37 Bunsen Burner Flame Diagram
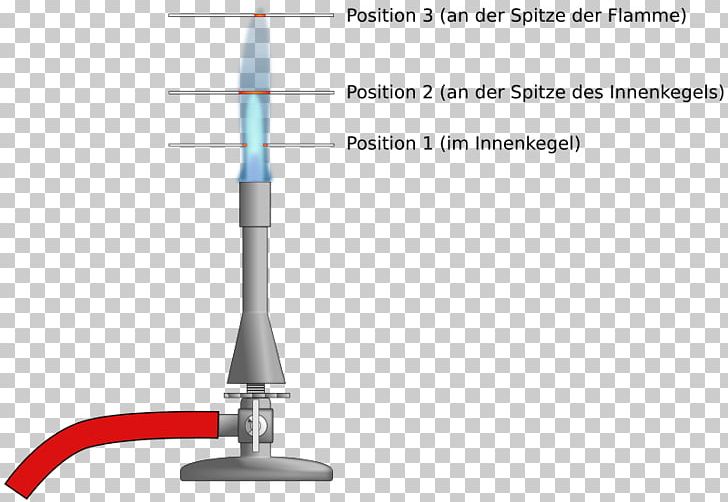
See diagram 3.1.2.2: Bunsen burner flame. See diagram 3.1.2.3: Burn gas from the cone of the flame. 1. Hold the end of a glass tube in the centre of the cone. You can light the gas coming out of the other end of the glass tube. 2. Hold a piece of wire in different parts of each kind of flame, moving it from the bottom to the top. and held the bunsen burner's bright blue inner cone of fiercest heat to sear CHEAT CHEAT. published in Magma 42 (Winter 2008/09) edited by Laurie Smith. Vicki Feaver's third collection, The Book of Blood, was published by Cape in 2006. She has won the Arvon International Poetry Competition and the Forward Poetry Prize for Best Single Poem.
A Bunsen burner is laboratory equipment that produces a flame used for heating, sterilization, and other experimental purposes. Learn the basics of a Bunsen burner, explore its parts, as well as.
