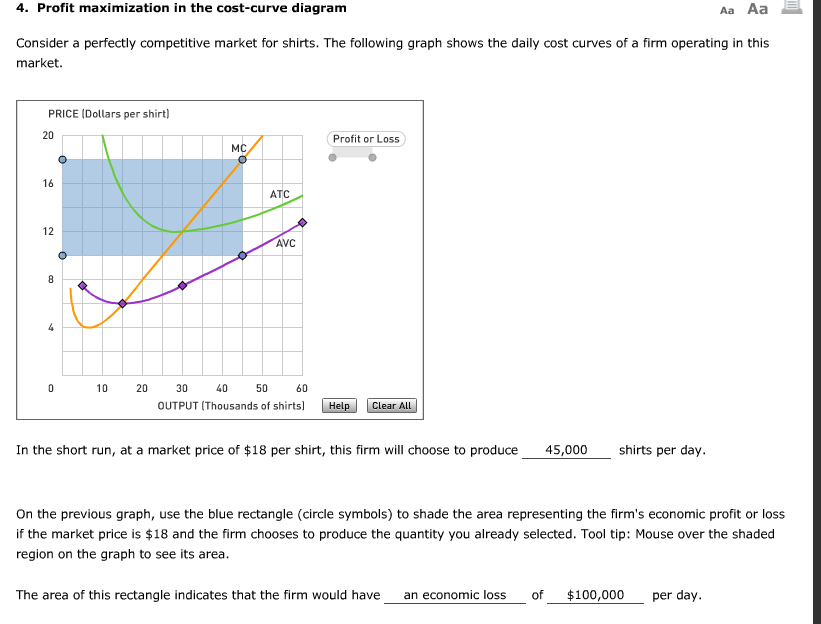
38 4. Profit Maximization In The Cost-curve Diagram
Chapter 9: Profit Maximization Profit Maximization The basic assumption here is that firms are profit maximizing. Profit is defined as: Profit = Revenue – Costs Π(q) = R(q) – C(q) To maximize profits, take the derivative of the profit function with respect to q and set this equal to zero. 4. Profit maximization in the cost-curve diagram Suppose that the market for candles is a competitive market. The following graph shows the daily cost curves of a firm