37 Sh6 Molecular Orbital Diagram
February 22, 2021 Draw and label the 5 x 3d orbitals. 2. Review pages 143 - 147 of your textbook. Why is the reduction of symmetry to D2h a valid simplification for constructing the M.O. diagram of CO2? 3. (Hand in) For both SiH4 and SH6 answer the following: (a) Construct their qualitative M.O. diagrams. Sulphur, on the other hand is large in size and possesses vacant d-orbitals in its valence shell. Why SH6 do not exist? This molecule is octahedral in shape. Hydrogen is a very weak oxidizing agent as compared to fluorine this means that hydrogen is not able to oxidise sulphur to its maximum oxidation state. Hence, SH6 does not exist.
Compound 'B' has the molecular formula C7H8O which on oxidation gives back compound 'A'. Compound 'C' is the sodium salt of an acid which when heated with soda lime yields an aromatic hydrocarbon 'D'. Deduce the structures of A, B, C and D. 7. An organic compound 'A' has the molecular formula C5H10O.
Sh6 molecular orbital diagram
The relative energy levels of atomic and molecular orbitals are typically shown in a molecular orbital diagram ((Figure)). For a diatomic molecule, the atomic orbitals of one atom are shown on the left, and those of the other atom are shown on the right. Each horizontal line represents one. Hydrogen sulfide can also result from industrial activities, such as food processing, coke ovens, kraft paper mills, tanneries, and petroleum refineries.Hydrogen sulfide is a flammable, colorless gas with a characteristic odor of rotten eggs. It is commonly known as hydrosulfuric acid, sewer gas, and stink damp. The 2pz orbitals of carbon and three O atoms are available for delocalized pi bonding. We have two electrons filling bonding molecular orbital, four filling non-bonding MOs. Therefore, the six pi electrons available are used up to occupy the lowest energy MOs - the bonding MOs.
