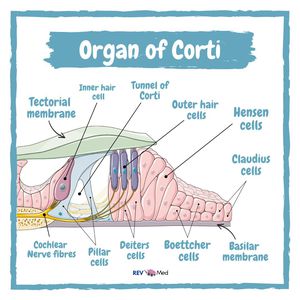
41 organ of corti diagram
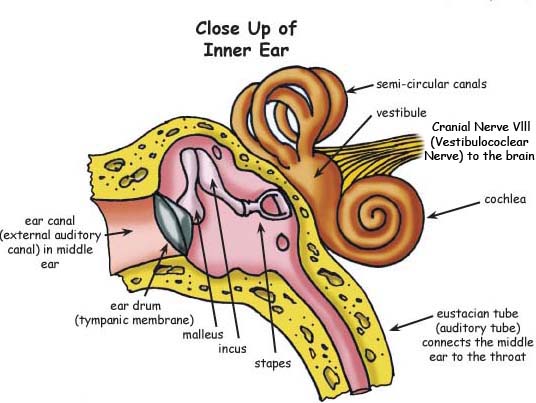
human ear | Structure, Function, & Parts | Britannica Sep 01, 2022 · human ear, organ of hearing and equilibrium that detects and analyzes sound by transduction (or the conversion of sound waves into electrochemical impulses) and maintains the sense of balance (equilibrium). The human ear, like that of other mammals, contains sense organs that serve two quite different functions: that of hearing and that of postural equilibrium and coordination of head and eye ... Internal carotid artery | Radiology Reference Article - Radiopaedia The internal carotid artery (C1 segment) enters the skull base through the carotid canal, where it begins a series of 90° turns which lead it to eventually terminate as the middle and anterior cerebral arteries. It first turns 90° anteromedially within the carotid canal as the C2 segment to run through the petrous temporal bone.
