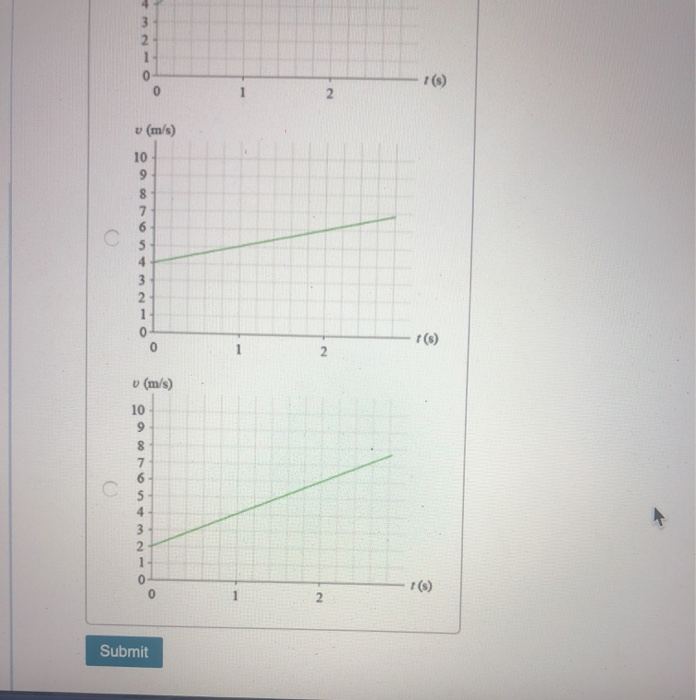
40 which diagram shows the equation v=2t+4?
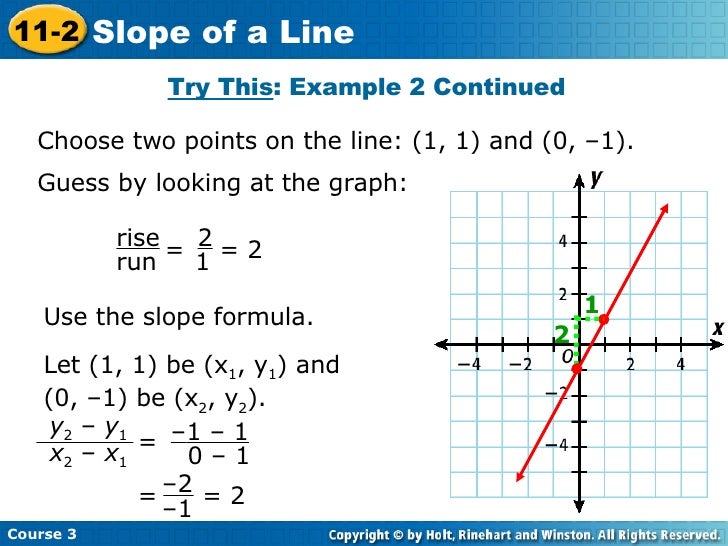
Phasor Diagram and Phasor Algebra used in AC Circuits This then gives us the rectangular expression for voltage V1 of: 10 + j17.32 The resultant voltage, VT is found by adding together the horizontal and vertical components as follows. VHorizontal = sum of real parts of V1 and V2 = 30 + 10 = 40 volts VVertical = sum of imaginary parts of V1 and V2 = 0 + 17.32 = 17.32 volts Calculus Archive | April 30, 2022 | Chegg.com Calculus Archive: Questions from April 30, 2022. An equation of the plane passing through the three points (3,−1,2), (8, 2, 4) and (−1, −2, −3) has the form ax + by + cz = 42. Find the value of a + b + c. 1 answer. Help me. Find the solution for the system of ODE: t dx/dt 2x + 3y = 8e 8e² dy/dt 4x + y = 4et Assume that y (0) = = 1, x ...
Differential Equations - Direction Fields Plugging this into (1) (1) gives the following differential equation. dv dt = 9.8−0.196v (2) (2) d v d t = 9.8 − 0.196 v Let's take a geometric view of this differential equation. Let's suppose that for some time, t t, the velocity just happens to be v =30 v = 30 m/s. Note that we're not saying that the velocity ever will be 30 m/s.

