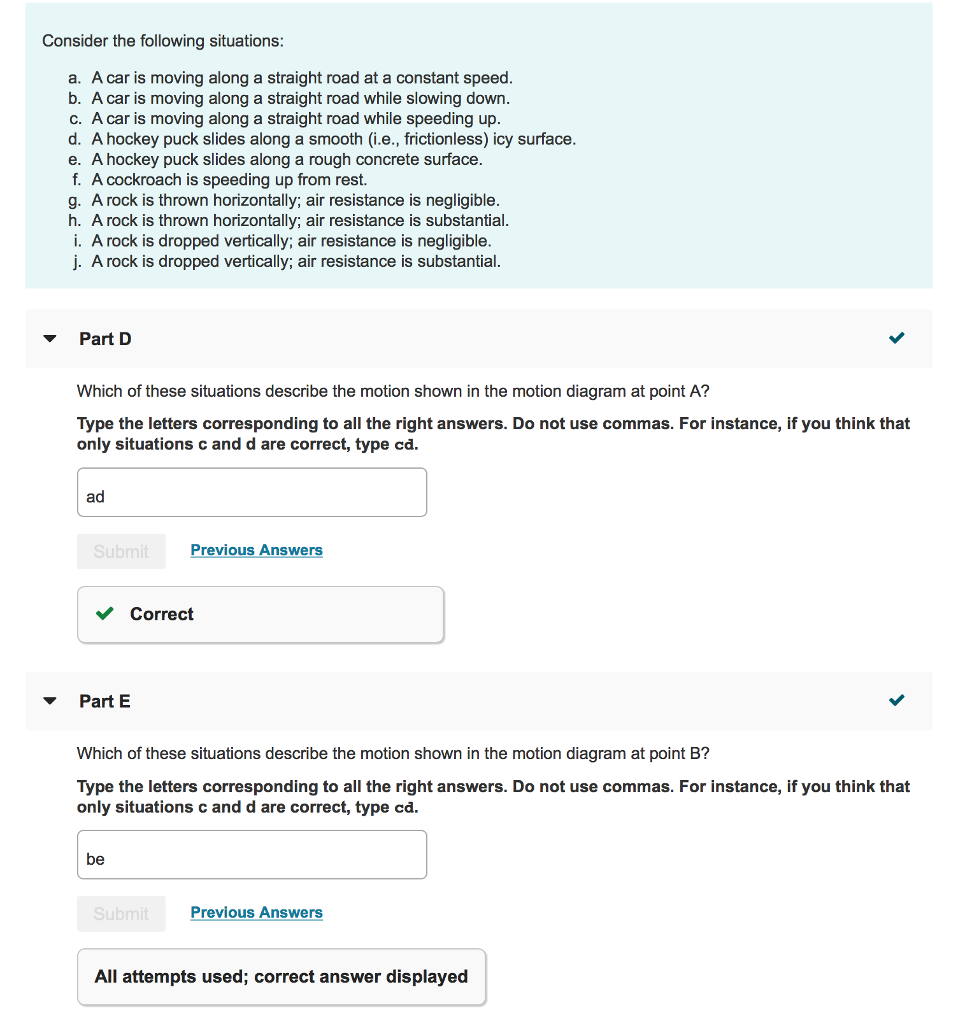
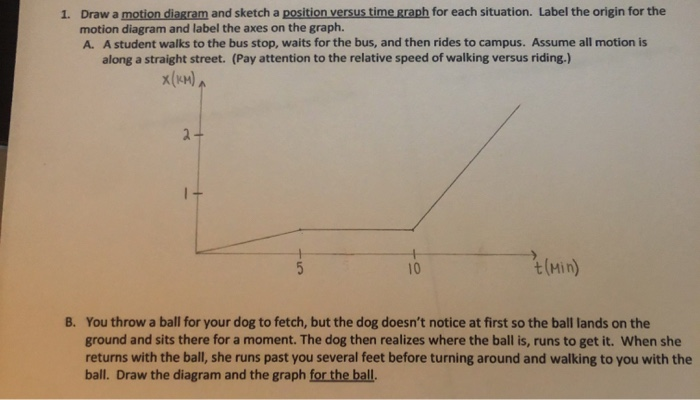
39 which of these situations describe the motion shown in the motion diagram at point a?
