37 Phase Diagram Of Sulfur
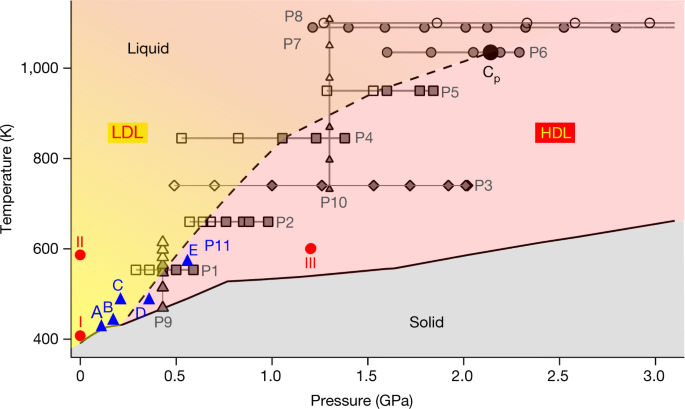
One Component Phase Systems: Sulphur System. The phase diagram of sulphur is somewhat more complicated than that of water although both are one component systems.A phase is defined as "a homogeneous, physically distinct and mechanically separable portion of the system, which is separated from other such parts of the system by definite boundary surface". The most recent in situ study on the low-pressure phase diagram of sulfur [9,10] provided the first high-quality diffraction data on high-pressure sulfur. This study showed a transformation of the ambient-pressure S8 ring molecule of the orthorhombic Fddd phase S-I to a new phase S-II, consisting of chains with trigonal geometry.
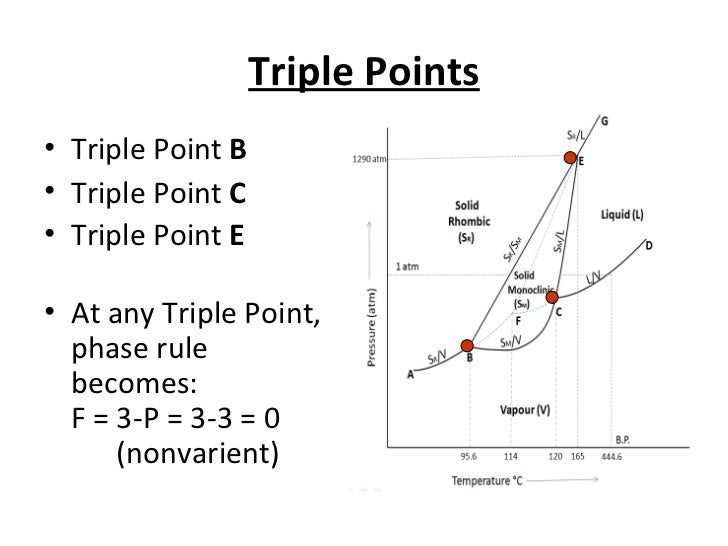
Sulphur can exists in four possible phases: o Two solid polymorphic phases Rhombic Sulphur (SR) (m.p. 114degC) o Sulphur Liquid o Sulfur vapours Components and Phase Rule All the four phases can be represented by the only chemical individual "SULPHUR" itself. Phase rule (F= C-P+2) becomes: F= 3-P = 3-2 = 1 (monovarient)

Phase diagram of sulfur
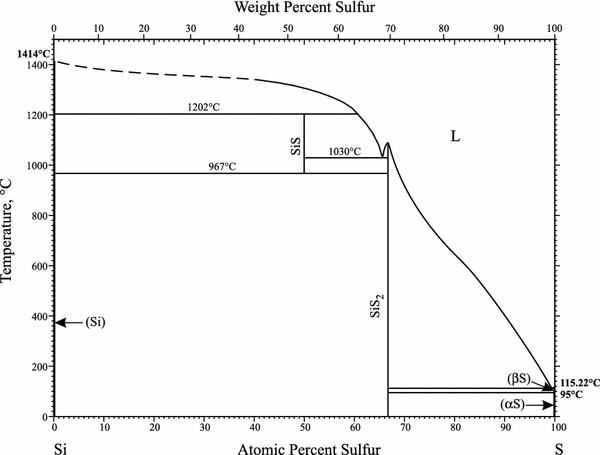
The pressure-temperature (P-T) phase diagram for sulfur is complex (see image). The region labeled I (a solid region), is α-sulfur. High pressure solid allotropes. In a high-pressure study at ambient temperatures, four new solid forms, termed II, III, IV, V have been characterized, where α-sulfur is form I. Solid forms II and III are polymeric, while IV and V are metallic (and are. Sulfur dioxide is a colorless gas with a pungent odor. It is a liquid when under pressure, and it dissolves in water very easily.Sulfur dioxide in the air comes mainly from activities such as the burning of coal and oil at power plants or from copper smelting. In nature, sulfur dioxide can be released to the air from volcanic eruptions. In the gas phase sulfur dioxide is oxidized by reaction with the hydroxyl radical via a intermolecular reaction: SO 2 + OH· → HOSOHOSO 22 · which is followed by: HOSO2· + O2→ HO 2 · + SO 3 In the presence of water sulfur trioxide (SOIn the presence of water sulfur trioxide (SO 3) is converted) is converted rapidly to sulfuric acid: SO 3.