Bunsen burner flame diagram
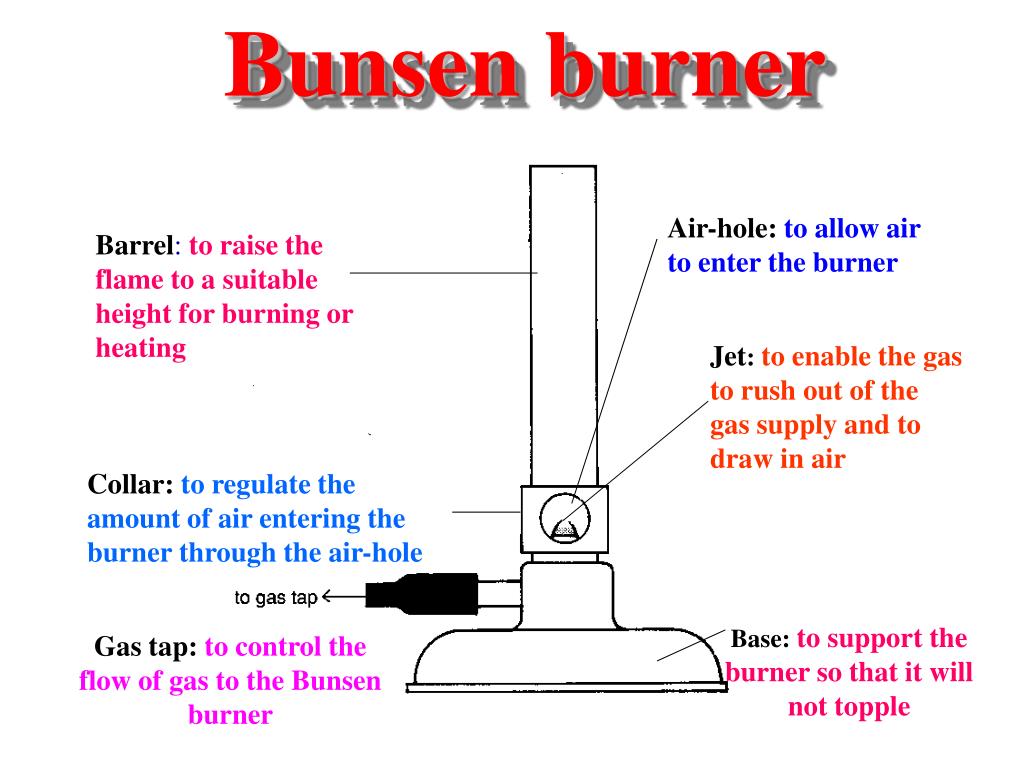
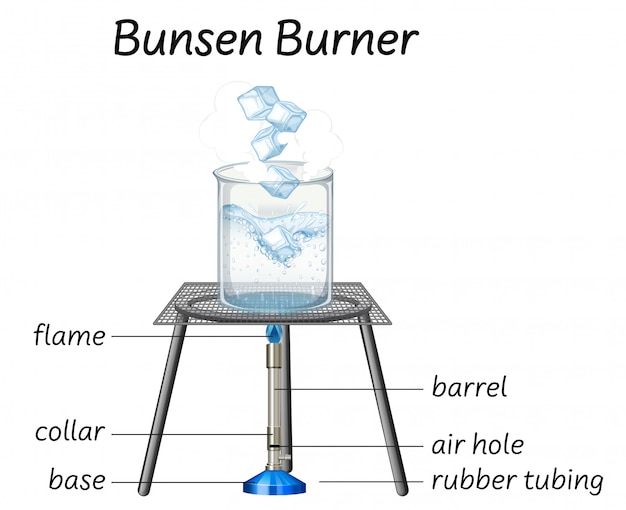
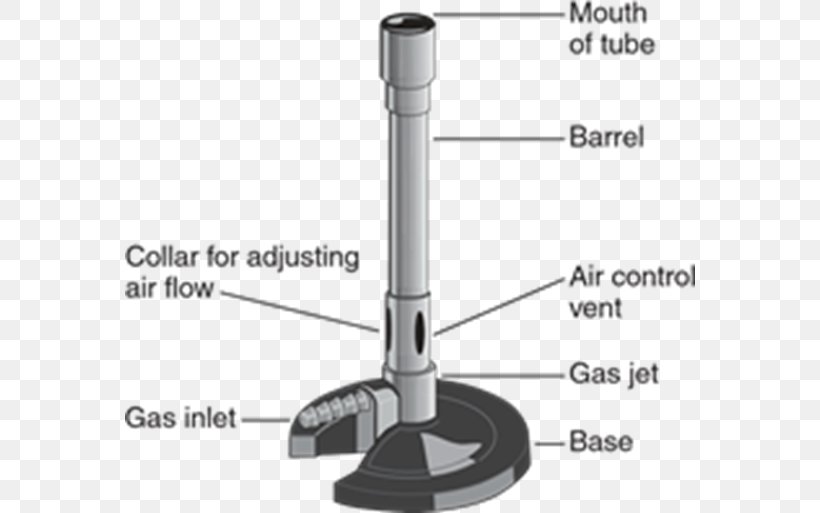
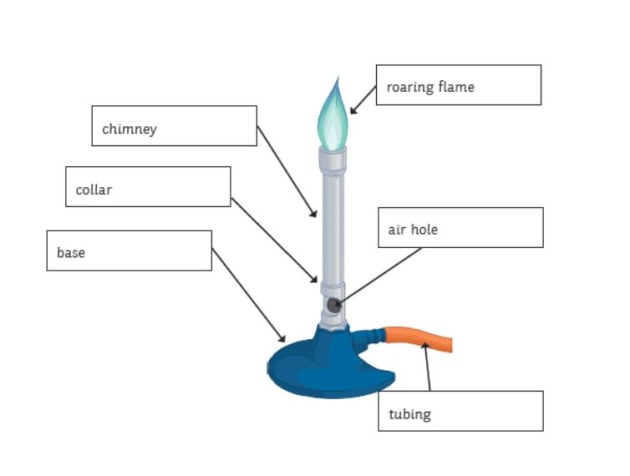
Collar, Base, Gas Valve, Chimney, Flame (Inner Cone), Rubber Tubing, Flame (Outer Cone), Air Hole, Heat Proof Surface. Labelling a Bunsen Burner Share Share Labelled diagram of a Bunsen burner. STUDY. Learn. Flashcards. Write. Spell. Test. PLAY. Match. Gravity. Created by. russellvanniekerk TEACHER.. to adjust the flame from a luminous flame to a non-luminous flame and allow mixing of gases (combustion) rubber tubing. carries the gas to the burner from the gas tap on the laboratory bench. base... Determining the hottest part of the Bunsen burner using a paper clip and match.Notice that the paperclip glows red hot at the top of the inner cone of the fl...