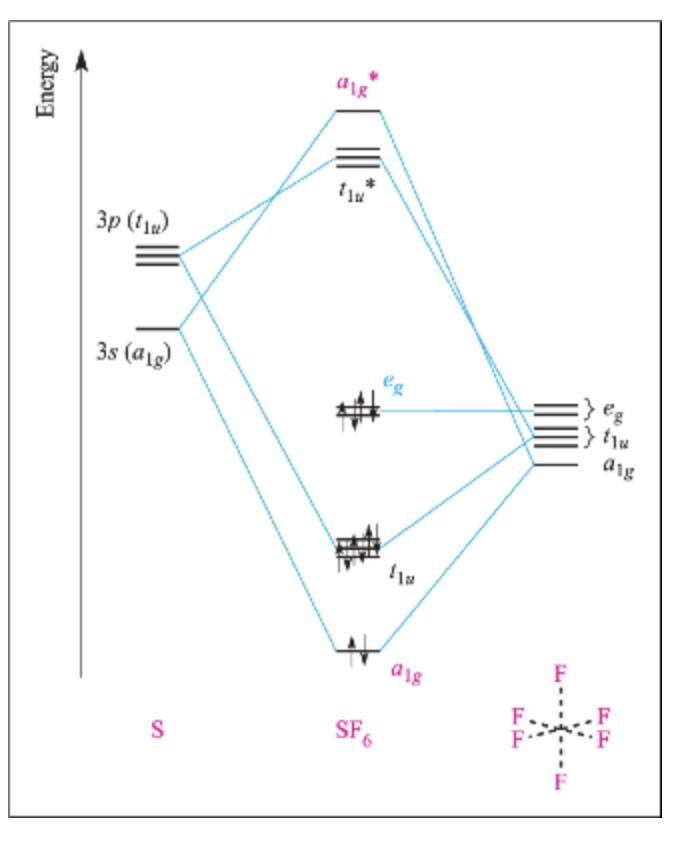
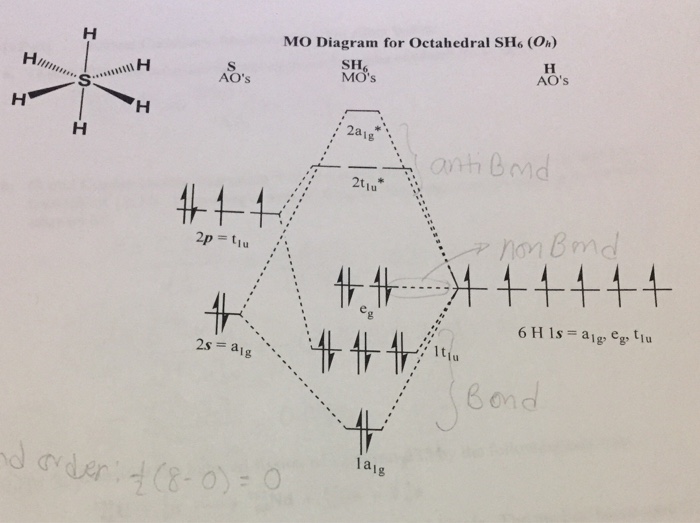
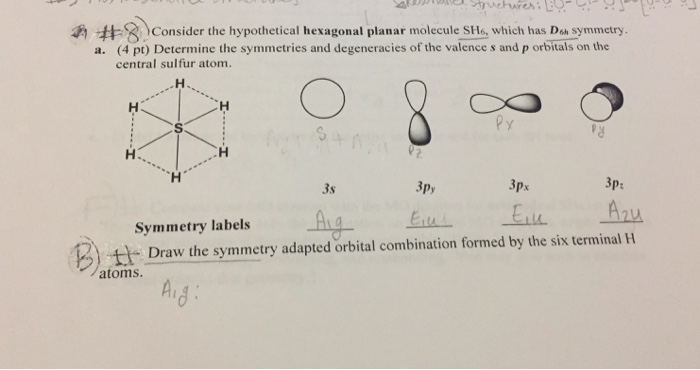
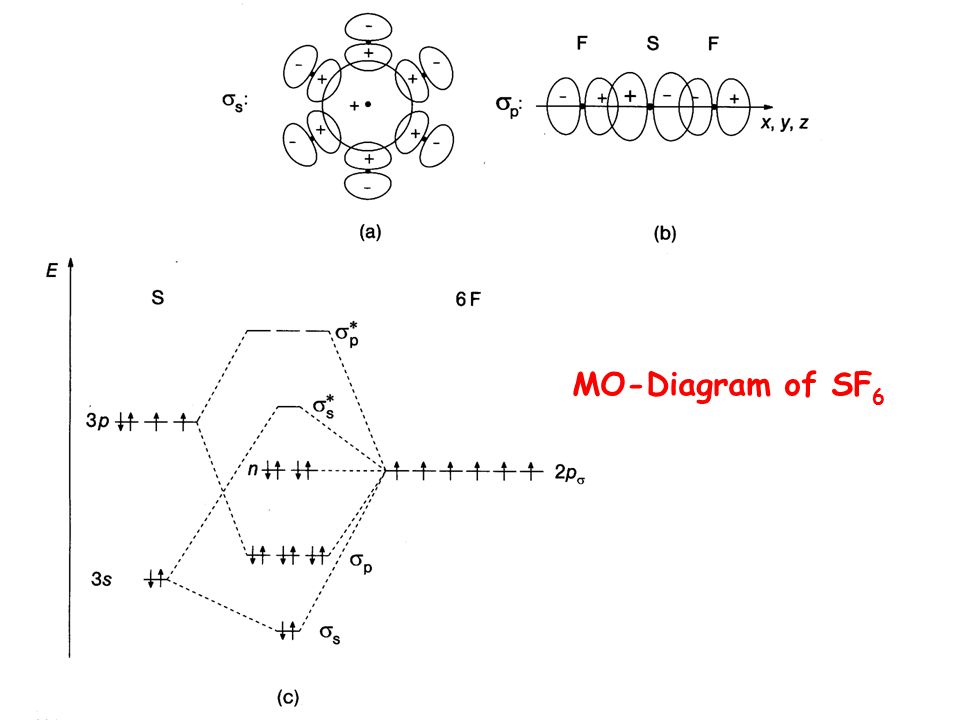
Sh6 molecular orbital diagram. Transcribed image text: 1.) Generate a molecular orbital diagram for SH6. Use the following steps as a guide: a) Draw the correct 3D structure and assign the point group symmetry: b) Break the molecule into two fragments and determine the basis sets for each fragment: c) Develop a reducible representation for the ligand orbitals and then break it down into the corresponding irreducible. About Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy & Safety How YouTube works Test new features Press Copyright Contact us Creators. The relative energy levels of atomic and molecular orbitals are typically shown in a molecular orbital diagram ((Figure)). For a diatomic molecule, the atomic orbitals of one atom are shown on the left, and those of the other atom are shown on the right. Each horizontal line represents one. Sulfur hexafluoride, taking a basis set of the one sulfur 3s-orbital, the three sulfur 3p-orbitals, and six octahedral geometry symmetry-adapted linear combinations of fluorine orbitals, a total of ten molecular orbitals are obtained, providing room for all 1 2 valence electrons. This is a stable configuration only for S X 6 molecules containing electronegative ligand atoms like fluorine.
January 28, 2017 - Molecular orbital : Stability of molecule is determined by bond order.Higher is the Bond order greater is the stability of molecule. Lewis Acids and Bases -Lewis Acids are the chemical species which have empty orbitals and are able to accept electron pairs from Lewis bases. Atomic or molecular chemical species having a highly localized HOMO (The Highest Occupied Molecular Orbital) act as Lewis