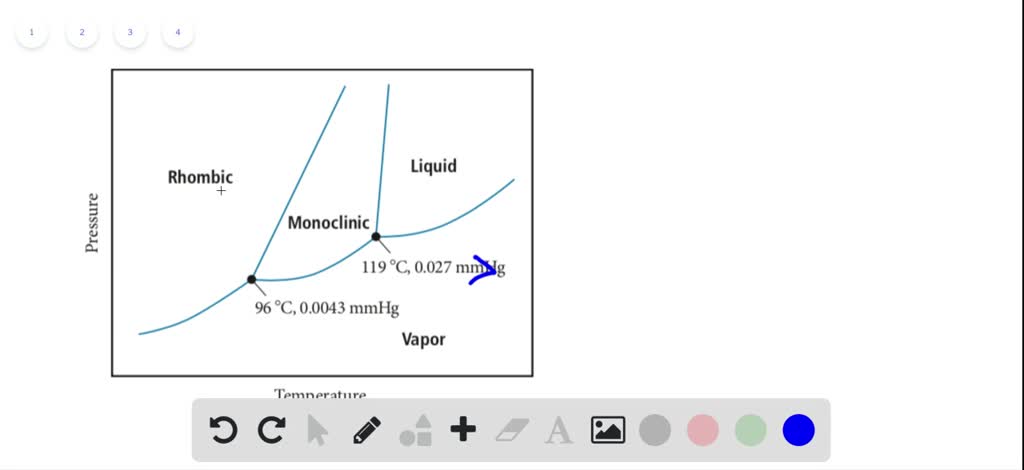
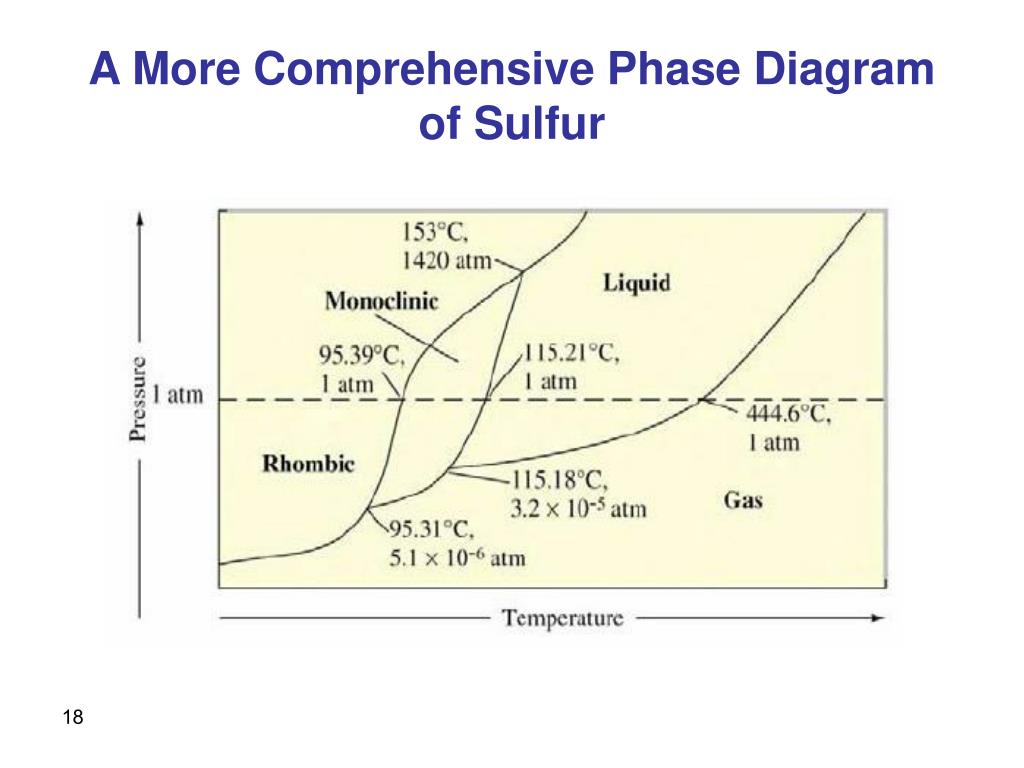
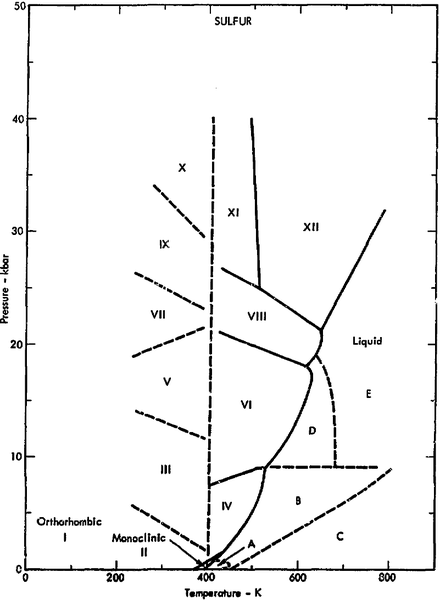
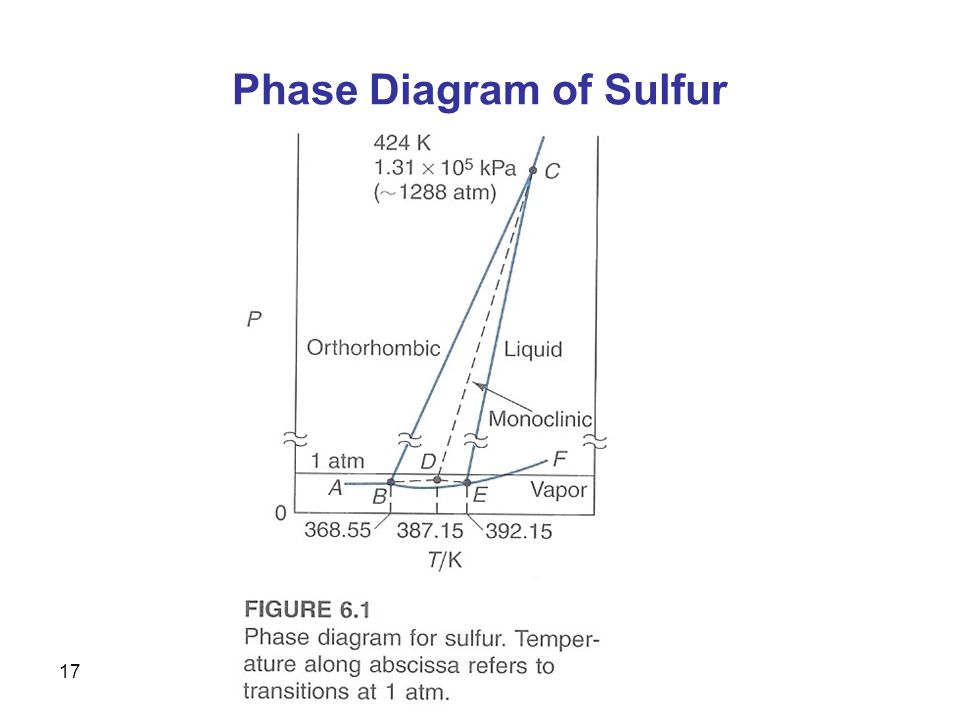
Phase diagram of sulfur. The low-pressure (p, T) phase diagram of sulfur as registered in many research works and textbooks has been schematically shown as in figure 1 which is useful in the following analysis and discussion.Download : Download full-size image FIGURE 1. Low-pressure phase diagram of sulfur (schematic). Legend: sr, sm, ℓ, and g are respectively the rhombic solid, monoclinic solid, liquid and gaseous. İçindekiler][] [ İçindekiler 100% (19 ratings) Answer:- a) there are three triple points as follows:- First triple point , rhombic S, monoclinic S and vapor are in equilibrium. Second triple point, monoclinic S, vapor and liquid S are in equilibrium.. View the full answer. Transcribed image text: The phase diagram of sulfur is shown at right. The phase diagram of sulfur contains a new feature: there are two solid phases, rhombic and monoclinic. The names refer to the crystal structures in which the S 8 molecules arrange themselves. This gives rise to three triple points, indicated by the numbers on the diagram.