Which diagram shows the equation v=2t+4?
Laplace Transforms - 1a. The Unit Step Function (Heaviside ... The value of t = 0 is usually taken as a convenient time to switch on or off the given voltage.. The switching process can be described mathematically by the function called the Unit Step Function (otherwise known as the Heaviside function after Oliver Heaviside).. The Unit Step Function. Definition: The unit step function, `u(t)`, is defined as Area Approximation - Mathematics Form 4 Notes - Easy Elimu Count all the whole squares fully enclosed within the region Count all the partially enclosed squares and take them as half square centimeter each Divide the number of half squares by two and add it to the number of full squares. Number of compete squares = 4 Number of half squares = 16/2 = 8 Therefore the total number of squares = 25 + 8 = 33 special relativity - Two Synchronised Clocks Problem ... Specifically in special relativity the equation is the Minkowksi metric, and the elapsed time, τ, is given by: (1) c 2 τ 2 = c 2 t 2 − ℓ 2. If the (constant) speed of the clock is v then the distance it travels in the time t is just ℓ = v t, and we can use this to substitute for ℓ in equation (1) to get: c 2 τ 2 = c 2 t 2 − v 2 t 2.
Which diagram shows the equation v=2t+4?. Which diagram shows the equation v=2t+4? - ForNoob Part A - Matching a graph to a line equation Which diagram shows the equation v = 2t + 4? 8 of 10 > Review | Constants Part A - Matching a graph to a line equation Which diagram shows the equation v = 2t +42 View Available Hint(s) (m/s) (m/s) Q Search or enter website name . Answer. Thanks Mathematics Notes: Topical Maths Assignments F1-4 With ... The badge has as symmetry of order 4 about O. Complete the figures to show the badge. A point (-5, 4) is mapped onto (-1, -1) by a translation. Find the image of (-4, 5) under the same translation. A triangle is formed by the coordinates A (2, 1) B (4, 1) and C (1, 6). It is rotated; clockwise through 90 0 about the origin. Find the coordinates ... 11.5E: Exercises for Equations of Lines and Planes in ... 15) Show that the line passing through points \( P(3,1,0)\) and \( Q(1,4,−3)\) is perpendicular to the line with equation \( x=3t, \quad y=-32+8t, \quad z=−9+6t, \quad t∈R.\) Answer: \( \vecd{PQ} = \langle -2, 3, -3 \rangle\) is the direction vector of the line through points \(P\) and \(Q\), and the direction vector of the line defined ... Calculus III - Equations of Planes - Lamar University Start with the first form of the vector equation and write down a vector for the difference. This is called the scalar equation of plane. Often this will be written as, where d = ax0 +by0 +cz0 d = a x 0 + b y 0 + c z 0. This second form is often how we are given equations of planes.
10.7: Routh Stability - Engineering LibreTexts The system in question must have a characteristic equation of a polynomial nature. as shown below: (10.7.1) P ( S) = a n S n + a n − 1 S n − 1 + ⋯ + a 1 S + a 0. In order to examine the roots, set P (S)=0, which will allow you to tell how many roots are in the left-hand plane, right hand plane, and on the j-omega axis. 3.3: Reversible and Irreversible ... - Chemistry LibreTexts The work of expansion can be depicted graphically as the area under the p-V curve depicting the expansion. Comparing examples \(\PageIndex{1}\) and \(3.1.2\), for which the initial and final volumes were the same, and the constant external pressure of the irreversible expansion was the same as the final pressure of the reversible expansion, such a graph looks as follows. Advanced Math Archive | April 30, 2022 | Chegg.com Question 2 [30] Consider the Bessel equation with v = 1 ty" + ty + (t²-1)y=0, t> 0. Find a series solution y₁ around the regular singular point t = 0. ... To solve y"+y'-2y = 2t with the initial values y(0)=0 and we first find the Ye= Ce 2 + De'. To get the solution, we assume Since neither equation this assumption will work. ... The diagram ... 16.2: van der Waals and Redlich-Kwong Equations of State ... so that. (16.2.9) P = n R T V − n b − a n 2 V 2. which is known as the van der Waals equation of state. Equation 16.2.9 can also be rewritten as. (16.2.10) ( P + n 2 a V 2) ( V − n b) = n R T. The first term in this equation is easy to motivate. In fact, it looks very much like the equation of state for an ideal gas.