Solved Which of these situations describe the motion shown - Chegg Which of these situations describe the motion shown in the motion diagram at point B? Type the letters corresponding to all the right answers. Do not use commas. For instance, if you think that only situations c and d are correct, type cd. Question: Which of these situations describe the motion shown in the motion diagram at point B? Type the ... Mastering Physics 4 - Subjecto.com Which of these diagrams may possibly correspond to the situation at point C on the motion diagram? 1,2,3,4,5. Which of these diagrams correspond to a situation where the moving object (not necessarily the one shown in the motion diagram) is changing its velocity? A car is moving along a straight road at a constant speed. A hockey puck slides ...
Plate Tectonics Map - Plate Boundary Map - Geology According the theory of plate tectonics, Earth's outer shell is made up of a series of plates.The map above shows names and generalized locations of Earth's major tectonic plates. These plates move and interact with one another to produce earthquakes, volcanoes, mountain ranges, ocean trenches and other geologic processes and features.Map prepared by the United States …

Which of these situations describe the motion shown in the motion diagram at point a?
Unit 1 Module 1 "Forces & Motion" Diagram | Quizlet A force that opposes motion. Newton (N) the unit of measurement for force, named after Sir Isaac Newton. Speed. The distance an object travels per unit of time, speed= distance/time. Newton's First Law. An object at rest stays at rest and an object in motion stays in motion with the same speed and in the same direction unless acted upon by an ... Part E Which of these diagrams may possibly correspond to the situation ... A rock is dropped vertically ; air resistance is substantial . J. Part H Which of these situations describe the motion shown in the motion diagram at point A? Type the letters corresponding to all the right answers in alphabetical order. Do not use commas. For instance, if you think that only situations C and D are correct, type CD. ANSWER: AD Section 1 Flashcards | Quizlet Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like If an object is in motion and changes its position several times during a time interval, then the object's distance is _______ to the path length travelled., A driver ignores the stop sign and continues driving west at constant speed., A driver ignores the stop sign and continues driving east at constant speed. and more.
Which of these situations describe the motion shown in the motion diagram at point a?. ANSWER Correct Part I Which of these situations describe the motion ... 1. According to Newton's 3rd law, every real force has a unique pair force. 2. The pair force is called a "fictitious force." 3. The force and pair force must act on different point masses. 4. The force and the pair force must always have the same magnitude and must also act in exactly opposite directions. Solved | Chegg.com A rock is dropped vertically; air resistance is substantial. Which of these situations describe the motion shown in the motion diagram at point B. Which of ... Cambridge IGCSE Physics Coursebook (second edition) - Issuu 9.6.2014 · The high-wire artiste shown in Figure 4.8 has to adjust her position so that her centre of mass remains above her ‘base’ – the point where her feet make contact with the wire. GSU PHYS 2211 Mastering Physics-ch 4 - 00732884 - Homework Minutes For instance, if you think that only situations C and D are correct, type CD. Part I Which of these situations describe the motion shown in the motion diagram at point B?Type the letters corresponding to all the right answersin alphabetical order. Do not use commas. For instance, if you think that only situations C and D are correct, type CD.
Superior colliculus - Wikipedia In neuroanatomy, the superior colliculus (from Latin 'upper hill') is a structure lying on the roof of the mammalian midbrain. In non-mammalian vertebrates, the homologous structure is known as the optic tectum, or optic lobe. The adjective form tectal is commonly used for both structures.. In mammals, the superior colliculus forms a major component of the midbrain. 6.2 Uniform Circular Motion - Physics | OpenStax Figure 6.7 shows an object moving in a circular path at constant speed. The direction of the instantaneous tangential velocity is shown at two points along the path. Acceleration is in the direction of the change in velocity; in this case it points roughly toward the center of rotation. Solved Which of these situations describe the motion shown - Chegg Transcribed image text: Figure 2 of 2 Part J 2 3 16 Which of these situations describe the motion shown in the motion diagram at point ? Type the letters corresponding to all the right answers in alphabetical order. Do not use commas. For instance, if you think that only situations C and D are correct, type CD. 24 14 16 11 #9 18 5 10 16 Submit Request Answer 关 Z 12 10 Provide Feedback Next > Physics Chapter Four Flashcards | Quizlet Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like An object starts at rest at the origin at t = 0 s. It travels 100 m in the +x-direction in 10 s at constant acceleration. What was the magnitude of its acceleration? 2 m/s2 1 m/s2 10 m/s2, The acceleration of an object moving along a straight line is constant. Select all of the possible shapes for the graph of its velocity versus ...
