39 cardiac muscle tissue diagram
Start studying Cardiac Muscle Tissue labeled. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools. Here you are! We collected 38+ Muscle Tissue Drawing paintings in our online museum of paintings - PaintingValley.com. A Labelled Diagram O... Draw A Well Labelled... Smooth Muscle Cell -... Draw A Diagram Of St... Labeled Cardiac Musc... Image Result For Dra... Animal Tissues Plant...
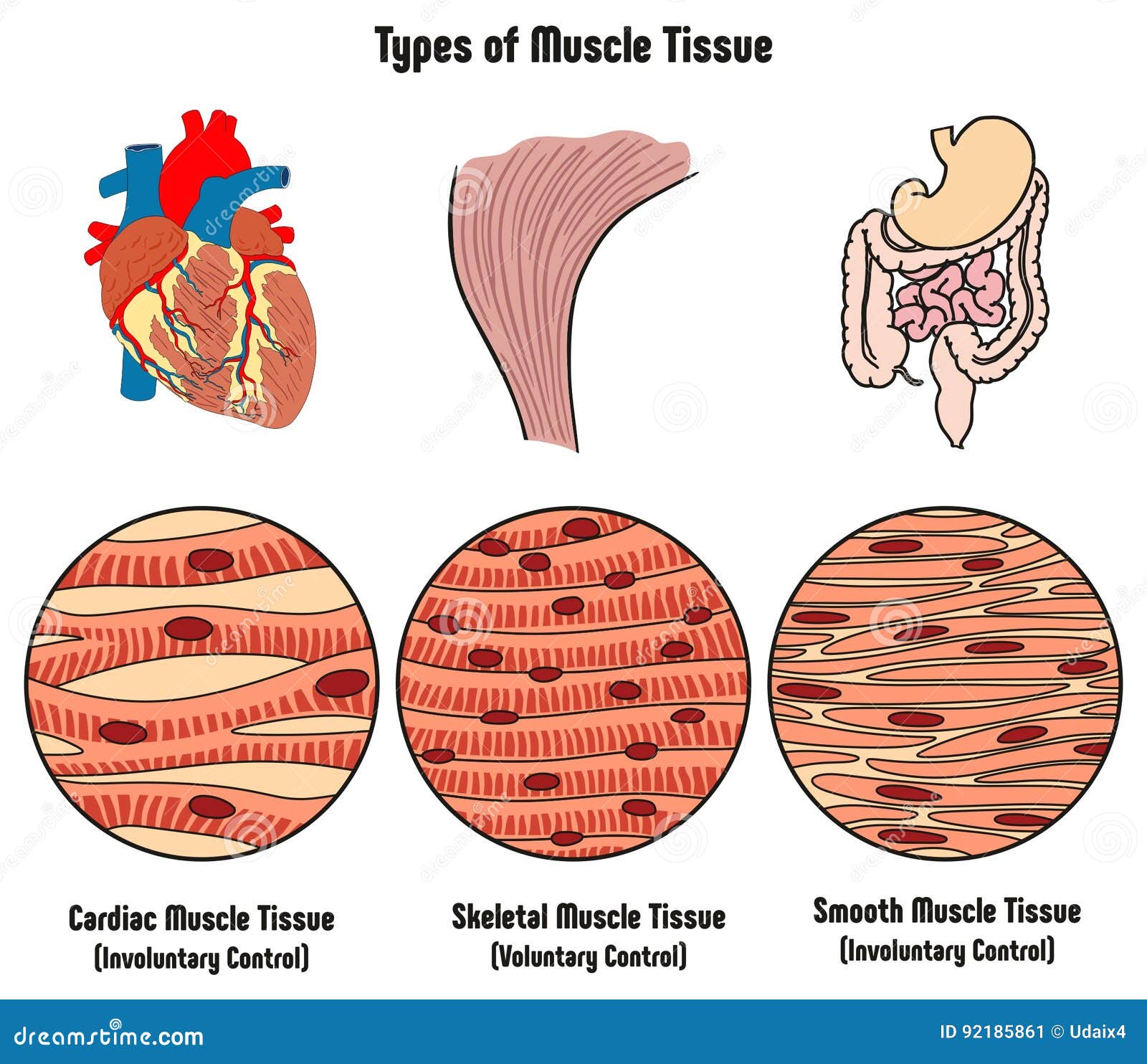
Download preview. Types of Muscle Tissue of Human Body Diagram including cardiac skeletal smooth. Examples of heart digestive system. Along with involuntary voluntary control for medical science education. muscle contraction, muscle fibers, science education, education, heart,
Cardiac muscle tissue diagram
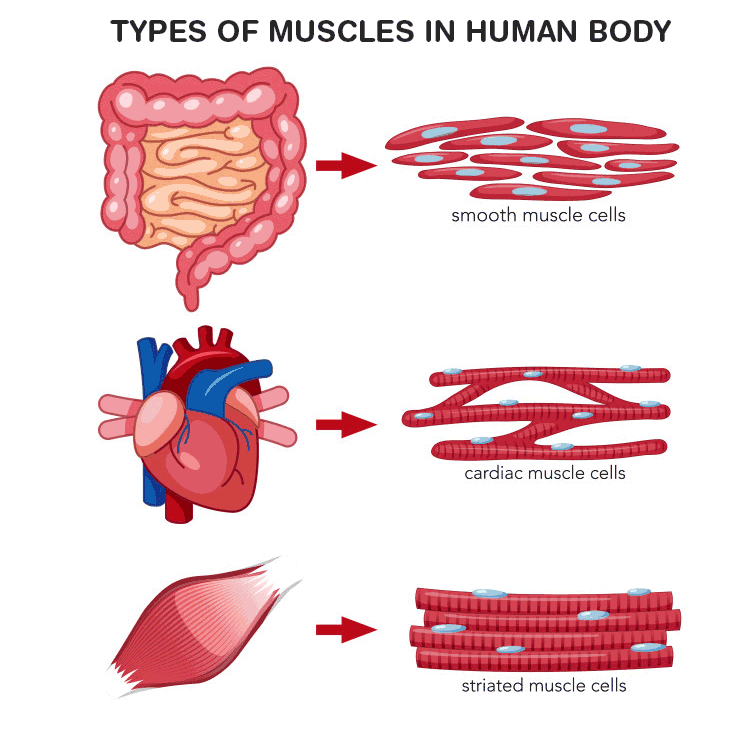
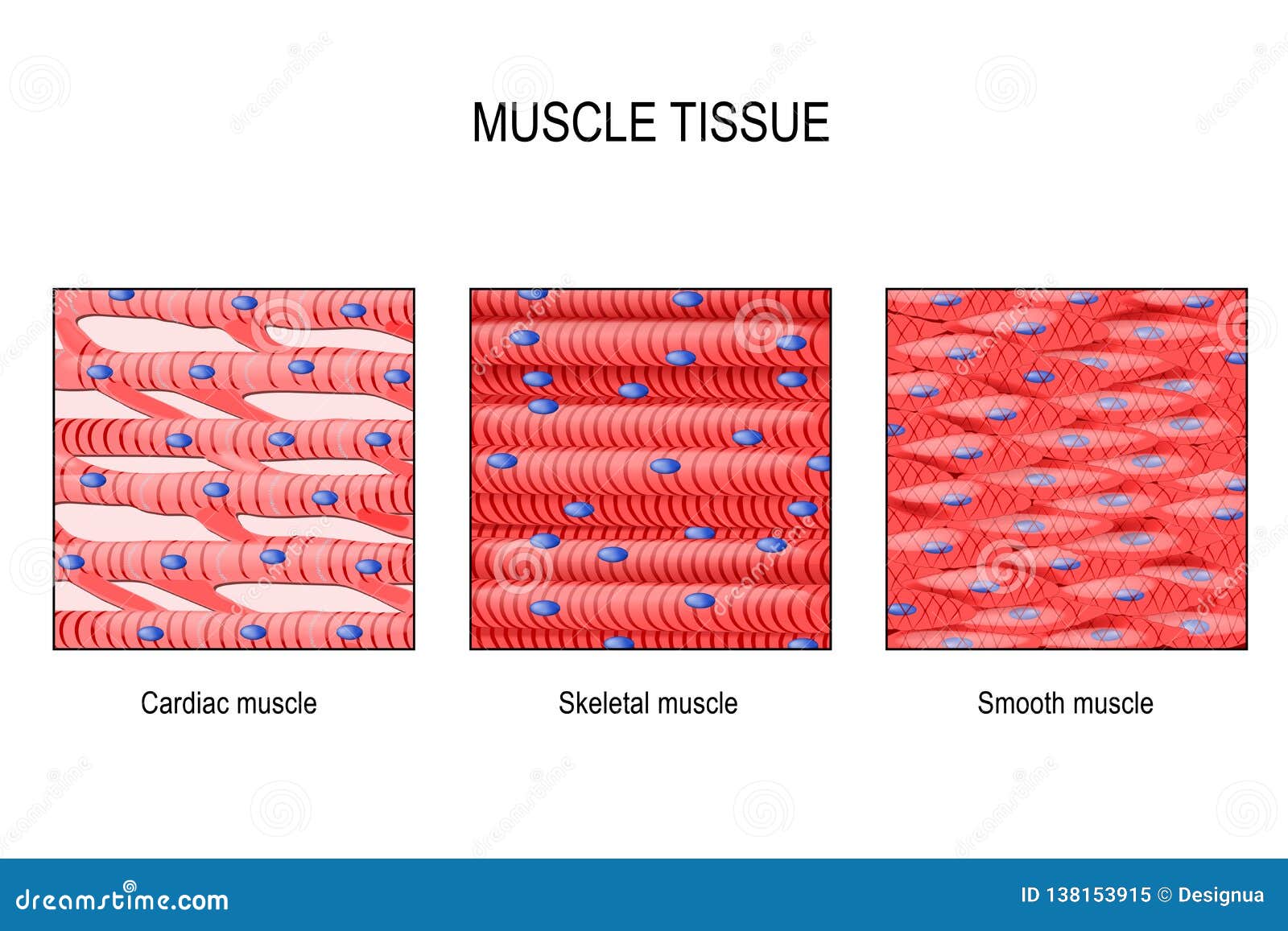
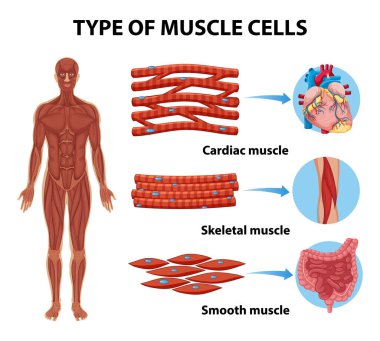
Muscle tissue: Contracts to cause movement. Epithelial tissue: Forms boundaries betweendifferent environments, protects, secretes, absorbs,filters. Connective tissue: Supports, protects, bindsother tissues together • Muscles attached to bones (skeletal) • Muscles of heart (cardiac) • Muscles of walls of hollow organs (smooth) Has anyone heard of the parasite Trypanosoma cruzi? I was doing some research earlier today and saw that there is an insect that’s called the “kissing bug” that after it bites a human, releases their fecal matter droppings which usually enters the opening of the bite and leads to human transmission of the trypanosoma parasite to humans which causes a disease called “African sleeping sickness”. It has been shown to lead to AIDS like responses(extreme fatigue, suppressed immune system due to death... Cardiac muscle is similar to skeletal muscle in that it is striated and that the sarcomere is the contractile unit, contraction being achieved by the relationship between calcium, troponins and the myofilaments. This article will consider the structure of cardiac muscle as well as relevant clinical conditions.
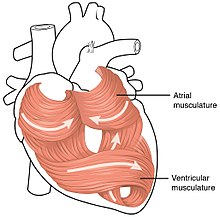
Cardiac muscle tissue diagram. Cardiac muscle tissue or myocardium forms the bulk of the heart. The heart wall is a three-layered structure with a thick layer of myocardium sandwiched between the inner endocardium and the outer epicardium (also known as the visceral pericardium). The inner endocardium lines the cardiac chambers, covers the cardiac valves, and joins with the endothelium that lines the blood vessels that ... if our heart muscle doesn’t tire, why wouldn’t our body have a non-tiring muscle for everything? wouldn’t it save energy or allow us to be more efficient? Cardiac muscle is able to contract and relax, unlike skeletal muscles which only contract. This means that cardiac tissue will have far more irregular shapes than skeletal muscles. Cardiac muscle cells contain T tubules that connect to the sarcoplasmic reticulum which stores the calcium ions needed for contraction of the cell. Striated musculature is comprised of two types of tissues: skeletal muscle and cardiac muscle. Skeletal muscle is the tissue that most muscles attached to bones are made of. Hence the word "skeletal". Cardiac muscle, on the other hand, is the muscle found on the walls of the heart. Microscopically both the skeletal and cardiac musculature have ...