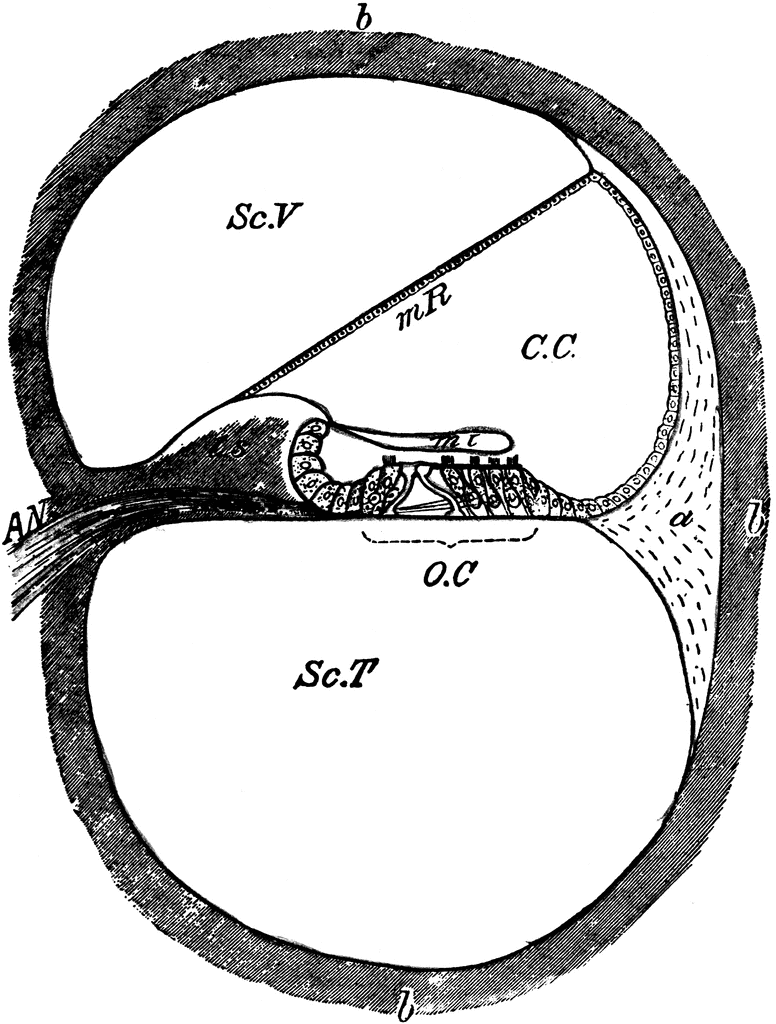
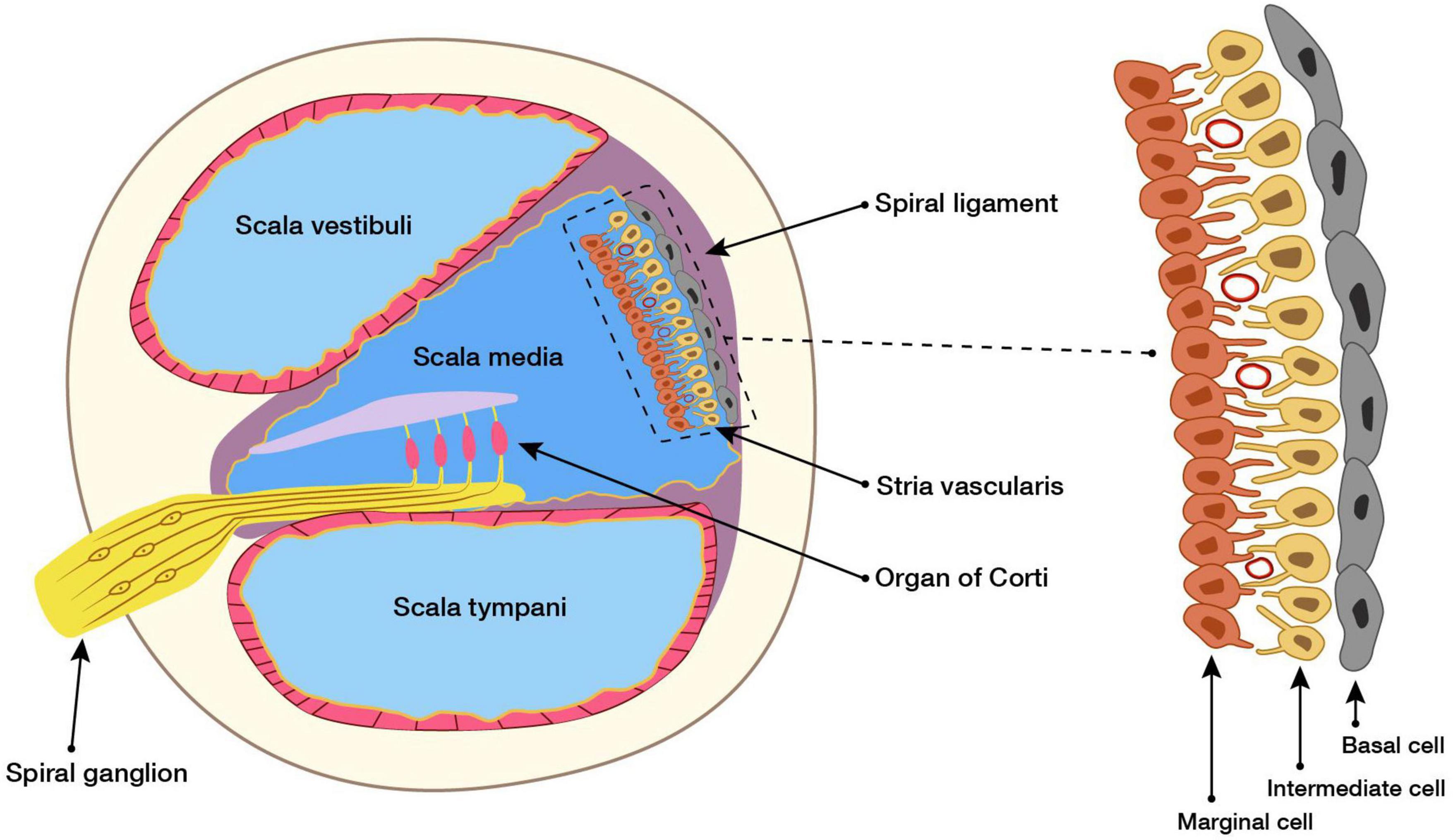
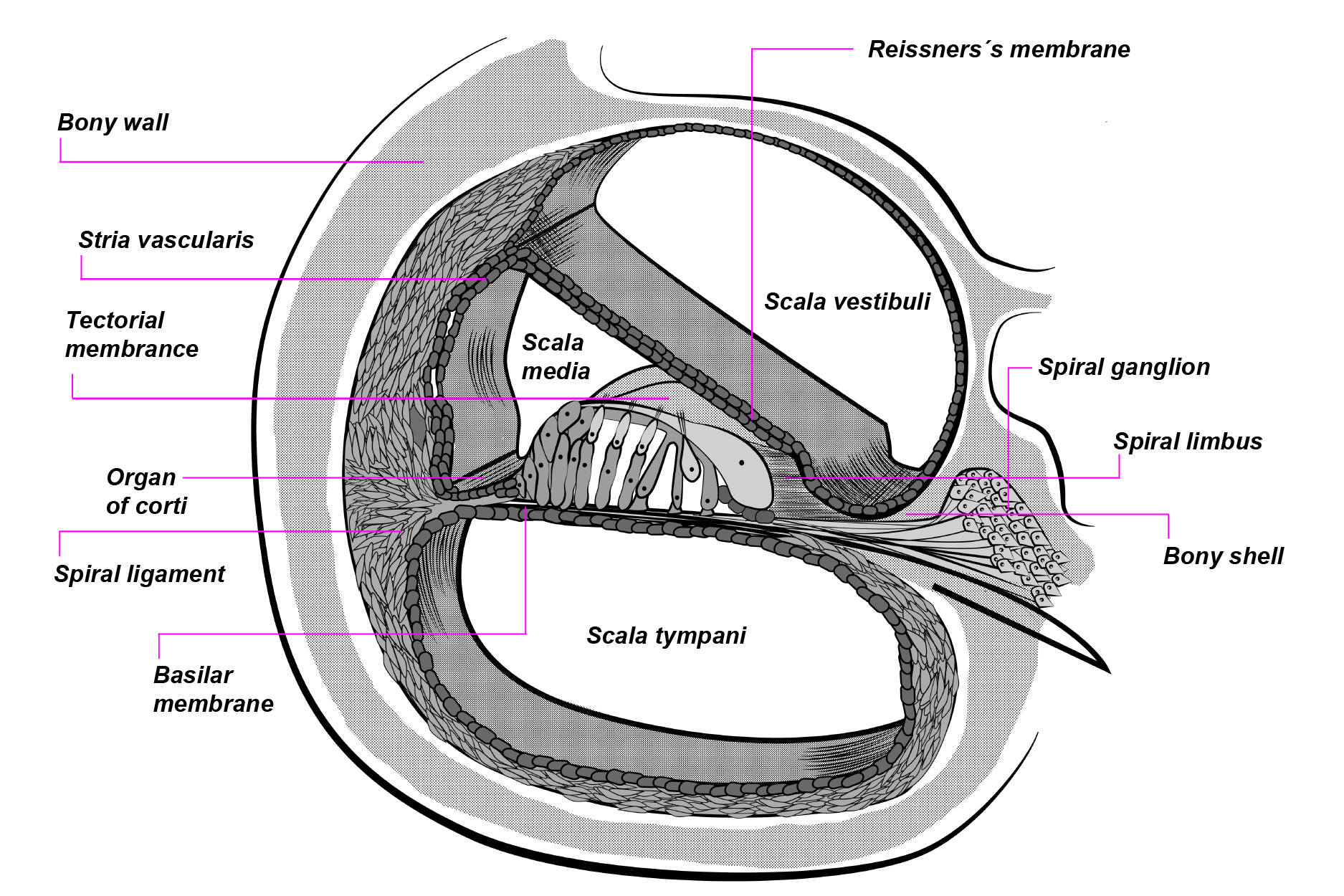
Connexin30 deficiency causes instrastrial fluid–blood barrier ... 04/04/2007 · OC, organ of Corti; Sc.V, scala vestibuli; Sc.M, scala media; Sc.T, scala tympani; SL, spiral ligament. The vascular system of the cochlea lateral wall is represented by red lines. The spiral ligament vessels penetrate into the SV and divide into numerous thin capillaries in the intrastrial space (red lines) 13 –18). Large diagram, SV consists of two epithelial cell layers; …
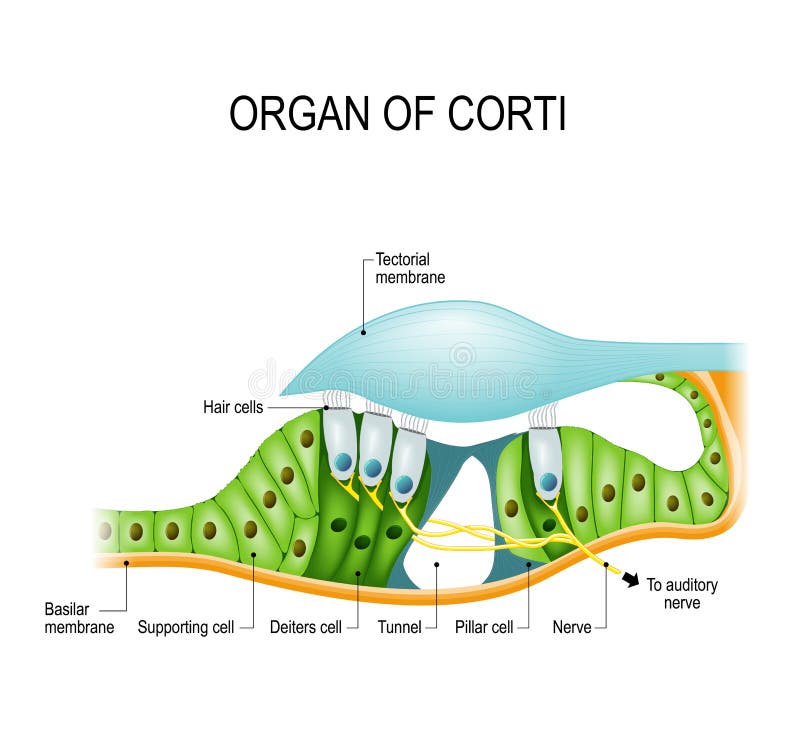
Organ of corti diagram
Organs on Left Side of Body: Inside and Out, From Head to Toe - Healthline Your cochlea is part of the inner ear. It contains the organ of Corti, which perceives sound using sensory hair cells. They transmit movement as electrical impulses to your brain. Left eye The eyes... healthjade.com › human-earHuman Ear Anatomy - Parts of Ear Structure, Diagram and Ear ... The inner ear, which includes the cochlea (organ of hearing) and vestibule (organ of balance) Sound waves enter the ear canal and cause a vibration of the tympanic membrane (ear drum) which is then passed through three tiny bones behind the ear drum in the middle ear space: the malleus (hammer), incus (anvil) and stapes (stirrup). The 12 Cranial Nerves: Overview and Functions - Lecturio Organ of corti, situated on the basilar membrane and overlaid by a gelatinous tectorial membrane, converts sound-induced mechanical waves to neural impulses to the brain. Auditory and Vestibular Pathways: Anatomy , which converts sound waves into neural signals within the cochlea Cochlea The part of the inner ear (labyrinth) that is concerned ...