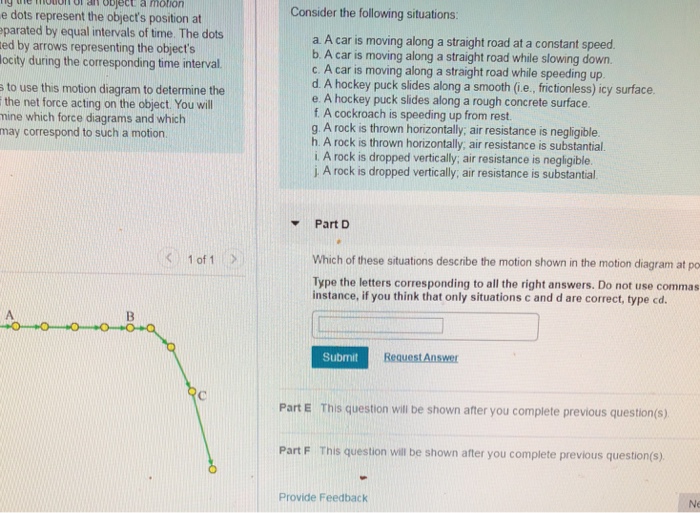
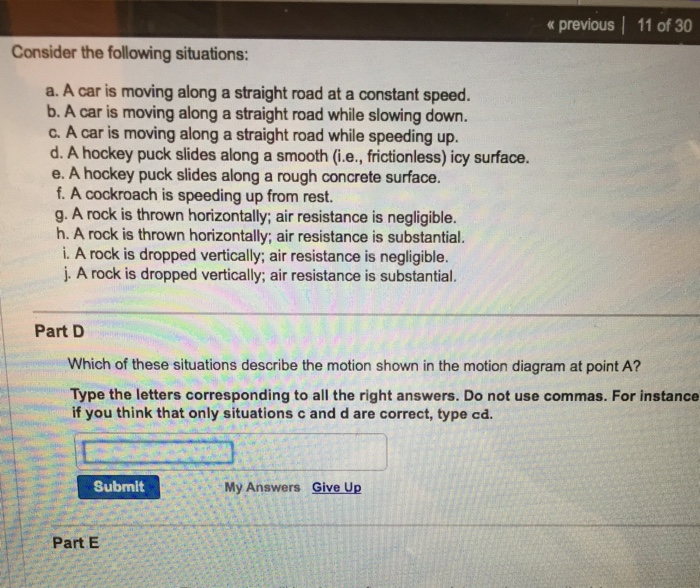
Force - Wikipedia In physics, a force is an influence that can change the motion of an object.A force can cause an object with mass to change its velocity (e.g. moving from a state of rest), i.e., to accelerate.Force can also be described intuitively as a push or a pull. A force has both magnitude and direction, making it a vector quantity. It is measured in the SI unit of newton (N). Important Questions for Class 12 Physics Chapter 3 Current 6.12.2019 · State Kirchhoff’s rules. Use these rules to write the expressions for the current I 1 I 2 and I 3 in the circuit diagram shown. (All India 2010) Answer: (i) Kirchhoff’s junction rule : At any junction, the sum of the currents entering the junction … OneClass: Consider the following situations: a. A car is moving along Consider the following situations: a. A car is moving along a straight road at a constant speed. b. A car is moving along a straight road while slowing down. c. A car is moving along a straight road while speeding up. d. A hockey puck slides along a smooth (i.e., frictionless) icy surface. e. A hockey puck slides along a rough concrete surface. f. Solved Part H Which of these situations describe the motion Transcribed image text: Part H Which of these situations describe the motion shown in the motion diagram at point A? Type the letters corresponding to all ...