operating in this market.In the short run, at a market price of $20 per candle, this firm will choose to produce candles per day.
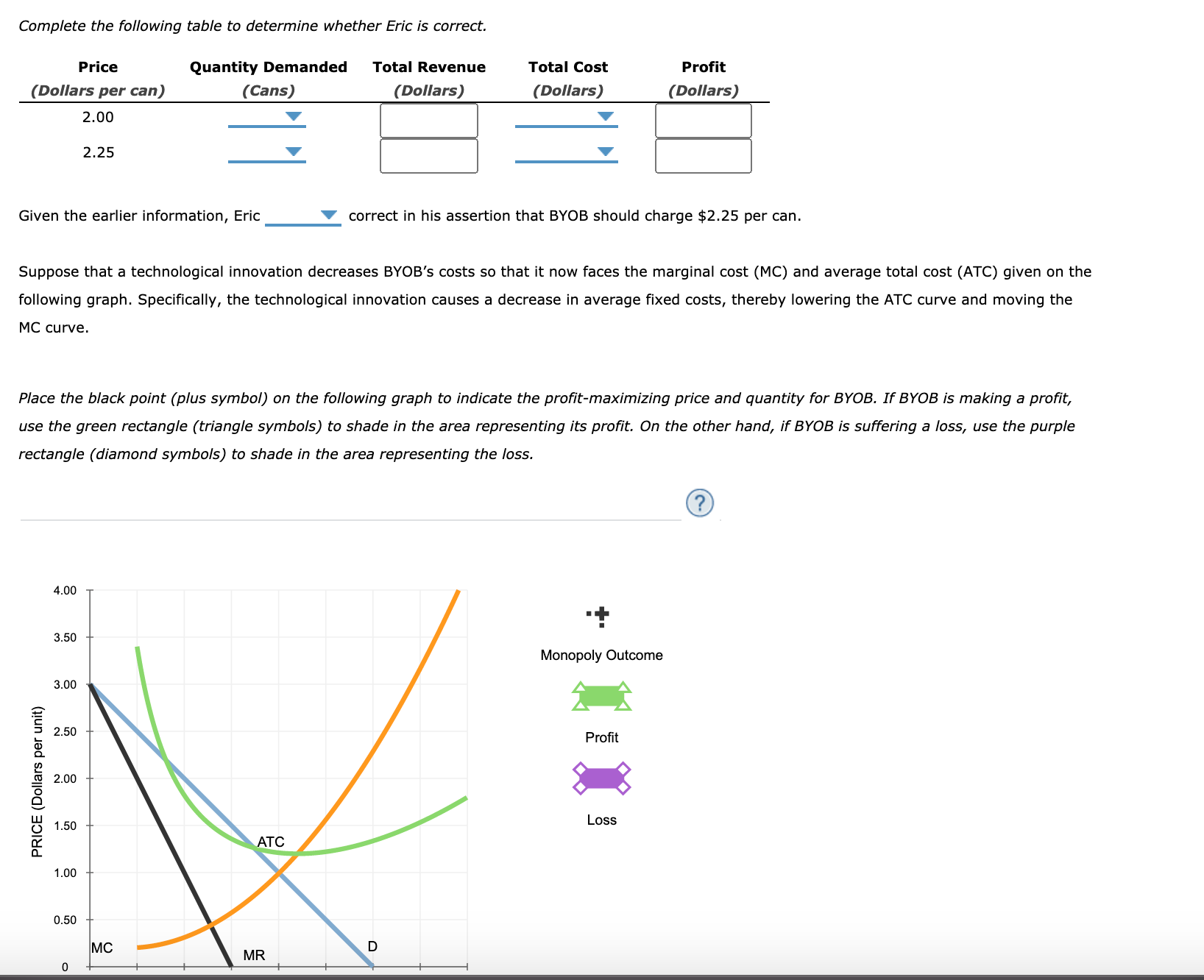
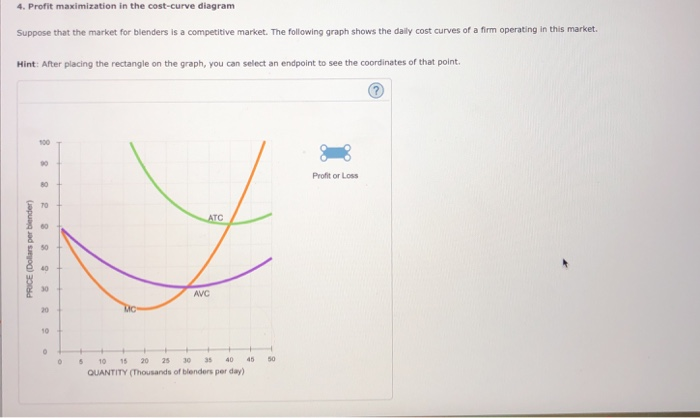
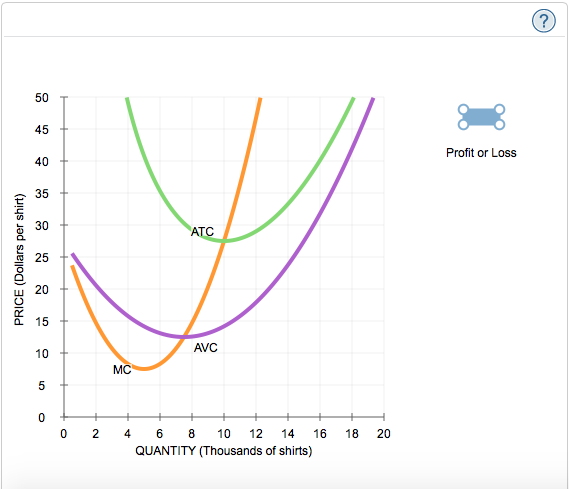
4. Profit maximization in the cost-curve diagram Suppose that the market for blenders is a competitive market. The following graph shows the daily cost curves of a firm operating in this market. Hint: After placing the rectangle on the graph, you can select an endpoint to see the coordinates of that point.
