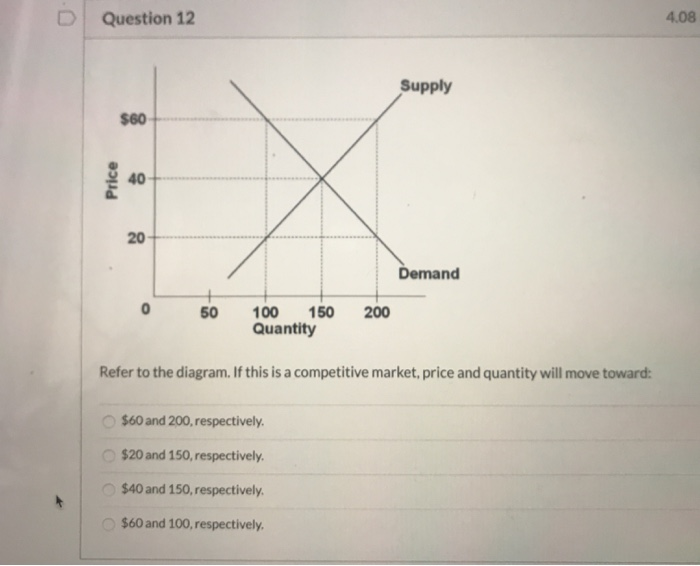
37 Refer To The Diagram. If This Is A Competitive Market, Price And Quantity Will Move Toward:
Step 1. Draw a demand and supply model to illustrate the market for salmon in the year before the good weather conditions began. The demand curve D 0 and the supply curve S 0 show that the original equilibrium price is $3.25 per pound and the original equilibrium quantity is 250,000 fish. (This price per pound is what commercial buyers pay at the fishing docks. Refer to the above diagram. A decrease in supply is depicted by a: C. shift from S2 to S1. 5. The law of demand states that: A. price and quantity demanded are inversely related. 6. Refer to the above diagram, which shows three demand curves for coffee.
Refer to the above diagram. If this is a competitive market, price and quantity will move toward:

Refer to the diagram. if this is a competitive market, price and quantity will move toward:
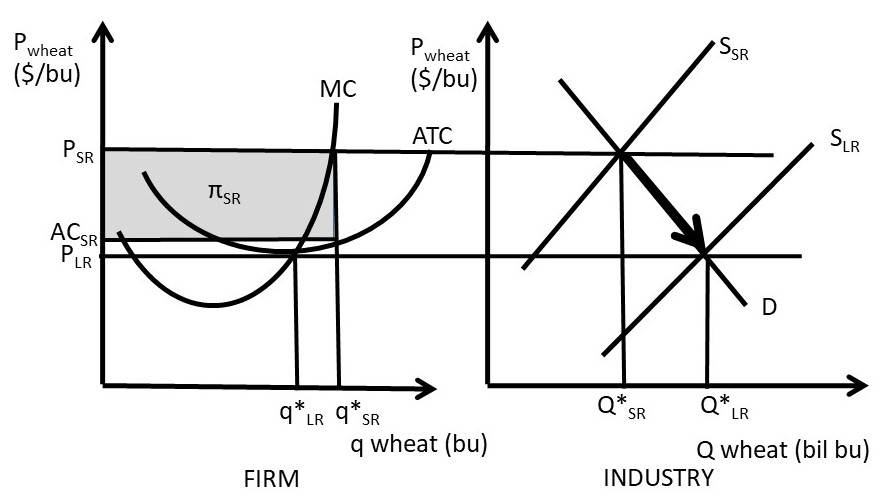
Demand for the whole market is downward sloping curve shown in the left graph. Demand for an individual seller is a horizontal line at the equilibrium price determined by the market. 2. Profit maximization in the short run 1) For a firm in a perfectly competitive market, price is equal to both average revenue and marginal revenue. P=MR=AR (only. Refer to the above diagram. The equilibrium price and quantity in this market will be: A. $1.00 and 200. B. $1.60 and 130. C. $.50 and 130. D. $1.60 and 290. 7. R-2 F03090: Refer to the above diagram. A price of $20 in this market will result in: A. Question: QUESTION 4 Supply $60 Price 40 20 Demand O 50 200 100 150 Quantity Refer to the diagram. If this is a competitive market price and quantity will move toward $60 and 100, respectively. $40 and 150, respectively, $60 and 200, respectively $20 and 150, respectively,
Refer to the diagram. if this is a competitive market, price and quantity will move toward:. Refer to the diagram if this is a competitive market price and quantity will move toward. 60 and 200 respectively. Pic35 60 and 100 respectively. 40 and 150 respectively. 20 and 150 respectively 40 and 150 respectively. 20 and 150 respectively. Chapter 03 demand supply and market equilibrium appendix 110. market, the a. demand curve shifts to the right. b. supply curve shifts to the right. c. price will rise. d. quantity sold will fall. ____ 48. In 1989, Hurricane Hugo devastated Charleston, South Carolina, leaving residents with no electricity for light or refrigeration, and completely cut off from the outside world by fallen trees and washed. Refer to the above diagram. The equilibrium price and quantity in this market will be: A. $1.00 and 200. B. $1.60 and 130. C. $.50 and 130. D. $1.60 and 290. 7. R-2 F03090: Refer to the above diagram. A price of $20 in this market will result in: A. Refer to the diagram. If this is a competitive market, price and quantity will move toward: A. $60 and 100, respectively. B. $60 and 200, respectively. C. $40 and 150, respectively. D. $20 and 150, respectively.