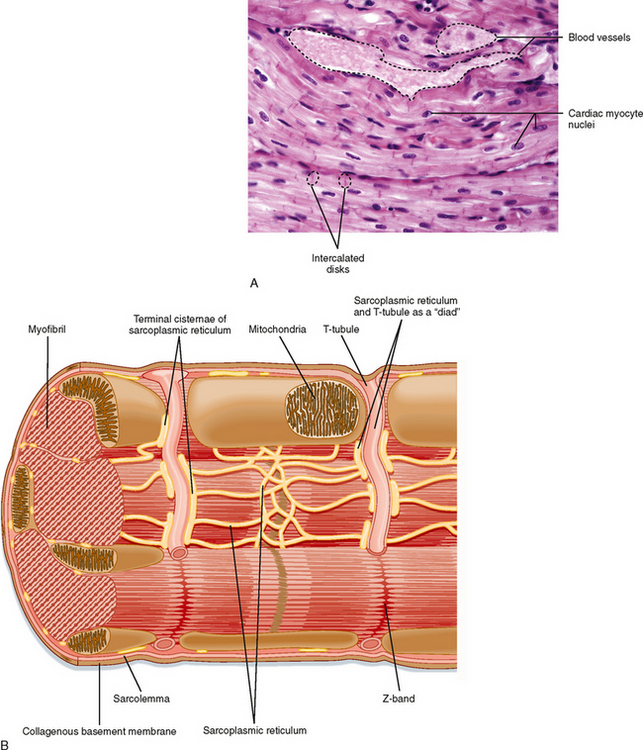
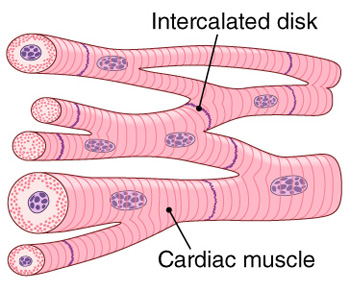
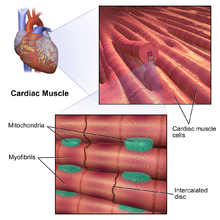
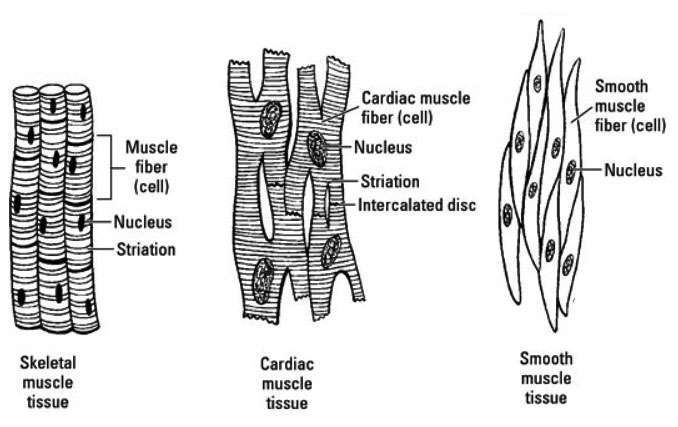
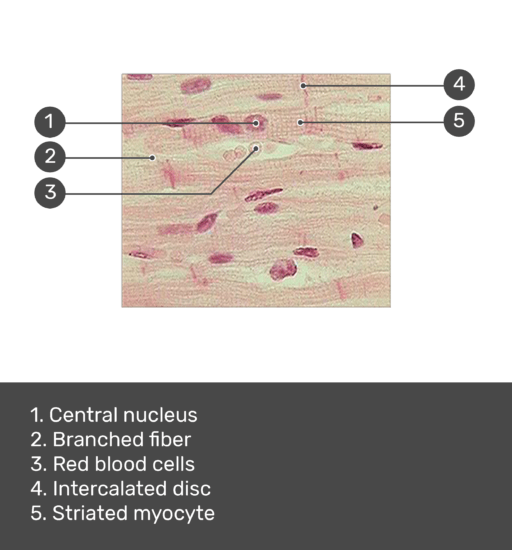
Cardiac muscle tissue, also known as myocardium, is a structurally and functionally unique subtype of muscle tissue located in the heart, that actually has characteristics from both skeletal and muscle tissues.It is capable of strong, continuous, and rhythmic contractions that are automatically generated. The contractility can be altered by the autonomic nervous system and hormones. Function of Cardiomyocytes (Mechanism) Cardiomyocytes go through a contraction-relaxation cycle that enables cardiac muscles to pump blood throughout the body. This is achieved through a process known as excitation-contraction coupling that converts action potential (an electric stimulus) into muscle contraction. But that does not make them a living being. The "beating heart" criteria as a measure is deeply ignorant. It seems predicated on the assumption that a clump of cells is imbued with an eternal human spirit. I am disappoint the press is not calling BS on this type of magical thinking. Cardiac muscle fibers cells also are extensively branched and are connected to one another at their ends by intercalated discs. An intercalated disc allows the cardiac muscle cells to contract in a wave-like pattern so that the heart can work as a pump. Cardiac Muscle Tissue. Cardiac muscle tissue is only found in the heart.