4. profit maximization in the cost-curve diagram
Profit maximization in the cost-curve diagram Suppose that the market for black sweaters is a competitive market. The following graph shows the daily cost curves of a firm operating in this market. Hint: After placing the rectangle on the graph, you can select an endpoint to see the coordinates of that point. Profit maximization in the cost-curve diagram Suppose that the market for candles is a competitive market, The following graph shows the daly cost curves of a firm operating in this market Hint: After placing the rectangle on the graph, you can select an endpoint to see the coordinates of that point 35 Proi or Loss ATC AVC MC 0 10 12 20 14 12. 4. Profit maximization in the cost-curve diagram Suppose that the market for blenders is a competitive market. The following graph shows the daily cost curves of a firm operating in this market. Hint: After placing the rectangle on the graph, you can select an endpoint to see the coordinates of that point. 100 Profit or Loss o 70 ATC 60 2 50 40.
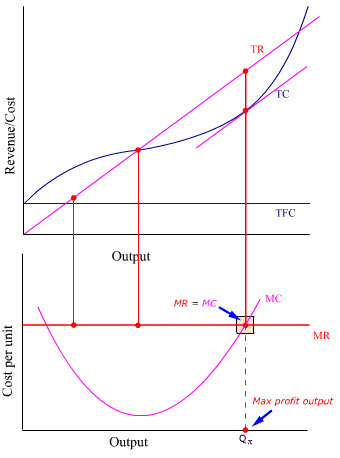
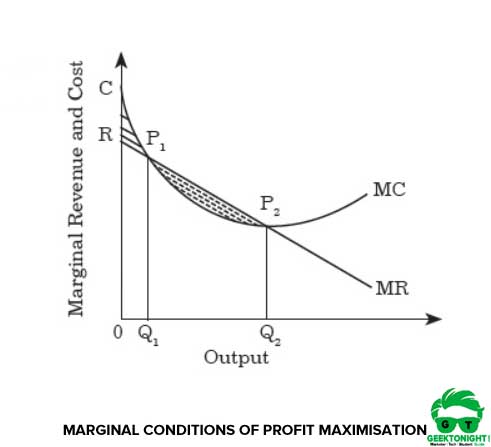
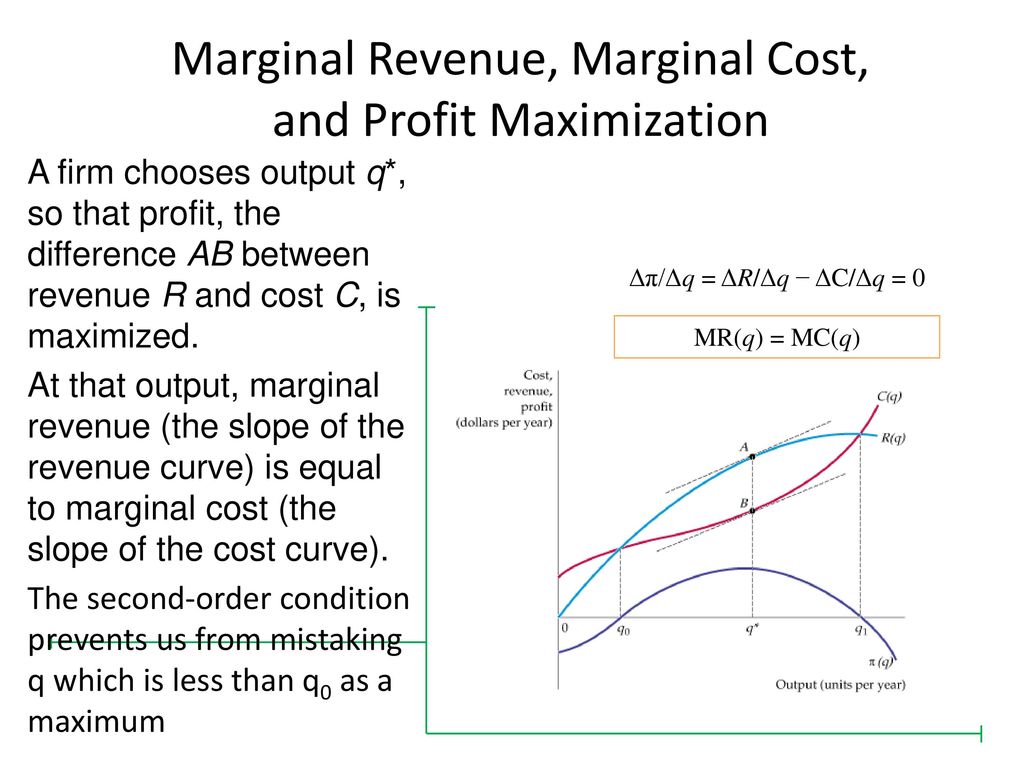
4. profit maximization in the cost-curve diagram. a. On a diagram, draw the marginal cost curves for the two factories, the average and marginal revenue curves, and the total marginal cost curve (i.e., the marginal cost of producing Q = Q 1 + Q 2). Indicate the profit-maximizing output for each factory, total output, and price. The average revenue curve is the demand curve, P = 700 - 5Q. Understanding the Profit Maximizing Rule. We can also understand the profit maximizing rule intuitively. In the graph below, Qpm is the profit maximizing quantity. If the firm produces at a point to the left of Qpm (for example, the point at which marginal cost is at its minimum), then we notice that marginal cost is less than marginal revenue. Question: 4. Profit maximization in the cost-curve diagram Suppose that the market for candles is a competitive market. The following graph shows the daily cost curves of a firm operating in this market.In the short run, at a market price of $20 per candle, this firm will choose to produce candles per day. Points: 0.5 / 1 Back to Assignment Attempts: 2.5 Keep the Highest: 2.5 / 3 4. Profit maximization in the cost-curve diagram Suppose that the market for candles is a perfectly competitive market. The following graph shows the daily cost curves of a firm operating in this market.
