45 meiosis crossing over diagram
Which meiosis phase does synapsis occur? Explained by FAQ Blog Synapsis and crossing over are two events that occur during the chromosome segregation in meiosis 1. ... Both synapsis and crossing over are important in exerting genetic variation among the individuals by allowing the exchange of genetic material between homologous chromosomes. (Get Answer) - Identify the stages of meiosis on the diagram. Answer ... Identify the stages of meiosis on the diagram. Answer Bank Interphase is the stage in which the chromosomes replicate. Homologous pairs of chromosomes line up in metaphase I. Telophase I and cytokinesis forms two cells. Sister chromatids line up in the center of the cell during metaphase II. In anaphase I, homologous pairs split up Telophase II ...
Meiosis and Mitosis Venn Diagram - Edraw Max The Meiosis and Mitosis Venn diagram is one of the most prominent ones that help to display every information accurately. Cells often use two options for overall growth (sexually and physical): mitosis and meiosis. The proper use of the diagram can play an essential role in representing data accurately for meiosis and mitosis.

Meiosis crossing over diagram
Difference between Mitosis and Meiosis - Laboratoryinfo.com Number of daughter cells. Cell division in mitosis results in the production of two daughter cells. Each cell is diploid, which means that they contain exact chromosomes. In meiosis, the resulting product is four daughter cells and each cell is diploid. Each contains only half of the parent cell's chromosomes. (6, 7) Does crossing over occur in meiosis? Explained by FAQ Blog What is meiosis with diagram? Diagram for Meiosis. Meiosis is a type of cell division in which a single cell undergoes division twice to produce four haploid daughter cells. The cells produced are known as the sex cells or gametes (sperms and egg). The diagram of meiosis is beneficial for class 10 and 12 and is frequently asked in the examinations. Phases of Meiotic cell division (Meiosis ... - Science online The meiotic division takes place in two stages: First meiotic division. Second meiotic division. First meiotic division It produces two cells, each of them contains half the number of chromosomes. Phases of first meiotic division are: Prophase I ⇒ Metaphase I ⇒ Anaphase I ⇒ Telophase I Phases of first meiotic division Prophase I
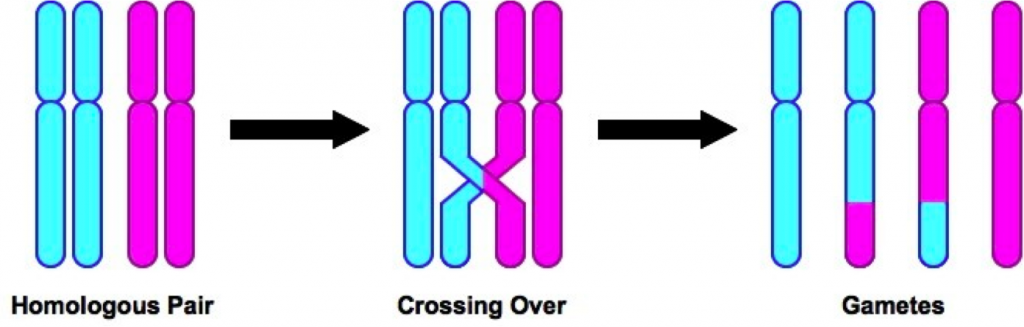
Meiosis crossing over diagram. Crossing Over - Genome.gov Crossing Over. Crossing over is a cellular process that happens during meiosis when chromosomes of the same type are lined up. When two chromosomes — one from the mother and one from the father — line up, parts of the chromosome can be switched. The two chromosomes contain the same genes, but may have different forms of the genes. What is Mitosis: Significance, Diagram, and Stages - Embibe What is Mitosis: Learn about its definition, diagram, stages, and significance. Students will also learn the difference between Meiosis and Mitosis here. ... Meiosis- It is a type of nuclear division that gives rise to four haploid daughter cells commonly referred to as gametes. ... Crossing over occurs during Prophase I. 6. Chromosome's ... (Solved) - Prophase I is the first phase of meiosis and includes ... Prophase 1 (Meiosis) The ... › meiosisMeiosis Interactive - CELLS alive Prophase I: Dyad pairs align to create "TETRADS", non-sister chromatids connect and trade sections at a "CHIASMA", a process called "CROSSING OVER". Metaphase I: SPINDLE FIBERS attach to each dyad at the KINETOCHORE. Tension from spindle fibers aligns the tetrads at the cell equator.