5.7 Drawing Free-Body Diagrams – General Physics Using Calculus I Figure 5.32 (a) The free-body diagram for isolated object A. (b) The free-body diagram for isolated object B. Comparing the two drawings, we see that friction acts in the opposite direction in the two figures. Because object A experiences a force that tends to pull it to the right, friction must act to the left. Because object B experiences a component of its weight that pulls it to the left ...
PDF Motion Diagrams - Physics & Astronomy Motion Diagram - 2b (a) Construct a motion diagram for a ball being thrown straight up while in the person's hand. Assume that the ball starts from rest. (b) Construct a motion diagram for the ball in (a) after it has left the person's hand and before it reaches maximum height. (c) Construct a motion diagram for a ball after it has reached
Motion Diagrams or Dot Diagrams - Physics Classroom Kinematics is the science of describing the motion of objects. One means of describing a motion is through the use of a diagram. A dot diagram (sometimes called ticker tape diagrams or oil drop diagrams) represents the position of an object at constant intervals of time (like every second) with a dot. The pattern of dots reveals information about the nature of the motion.
Consider the following situations: A car is moving along a straight ... A motion diagram is used to represent the motion of an object. Each point represents the location of the object after equal intervals of time, and the velocity of the object is represented using arrows. The motion diagram for this problem has been attached here. The question is asking us to analyze the motion at point A.
GSU PHYS 2211 Mastering Physics-ch 4 - Gudwriter.com Part H Which of these situations describe the motion shown in the motion diagram at point A?Type the letters corresponding to all the right answers in alphabetical order. Do not use commas. For instance, if you think that only situations C and D are correct, type CD.
which of these situations describe the motion shown in the motion ... which of these situations describe the motion shown in the motion diagram at point a? ... We accept that everybody has the option to get to the web and use it unreservedly and completely — and these standards support all our work. Recent Posts. Karen radio host fired: Trump-supporting radio talk show host is fired after racist 'Karen ...
Motion Graph | Other Quiz - Quizizz The two students then walk another 1.5 km to school in 30 minutes. A student walks 1.5 km to a friend's house in 20 minutes. The two students then walk another 1.5 km to school in 60 minutes. Question 6. 60 seconds. Q. A meteor moving 468 km per minute traveling in a south-to-north direction passed near Earth in 2013.
Mastering Physics 4 Flashcards | Quizlet However, this time, the string is disconnected and the block is given a quick push to the right. The block slides to the right and eventually stops. The following questions refer to the motion of the block after it is pushed but before it stops. What is the force acting on the block that is directed to the left called? tension normal force weight
Question: Consider the following situations: Part E - Chegg Question: Consider the following situations: Part E: which of these situations describe the motion shown in the motion diagram at point B? · This question hasn't ...
2.2 Speed and Velocity - Physics | OpenStax (4) Science concepts. The student knows and applies the laws governing motion in a variety of situations. The student is expected to: (B) describe and analyze motion in one dimension using equations with the concepts of distance, displacement, speed, average velocity, instantaneous velocity, and acceleration.
Solved Which of these situations describe the motion shown | Chegg.com A rock is dropped vertically; air resistance is negligible. J. A rock is dropped vertically; air resistance is substantial. Part 1 Part 1 Part J Which of these situations describe the motion shown in the motion diagram at point C? Type the letters corresponding to all the right answers in alphabetical order.
which of these situations describe the motion shown in the ... 10 Jan 2022 · 1 answerBest Answer for which of these situations describe the motion shown in the motion diagram at point c? A rock is thrown horizontally; ...
[ROS Projects] – Exploring ROS using a 2 Wheeled Robot 30.1.2018 · We start building the robot from the scratch, using URDF (Unified Robot Description Format) and RViz to visualize it. Further, we describe the inertia and show how to simplify the URDF using XACROS. Later, motion planning algorithms, such as Obstacle Avoidance and Bugs 0, 1 and 2 are developed to be used in the built robot.