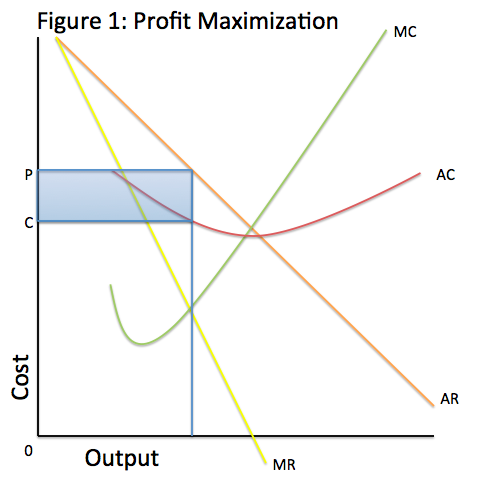
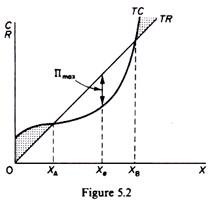
Profit = Total Revenue (TR) - Total Costs (TC). Therefore, profit maximisation occurs at the biggest gap between total revenue and total costs. A firm can maximise profits if it produces at an output where marginal revenue (MR) = marginal cost (MC) Diagram of Profit Maximisation. To understand this principle look at the above diagram. Profit maximization in the cost-curve diagram Suppose that the market for black sweaters is a competitive market. The following graph shows the daily cost curves of a firm operating in this market. Hint: After placing the rectangle on the graph, you can select an endpoint to see the coordinates of that point. 4. Profit maximization in the cost-curve diagram Suppose that the market for microwave ovens is a competitive market. The following graph shows the daily cost curves of a firm operating in this market. Hint: After placing the rectangle on the graph, you can select an endpoint to see the coordinates of that point. 100 90 80 70 60 50 Proft or. Maximize profit calculator
A monopolist faces the following demand: P = 2,078 - 8 Q The monopolist's cost function is: C = 1 Q^3 - 6 Q^2 + 188 Q + 1,158 Find the quantity, Q, that maximizes profit. iv. Given such behaviour, a profit maximizing situation will be in the output range OQ 2 to OQ 4 or between point R and R 1. Profit will be at its maximum where the slope of TC curve equals to slope of TR curve, as stated above under the conditions of equilibrium. As we know, two parallel lines have same slope. An economic profit is the difference between the revenue a commercial entity has received from its outputs and the opportunity costs of its inputs. [need quotation to verify] Unlike an accounting profit, an economic profit takes into account both a firm's implicit and explicit costs, whereas an accounting profit only relates to the explicit costs which appear on a firm's financial statements. 