Prophase in mitosis and meiosis (Prophase 1 and 2) - The Biology Notes Figure: Prophase 1 stages of Meiosis. Image Source: Toppr. Pachytene- This is the phase where the cross over of genetic materials takes place between non-sister chromatids i.e pairs of homologous chromosomes. This forms chiasmata. Crossing over is achieved by synapsis by the attachment created by the chromatid in a homologous chromosome. › mitosis-vs-meiosisMitosis vs Meiosis: 14 Main Differences Along With Similarities Nov 03, 2020 · Prophase is shorter than prophase I in meiosis. Prophase I is longer than the prophase of mitosis. 9. Formation of Synapsis and Crossing Over: Both are absent. Both take place during prophase I. 10. Formation of Tetrad: Absent: Occurs during prophase I. 11. Number of Chromatids and Centromere: Each chromosome contains two chromatids and a ... Instructions: Refer to the Venn diagram on mitosis and meiosis. Choose ... Instructions: Refer to the Venn diagram on mitosis and meiosis. Choose if the description describes mitosis or meiosis. A. One division B. Two divisions C. No crossing over D. Crossing over occurs E. Haploid daughter cells F. Produces 2 daughter cells G. Produces 4 daughter cells H. Occurs in all body cells I. Occurs in sex cells J. Diploid ... thebiologynotes.com › meiosisMeiosis- definition, purpose, stages, applications with diagram The meiosis maintains a constant number of chromosomes in sexually reproducing organisms through the formation of gametes. By crossing over, the meiosis results in the exchange of the genes and, thus, causes the genetic variations among the species. These variations are the raw materials of the evolutionary process.
Department of Animal Science - Basic Animal Genetics - Cornell University A lethal allele's phenotype, when expressed, causes the death of an organism.Lethal alleles arise when a mutation to a normal allele disrupts the function of an essential gene. Without this essential gene, the organism dies. Lethal alleles can be embryonic or postnatal. Embryonic lethals cause the death of the fetus, and fertility studies are often required in order to positively determine ... Meiosis - Genome.gov Meiosis is a type of cell division in sexually reproducing organisms that reduces the number of chromosomes in gametes (the sex cells, or egg and sperm). In humans, body (or somatic) cells are diploid, containing two sets of chromosomes (one from each parent). Why meiosis is called reduction division? - TimesMojo In meiosis II, these chromosomes are further separated into sister chromatids. Meiosis I includes crossing over or recombination of genetic material between chromosome pairs, while meiosis II ... What is meiosis with diagram? Meiosis is a process where a single cell divides twice to produce four cells containing half the original amount of ... › science › meiosis-cytologymeiosis | Definition, Process, & Diagram | Britannica Jul 06, 2022 · meiosis, also called reduction division, division of a germ cell involving two fissions of the nucleus and giving rise to four gametes, or sex cells, each possessing half the number of chromosomes of the original cell. A brief treatment of meiosis follows. For further discussion, see cell: Cell division and growth. The process of meiosis is characteristic of organisms that reproduce sexually ...
AP Bio Unit 5 Study Guide: Meiosis Notes | Fiveable Meiosis is the process that all organisms go through in order to produce gametes, or sex cells. The process differs from mitosis, the process of somatic cell division, in a number of key ways. Meiosis involves one round of DNA replication and two rounds of cellular division. The resulting cells are all genetically unique from one another and ...
Teaching meiosis with the DNA triangle framework: A classroom ... - IUBMB The crossing over activity is based on the Chromosome Kit® from 3D molecular designs. It contains foam pieces that interlock and can be used to build chromosomes. (a) Red and blue pieces can be used to represent maternal and paternal chromosomes.
AP Bio Unit 5 Study Guide: Meiosis & Genetic Diversity | Fiveable See Units. There are a few key concepts within meiosis that contribute to genetic diversity. Remember that diversity is the key to life. When all else fails, focus on diversity in your answers for the AP exam. Some key contributors to genetic diversity in meiosis are the concepts of crossing over, independent assortment, and random fertilization.
What is Crossing Over in Meiosis? | Crossing Over Example ... This image shows the process of meiosis from start to finish. Chromosomes are duplicated at the step labeled 1. Crossing over occurs at step 3, which is prophase. The result is four gametes with...
Meiosis Process | Crossing Over & Mitosis - Study.com Meiosis occurs in two steps: meiosis I and meiosis II, while mitosis occurs in only one round. Both types of division occur following the same basic steps (prophase, prometaphase, metaphase,...