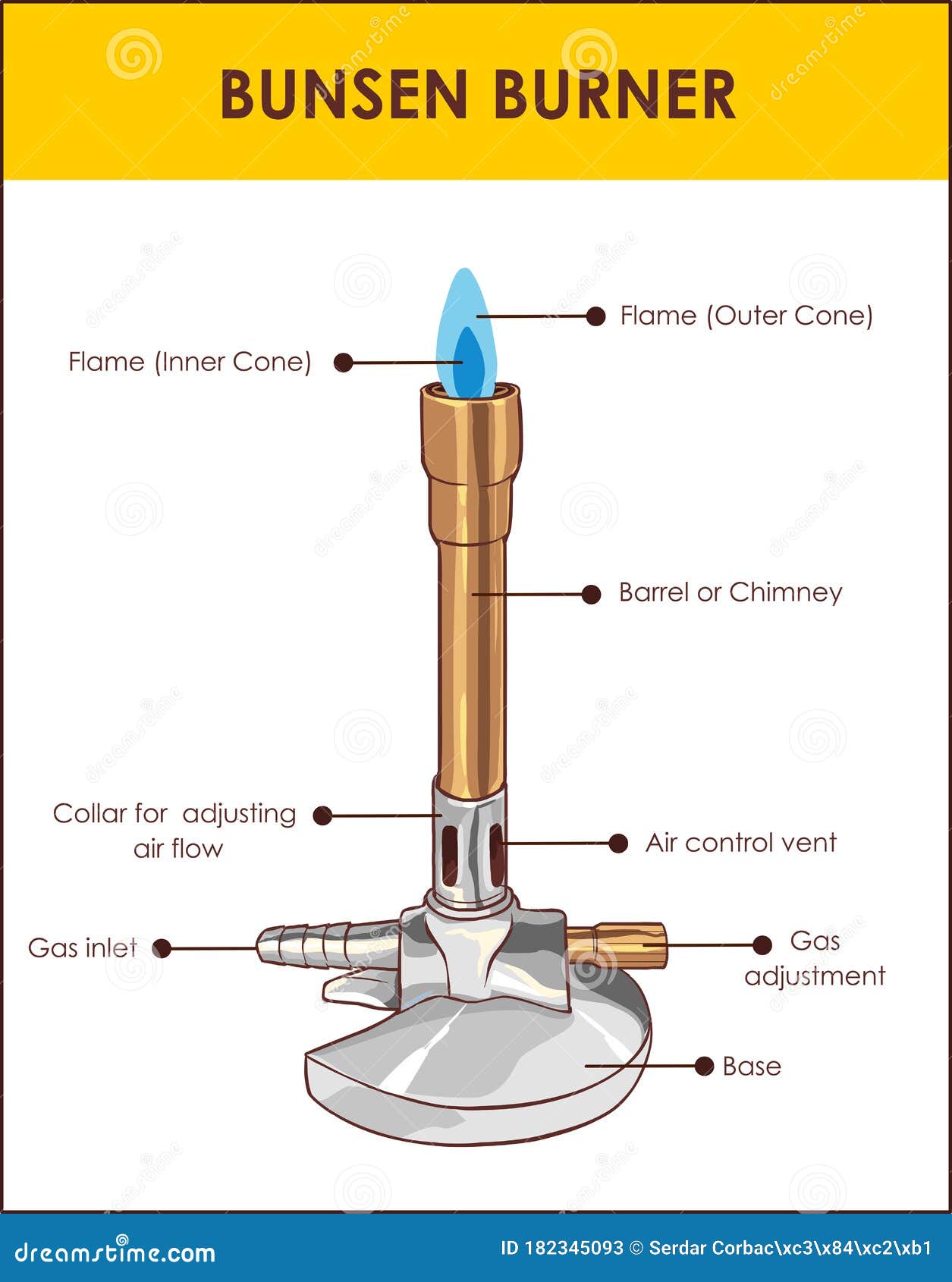
Bunsen burner flame diagram. Bunsen&Burner&Lab!!!!& & Background: Often a chemist needs to heat materials. The Bunsen Burner is one of the most efficient ways of doing this. Burners come in a variety of designs but most operate on the principle of mixing gas with air to produce a hot flame. In this lab you will learn how to light and adjust a burner flame and to locate the. Region 1 is where the mostly unburned gas and oxygen mixture are pushing above the lip of the Bunsen Burner. Region 1 exists because the gas coming out of the tube is cool. If the air port is open and the gas flow is too low then the gas will start to burn down the tube and you'll get a "strike back" where the flame is either (1) blown out or. Wooden splints F and G were placed in different zones of a Bunsen burner flame. The diagram below gives the observations that were made (a) Explain the difference between F and G (b) Name the type of flame that was used in the above experiment. Date posted: October 11, 2019. Answers (1) (Solved) Date posted: October 1, 2019. Answers (1) A Bunsen Burner is commonly used in laboratory Apparatus. it is named by the inventor Robert bunsen the basic function of a bunsen burner in the laboratory is heating, sterilization, and combustion. it produces a single open gas flame. there are 6 major bunsen burner parts i.e, barrel, a collar, air holes, gas intake, gas valve, and stand.
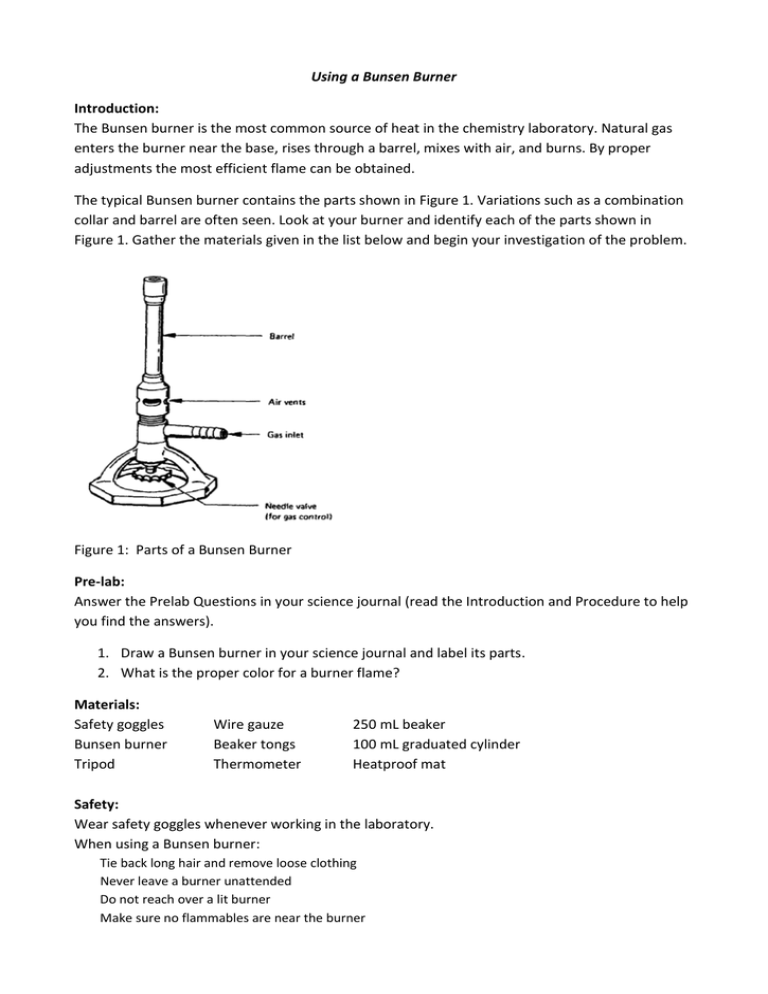
