37 Atomic Energy Level Diagram
NIST Atomic Spectra Database Levels Form. This form provides access to NIST critically evaluated data on atomic energy levels. Spectrum: e.g., Fe I or Mg Li-like or Z=59 II or 198Hg I. Description. Atomic Energy Levels and Grotrian Diagrams, Volume I: Hydrogen I - Phosphorus XV presents diagrams of various elements that show their energy level and electronic transitions. The book covers the first 15 elements according to their atomic number. The text will be of great use to researchers and practitioners of fields such as.
Energy level diagrams are the representation of placements or arrangements of orbitals (also known as subshells) according to their increasing energy levels. Image will be uploaded soon. Above is the blank energy level diagram which can be used to represent the electrons for any atom under study.

Atomic energy level diagram
Atomic Physics Problem C INTERPRETING ENERGY-LEVEL DIAGRAMS PROBLEM Although neutral lithium has three electrons, two of the electrons are in the n 1 energy level, which is filled. The third electron is in the n 2 energy level, and behaves like the single electron in a hydrogen atom, except that the nucleus has a 3 charge and the two inner. The energy diagram for carbon in CO 2 is shown below. What is the hybridization of oxygen in CO 2. Each oxygen has two lone pairs and forms one s bond and one p bond. This means that there must be three hybridized orbitals and one unhybridized p orbital to make the p bond. This is sp 2 hybridization. Definition of atomic orbital diagram for oxygen: An orbital is the region of space around the nucleus within which the probability finding an electron of given energy is maximum. The diagram of this region gives the diagram of the orbital. The plot of angular wave function or square of angular wave functions give us the…
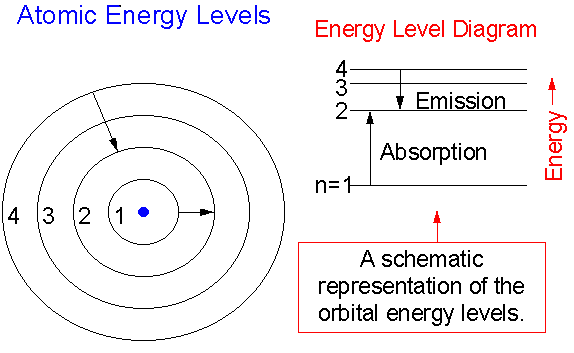
Atomic energy level diagram. This chemistry video tutorial focuses on the bohr model of the hydrogen atom. It explains how to calculate the amount of electron transition energy that is... The n = 2 level is called the first excited state. Its energy is 2 E 2=−E R2=−3.4 eV.The n = 3 level is the second excited state, and so forth. The atomic energy states are often schematically depicted as an energy level diagram. Each level corresponds to the energy of an electron state. Arrows show the transitions between levels. AES - Energy Level Diagrams - Scheeline & Spudich. Prior to 1922, atomic emission was used to qualitatively identify elements, but was too imprecise for quantitative analysis. Lester Strock developed the use of internal standards ( see our page on internal standards as well) to compensate for the sample-to-sample and time-dependent variations. We like representing these energy levels with an energy level diagram. The energy level diagram gives us a way to show what energy the electron has without having to draw an atom with a bunch of circles all the time. Let's say our pretend atom has electron energy levels of zero eV, four eV, six eV, and seven eV.