4. Profit maximization in the cost-curve diagram Suppose that the market for microwave ovens is a competitive market. The following graph shows the daily cost curves of a firm operating in this market. Hint: After placing the rectangle on the graph, you can select an endpoint to see the coordinates of that point. 100 Profit or Loss 70 50 30 AVC 10
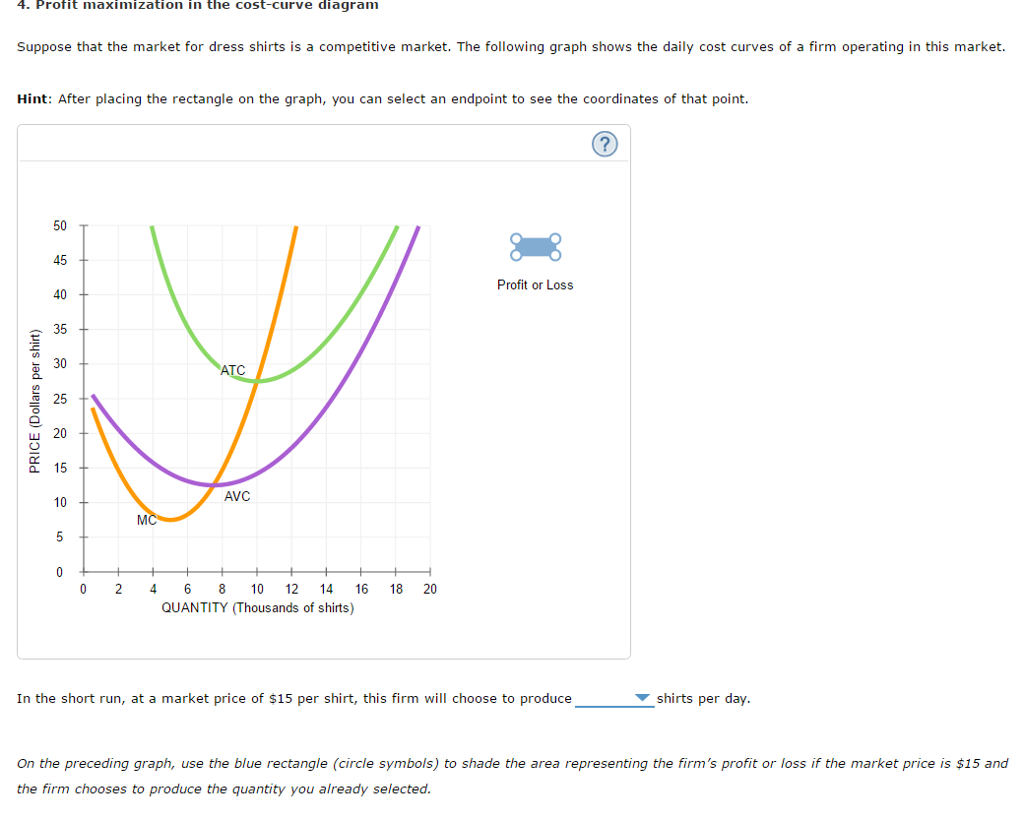
4. Profit maximization in the cost-curve diagram Suppose that the market for blenders is a competitive market. The following graph shows the daily cost curves of a firm operating in this market. 5. Profit maximization and shutting down in the short run Suppose that the market for dress shirts is a competitive market.
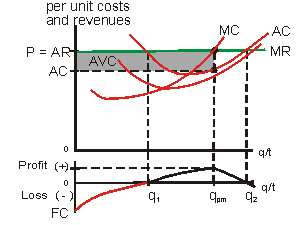
Figure 1 shows total revenue, total cost and profit using the data from Table 1. The vertical gap between total revenue and total cost is profit, for example, at Q = 60, TR = 240 and TC = 165. The difference is 75, which is the height of the profit curve at that output level. The firm doesn't make a profit at every level of output.
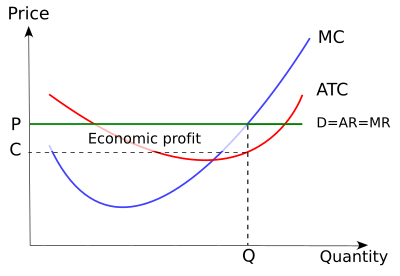
Other firms may be making normal profits where total revenue equals total cost (i.e. they are at the break-even output). In the diagram below, the firm shown has high costs such that the market price is below the average cost curve. At the profit maximising level of output, the firm is making an economic loss. E is the equilibrium point.
Profit maximization in the cost-curve diagram Suppose that the market for candles is a competitive market, The following graph shows the daly cost curves of a firm operating in this market Hint: After placing the rectangle on the graph, you can select an endpoint to see the coordinates of that point 35 Proi or Loss ATC AVC MC 0 10 12 20 14 12.