Sulfur dioxide is a colorless gas with a pungent odor. It is a liquid when under pressure, and it dissolves in water very easily.Sulfur dioxide in the air comes mainly from activities such as the burning of coal and oil at power plants or from copper smelting. In nature, sulfur dioxide can be released to the air from volcanic eruptions. The phase diagram of sulfur is shown here. (a) How. Need more help! The phase diagram of sulfur is shown here. (a) How many triple points are there? (b) Monoclinic and rhombic are two allotropes of sulfur. Which is more stable under atmospheric conditions? (c) Describe what happens when sulfur at 1 atm is heated from 80°C to 200°C. Ni-S (Nickel-Sulfur) The Ni-S phase diagram in [Massalski2] was redrawn from [ 1991Sin ]. Figure 1 shows the Ni-S phase diagram determined by thermodynamic calculations by [ 2004Wal ]. In the diagram of [ 1991Sin ], β1 and β2 phases existed in the β phase field in Fig. 1. The presence or absence of these phases must be confirmed. Phase Diagram: In this phase diagram, which is typical of most substances, the solid lines represent the phase boundaries.The green line marks the freezing point (or transition from liquid to solid), the blue line marks the boiling point (or transition from liquid to gas), and the red line shows the conditions under which a solid can be converted directly to a gas (and vice-versa).
Phase Diagram of Phosphorus Similarly, the phase diagram of phosphorus (Fig. can be developed. The difference is that there is no intersection of line 1' and line 4' (they correspondto lines 1 and 4 respectively, in the phase diagram of sulphur), because line 1' and line 4' tend to be parallel (see Fig. 10). The experimental values of the (p, T) phase diagram of sulfur have been assessed through empirical equations commonly used. This treatment shows insufficiencies, namely those leading to. The phase diagram of sulfur is shown here, (a) How many triple points are there? (b) Monoclinic and rhombic are two allotropes of sulfur. Which is more stable under atmospheric conditions? (c) Describe what happens when sulfur at I atm is heated from 80 ° C to 200°C. In the gas phase sulfur dioxide is oxidized by reaction with the hydroxyl radical via a intermolecular reaction: SO 2 + OH· → HOSOHOSO 22 · which is followed by: HOSO2· + O2→ HO 2 · + SO 3 In the presence of water sulfur trioxide (SOIn the presence of water sulfur trioxide (SO 3) is converted) is converted rapidly to sulfuric acid: SO 3.
Consider the phase diagram for carbon dioxide shown in Figure 5 as another example. The solid-liquid curve exhibits a positive slope, indicating that the melting point for CO 2 increases with pressure as it does for most substances (water being a notable exception as described previously). Notice that the triple point is well above 1 atm, indicating that carbon dioxide cannot exist as a liquid.
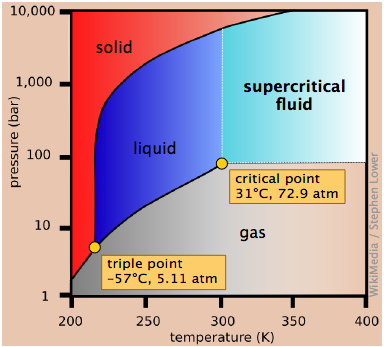
• The phase diagram for sulfur dioxide, SO 2, is shown below. Marks 4 Io, the innermost of the four Galilean moons orbiting Jupiter, is the most geologically active body in the solar system. Its surface is covered with a frost of solid SO 2.
• The phase diagram for sulfur dioxide, SO 2, is shown below. Marks 4 Io, the innermost of the four Galilean moons orbiting Jupiter, is the most geologically active body in the solar system. Its surface is covered with a frost of solid SO 2.