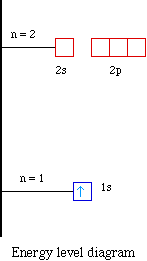
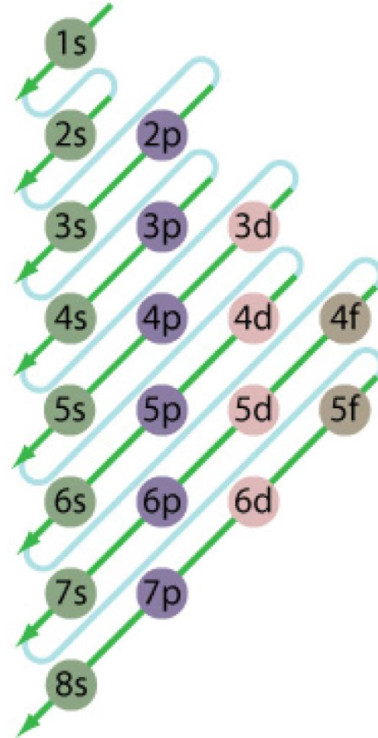
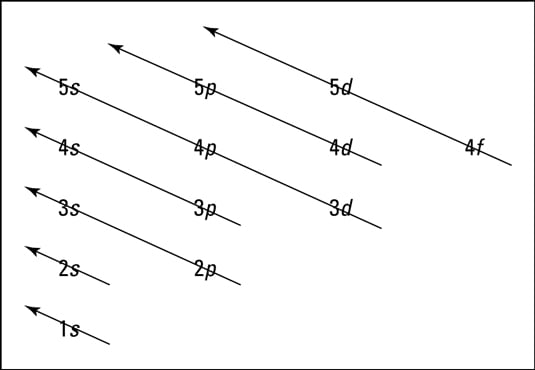
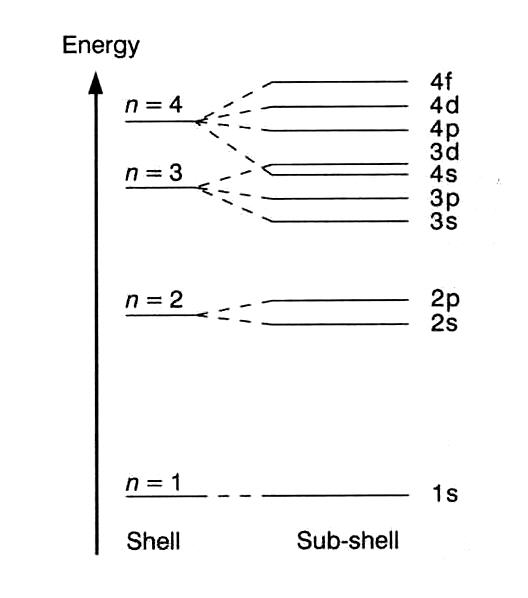
The energy level diagram is therefore as shown below. Note that the total pi electron energy is more negative (more bonding) than the two electrons of the ethene pi bond, by 0.82b. This is the delocalization energy, i.e., the additional stabilization of these two electrons derived from their delocalization over three atoms, instead of just two. What is energy level diagram? In chemistry, an electron shell, or energy level, may be imagined as an orbit with electrons around the nucleus of an atom. The closest shell to the nucleus is called the “K shell” followed by the “L shell” then the “M shell” and so on away from the nucleus. The shells can be denoted by alphabets (K, L. Atomic Energy Level Diagrams Energy level diagrams can be useful for visualizing the complex level structure of multi-electron atoms. Forms of such diagrams are called Grotrian diagrams or term diagrams in various parts of the literature. •Total electrons = atomic number •Fill energy levels with electrons until you run out •A superscript states how many electrons are in each level –Hydrogen – 1s1 – 1 electron total –Helium – 1s2 – 2 electrons total –Lithium – 1s22s1 – 3 electrons total –Beryllium – 1s22s2 – 4 electrons total
Electron Energy Level 3 •Level 3: a)has 3 sublevels: s, p, and d b)2 electrons in s c)6 electrons in p d)5 different d orbitals, and 2 electrons can fit in each—total of 10. a)total of 18 electrons in level 3 Energy diagram for interface electron transition induced photo emission. (A) The schematic diagram of FEP and quartz interface at atomic level. (B) Energy diagram of electron transition between. The energy diagram for carbon in CO 2 is shown below. What is the hybridization of oxygen in CO 2. Each oxygen has two lone pairs and forms one s bond and one p bond. This means that there must be three hybridized orbitals and one unhybridized p orbital to make the p bond. This is sp 2 hybridization. D3.3 Orbital Energy Level Diagrams An orbital energy level diagram (or just orbital diagram) shows the relative energies of orbitals and how electrons are distributed among orbitals within a subshell.In an orbital energy level diagram, individual orbitals are usually represented by horizontal lines whose vertical position conveys the qualitative relative energies of the orbitals.