flame that wouldn't interfere with the colored flame emitted by chemicals being tested. Peter Desaga was a University of Heidelberg (where Bunsen worked) mechanic who actually invented and built the first Bunsen burner to Bunsen's specifications. Bunsen also invented the hydrojet filter pump, a photometer (to measure the intensity of light. Wooden splints F and G were placed in different zones of a Bunsen burner flame. The diagram below gives the observations that were made (a) Explain the difference between F and G (b) Name the type of flame that was used in the above experiment. Answers. MIX, as used in the Bunsen burner modeling calculations does not account for radi-ation heat{loss. The formula given in Equation 7.3 assumes that both heat{loss by radiation and conduction are based on the °ame temperature, T°ame. The major heat sink for the Bunsen burner °ame is the stainless steel burner rim with a temperature of Trim. A. Parts of the Bunsen burner 1. Examine the Bunsen burner and take note of the following parts: base, barrel, air inlet, collar, gas spud and gas inlet 2. Label the parts on the diagram and give the function of each part. B. Operation of the Bunsen burner 1. Connect the burner to the gas cock with rubber tubing.
Determining the hottest part of the Bunsen burner using a paper clip and match.Notice that the paperclip glows red hot at the top of the inner cone of the fl... A typical Bunsen burner diagram shown below: Bunsen burner parts and functions. Bunsen burner one of the important components of laboratory equipment, which mainly used to heat various materials in the laboratory. Is located below the support frame, and there is a glass test tube on the support