What is Meiosis? Phases, Cell Division, Comparison - Embibe The two stages of meiosis are- Meiosis I- Homologous pairs of chromosomes separate during meiosis I. 2. Meiosis II- Sister chromatids are formed due to replication in 'S' phase are separated during Meiosis-II. Meiosis Diagram Figure showing stages of meiosis. Meiosis I
en.wikipedia.org › wiki › Homologous_chromosomeHomologous chromosome - Wikipedia The process of meiosis I is generally longer than meiosis II because it takes more time for the chromatin to replicate and for the homologous chromosomes to be properly oriented and segregated by the processes of pairing and synapsis in meiosis I. During meiosis, genetic recombination (by random segregation) and crossing over produces daughter ...
In meiosis what is crossing over? Explained by FAQ Blog What is crossing over explain with diagram? Crossing over is the exchange of genetic material between non-sister chromatids of homologous chromosomes during meiosis, which results in new allelic combinations in the daughter cells. Does crossing over occur in both mitosis and meiosis?
Rec8 Cohesin: A Structural Platform for Shaping the Meiotic Chromosomes Cohesin complex in mitosis and meiosis. (A). A schematic diagram of cohesin complexes in Schizosaccharomyces pombe. ... Frequent crossing over at the centromere causes loss of centromeric cohesion leading to meiosis II failure and aneuploid gametogenesis [84,85]. Therefore, suppression of crossing over at centromeric regions is essential for ...
Homologous chromosomes may exchange segments; this is called crossing ... A) Crossing over occurs in : Meiosis I ( D ) B) DNA replication would occur : Prior to meiosis I and meiosis II ( B ) C) The embryo's development represents ; meiosis and cell differentiation ( D ) . D) Some organisms reproduce aseggsually; To rapidly produce like offspring. What is Crossing over and DNA replication. Crossing over involves the swapping of genetic materials, and it occurs in ...
Why is crossing over so important? - Foley for Senate The Punnett square is a square diagram that is used to predict an outcome of a particular cross or breeding experiment. It is named after Reginald C. Punnett, who devised the approach. The diagram is used by biologists to determine the probability of an offspring having a particular genotype. What is crossing over and when does it occur?
Mitosis and Meiosis: What's the Difference? - Visible Body Meiosis consists of two rounds of division: meiosis I and meiosis II. Each round has a prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. Meiosis vs. mitosis. Image from A&P 6. Prophase I is, in my opinion, the coolest phase of meiosis. The 46 chromosomes in your body's diploid cells are organized into 23 homologous pairs.
en.wikipedia.org › wiki › MeiosisMeiosis - Wikipedia Sites of crossing over entangle together, effectively overlapping, making chiasmata clearly visible. Other than this observation, the rest of the stage closely resembles prometaphase of mitosis; the nucleoli disappear, the nuclear membrane disintegrates into vesicles, and the meiotic spindle begins to form. Meiotic spindle formation
Make Like a Cell and Split: Comparing Mitosis and Meiosis The second division creates four cells that each contain one set of chromosomes, because the genetic information isn't copied a second time. One unique feature of meiosis, which takes place during the first round of prophase (prophase I), is a process called crossing over. DNA is mixed between matching chromosomes from the different parents ...
biologydictionary.net › meiosisMeiosis - Definition, Stages, Function and Purpose | Biology ... Dec 08, 2016 · Before meiosis takes place, each chromosome is replicated, leaving 8 chromosomes and 16 sister chromatids. Meiosis I takes place, and there are 2 cells, each with only 4 chromosomes. Each chromosome is still made of sister chromatids, and some crossing-over may have occurred during metaphase I. Meiosis II now takes place on those two cells.
Phases of Meiotic cell division (Meiosis ... - Science online The meiotic division takes place in two stages: First meiotic division. Second meiotic division. First meiotic division It produces two cells, each of them contains half the number of chromosomes. Phases of first meiotic division are: Prophase I ⇒ Metaphase I ⇒ Anaphase I ⇒ Telophase I Phases of first meiotic division Prophase I
Does crossing over occur in meiosis? Explained by FAQ Blog What is meiosis with diagram? Diagram for Meiosis. Meiosis is a type of cell division in which a single cell undergoes division twice to produce four haploid daughter cells. The cells produced are known as the sex cells or gametes (sperms and egg). The diagram of meiosis is beneficial for class 10 and 12 and is frequently asked in the examinations.







0 Response to "45 meiosis crossing over diagram"
Post a Comment