bases. Learn about Lewis Acids and Bases Examples, Applications, Reactions and FAQs, Visit BYJU'S for detailed explanations.. but set the isovalue to -0.05. The resulting displayed volumes correspond to the molecular orbital 39 with an absolute value greater than 0.05, shown in figure 4. Figure 4: The highest occupied molecular orbital of methionine plotted at isovalues ±0.05 (left) and ±0.01 (right). 5. Following Molecular Orbitals Through a Trajectory Sigma pi bond formation Orbital overlap concept ncert
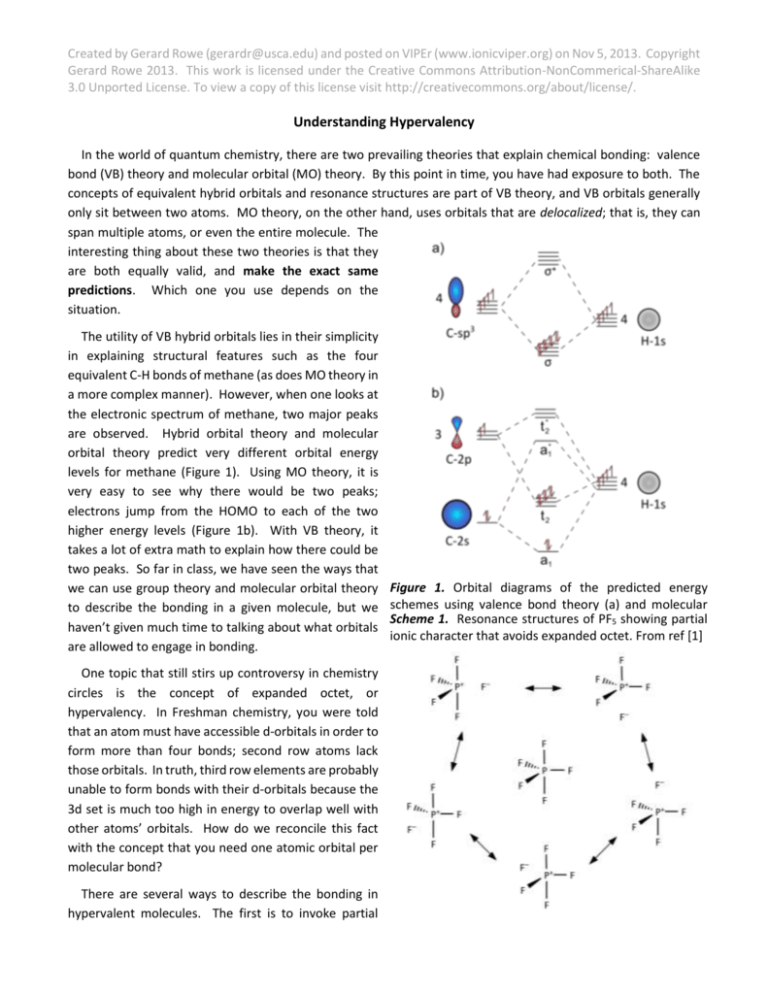
From the LCAO point of view this can be viewed as the contribution of higher atomic orbitals (d-orbitals, for example) to the bonding molecular orbitals. In the case of $\ce{SF6}$ the contribution of sulfur atomic orbitals to the bonding states is lower (because most of the electrons are localized on fluorines). In general, this mixing of n atomic orbitals always generates n molecular orbitals. The hydrogen molecule provides a simple example of MO formation. In the following diagram, two 1s atomic orbitals combine to give a sigma (σ) bonding (low energy) molecular orbital and a second higher energy MO referred to as an antibonding orbital. August 11, 2020 - The molecular orbital (MO) theory is a powerful and extensive approach which describes electrons as delocalized moieties over adjacent atoms. The applications of the MO theory extend beyond the. Answer to 3.) Generate a molecular orbital diagram for SH6. Use the following steps as a guide: a) Draw the correct 3D structure a...
d orbitals are of very high energy and Sp 3 d 2 hybridization is possible only with highly electronegative elements only like F. Electronegativety value of H is not sufficient to bring the energy of d orbitals equal to the energy of p orbitals which is required for formation of Sp 3 d 2 hybrid molecular orbitals.