The diagram shows a pattern using four identical rhombuses ... The diagram shows a pattern using four identical rhombuses. Diagram NOT. accurately drawn. 25. 25. 25. Work out the size of the angle marked a. You must show your working, AditiKaz is waiting for your help. MATHEMATICA tutorial, Part 2.7: Mathieu Functions The Mathieu equation is an ordinary differential equation with real coefficients. Its standard form with parameters ( a, q) is. (1) w ″ + ( a − 2 q cos. . ( 2 t)) = 0. It was introduced by the French mathematician Émile Léonard Mathieu (1835--1890) in 1868 in context of the vibrations of an elliptic membrane. Magnetic Force on a Current carrying Wire - GeeksforGeeks Question 4: What is the angle between a wire carrying a 4.00-A current and the 2-T field it is in if 50.0 cm of the wire experiences a magnetic force of 8.0 N? Answer: The force on the current carrying conductor is given by, F = ilBsin(θ) Where, i = 4A, B = 2T and l = 2 m, θ = ? And F = 8.0N . Plugging these values into the equation, F ... 1.3: Calculus of Vector-Valued Functions - Mathematics ... The first component of ⇀ r(t) = (6t + 8)ˆi + (4t2 + 2t − 3)ˆj is f(t) = 6t + 8. The second component is g(t) = 4t2 + 2t − 3. We have f′ (t) = 6 and g′ (t) = 8t + 2, so the Theorem 1.3.1 gives ⇀ r′ (t) = 6ˆi + (8t + 2)ˆj. The first component is f(t) = 3cost and the second component is g(t) = 4sint.
4.3: Acceleration Vector - Physics LibreTexts We take the first derivative with respect to time of the velocity function to find the acceleration. The derivative is taken component by component: a → ( t) = 5.0 i ^ + 2.0 t j ^ − 6.0 t 2 k ^ m / s 2. Evaluating a → ( 2.0 s) = 5.0 i ^ + 4.0 j ^ − 24.0 k ^ m / s 2 gives us the direction in unit vector notation. The magnitude of the acceleration is
Find equation of tangent to curve at given point. x=cos(t ... Values for x and y in our tangent line depend on what t is at x (t) and y (t). To evaluate the derivative and find the slope, we need to find a t where x (t) = cos (t) + cos (2t) = -1 (because our x-coordinate is -1). That occurs at t = pi/2. Verify this by evaluating x (t) = x (pi/2) = -1.
5.6: The Lorentz Transformation - Physics LibreTexts We combine this with Equation 5.6.11 that relates x and x′ to obtain the relation between t and t ′: t ′ = t − vx / c2 √1 − v2 / c2. The equations relating the time and position of the events as seen in S are then t = t ′ + vx ′ / c2 √1 − v2 / c2. x = x ′ + vt ′ √1 − v2 / c2. y = y ′ z = z ′.
special relativity - Two Synchronised Clocks Problem ... Specifically in special relativity the equation is the Minkowksi metric, and the elapsed time, τ, is given by: (1) c 2 τ 2 = c 2 t 2 − ℓ 2. If the (constant) speed of the clock is v then the distance it travels in the time t is just ℓ = v t, and we can use this to substitute for ℓ in equation (1) to get: c 2 τ 2 = c 2 t 2 − v 2 t 2.
Area Approximation - Mathematics Form 4 Notes - Easy Elimu Count all the whole squares fully enclosed within the region Count all the partially enclosed squares and take them as half square centimeter each Divide the number of half squares by two and add it to the number of full squares. Number of compete squares = 4 Number of half squares = 16/2 = 8 Therefore the total number of squares = 25 + 8 = 33
Laplace Transforms - 1a. The Unit Step Function (Heaviside ... The value of t = 0 is usually taken as a convenient time to switch on or off the given voltage.. The switching process can be described mathematically by the function called the Unit Step Function (otherwise known as the Heaviside function after Oliver Heaviside).. The Unit Step Function. Definition: The unit step function, `u(t)`, is defined as



0 Response to "40 which diagram shows the equation v=2t+4?"
Post a Comment