38 in the diagram, the range of diminishing marginal returns is
The Law of Diminishing Marginal Returns - Economics Help As extra workers produce less, the MC increases. Diagram of diminishing returns In this example, after three workers, diminishing returns sets in. After employing 4 workers or more - the marginal product (MP) of the worker declines and the marginal cost (MC) starts to rise. Difference between diminishing returns and dis-economies of scale The Law of Diminishing Return Definition, Graph | Study ... The law of diminishing return indicates that if the number of variable inputs is increased with some fixed inputs, the total output will first increase but then start to decline. It is the third stage of the law of variable proportions. The law is applicable both in agricultural and industrial sectors.
Law of Diminishing Returns (Explained With Diagram) The law of diminishing returns is described by different economists in different ways, which are as follows: ADVERTISEMENTS: According to G. Stigler, "As equal increments of one input are added; the inputs of other productive services being held, constant, beyond a certain point the resulting increments of product will decrease, i.e., the marginal product will diminish."
In the diagram, the range of diminishing marginal returns is
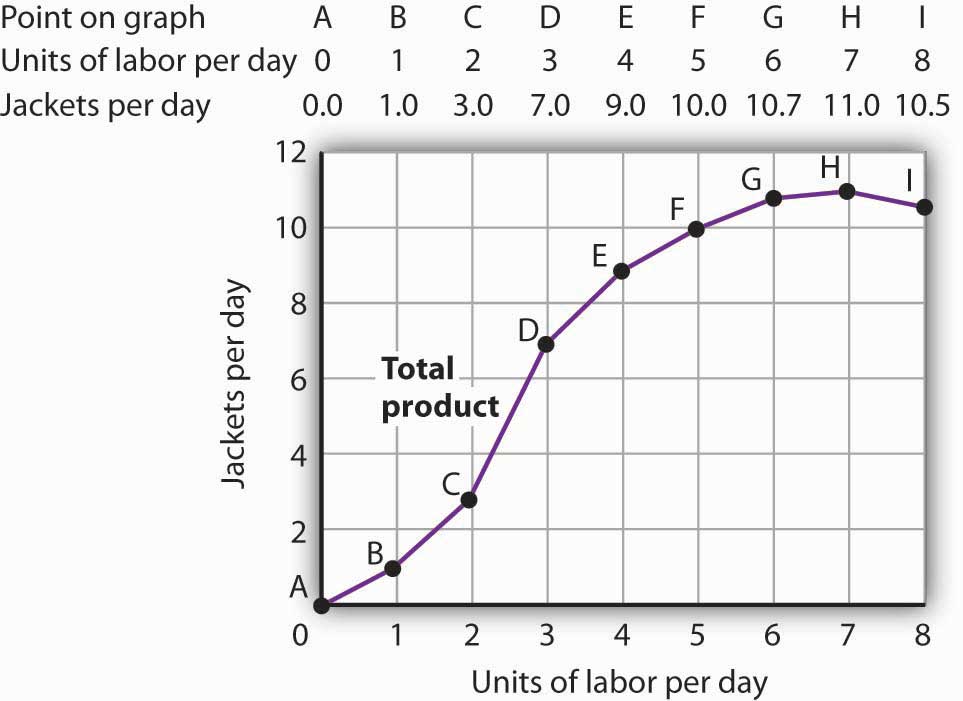
in the diagram below, the range of diminishing returns is: in the diagram below, the range of diminishing returns is: Image transcription text Marginal Product Marginal and Average Product Average Product Inputs of Labor A. O - Q3 B. O - Q2 C. Q1. study.com › learn › production-function-questionsProduction Function Questions and Answers | Study.com The table represents a logarithm function f(x). Use the description and table to graph the function, and determine the domain and range of f(x). Represent the domain and range with inequality notat... › the-economy › bookUnit 3 Scarcity, work, and choice – The Economy - CORE Also known as: diminishing marginal returns in production. Alexei’s production function in Figure 3.5 gets flatter the more hours he studies, so the marginal product of an additional hour falls as we move along the curve. The marginal product is diminishing. The model captures the idea that an extra hour of study helps a lot if you are not ...
In the diagram, the range of diminishing marginal returns is. tutor2u | Law of Diminishing Returns, Marginal Cost and ... In this short revision video we go through the law of diminishing returns and explain the link between declining marginal productivity and rising short run marginal and average variable cost. Law of Diminishing Returns, Marginal Cost and Average Variable Cost Diminishing returns to labour in the short run Free Essay: Explain and Illustrate with Diagrams the ... Q (1) Explain and illustrate with diagrams the differences between diminishing marginal returns and decreasing economies of scale and cite causes and examples. Ans. The law of diminishing returns is also called the law of variable proportion, as the proportions of each factor of production employed keep changing as more of one factor is added. The Law of Diminishing Returns: Definition, Explanation ... Stage II: Diminishing Returns Throughout the stage of diminishing returns, the total product keeps on increasing. However unlike the stage of increasing returns, here the total product increases at a diminishing rate. This happens because the marginal product falls and becomes less than the average product, which also sees a downwards slope. The law of diminishing returns is a key one in economics Marginal costs are the additional cost of producing one more unit (Daly, Farley, 2004). Marginal costs decrease at low output and through a short range because economic from greater specialisation ( MC Taggart, Findlay, & Parkin, 2007 ).Marginal costs begin to rise because of diminishing returns.