In 1923 G. N. Lewis suggested another way of looking at the reaction between H + and OH-ions. In the Brnsted model, the OH-ion is the active species in this reaction it accepts an H + ion to form a covalent bond. In the Lewis model, the H + ion is the active species it accepts a pair of electrons from the OH-ion to form a covalent bond.. In the Lewis theory of acid-base reactions, bases donate.
February 3, 2018 - Answer (1 of 6): Here is the solution, > * For O2 molecule, > * For F2 molecule, Thanks for reading.
Answer (1 of 8): First of all, the order of increasing in electronegativites of Hydrogen, Sulfur and Fluorine is: H (2.2) < S (2.6) < F (4.0) Therefore, in SF6 you can imagine, F is "oxidizing" S so S atom exhibits a positive oxidation state, which is +6 in this case. However, when H and S are.
A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) method in particular. A fundamental principle of these theories is that.
August 12, 2020 - So far, we have looked at the ways in which pairs of atomic orbitals could combine to form molecular orbitals -- to form bonds. Just as we think of there being a progression of atomic orbitals from lowest energy to highest (1s, 2s, 2p, 3s...), we can organize these molecular orbitals by order.
The 2pz orbitals of carbon and three O atoms are available for delocalized pi bonding. We have two electrons filling bonding molecular orbital, four filling non-bonding MOs. Therefore, the six pi electrons available are used up to occupy the lowest energy MOs - the bonding MOs.
The molecular orbital belongs more to the atom that it is closer to in energy. The "#"H"_2#" in the diagram doesn't mean the molecule #"H"_2#, it means two hydrogen atoms. Other diagrams might switch the labeling of the #2p_x# and #2p_y# orbitals due to different conventions, so don't worry if you see things like that occurring.