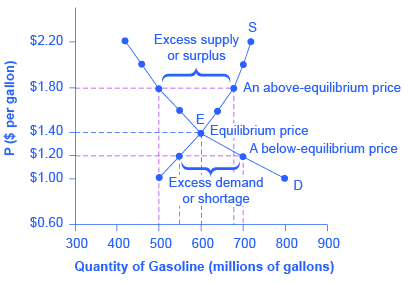
The reason as to why competitive markets move toward equilibrium is because the process by which markets move to equilibrium is so predictable that economists sometimes refer to markets as being governed by the law of supply and demand.. 2:41 PM EST. Chapter Eight: The Stock Market - 21 cards. any price or quantity not at equilibrium. More... However, if a market is not at equilibrium, then economic pressures arise to move the market toward the equilibrium price and equilibrium quantity. This happens either because there is more supply than what the market is demanding or because there is more demand than the market is supplying. This balance is a natural function of a free-market. Refer to the above diagram. If this is a competitive market, price and quantity will move toward: Definition. $40 and 150 respectively. Term.. Assume that in a competitive market price is initially above the equilibrium level. We can predict that price will: Definition. good and the market price will rise until it reaches equilibrium. If the existing market price is above the equilibrium price, there will be a surplus of the good and the market price will fall until it reaches equilibrium. Price of TVs Quantity Demanded/month Quantity Supplied/month $200 1,000 2,500 180 1,200 2,200 160 1,400 1,900
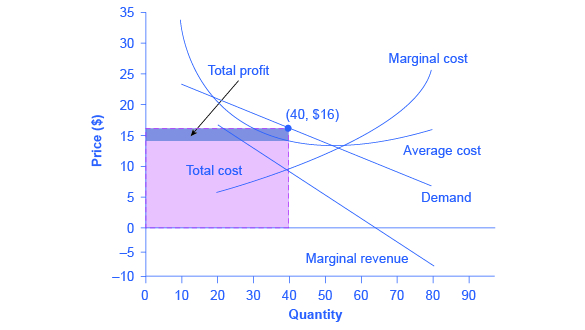
Figure 12 - 5 shows cost and demand curves facing a typical firm in a constant - cost, perfectly competitive industry. 4) Refer to Figure 12 -5. If the market price is $20, what is the firm's profit - maximizing output? 4) A) 750 units B) 1,100 units C) 1,350 units D) 1,800 units 5) Refer to Figure 12 -5. The following diagram shows the domestic demand and domestic supply in a market. In addition, assume that the world price in this market is $40 per unit. Refer to Figure 9-22. With free trade, consumer surplus is a. $48,000 and producer surplus is $48,000. b. $18,000 and producer surplus is $12,000. c. $108,000 and producer surplus is $12,000. d. As the price falls, the quantity demanded increases since consumers are willing to buy more of the product at the lower price. In a competitive market, this process continues till the market reaches equilibrium. While a market may not be in equilibrium, the forces in the market move the market towards equilibrium. However, if a market is not at equilibrium, then economic pressures arise to move the market toward the equilibrium price and the equilibrium quantity. Imagine, for example, that the price of a gallon of gasoline was above the equilibrium price—that is, instead of $1.40 per gallon, the price is $1.80 per gallon.