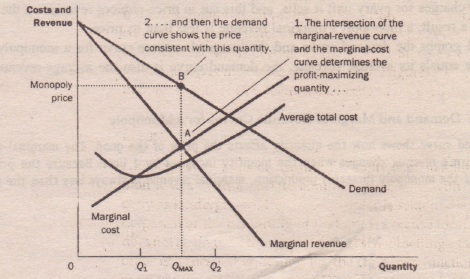
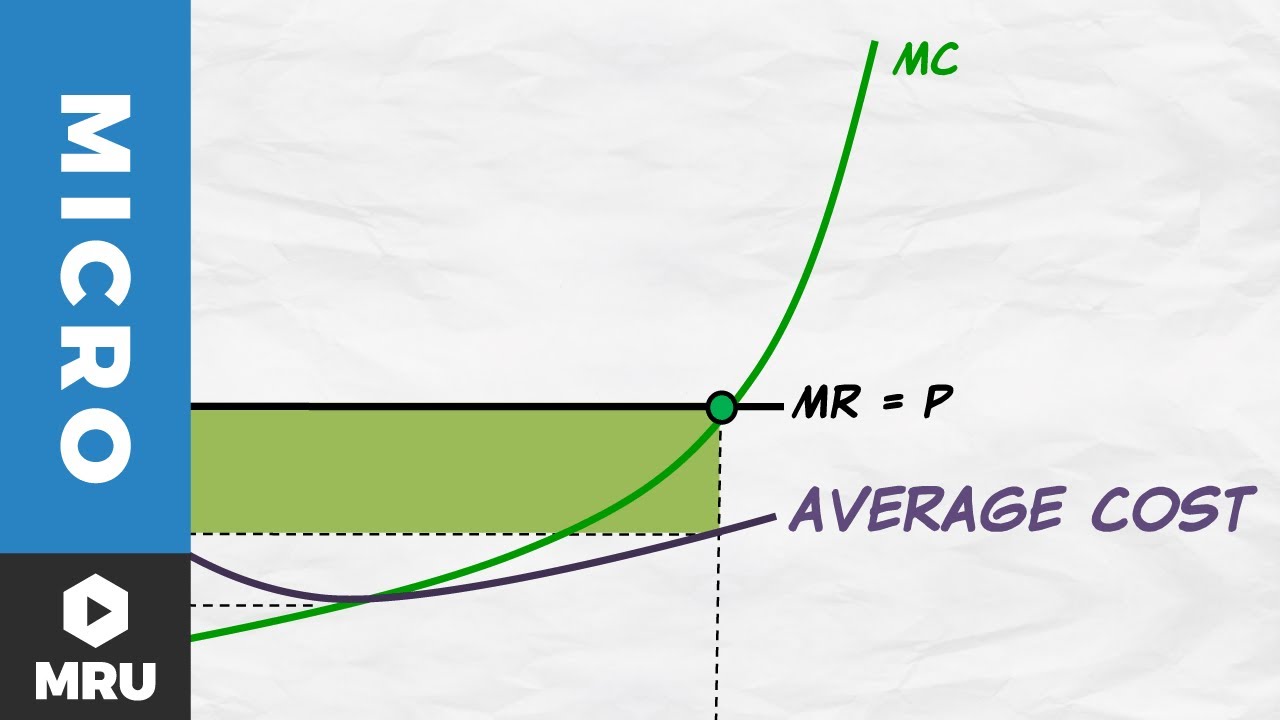
Profit (producer surplus) is the area below the equilibrium price and above the supply curve.. The supply curve is the same thing as the Marginal Cost curve for the firm. Figure 5.2 Supply and Demand diagram showing profit (producer surplus)... understand and apply the rule for profit maximization in a monopoly; find the marginal revenue curve:
4. Profit maximization in the cost-curve diagram Suppose that the market for blenders is a competitive market. The following graph shows the daily cost curves of a firm operating in this market. Hint: After placing the rectangle on the graph, you can select an endpoint to see the coordinates of that point. 100 Profit or Loss o 70 ATC 60 2 50 40.