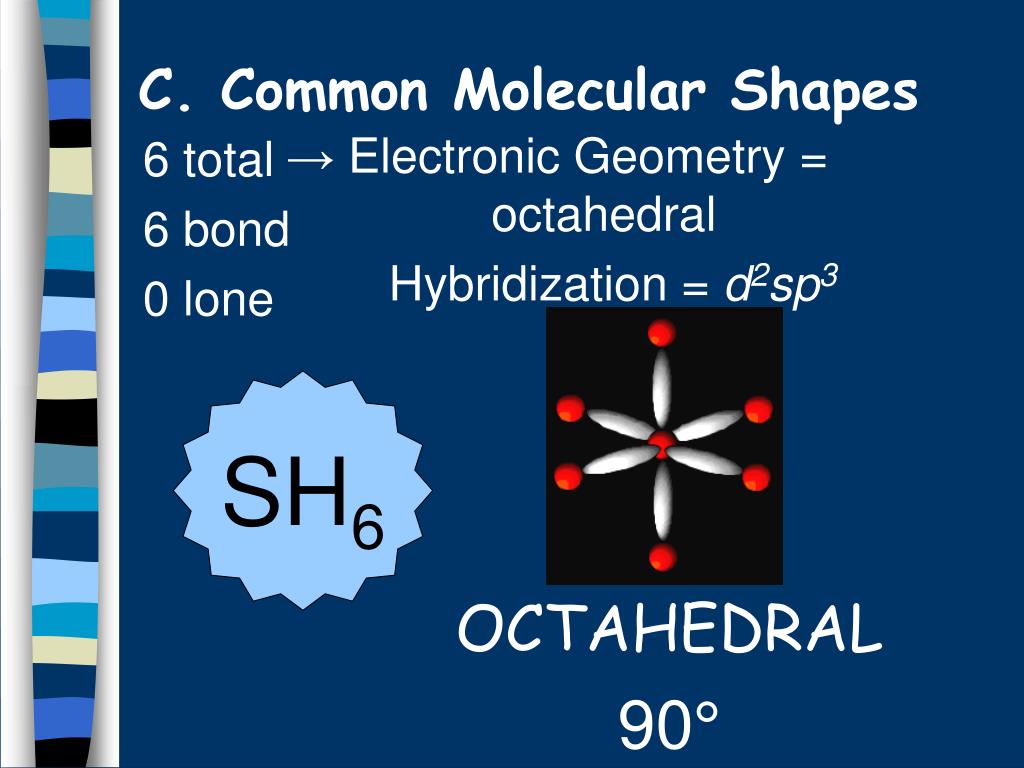
Molecular Shape determined by the # of bonds and lone pairs.. SH6. Hybridization. The Blending of Orbitals The combining of two or more orbitals of nearly equal energy within the same atom into orbitals of equal energy Ex: Cockapoo. sp3 Hybrid Orbitals.
The 3c-4e bond is described as three molecular orbitals given by the combination of a p atomic orbital on the central atom and an atomic orbital from each of the two ligands on opposite sides of the central atom. Only one of the two pairs of electrons is occupying a molecular orbital that involves bonding to the central atom, the second pair.
For this we need to picture atomic and molecular orbitals. l = 0 2. ATOMIC ORBITALS 2p x 2p y 2p z l = 1 x y z n = 2 This is an accurate representation of a 2p x orbital. This is a common picture of a p x orbital This simplifi ed p x orbital is often useful. A hand drawn version does not have to be exact.
Answer to Draw the Molecular Orbital (MO) Diagram for SH6....
Further, the sp 3 d 2 hybrid orbitals overlap with a 2p orbital of fluorine, and they form the S-F bond. Important Points To Remember. There are six hybrid orbitals formed. One 3s-orbital, three 3p-orbitals and two 3d-orbital take part in hybridization. The six sp 3 d 2 hybrid orbitals are projected towards the six corners of a regular octahedron.