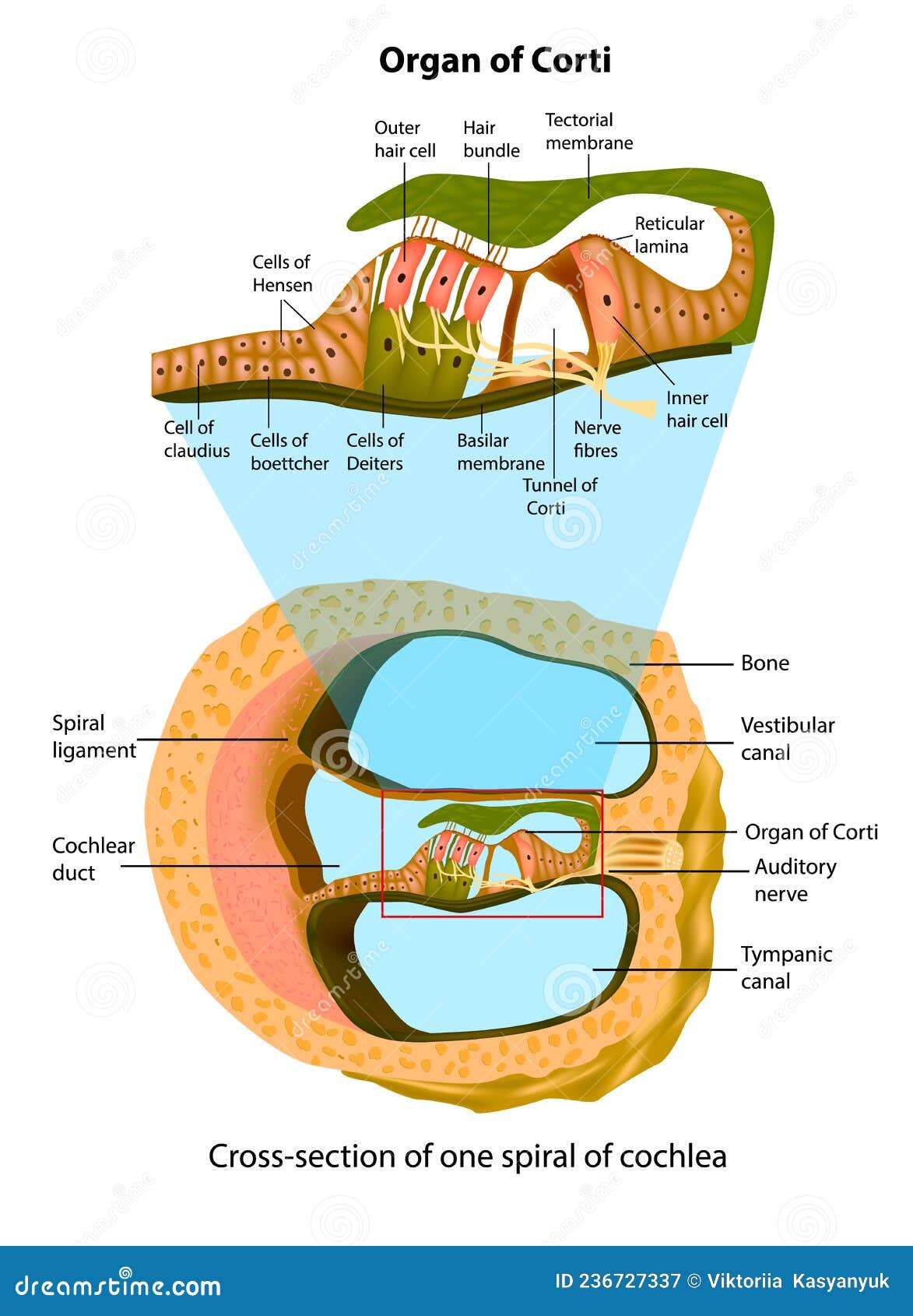
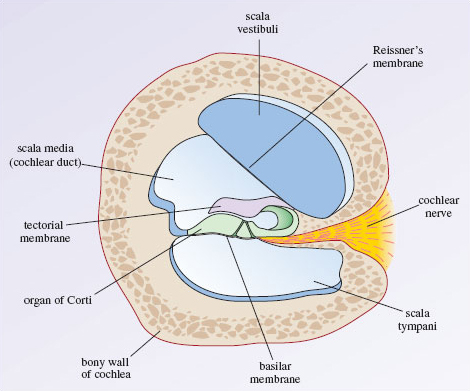
Organ of corti diagram. Stratified Squamous Epithelium: Function & Location - Study.com 21/03/2022 · The stratified squamous epithelium locations are in many places around the body. The skin is the largest organ and consists of stratified squamous epithelium. Stratified squamous epithelium even ... ACTIVITY FIVE: The Path From the Ear to the Brain Goal of this activity ... Organ of Corti ---> Auditory Nerve ---> Superior Olivary Complex Dorsal Cochlear aucleus ---> Inferior colliculus ---> Medial Geniculate body Auditory Cortex ---> Therefore, sound waves travel from the air into the ear canal to the brain where they are processed. Learn more about auditory signals at: brainly.com/question/8474453 Still stuck? Immunohistochemistry localises myosin-7a... | Wellcome Open Research A section through the cochlea, rectangle depicts the location of the organ of Corti. B. A diagram representation showing a cross-section through the organ of Corti. Hair cells (red) can be subdivided into outer hair cells organised into three rows and inner hair cells. The medial and lateral efferent boutons and fibres (MOC and LOC) are ... Chapter 11 Hearing & Equilibrium Lecture B-3 Part A: Hearing 8/26/2022 ... Labyrinth has 3 components - Cochlea - Semicircular canals - Otolith organs Cochlea For hearing semicircular canals measures head rotation Otolith organs responds to gravity & head tilt Utricle & saccule Inner ear ... Figure 11-4 cross section of the cochlea Note: Organ of Corti, Scala vestibuli, Scala media, Scala tympani
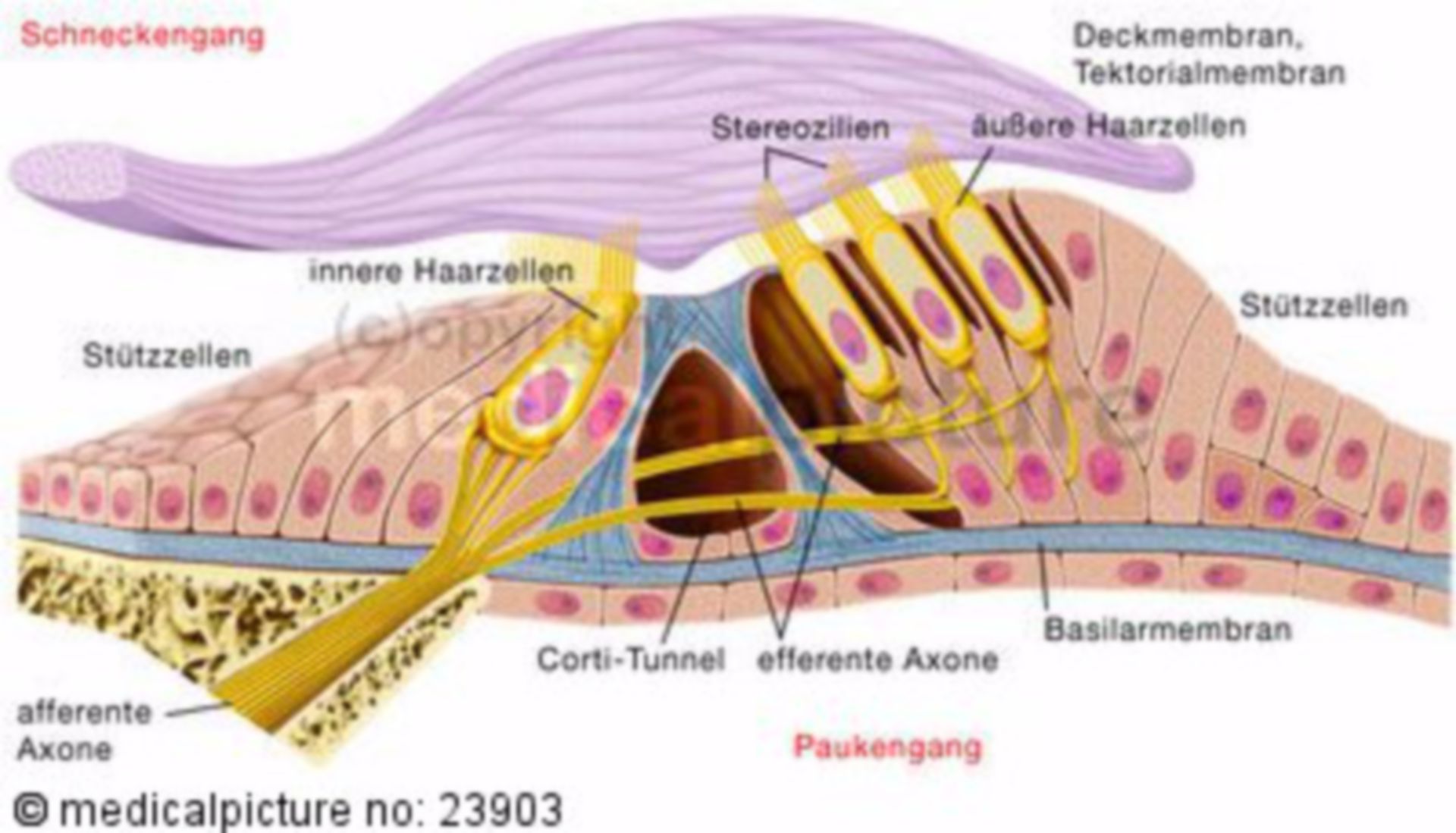
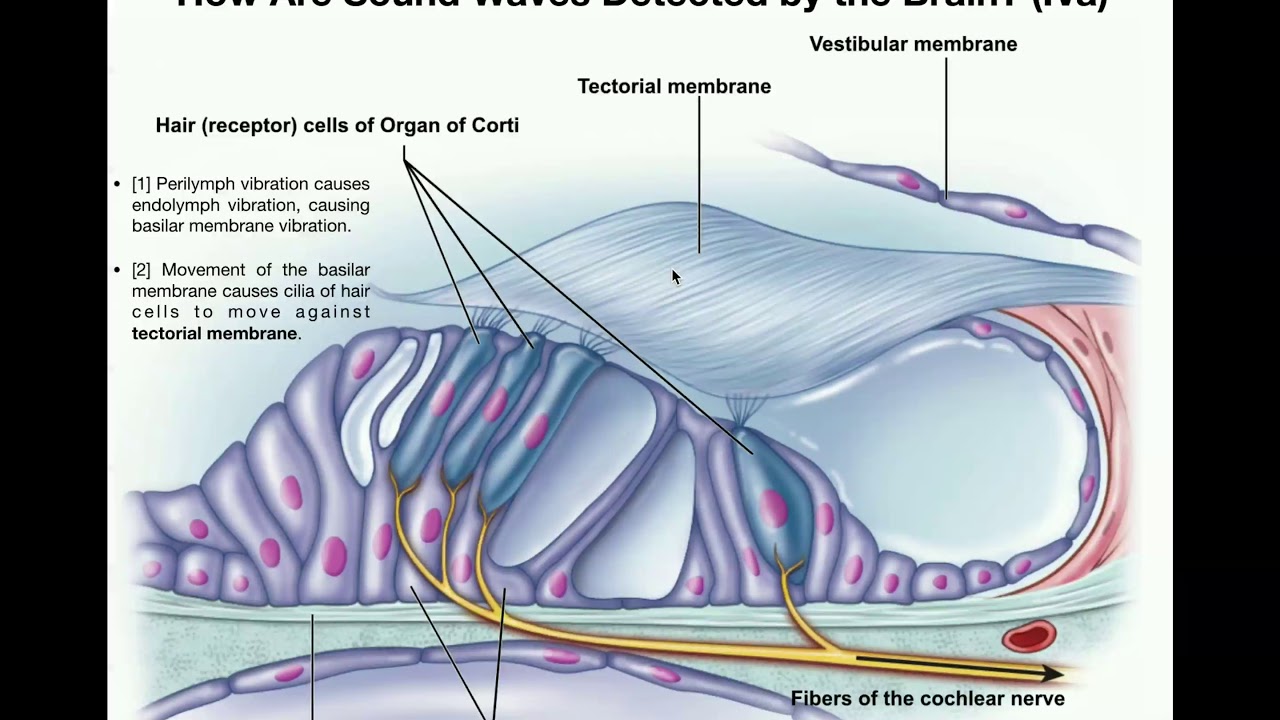
Vestibulocochlear nerve (CN VIII): Anatomy and pathway - Kenhub The dendrites (peripheral extensions) of these neurons receive the stimuli from the receptors in the organ of Corti, whereas their axons (central extensions) together form the cochlear part of the vestibulocochlear nerve. The cochlear nerve enters the brainstem and terminates within its cochlear nuclei. Each cochlear fiber has two branches: Ear: Anatomy | Concise Medical Knowledge - Lecturio Organ of corti, situated on the basilar membrane and overlaid by a gelatinous tectorial membrane, converts sound-induced mechanical waves to neural impulses to the brain. Auditory and Vestibular Pathways: Anatomy; Organ of Corti Organ of Corti The spiral epithelium containing sensory auditory hair cells and supporting cells in the cochlea ... Lymph node levels of the neck | Radiology Reference Article ... 26/08/2022 · The lymph nodes in the neck have historically been divided into at least six anatomic neck lymph node levels for the purpose of head and neck cancer staging and therapy planning. Differing definitions exist across specialties 1-4.The following is a synthesis of radiologically useful boundaries for each level. Level I: submental and submandibular Basilar Membrane: Lining & Function - Video & Lesson Transcript - Study.com At the top of the hair cells are teensy tiny little cilia. These tiny little hair-like extensions gently touch against a sturdy ceiling-like structure called the tectorial membrane. Together, the...
The Ear: Anatomy, Function, and Treatment - Verywell Health It is composed of a membrane attached by fibrous cartilage to the surrounding bone. It has a more flaccid part (pars flaccida), and a more taut part (pars tensa). The inner, medial surface is convexed towards the middle ear and connects with the malleus bone of the middle ear. Middle Ear › pmc › articlesConnexin30 deficiency causes instrastrial fluid–blood barrier ... Apr 04, 2007 · OC, organ of Corti; Sc.V, scala vestibuli; Sc.M, scala media; Sc.T, scala tympani; SL, spiral ligament. The vascular system of the cochlea lateral wall is represented by red lines. The spiral ligament vessels penetrate into the SV and divide into numerous thin capillaries in the intrastrial space (red lines) (13 –18). Large diagram, SV ... Human Ear Anatomy - Parts of Ear Structure, Diagram and Ear … The inner ear, which includes the cochlea (organ of hearing) and vestibule (organ of balance) Sound waves enter the ear canal and cause a vibration of the tympanic membrane (ear drum) which is then passed through three tiny bones behind the ear drum in the middle ear space: the malleus (hammer), incus (anvil) and stapes (stirrup). The sound ... Vascular Anatomy of the Head and Neck - FPnotebook.com Ontology: Vascular structure of head and neck (C0460028) Concepts. Body System ( T022 ) SnomedCT. 281232002. English. Vascular structure head & neck, Vascular structure of head and neck, Vascular structure of head and neck (body structure) Spanish. estructura vascular de cabeza y cuello (estructura corporal), estructura vascular de cabeza y cuello.
Oval window - Wikipedia The oval window (or fenestra vestibuli or fenestra ovalis) is a membrane-covered opening from the middle ear to the cochlea of the inner ear.. Vibrations that contact the tympanic membrane travel through the three ossicles and into the inner ear. The oval window is the intersection of the middle ear with the inner ear and is directly contacted by the stapes; by the time vibrations …
radiopaedia.org › articles › pterygopalatine-fossaPterygopalatine fossa | Radiology Reference Article ... Jun 16, 2022 · thin slice (<1 mm) bone algorithm reconstruction of non-contrast axial sections is the best approach to image the bony walls of the pterygopalatine fossa 4 (see attached diagram) MRI. appears as a narrow cleft situated between the posterior wall of the maxillary sinus and the pterygoid plates 5
Nervous System and Sense Organs Class-10 Structured ... - ICSEHELP The diagram given below is a representation of a certain phenomenon pertaining to the nervous system. Study the diagram and answer the following questions : ... Organ of corti. (v) Endolymph. Question 6. Given below is a diagram depicting a defect of the human eye. Study the same and then answer the questions that follow :
en.wikipedia.org › wiki › Oval_windowOval window - Wikipedia The oval window (or fenestra vestibuli or fenestra ovalis) is a membrane-covered opening from the middle ear to the cochlea of the inner ear.. Vibrations that contact the tympanic membrane travel through the three ossicles and into the inner ear.