The pressure-temperature (P-T) phase diagram for sulfur is complex (see image). The region labeled I (a solid region), is α-sulfur. High pressure solid allotropes. In a high-pressure study at ambient temperatures, four new solid forms, termed II, III, IV, V have been characterized, where α-sulfur is form I. Solid forms II and III are polymeric, while IV and V are metallic (and are.
Phase Diagram Video Lessons. Concept: Concept: Problem: Sulfur can exist as a gas, a liquid, or as one of two solid states: rhombic and monoclinic. A phase diagram for sulfur is shown below: a. What is (are) the thermodynamically-stable phase (s) of sulfur at room temperature and pressure (i.e. 1.0 atm at 25°C)?
A phase diagram is a chart that shows the conditions of pressure and temperature at which distinct phases occur and coexist at equilibrium.. The lines on a phase diagram divide into regions – solid, liquid, and gas. The phase diagram of sulfur is. The diagram is complicated by the fact that sulfur can exist in two crystalline forms: rhombic and monoclinic.
- The phase diagram of an element or a compound tells the inter-conversion properties or relation between the solid phase, liquid phase, and gas phase of that substance. The graph is drawn between the temperature and pressure. - Sulfur is the element of group 16 of the p-block and it is the element of period 2.
Beginarrayltext The Phase Diagram For Sulfur Is Shown Here The Rhombic And Text Monoclinic States Ar
The experimental values of the ( p, T) phase diagram of sulfur have been assessed through empirical equations commonly used. This treatment shows insufficiencies, namely those leading to significant uncertainties in the coordinates of the low-pressure triple points. An alternative way to try and find reliable equations for the phase equilibrium.
Problem: The phase diagram for sulfur is shown below. The rhombic and monoclinic phases are two solid phases.Below what pressure will solid sulfur sublime?Express your answer using two significant figures. FREE Expert Solution Show answer. 95% (321 ratings) FREE Expert Solution.
phase diagrams for elements will pro mote the more complex task of describ ing phase behavior in compounds and multi~component systems. This report is aimed at encour aging theoretical and experimental research on phase transitions. It is a summary of the experimental data obtained to date on the phase diagrams of the elements. Only solid and
This video is meant to strengthen the basics of chemistry.
The pressure-temperature (P-T) phase diagram for sulfur is complex (see image). The region labeled I (a solid region), is α-sulfur. High pressure solid allotropes. In a high-pressure study at ambient temperatures, four new solid forms, termed II, III, IV, V have been characterized, where α-sulfur is form I. Solid forms II and III are polymeric, while IV and V are metallic (and are.
A phase diagram is a chart that shows the conditions of pressure and temperature at which distinct phases occur and coexist at equilibrium. The lines on a phase diagram divide into regions solid, liquid, and gas. The diagram is complicated by the fact that sulfur can exist in two crystalline forms: rhombic and monoclinic.
The complete 2D phase diagram has been obtained and compared with MC simulations yielding the sulphur-sulphur lateral interactions.. The adsorption of sulfur at 0.5 ML in both c(2×2) and [21 2...
Journal of Phase Equilibria - 24Tho: J.S. Thomas and J.H. Jones, "The Polysulphides of the Alkali Metals.