Law of Diminishing Marginal Returns (Definition and 3 ... Diminishing Marginal Returns occur when increasing one unit of production, whilst holding other factors constant - results in lower levels of output. In other words, production starts to become less efficient. For example, a worker may produce 100 units per hour for 40 hours. In the 41st hour, the output of the worker may drop to 90 units per hour. Diminishing Marginal Returns vs. Returns to Scale: What's ... the law of diminishing marginal returns states that with every additional unit in one factor of production, while all other factors are held constant, the incremental output per unit will decrease... Assignment Topic: DIMINISHING MARGINAL RETURNS - My ... The diagram above shows the diminishing marginal returns as the number of workers are increased but the land and other factors are kept constant (Gillespie, 2011). As shown after a certain number of workers is increased the output first increases at a lower rate and after some time it starts declining. en.wikipedia.org › wiki › IsoquantIsoquant - Wikipedia In managerial economics, isoquants are typically drawn along with isocost curves in capital-labor graphs, showing the technological tradeoff between capital and labor in the production function, and the decreasing marginal returns of both inputs. In managerial economics, the unit of isoquant is commonly the net of capital cost.
diminishing marginal returns - Concept of diminishing ... View Notes - diminishing marginal returns from IBS MBSA 1213 at University of Technology Malaysia, Kuala Lumpur. Concept of diminishing marginal returns In economics, diminishing returns › firm › top-3-theoriesTop 3 Theories of Firm (With Diagram) - Economics Discussion He assumes that the marginal utility of each of the component of the utility function is positive but diminishing. The implication is that S>0, M>0 and I d >0. As soon as this assumption is made the constraint loses it relevance. This enables Williamson to treat this optimisation case as a simple case of unconstrained utility maximization. Law of Diminishing Returns & Point of Diminishing Returns ... At such a point, the marginal output is maximized but will decrease if the units of a production factor continue to increase. As the diagram above shows, the point of diminishing return is at L2. Before reaching an L2 number of laborers, putting additional laborers into the production process can efficiently increase the output. econ exam #2 Flashcards - Quizlet In the above diagram the range of diminishing marginal returns is: Q1Q3. In the above diagram, total product will be at a maximum at: Q3 units of labor. Refer to the above diagram. At output level Q total variable cost is: ... The above diagram indicates that the marginal revenue of the sixth unit of output is. not 4.
› economics › productionProduction Function: Law of Variable Proportions and Law of ... The table shows that when output is increased from the 6th, 7th and 8th units, the total returns increase at a lower rate than before so that the marginal returns start diminishing successively to 10, 9 and 8. In the figure, the portion from D to S of the RS curve shows diminishing returns. Causes of Diminishing Returns to Scale:
Law of Diminishing Marginal Returns Definition Diminishing marginal returns are an effect of increasing input in the short-run, while at least one production variable is kept constant, such as labor or capital. Returns to scale, on the other...
34 In The Diagram The Range Of Diminishing Marginal Returns Is In the above diagram the range of diminishing marginal returns is. In the diagram the range of diminishing marginal returns is. Start studying microeconomics exam 2. At output level q total variable cost is. In the diagram the range of diminishing marginal returns is a q 3 b q 2 c q 1 q from business 1111 at university of texas dallas.
cbseacademic.nic.in › web_material › CurriculumMain22ECONOMICS (Code No - CBSE Consumer's equilibrium - meaning of utility, marginal utility, law of diminishing marginal utility, conditions of consumer's equilibrium using marginal utility analysis. Indifference curve analysis of consumer's equilibrium-the consumer's budget (budget set and budget line), preferences of the consumer (indifference curve, indifference
quizlet.com › 463271892 › econ-flash-cardsEcon Flashcards - Quizlet Suppose that a firm is producing the profit-maximizing output under conditions of diminishing returns. Its output price is $25, and its marginal cost of production at its current output level is $25. Based on this information, it can be concluded that this firm must A be a single-price monopoly B be a perfectly competitive firm C
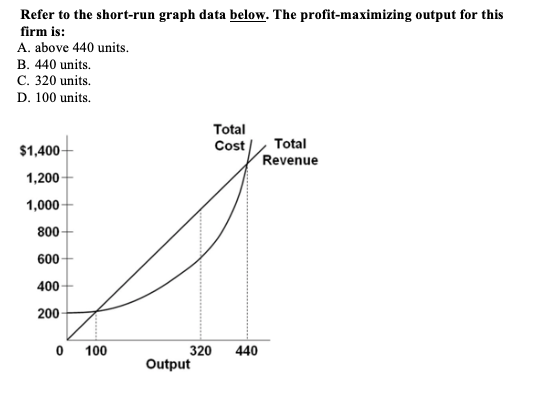
Solved 13. In the diagram below, the range of diminishing ... In the diagram below, the range of diminishing marginal returns is: А. 00з. В. О2. C. Qi2 D. Qi Marginal Product Average Product Q2 Inputs of Labor o Marginal and Average Product Refer to the short-run graph data below. The profit-maximizing output for this firm is A. above 440 units B. 440 units C. 320 units D. 100 units Total Cost Total $1,400
diminishing returns | Definition & Example | Britannica diminishing returns, also called law of diminishing returns or principle of diminishing marginal productivity, economic law stating that if one input in the production of a commodity is increased while all other inputs are held fixed, a point will eventually be reached at which additions of the input yield progressively smaller, or diminishing, increases in output.
Marginal mean plots illustrating associations between overall predicted... | Download Scientific ...
PDF Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge ... Diminishing marginal returns to labour will set in when A the second worker is employed. B the third worker is employed. C the fourth worker is employed. D the fifth worker is employed. 4 In the diagram S 1 is an individual worker's supply of labour curve. O hours of work wage rate S 1 S 2 What could cause the curve to shift from S 1 to S 2?


0 Response to "38 in the diagram, the range of diminishing marginal returns is"
Post a Comment