Refer to the above diagram. If this is a competitive market, price and quantity will move toward: A. $60 and 100 respectively. B. $60 and 200 respectively. C. $40 and 150 respectively. D. $20 and 150 respectively. #10 A In a competitive market, price will increase and quantity will decrease. #1 B Marginal benefit refers to what consumers are.
Refer to the diagram. If this is a competitive market, price and quantity will move toward: A. $60 and 100, respectively. B. $60 and 200, respectively. C. $40 and 150, respectively. D. $20 and 150, respectively.
Refer to Exhibit 2-5. As more fax machines are produced, the opportunity cost of producing them. In the simple circular economic flow diagram, if goods produced by business firms flow counterclockwise, then the services of labor flow... If this is a competitive market, price and quantity will gravitate toward. a. $6 and 10 units ...
Capitalism is an economic system based on the private ownership of the means of production and their operation for profit. Central characteristics of capitalism include capital accumulation, competitive markets, a price system, private property and the recognition of property rights, voluntary exchange and wage labor. In a capitalist market economy, decision-making and investments are.
Refer to diagram below. If this is a competitive market, price and quantity will move toward: A. $20 and 150 respectively. B. $60 and 100 respectively. C. $60 and 200 respectively. D. $40 and 150 respectively.
In microeconomics, supply and demand is an economic model of price determination in a market.It postulates that, holding all else equal, in a competitive market, the unit price for a particular good, or other traded item such as labor or liquid financial assets, will vary until it settles at a point where the quantity demanded (at the current price) will equal the quantity supplied (at the.
7. Refer to the above diagram. Other things equal, this economy will achieve the most rapid rate of growth if: A. it chooses point A. B. it chooses point B. C. it chooses point C. D. it chooses point D. 8. Refer to the above diagram. This economy will experience unemployment if it produces at point: A. A. B. B. C. C. D. D. 9.
If this is a competitive market, price and quantity will move toward: Selected Answer: Correct Answer: $40 and 150 respectively. Question 2 1 out of 1 points College students living off-campus frequently consume large amounts of ramen noodles and boxed macaroni and cheese.
##Key Terms Term | Definition -|- **market** | an interaction of buyers and sellers where goods, services, or resources are exchanged **shortage** | when the quantity demanded of a good, service, or resource is greater than the quantity supplied **surplus** | when the quantity supplied of a good, service, or resource is greater than the quantity demanded **equilibrium** | in a market setting.
Refer to the diagram. The highest price that buyers will be willing and able to pay for 100 units of this product is: (Pic34) $30. $60. $40. $20. $60. Refer to the diagram. If this is a competitive market, price and quantity will move toward: (Pic35) $60 and 100, respectively. $60 and 200, respectively. $40 and 150, respectively. $20 and 150.
D. increase equilibrium price and decrease equilibrium quantity. 96. Refer to the above diagram. If this is a competitive market, price and quantity will move toward: A. $60 and 100 respectively. B. $60 and 200 respectively. C. $40 and 150 respectively. D. $20 and 150 respectively.
Refer to the diagram, which shows demand and supply conditions in the competitive market for product X. If the initial demand and supply curves are D0 and S0, equilibrium price and quantity will be: 0F and 0C, respectively.
C) capacity of a competitive market to equalize quantity demanded and quantity supplied. D) ability of the market system to generate an equitable distribution of income. 21) 22) Refer to the diagram. If this is a competitive market, price and quantity will move toward: A) $20 and 150, respectively. B) $60 and 200, respectively. C) $60 and 100.