frame. The typical Bunsen-burner flame is a dual flame: a fuel rich premixed inner flame surrounded by a diffusion flame. illustrates a Bunsen burner. The diffusion flame results when CO and OH from the rich inner flame encounter the ambient air. The shape of the flame is determined by the combined effects of The Bunsen Burner The Bunsen burner is the object most frequently associated with a chemistry laboratory. In this lab, it will serve as the primary heat source. The burner operates on natural gas, much like the burners of a gas stove. Take a moment to examine the burner; there are two parts to it: a tube (or barrel or stack) and a base.
Bunsen Burner Flame Figure 3. 3 21 inn cieniic nc is esere Bunsen Burner Basics continued by turning the handle on the natural gas valve. The height and intensity of the Bunson burner flame depend on both the gas flow. Draw a diagram of a correct Bunsen burner flame and label the hottest spot. 3. List three (3) safety rules when lighting a...
Flame can be classified into two classes. Namely, 1. Premixed Flames: Premixed flames are of two types: laminar premixed Flame and turbulent premixed Flame. For example, Bunsen burner, LPG domestic burner, SI engine. 2. Non-premixed Flames or Diffusion Flames: An example of non-premixed Flame is candle flame.
Browse 250 bunsen burner flame stock illustrations and vector graphics available royalty-free, or search for gas to find more great stock images and vector art. Newest results. gas. The symbol of the burning Gas. A burner for a gas stove. The hob is in the kitchen. The symbol of the burning Gas.