Answered: Figure 1 of 2 Consider the following… | bartleby Figure 1 of 2 Consider the following situations: A. A car is moving along a straight road at a constant speed B.A car is moving along a straight road while slowing down. C. A car is moving along a straight road while speeding up. D. A hockey puck slides along a horizontal icy (frictionless) surface. E.
ANSWER Correct Part I Which of these situations describe the motion ... ANSWER: CorrectGAD BE. AD. Objective:By the end of this tutorial, the student should be able to understand how to solve problems in a motion diagram Given: Unknown:Which of the situations describe the motion shown in the motion diagram at point B Solution:Using the motion diagram above, point A has a constant speed and the direction is horizontal.
Mastering Physics 4 Flashcards | Quizlet Which of these situations describe the motion shown in the motion diagram at point A? A car is moving along a straight road while slowing down. A hockey puck slides along a rough concrete surface. ... Which of these situations describe the motion shown in the motion diagram at point C?
Solved Which of these situations describe the motion shown - Chegg Consider the following situations: a A car is moving along a straight road at a constant speed. b. A car is moving along a straight road while slowing down c. A car is moving along a straight road while speeding up d. A hockey puck slides along a smooth (i.e., frictionless) icy surface e. A hockey puck slides along a rough concrete surface f.
Part J Which of these situations describe the motion shown in the ... The acceleration of an object tells you nothing about its velocity--the direction and speed at which it is moving. In this case, the net force on (and therefore the acceleration of) the block is to the right, but the block could be moving left, right, or in any other direction. ANSWER : It must be moving to the left .
Solved Consider the following situations:A car is moving A rock is dropped vertically; air resistance is substantial. Part H. Which of these situations describe the motion shown in the motion diagram at point A? Type ...
Consider the following situations: - Brainly.com Consider the following situations: A) A car is moving along a straight road at a constant speed. B) A car is moving along a straight road while slowing down. C) A car is moving along a straight road while speeding up. D) A hockey puck slides along a smooth (i.e., frictionless) icy surface. E) A hockey puck slides along a rough concrete surface.
Laws of Motion Class 11 Important Extra Questions Physics … Mar 20, 2021 · To determine T 2: Consider the free body diagram (1). Here F and T2 act towards the right and left respectively. As the motion is towards the right side, so according to Newton’s Second law of motion: To determine T 3: Consider the free body diagram (2) Question 11. A monkey is descending from the branch of a tree with constant acceleration.
Part J Which of these situations describe the motion shown in the ... To find the net force, you must first identify all of the forces acting on the object and then add them as vectors. Such a procedure is not always trivial. It is helpful to replace the sketch of the situation by a drawing of the object (represented as a particle) and all the forces applied to it. Such a drawing is called a free-body diagram.
Which of these situations describe the motion shown in the motion ... 3 subscribers Part D Which of these situations describe the motion shown in the motion diagram at point A? Type the letters corresponding to all the right answers. Do not use commas. For instance,...
Section 1 Flashcards | Quizlet Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like If an object is in motion and changes its position several times during a time interval, then the object's distance is _______ to the path length travelled., A driver ignores the stop sign and continues driving west at constant speed., A driver ignores the stop sign and continues driving east at constant speed. and more.
Part E Which of these diagrams may possibly correspond to the situation ... A rock is dropped vertically ; air resistance is substantial . J. Part H Which of these situations describe the motion shown in the motion diagram at point A? Type the letters corresponding to all the right answers in alphabetical order. Do not use commas. For instance, if you think that only situations C and D are correct, type CD. ANSWER: AD
Unit 1 Module 1 "Forces & Motion" Diagram | Quizlet A force that opposes motion. Newton (N) the unit of measurement for force, named after Sir Isaac Newton. Speed. The distance an object travels per unit of time, speed= distance/time. Newton's First Law. An object at rest stays at rest and an object in motion stays in motion with the same speed and in the same direction unless acted upon by an ...


























0 Response to "39 which of these situations describe the motion shown in the motion diagram at point a?"
Post a Comment