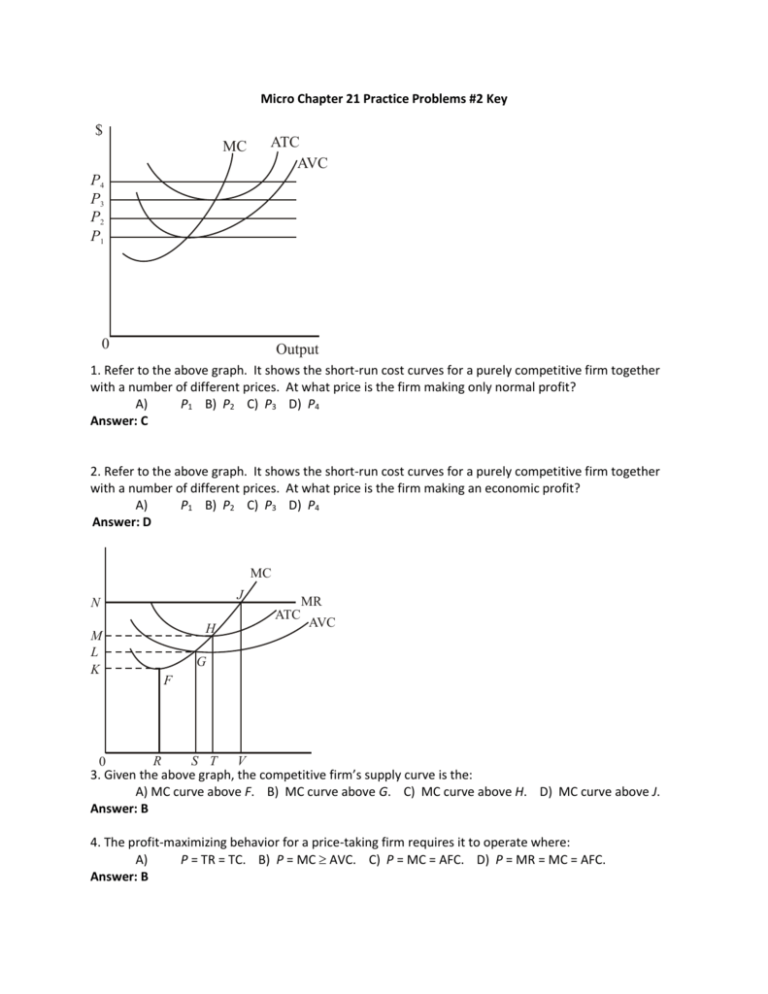
We call the point where the marginal cost curve crosses the average cost curve, at the minimum of the average cost curve, the “zero profit point.” If the market price that a perfectly competitive firm faces is below average variable cost at the profit-maximizing quantity of output, then the firm should shut down operations immediately.
4 profit maximization in the cost curve diagram. Profits and losses with the average cost curve. The objective of the firm is to maximise its profits where profits are the difference between the firms revenue and costs. The entrepreneur is the sole owner of the firm. Sign up to access the rest of the document.
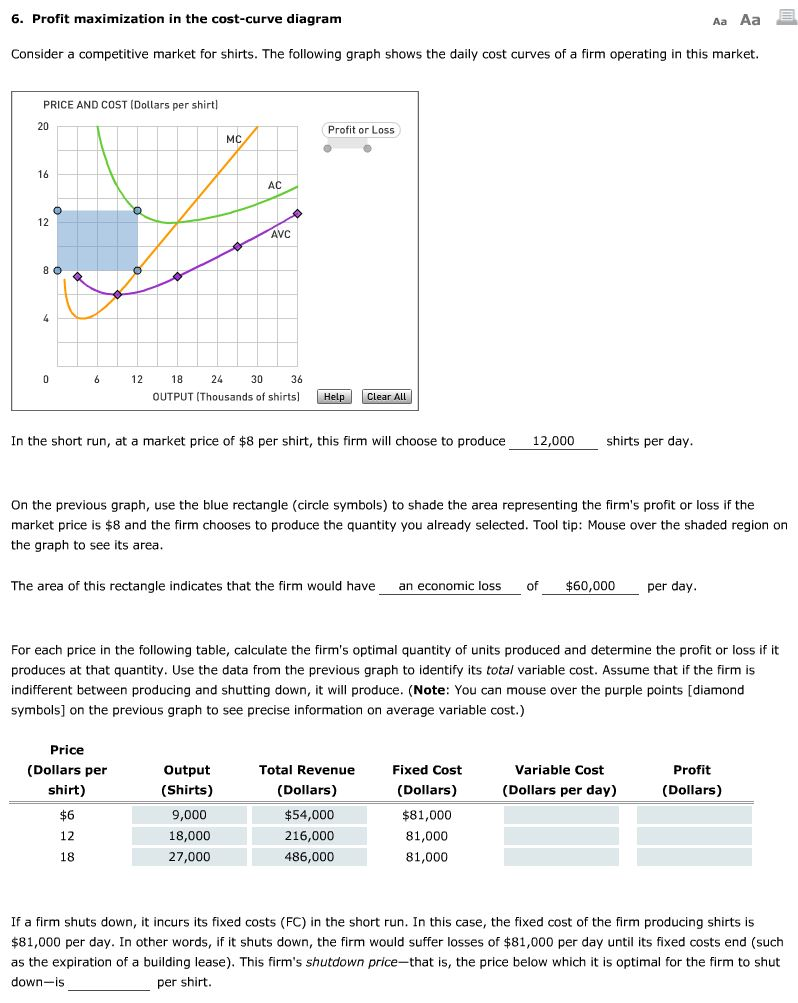
Profit maximization in the cost-curve diagram Consider a competitive market for shirts. The following graph shows the. labeled graph; makes sure you indicate where the optimal consumption now 3 ($5) or $15 and the price of good Y is now 3($10) or $30), the budget line Giffen goods are a type of goods whose demand curve is an upward sloping line.
Profit maximization in the cost-curve diagram Suppose that the market for wind chimes is a competitive market. The following graph shows the daily cost curves of a firm operating in this market. In the short run, at a market price of $20 per wind chime, this firm will choose to produce 9,000 wind chimes per day.
The profit maximisation theory is based on the following assumptions: 1. The objective of the firm is to maximise its profits where profits are the difference between the firm's revenue and costs. 2. The entrepreneur is the sole owner of the firm. 3. Tastes and habits of consumers are given and constant. 4.
4. Profit maximization in the cost-curve diagram Suppose that the market for polo shirts is a competitive market. The following graph shows the daily cost curves of a firm operating in this market.
4. Profit maximization in the cost-curve diagram. Suppose that the market for dress shirts is a competitive market. The following graph shows the daily cost curves of a firm operating in this market. Hint: After placing the rectangle on the graph, you can select an endpoint to see the coordinates of that point.