The 3c-4e bond is described as three molecular orbitals given by the combination of a p atomic orbital on the central atom and an atomic orbital from each of the two ligands on opposite sides of the central atom. Only one of the two pairs of electrons is occupying a molecular orbital that involves bonding to the central atom, the second pair.
Generate a molecular orbital diagram for SH6. Use the following steps as a guide: a) Draw the correct 3D structure and assign the point group symmetry: b) Break the molecule into two fragments and determine the basis sets for each fragment: c) Develop a reducible representation for the ligand orbitals and then break it down into the corresponding irreducible representations: d) Using.
View F16_PS4 from CHE 3340 at St. John's University. Graded Problem # 4 Inorganic Chemistry Symmetry, Group Theory, Polyatomics 1 Due: Mon. September 26, 2016 You must show ALL of your work to
Hydrogen sulfide can also result from industrial activities, such as food processing, coke ovens, kraft paper mills, tanneries, and petroleum refineries.Hydrogen sulfide is a flammable, colorless gas with a characteristic odor of rotten eggs. It is commonly known as hydrosulfuric acid, sewer gas, and stink damp.
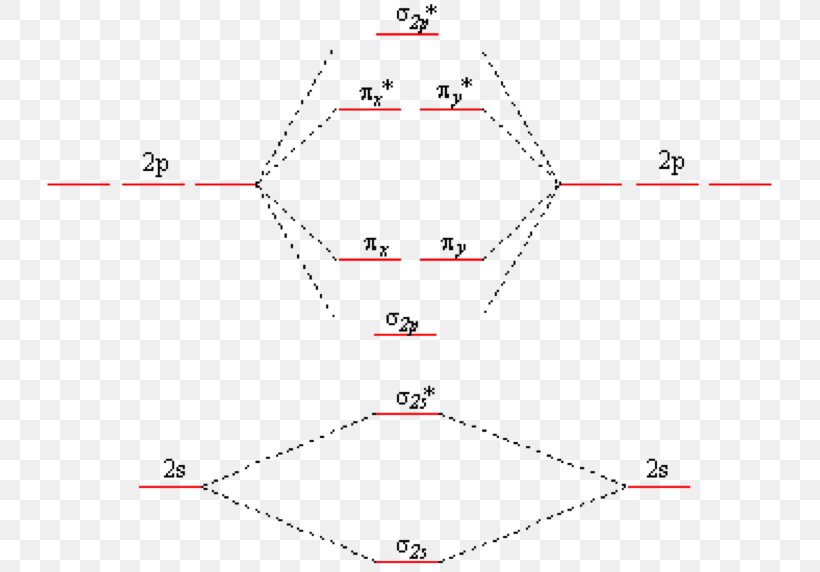
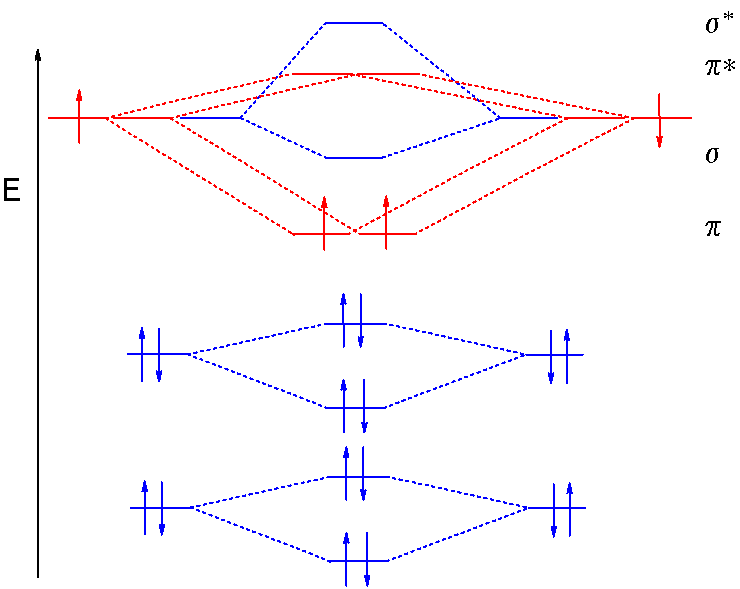
Molecular orbital diagram for hydrogen: For a diatomic molecule, an MO diagram effectively shows the energetics of the bond between the two atoms, whose AO unbonded energies are shown on the sides. The unbonded energy levels are higher than those of the bound molecule, which is the energetically-favored configuration.
