of the head is known as the auricle.Some sources will also refer to this structure as the pinna, though that term is more appropriate for a structure that can be moved.
appropriate model or diagram. Size, Location, and Orientation The modest size and weight of the heart give few hints of its incredible strength. Approximately the size of a person's fist, the hollow, cone-shaped heart weighs less than a pound. Snugly enclosed within the inferior mediastinum (me″de-as-ti′num), the
Biology. Biology questions and answers. Drag the labels onto the diagram to identify aspects of gas transport and exchange ResetHel CO2 diffuses out of pulmonary capillaries CO2 O2 Airways CO2 diffuses into systemic capillaries Alveoli of lungs co, o O2-rich blood 02 CO2-rich blood 02 diffuses from alveolus to capillary Blood flow to and from.
Drag the labels onto the diagram to identify the processes of reabsorption in the tubular epithelium. Most reabsorption of fluid from the filtrate back into the blood occurs from the _____. proximal tubule. In which process can glucose transport reach saturation? Reabsorption.
Exchange of Oxygen and Carbon Dioxide Dalton's Law Each gas in a mixture of gases exerts its own pressure as if no other gases were present Pressure of a specific gas is partial pressure P x Total pressure is the sum of all the partial pressures Atmospheric pressure (760 mmHg) = P N2 + P O2 + P H2O + P CO2 + P other gases
Structure of Nephron. The mammalian nephron is a long tube-like structure, its length varying from 35-55 mm long. At one end, the tube is closed, folded and expanded, into a double-walled, a cuplike structure called the Bowman's capsule or renal corpuscular capsule, which encloses a cluster of microscopic blood vessels called the glomerulus.
There are three planes commonly referred to in anatomy and medicine, as illustrated in Figure 1.4.3. The sagittal plane divides the body or an organ vertically into right and left sides. If this vertical plane runs directly down the middle of the body, it is called the midsagittal or median plane.
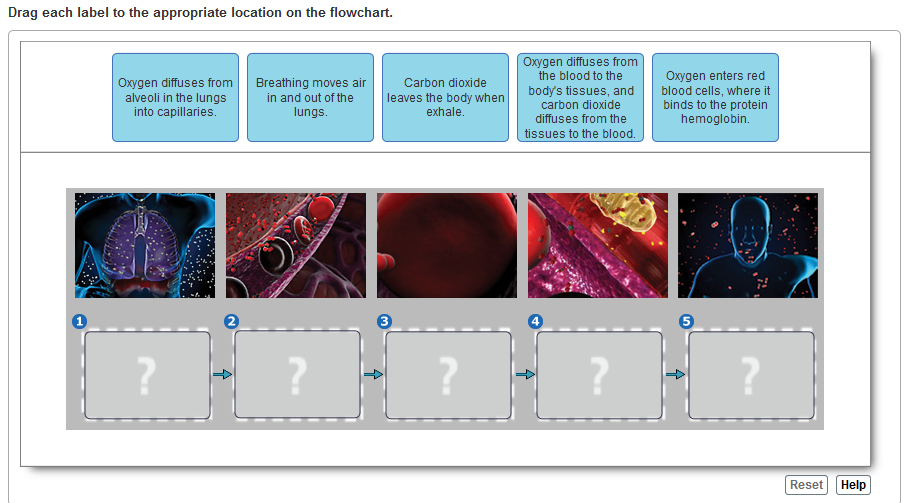
BioFlix Activity: Gas Exchange -- Oxygen Transport Drag each label to the appropriate location on the flowchart. Left to right: 1: Oxygen diffuses from the alveoli into surrounding capillaries 2:Oxygen enters a red blood cell. Drag the labels onto the diagram to identify the structures of the upper respiratory system.
Labeling, ranking, sorting, or sentence completion questions. All of these question types require you to position items into an area of the answer box. Answer these kinds of questions on a computer, not on a smartphone. Press Tab to move forward or Shift/Tab to move backwards through the provided answer items.
Question: Drag the labels onto the diagram to identify the processes of reabsorption in the tubular epithelium. This problem has been solved!. Sodium reabsorption in the proximal tubule Primary active Low Na concentration Leak channel transport of Na (c) Sodium-linked reabsorption Glucose and Nat SGLT 缄. GALUT " Apical membrane...
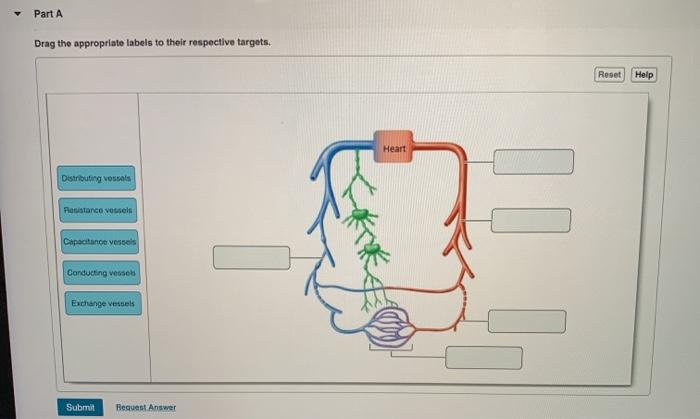
Virtually every cell, tissue, organ, and system in the body is impacted by the circulatory system. This includes the generalized and more specialized functions of transport of materials, capillary exchange, maintaining health by transporting white blood cells and various immunoglobulins (antibodies), hemostasis, regulation of body temperature, and helping to maintain acid-base balance.
Drag the labels onto the diagram to identify the structures and functions of the nephron. (Refer to the posted image at the right for labeled answers) What is the primary driving force for glucose transport into proximal tubule cells? Sodium concentration gradient allows secondary active transport of glucose.
Drag the labels onto the diagram to identify aspects of gas transport and exchange Learn this topic by watching Gas Transport in the Blood II: Carbon Dioxide Concept Videos All Anatomy & Physiology Practice Problems Gas Transport in the Blood II: Carbon Dioxide Practice Problems
Discuss the parts of a rib and rib classifications. The thoracic cage (rib cage) forms the thorax (chest) portion of the body. It consists of the 12 pairs of ribs with their costal cartilages and the sternum ( Figure 7.5.1 ). The ribs are anchored posteriorly to the 12 thoracic vertebrae (T1-T12). The thoracic cage protects the heart and lungs.
The pH scale is a logarithmic scale representing the concentration of H + ions in a solution. Remember that as the H + concentration increases the OH-concentration decreases and vice versa.If we have a solution with one in every ten molecules being H +, we refer to the concentration of H + ions as 1/10. Remember from algebra that we can write a fraction as a negative exponent, thus 1/10.
Drag the labels onto this diagram of the carbon cycle. Mastering environmental science 5th ed. In fuels in water co2 in. Drag the labels onto the flowchart to identify the sequence in which carbon moves through these organisms 1. Then drag the pink labels onto the pink targets to identify the processes and reservoirs in the carbon cycle.



















0 Response to "38 Drag The Labels Onto The Diagram To Identify Aspects Of Gas Transport And Exchange."
Post a Comment