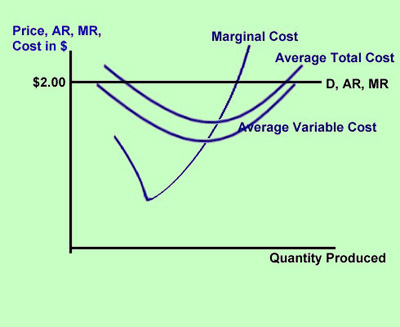
In economics, profit maximization is the short run or long run process by which a firm may determine the price, input and output levels that lead to the highest profit. Neoclassical economics, currently the mainstream approach to microeconomics, usually models the firm as maximizing profit.. An example diagram of Profit Maximisation:
4. Profit maximization in the cost-curve diagram Suppose that the market for black sweaters is a competitive market. The following graph shows the daily cost curves of a firm operating in this market Hint: After placing the rectangle on the graph, you can select an endpoint to see the coordinates of that point. 45 40 Profit or loss ATC PRICE.
4) A competitive firm is maximizing profits by producing 250 units of output at the current market price of RM1000 per unit. The firm has average fixed cost (AFC) of RM300 and total costs of RM300,000 at this output level. (a) Draw a diagram showing all the relevant cost and demand curves. That is, include the MR, MC, AVC, and ATC curves.
Profit Maximization In the Cost Curve Diagram. solved 6 profit maximization in the cost curve diagram c in this case the fixed cost of the firm producing shirts is $81 000 per day in other words if it shuts down the firm would suffer losses of $81 000 per day until its fixed costs end such as the expiration of a building lease solved 4 profit maximization in the cost curve diagram s answer to.
4. Profit maximization in the cost-curve diagram Suppose that the market for candles is a competitive market. The following graph shows the daily cost curves of a firm operating in this market. Hint: After placing the rectangle on the graph, you can select an endpoint to see the coordinates of that point. 40 36 Profit or Loss 32 28 24 20 ATC 16.















0 Response to "38 4. Profit Maximization In The Cost-curve Diagram"
Post a Comment