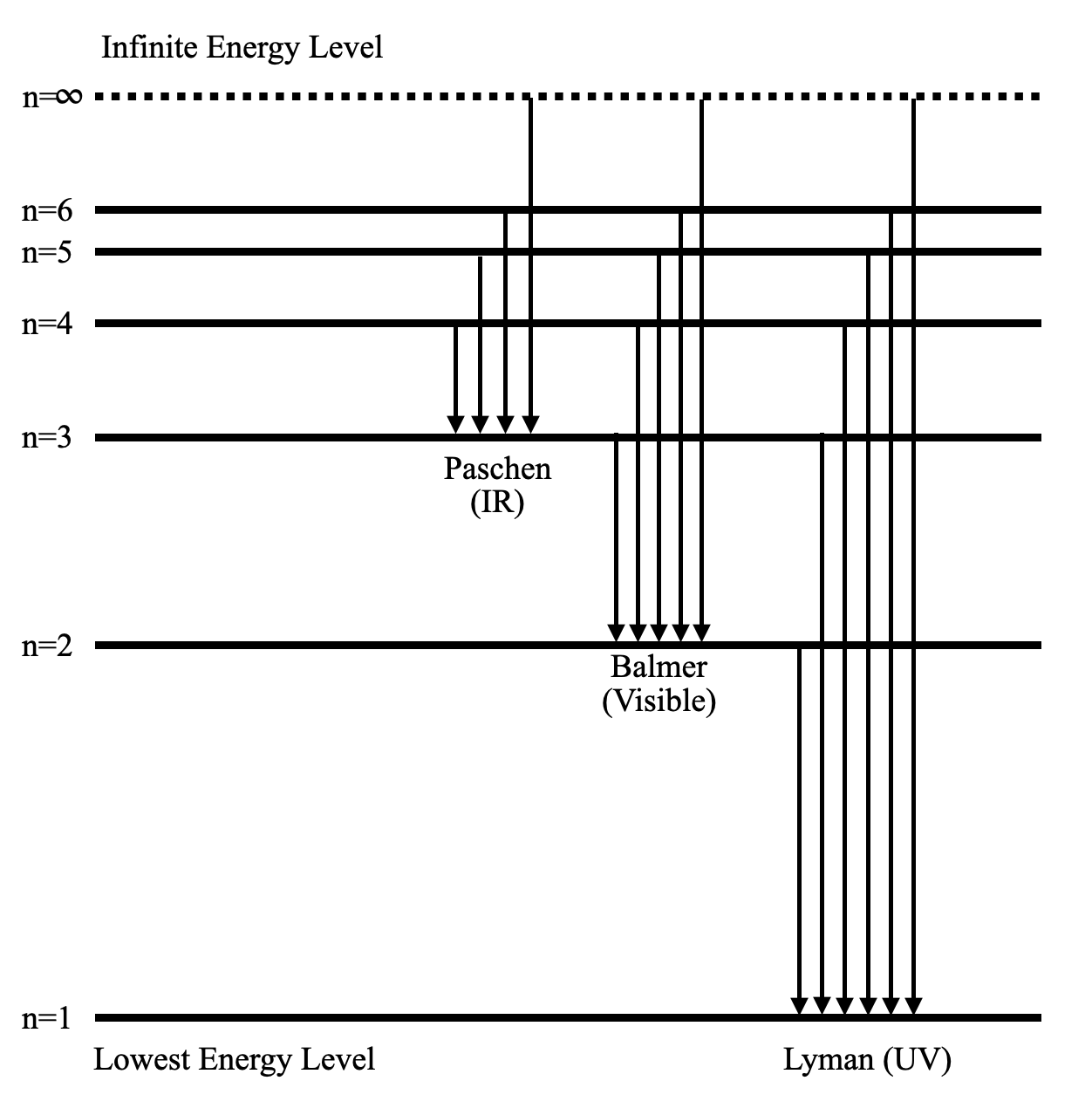
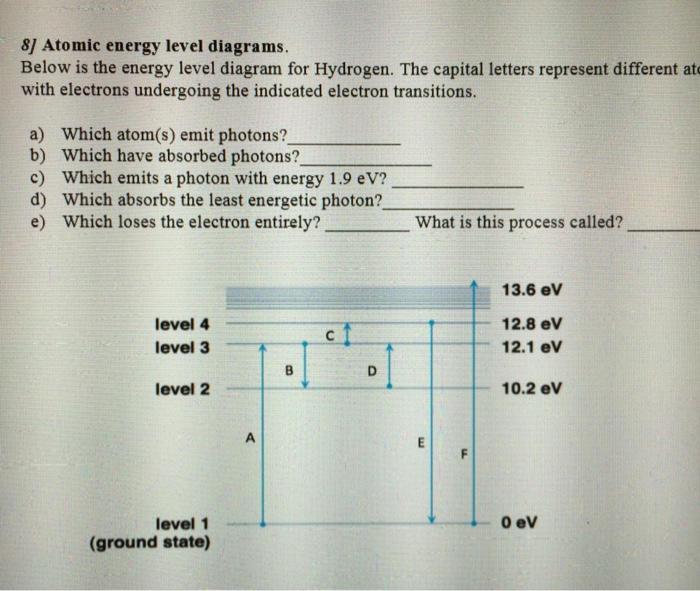
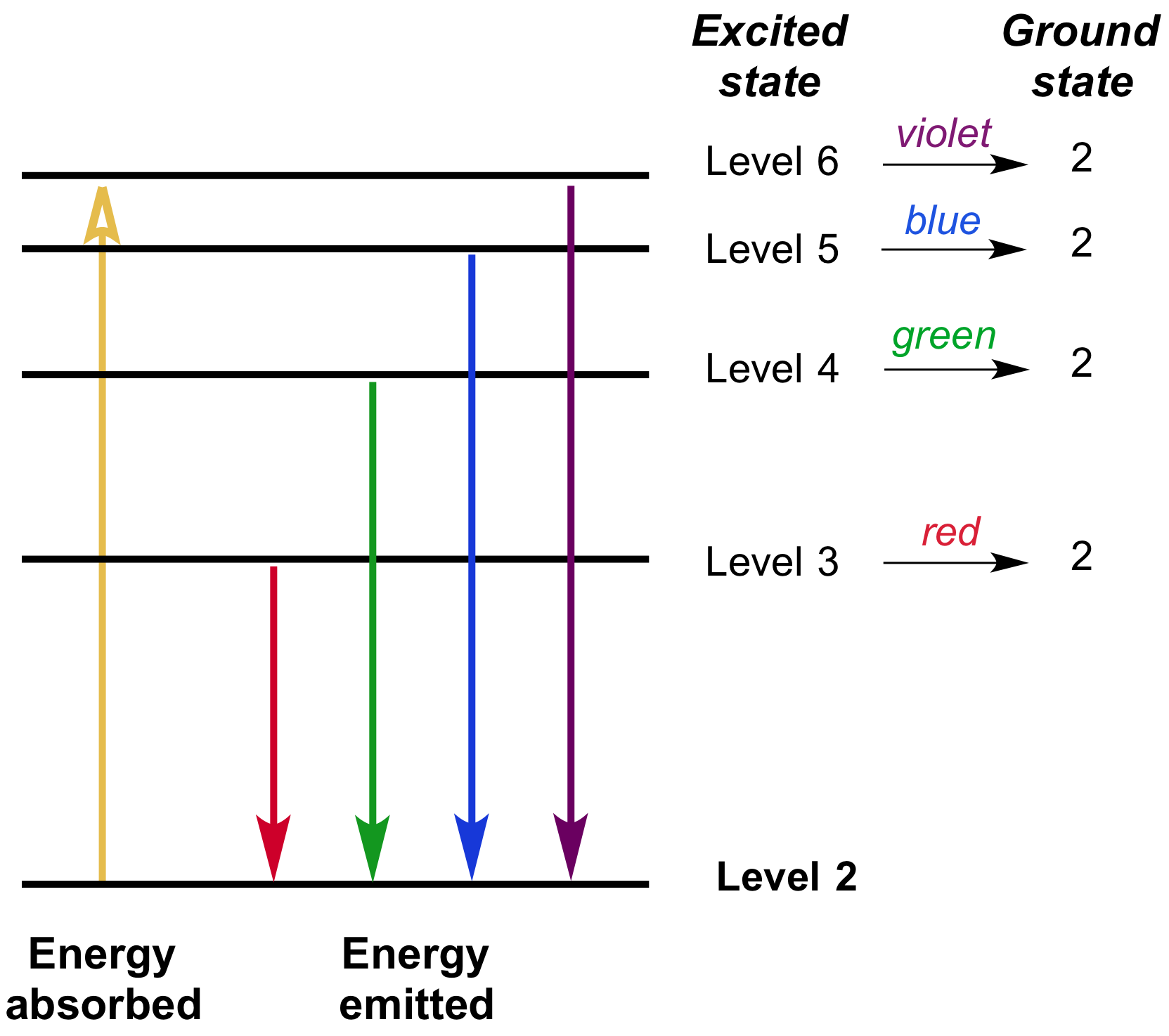
The ionization energy of an atom is the energy required to remove the electron completely from the atom. (transition from ground state n = 0 to infinity n = ∞ ). For hydrogen, the ionization energy = 13.6eV. When an excited electron returns to a lower level, it loses an exact amount of energy by emitting a photon.