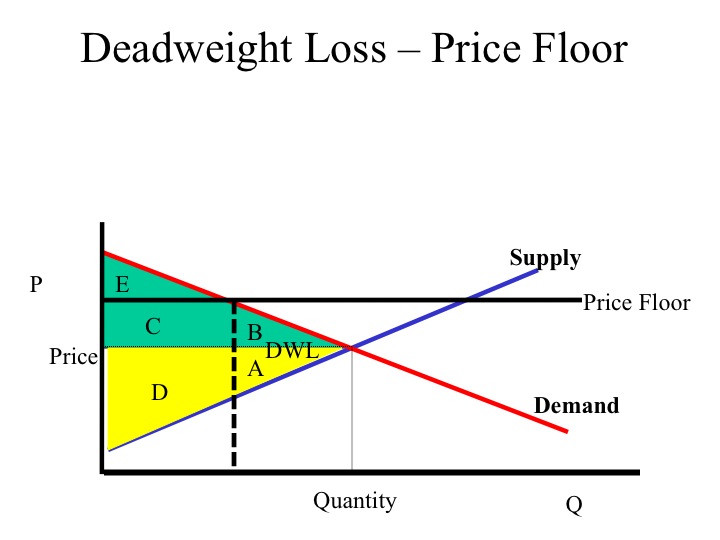
some firms leaving an industry. In the above market, economists would call a government-set maximum price of $40 a: price ceiling. A demand curve: indicates the quantity demanded at each price in a series of prices. Refer to the above diagram. A price of $60 in this market will result in: a surplus of 100 units.
Question: QUESTION 4 Supply $60 Price 40 20 Demand O 50 200 100 150 Quantity Refer to the diagram. If this is a competitive market price and quantity will move toward $60 and 100, respectively. $40 and 150, respectively, $60 and 200, respectively $20 and 150, respectively,
In a competitive goods market, individual buyers cannot bargain for a lower price than others are willing to pay. Therefore they are price-takers. In the labour market the firms set the wage to minimize the cost of getting the worker to work and would not benefit by offering the lowest wage at which the worker (the seller) would accept the job.
Refer to the above diagram. If this is a competitive market, price and quantity will move toward:
Question 3 1 / 1 pts Refer to the above diagram. If this is a competitive market, price and quantity will move toward: $60 and 100 respectively. $60 and 200 respectively. Correct! $40 and 150 respectively. $20 and 150 respectively.
Refer to the diagram. If this is a competitive market, price and quantity will move toward $40 and 150, respectively. 2. In moving along a demand curve, which of the following is not held constant? The price of the product itself. 3. (1) Q d (2) Q d (3) Price (4) Q s (5) Q s 50 40 $ 10 70 80 60 50 9 60 70 80 60 8 50 60 90 70 7 40 50 100 80 6 30.
If the price elasticity of supply is 1.5, and a price increase led to a 3% increase in quantity supplied, then the price increase is about: a. 0.2% b. 0.5% c. 2.0% d. 4.5% View Answer 1.
Refer to the diagram, which shows demand and supply conditions in the competitive market for product X. If the initial demand and supply curves are D0 and S0, equilibrium price and quantity will be: A) 0F and 0A, respectively. B) 0G and 0B, respectively. C) 0E and 0B, respectively. D) 0F and 0C, respectively.
Demand for the whole market is downward sloping curve shown in the left graph. Demand for an individual seller is a horizontal line at the equilibrium price determined by the market. 2. Profit maximization in the short run 1) For a firm in a perfectly competitive market, price is equal to both average revenue and marginal revenue. P=MR=AR (only.
Move from point y to point X to the right. Refer to the above diagram. If this is a competitive market, price and quantity will move toward: $40 and 150 respectively. Where supply and demand meet.. Refer to the above diagram. The quantity of demand is 100 and the quantity of supply is 200. A price of $60 in this market will result in...