Draw the molecular orbital diagram of N2 and calculate the bond order. - Get the answer to this question and access a vast question bank that is tailored for students.
From the LCAO point of view this can be viewed as the contribution of higher atomic orbitals (d-orbitals, for example) to the bonding molecular orbitals. In the case of $\ce{SF6}$ the contribution of sulfur atomic orbitals to the bonding states is lower (because most of the electrons are localized on fluorines).
Notice in Figure 9.19 “Hydrogen molecular orbital combination diagram” that the electron density of this orbital is concentrated between the two nuclei. These electrons are stabilized by attractions to both nuclei, and they hold the atoms together with a covalent bond.
April 3, 2021 - The molecular orbital model is by far the most productive of the various models of chemical bonding, and serves as the basis for most quantiative calculations, including those that lead to many of.
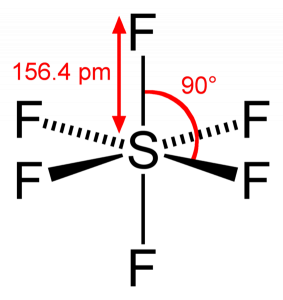
SF6 Molecular Geometry, Lewis Structure, Shape, and Polarity. July 23, 2021. Posted by Priyanka. 16 Apr. Sulfur hexafluoride or SF6 is an inorganic, greenhouse gas. It is non-flammable, odourless, and colourless, and is an excellent insulator. It is a hypervalent octahedral molecule that has been an interesting topic of conversation among.
The two such half field atomic orbitals combine to from a molecular orbital which contains both these electrons. But helium (Z=2) has already a filled orbital (1 s 2). Therefore, the atomic orbitals of the helium atoms do not combine. Thus, a molecule of H 2 exists while that of H e 2 does not!
The two electrons associated with a pair of hydrogen atoms are placed in the lowest energy, or bonding, molecular orbital, as shown in the figure below. This diagram suggests that the energy of an H2 molecule is lower than that of a pair of isolated atoms. As a result, the H2 molecule is more.
This section illustrates pictorially molecular orbitals for several organic and inorganic molecules. If possible - the energy level diagram is included and clicking upon the relelvant level will generate the accompanying molecular orbital in the right-hand frame. Please choose from:
Q-Chem has three post-SCF localization methods available. These can be performed separately over both occupied and virtual spaces. The localization scheme attributed to Boys 98, 99 minimizes the radial extent of the localized orbitals, i.e., ∑ i i i | | 𝐫 1-𝐫 2 | 2 | i i , and although is relatively fast, does not separate σ and π orbitals, leading to two ‘banana.
The relative energy levels of atomic and molecular orbitals are typically shown in a molecular orbital diagram (Figure 8). For a diatomic molecule, the atomic orbitals of one atom are shown on the left, and those of the other atom are shown on the right. Each horizontal line represents one.
July 22, 2021 - This scheme of bonding and antibonding orbitals is usually depicted by a molecular orbital diagram such as the one shown here for the dihydrogen ion H2+. Atomic valence electrons (shown in boxes on the left and right) fill the lower-energy molecular orbitals before the higher ones, just as.
An online LaTeX editor that’s easy to use. No installation, real-time collaboration, version control, hundreds of LaTeX templates, and more.