Energy Level Diagrams. Energy level diagram (Mg atom) Energy Level Diagrams for lower states of Na, Mg, Al. Ionic spectra versus atomic spectra. • Atomic Absorption: it measures the radiation absorbed by the unexcited atoms that are determined.
The energy of an electron when it is far away from the influence of the nucleus is taken as zero. Principal quantum number of an electron existing in such a stationary state is taken as, n = ∞. Such kind of hydrogen atom is called an ionized hydrogen atom. A negative sign is placed in the above equation as, due to the transition of an.
Orthohelium and Parahelium Energy Levels In the helium energy level diagram, one electron is presumed to be in the ground state of a helium atom, the 1s state.An electron in an upper state can have spin antiparallel to the ground state electron (S=0, singlet state, parahelium) or parallel to the ground state electron (S=1, triplet state, orthohelium).
The molecular energy levels are labelled by the molecular term symbols. The specific energies of these components vary with the specific energy state and the substance. Energy level diagrams. There are various types of energy level diagrams for bonds between atoms in a molecule. Examples
You look on the periodic table and find that oxygen is atomic number 8. This number means that oxygen has 8 protons in its nucleus and 8 electrons. So you put 8 electrons into your energy level diagram. You can represent electrons as arrows. If two electrons end up in the same orbital, one arrow faces up and the other faces down.
Energy level diagram for unhybridized oxygen atom -. Hybridization is the combining of valence electrons or valence orbitals to create orbitals of equal energy. Oxygen has 2s22p4 2 s 2 2 p 4.
Definition of atomic orbital diagram for oxygen: An orbital is the region of space around the nucleus within which the probability finding an electron of given energy is maximum. The diagram of this region gives the diagram of the orbital. The plot of angular wave function or square of angular wave functions give us the…
Energy level diagram is a part of CBSE Class 11 chemistry first term syllabus. It carries a total of 12 periods and 5 to 6 marks. Atomic radius value: r(n) = n 2 x r(1) An atomic energy present in the nth level of hydrogen atom: E(n) = -1/n 2 x 13.6eV; The energy value exerted for a particular transition: hv = E =.
Atomic energy levels are subdivided into sub-energy levels. These sub-energy levels are called orbital. The sub energy levels are expressed by 'l'. The value of 'l' is from 0 to (n - 1). The sub-energy levels are known as s, p, d, f. Determining the value of 'l' for different energy levels is-If n = 1, (n - 1) = (1-1) = 0
The number of protons is the same as the atomic number, so the atom is oxygen. Have groups work together to place each card with its correct atom. Show students that you have 80 cards (4 for each of the first 20 elements). Before distributing the cards, explain that each card contains information about electrons and energy levels for the first.
Figure 13: A molecular orbital energy-level diagram showing the relative energies of the atomic orbitals of atoms A and B (1 sA and 1 sB) and the bonding (1σ) and antibonding (2σ) molecular orbitals they form. Energy levels of the hydrogen atom, according to Bohr's model and quantum mechanics using the Schrödinger equation and the Dirac.
Energy level diagram for Molecular orbitals.. Diagram for O2+ is wrong because 2p atomic orbital of 2nd O atom will have only 3 e-. Reply. Mrs Shilpi Nagpal says. September 26, 2018 at 11:06 am. Thanks for the correction and letting us know, we have made the changes, keep reading this website.
3. Draw two electrons in the first energy level and label them with their charge. 4. Draw three electrons in the second energy level and label them with their charge. 5. What element is represented by the diagram? _____ Part B: Atomic Calculations 6. Label the information provided in the periodic table. 7. What does the atomic number represent?8
Energy level diagrams are a means of analyzing the energies electrons can accept and release as they transition from one accepted orbital to another. These energies differences correspond to the wavelengths of light in the discreet spectral lines emitted by an atom as it goes through de-excitation or by the wavelengths absorbed in an absorption.