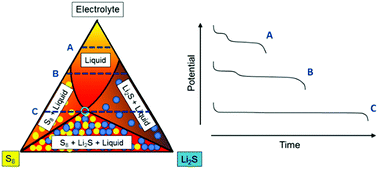



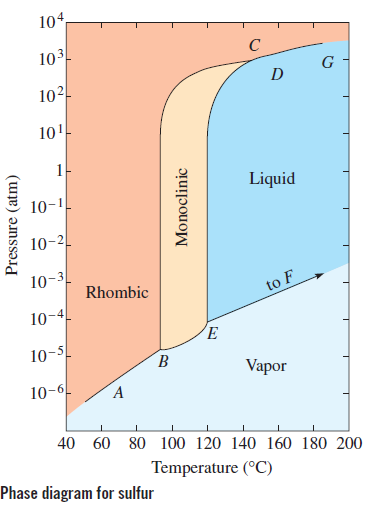
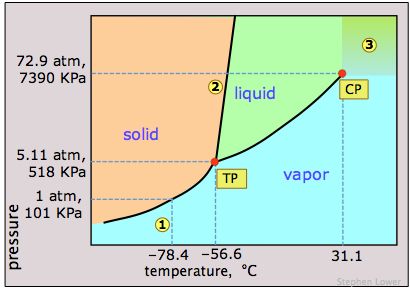

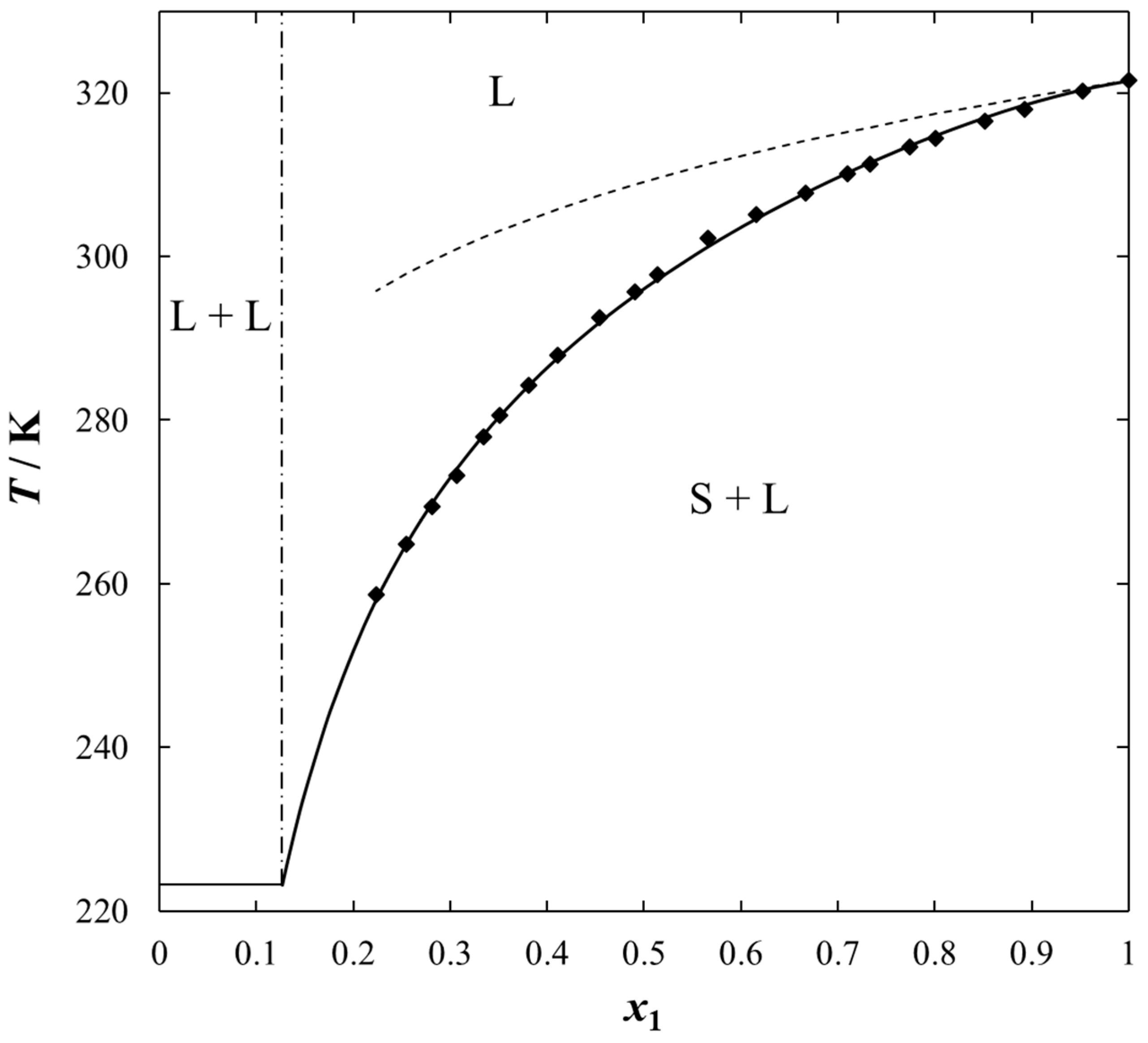



37Figure2.gif)




0 Response to "37 Phase Diagram Of Sulfur"
Post a Comment