Physiology, Cochlear Function - StatPearls - NCBI Bookshelf The organ of Corti contains hair cells that respond to vibration by brushing their stereocilia against a fixed structure called the tectorial membrane. The result of the hair cells bending against the tectorial membrane is the depolarization of the attached nerve fibers. The frequency of the vibration traveling through the perilymph will ...
human ear | Structure, Function, & Parts | Britannica 01/09/2022 · human ear, organ of hearing and equilibrium that detects and analyzes sound by transduction (or the conversion of sound waves into electrochemical impulses) and maintains the sense of balance (equilibrium). The human ear, like that of other mammals, contains sense organs that serve two quite different functions: that of hearing and that of postural equilibrium …
Organ of Corti, Auditory Nerve & Ear Hair Cells - Study.com The organ of Corti is a structure in the inner ear essential to the processing of sound and the production of nerve signals that the brain can interpret. The transformation of vibration to nerve...
Sense Organs: Check Types, Sense organs notes- Embibe Q.5: What is the Organ of Corti? Ans: The Organ of Corti is an organ of the inner ear located within the cochlea which contributes to hearing. Q.6: How many taste buds are present in the tongue? Ans: On average, a person has about ten thousand taste buds. Q.7: What is deafness?
3 phases of uterine cycle Diagram | Quizlet Trace the pathway of vibrations from the eardrum to the spiral organ of Corti, where the hair cells are stimulated. Verified answer. Other Quizlet sets. Menstrual Cycle and Fetal Development. 33 terms. jamesallenellis PLUS. 3260: menstrual cycle. 20 terms. sleath. Pharm - Contraceptives. 108 terms. twinbaby. Womens Health Unit 1.
radiopaedia.org › articles › lymph-node-levels-ofLymph node levels of the neck | Radiology Reference Article ... Aug 26, 2022 · The lymph nodes in the neck have historically been divided into at least six anatomic neck lymph node levels for the purpose of head and neck cancer staging and therapy planning. Differing definitions exist across specialties 1-4. The following i...
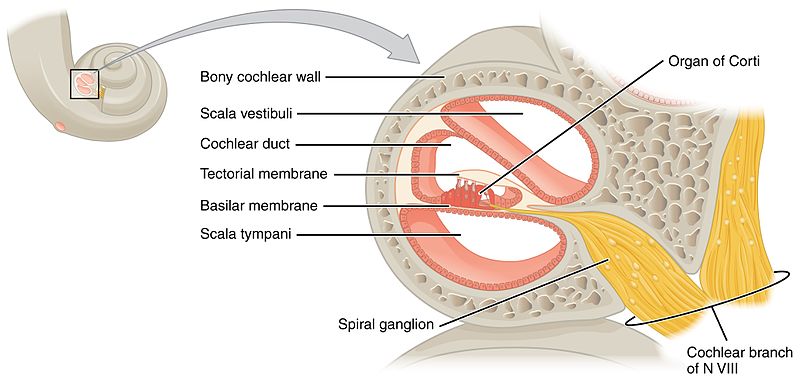
Modiolus (cochlea) | Radiology Reference Article | Radiopaedia.org The modiolus (plural: modioli) is part of the cochlea and is a conical-shaped structure that consists of spongy (porous) bone located in the center of the cochlea and contains the spiral ganglion. The spiral lamina projects from the modiolus. Abnormality of the modiolus results in sensorineural hearing loss. History and etymology
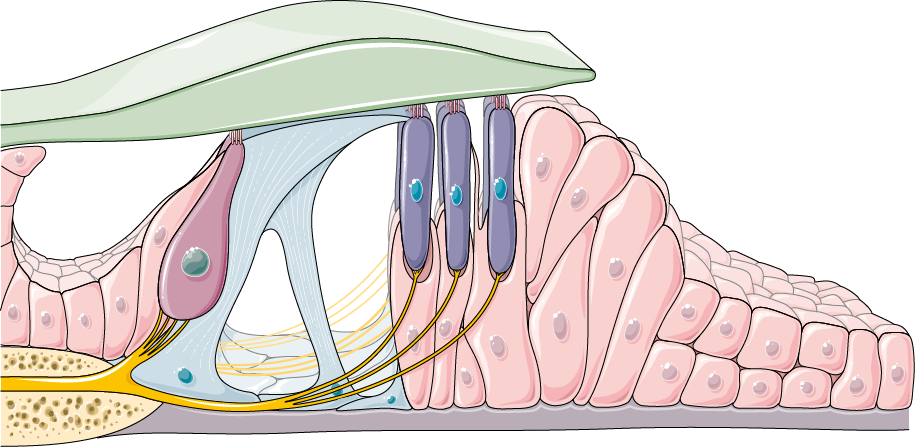
Anatomy, Head and Neck, Ear Organ of Corti - NCBI Bookshelf The Organ of Corti is an organ of the inner ear located within the cochlea which contributes to audition. The Organ of Corti includes three rows of outer hair cells and one row of inner hair cells. Vibrations caused by sound waves bend the stereocilia on these hair cells via an electromechanical force. The hair cells convert mechanical energy into electrical energy that is transmitted to the ...
Pterygopalatine fossa | Radiology Reference Article 16/06/2022 · Gross anatomy Borders. The walls of the pterygopalatine fossa are as follows: medial: perpendicular plate of the palatine bone lateral: narrowing to the pterygomaxillary fissure anterior: posterior wall of the maxillary sinus posterior: sphenoid bone (pterygoid process and inferior aspect of the greater wing) roof: body of the sphenoid bone and orbital process of …
study.com › academy › lessonFive Senses Functions & Examples | What Are the 5 Senses ... Nov 30, 2021 · The Corti has many tiny hair cells that translate the vibrations into sensory information that is then perceived by the brain as sound. Hearing sound is an important part of human life for ...