Atomic Physics Problem C INTERPRETING ENERGY-LEVEL DIAGRAMS PROBLEM Although neutral lithium has three electrons, two of the electrons are in the n 1 energy level, which is filled. The third electron is in the n 2 energy level, and behaves like the single electron in a hydrogen atom, except that the nucleus has a 3 charge and the two inner.
Energy Level Diagrams Atomic Number Atomic # represents the number of protons (p+) in the nucleus of an atom. For a neutral atom the # protons = # electrons. (total positive charge equals the total negative charge). The atomic number is the top right number on the periodic table for each atom. Example: Carbon has atomic # 6 which means C has
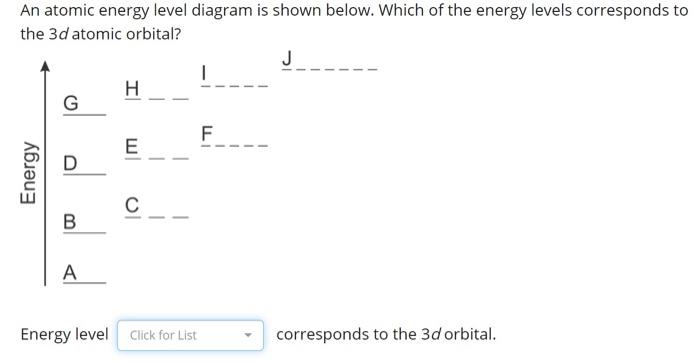



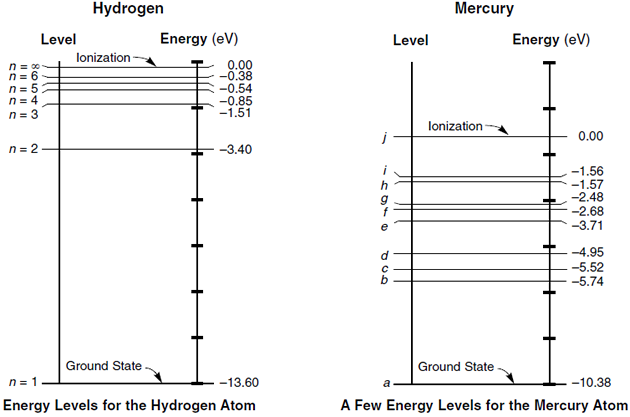

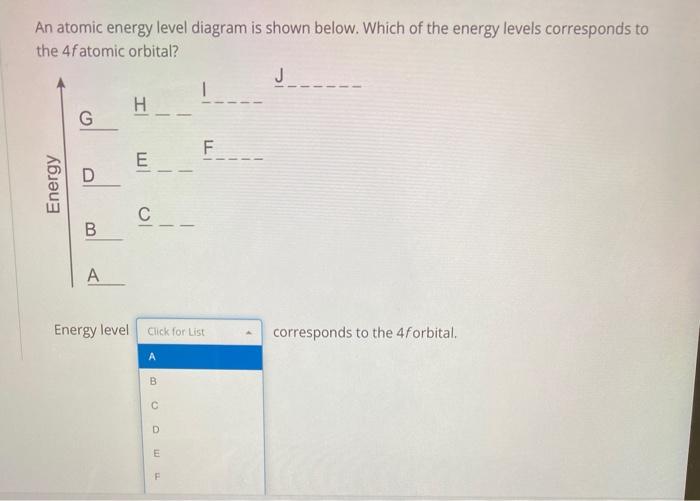


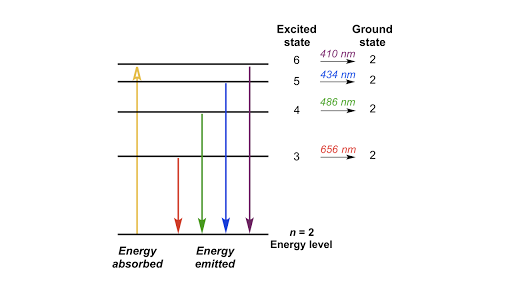












0 Response to "37 Atomic Energy Level Diagram"
Post a Comment