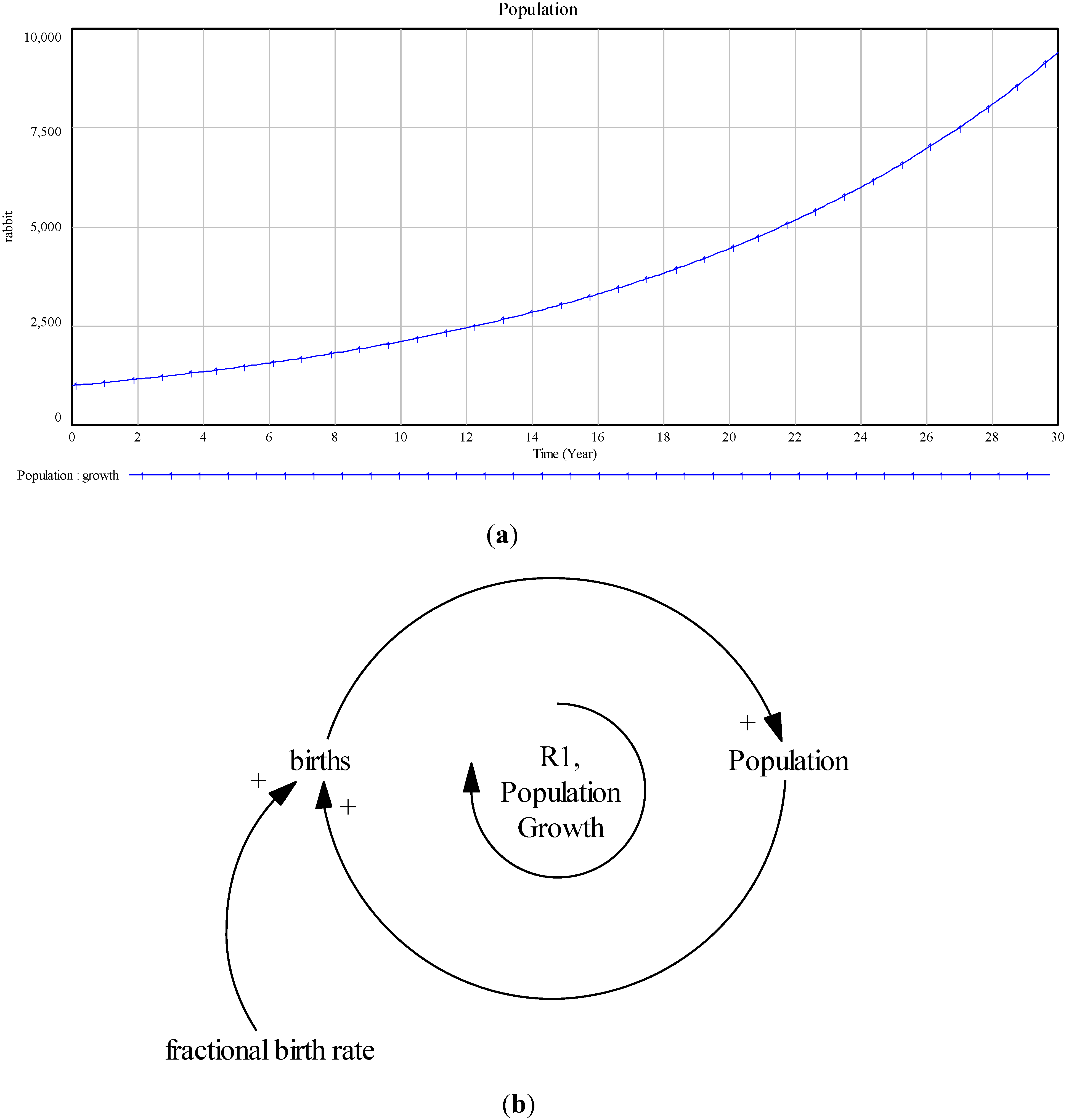



:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/disequilibrium-498e9ba4154c4a7c8739b3443da14b17.png)







0 Response to "37 Refer To The Diagram. If This Is A Competitive Market, Price And Quantity Will Move Toward:"
Post a Comment