PCl5 forms five bonds by using the d-orbitals to "expand the octet" and have more places to put bonding pairs of electrons. NCl5 does not exist because there are no d-orbitals in the second energy level. Therefore there is no way to arrange five pairs of bonding electrons around a nitrogen atom. Why of4 does not exist?
Representation Reduction for Molecular Orbitals To determine the linear combination of irreducible representations that comprise a reducible represen-tation, we need only treat rows of the character table as vectors and take the dot product of the reducible vector with every irreducible vector and normalize by the order of the group.
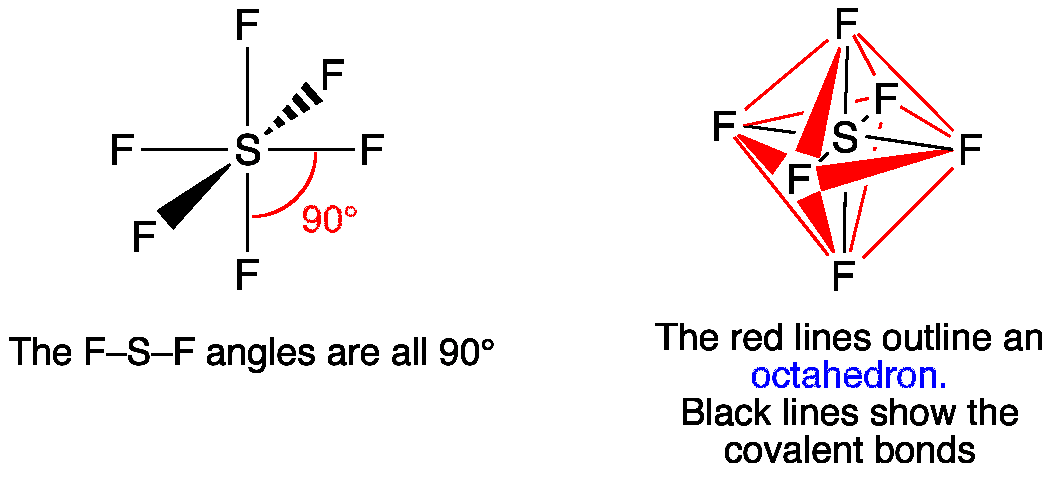
O h point group contains 3 C 4, 4 C 3, 9 C 2, 4 S 6, 3 S 4, 3 σ h, 6 σ d and a centre of inversion. Inversion operation is a reflection through the centre of the molecule. In this case, the centre of the molecule is the Sulfur atom. Click the arrow to show an animation of the inversion in 3D. Pointgroup Flow Chart.
October 27, 2016 - Drawing molecular orbital diagrams is one of the trickier concepts in chemistry. The first major step is understanding the difference between two major theories: Valence Bond Theory and Molecular…
The relative energy levels of atomic and molecular orbitals are typically shown in a molecular orbital diagram (Figure 9). For a diatomic molecule, the atomic orbitals of one atom are shown on the left, and those of the other atom are shown on the right. Each horizontal line represents one.
(An answer well written btw.). asked Jun 8, 2018 in Chemistry by Nisa (59.6k points) chemical bonding and molecular structure; class-11 +2 votes. Hypervalency is a bit of a touchy subject since there are strong opposing proponents for both the hybridization camp and the 3-center-4-electron bond camp. Thus an atoms lacking or exceeding by 2 tends to form 2:1 ratios with atoms lacking or.
pause-rounded-fill. 00:00. 1x 1.25x 1.5x 1.75x 2x. Problem Details. Draw a molecular orbital diagram for Ar 2+. This ion has been observed in the gas phase. Calculate bond order and describe how the bond distance in this ion would differ from that in Cl 2. Frequently Asked Questions.













0 Response to "37 Sh6 Molecular Orbital Diagram"
Post a Comment