The Bunsen Burner. The full lesson can be viewed by enrolling in the Year 7 Chemistry Online Course or by purchasing the Year 7 Chemistry Lesson Notes. Learning Objective. In this lesson we will learn about the different parts of a Bunsen burner, and how to use a Bunsen burner correctly and safely in a science laboratory. Learning Outcomes.
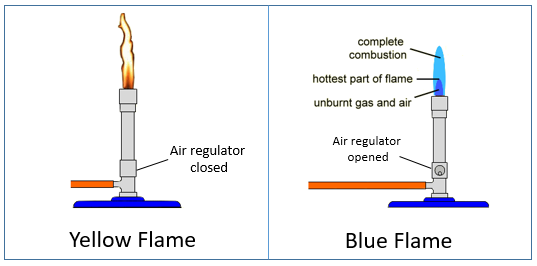
The Bunsen burner flames can range from a bright yellow to orange to purple to blue flame. A bright yellow flame indicates a flame that is starved of oxygen or contains the least amount of air.
Label the bunsen burner. The tip of the blue inner flame is the hottest part. Labelled diagram of a bunsen burner. Label a bunsen burner. Bunsen burner device for combining a flammable gas with controlled amounts of air before ignition. Hold bottles with your hand over the label while pouring. Available to members only. Learn the parts of the.
Collar, Base, Gas Valve, Chimney, Flame (Inner Cone), Rubber Tubing, Flame (Outer Cone), Air Hole, Heat Proof Surface. Labelling a Bunsen Burner Share Share
state the colour of the Bunsen flame when the air hole is open/closed, e.g., -The flame is blue when the air hole is open. -The flame is yellow when the air hole is closed. Activities: 1. Introducing the Bunsen burner and its structure - group work(8 minutes) 2. Demonstrating lighting a Bunsen burner - whole class (12 minutes) 3.
Alkali metals all give characteristic flame colors in a flame test. The Bunsen flame should be nonluminous and will have a pale-blue color. This is achieved by having the air hole on the Bunsen burner fully open. The colors produced by the alkali metals are quite distinct, in comparison to the nonluminous Bunsen flame.
Basic Bunsen Burner Introduction The Bunsen Burner will be used throughout the year as part of various labs. There are several ways to adjust the burner, and at various times a lab will ask you for a particular kind of flame. Through experimentation with the burner, you should learn to create any kind of flame asked for. Procedure
This flame burns yellow and is the coolest flame, often called the safety flame. When the burner is not in use the collar should be rotated to close the air ports and produce the cool safety flame. The needle valve and the collar are used in conjunction to control the volume and the the mixture ratio of gas to air.
Labelled diagram of a Bunsen burner. STUDY. Learn. Flashcards. Write. Spell. Test. PLAY. Match. Gravity. Created by. russellvanniekerk TEACHER.. to adjust the flame from a luminous flame to a non-luminous flame and allow mixing of gases (combustion) rubber tubing. carries the gas to the burner from the gas tap on the laboratory bench. base...
The coolest? (Explain using the diagram.) 4. Here are safety rules when using a Bunsen burner. Explain why it is important to follow these rules: a Never turn the gas tap on until you are ready to light the Bunsen burner. b If your Bunsen burner goes out, turn the gas tap off immediately.
Bunsen burner use and safely heating test tubes bunsen burner parts. Start studying labelled diagram of a bunsen burner. In order to function properly bunsen burners must have a barrel a thats approximately five inches long a collar b with air holes. Draw a diagram of a correct bunsen burner flame and label the hottest spot.
Matchstick on barrel in flame: The matchstick lighted; Illustration of Bunsen burner lame with inserted tubes; Scorched cardboard; Diagram of the flame Justification; The color of the fire from the Bunsen burner is blue on the bottom and orange on the top. This is because there is more gas concentrated at the bottom of the Bunsen burner rather.























0 Response to "37 Bunsen Burner Flame Diagram"
Post a Comment