What part of henry's cochlea may have damaged hair cells? What part of ... Small hair cells make up the lining of the cochlea. These cells convert vibrations into electrical impulses that sensory nerves then transmit to the brain. the Corti organ, which has four rows of hair cells. On the left, there is an inner row, and on the right, there are three outside rows. The stapes first sways against the oblong glass.
COD Library Model Guide: Special Senses - College of DuPage The model depicts a section through the central spiral of the cochlea and has been enlarged approximately 350 times. It shows the vestibular, cochlear, and tympanic ducts; Corti's organ with hair cells and tectorial and basilar membranes; and spiral ganglia, nerves, and arteries of the ear. Location: Main Circulation Desk (SRC, Library, 2nd ...
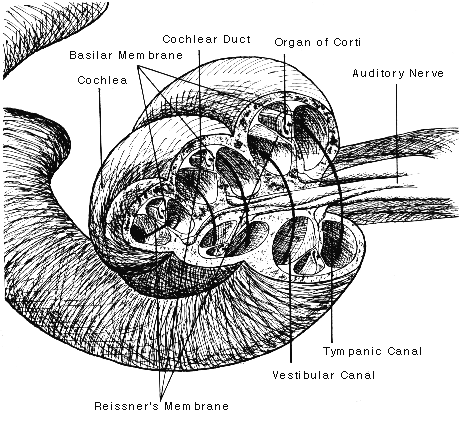
Cochlea: Anatomy, Function, and Treatment - Verywell Health Two of these fluid-filled chambers sense pressure changes (caused by sound) while the third chamber contains the organ of Corti, the cochlear duct and the basilar membrane. The cochlear duct is another bony, hollow tube that sits between the scala vestibuli and the scala tympani. The cochlear duct contains endolymph.
Vinyl and the World's Best Stereo System - PS Audio The Organ of Corti has three rows of outer hair cells and one row of inner hair cells, all of which physically vibrate in a uniquely amazing way. At the ends of the hair cells are minuscule projecting groups of protrusions called…stereocilia.
The Vestibulocochlear Nerve (CN VIII) - Geeky Medics The scala media contains the organ of Corti and hair cells of the cochlea. Lying between the scala vestibuli and the scala media is Reissner's membrane. Reissner's membrane is a flexible membrane that moves as sound is transmitted into the scala vestibuli from the oval window.
Parts of the Ear and their Functions | Interesting Anatomy of Hearing The Membranous labyrinth has an organ of Corti, which helps in hearing. It has hair cells that move during the vibrations, which are passed by the stapes to the round window, and this opens the sodium-potassium channels among the perilymph and endolymph.
Head and Neck Anatomy - FPnotebook.com Definition (NCI) For oncology, an area of the body generally construed to comprise the base of skull and facial bones, sinuses, orbits, salivary glands, oral cavity, oropharynx, larynx, thyroid, facial and neck musculature and lymph nodes draining these areas. Concepts. Body Location or Region ( T029 ) SnomedCT.
Auditory pathway: Anatomy, ear structures, transduction | Kenhub The cochlea (the region responsible for hearing) is a spiral shaped hollow organ. The cochlear duct is the triangular shaped section of the cochlea, which contains the organ of Corti. The oval window is quite simply an oval shaped window that is moved inwards by the movement of the stapes footplate.
Frontiers | Cochlear Development; New Tools and Approaches Located in the middle third of the floor of the scala media is the auditory sensory epithelium, also called the organ of Corti (OC). The OC is comprised of a band of cells that extends along the full length of the spiral ( Figure 1C ). Medial to the OC is the inner sulcus while the lateral third of the scala media floor contains the outer sulcus.
Hearing Loss Organ Of Corti - Guide to Curing - Harrielle Hearing Loss Organ Of Corti Tinnitus, the word for "ringing in the ears," occurs when the nerves that provide us with hearing lose their ability to transmit sound from the external environment to the inner ear. Sound waves travel through the hair cells on both sides of the auditory canal.
Five Senses Functions & Examples | What Are the 5 Senses? 30/11/2021 · Humans have five basic senses that correspond to five sensory organs and the type of sensory input received by each organ. The five senses are sight, sound or hearing, smell, taste, and touch.
The 12 Cranial Nerves: Overview and Functions - Lecturio Organ of corti, situated on the basilar membrane and overlaid by a gelatinous tectorial membrane, converts sound-induced mechanical waves to neural impulses to the brain. Auditory and Vestibular Pathways: Anatomy , which converts sound waves into neural signals within the cochlea Cochlea The part of the inner ear (labyrinth) that is concerned ...
healthjade.com › human-earHuman Ear Anatomy - Parts of Ear Structure, Diagram and Ear ... The inner ear, which includes the cochlea (organ of hearing) and vestibule (organ of balance) Sound waves enter the ear canal and cause a vibration of the tympanic membrane (ear drum) which is then passed through three tiny bones behind the ear drum in the middle ear space: the malleus (hammer), incus (anvil) and stapes (stirrup).
Organs on Left Side of Body: Inside and Out, From Head to Toe - Healthline Your cochlea is part of the inner ear. It contains the organ of Corti, which perceives sound using sensory hair cells. They transmit movement as electrical impulses to your brain. Left eye The eyes...























0 Response to "41 organ of corti diagram"
Post a Comment