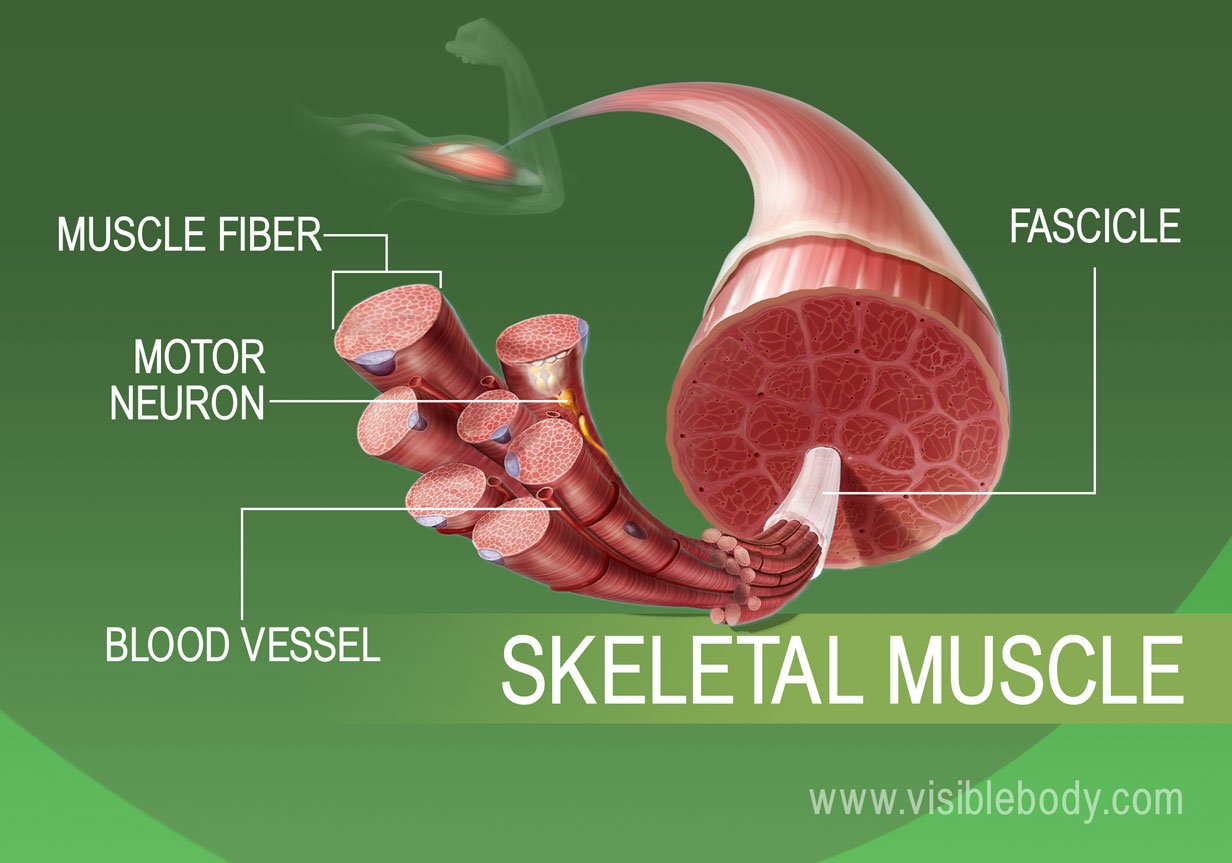
During systole, cardiac muscle tissue is contracting to push blood out of the chamber. Diastole. During diastole, the cardiac muscle cells relax to allow the chamber to fill with blood. Blood pressure increases in the major arteries during ventricular systole and decreases during ventricular diastole. Cardiac muscle images. 13,690 cardiac muscle stock photos, vectors, and illustrations are available royalty-free. See cardiac muscle stock video clips. Image type. Orientation. Sort by. As with skeletal muscle, delicate, highly vascularized connective tissue (endomysium) surrounds each cardiac muscle cell. Fibers are bundled into fascicles, so there is also . perimysium. However, there really isn't an . epimysium; instead, the connective tissue ensheathing the muscle of the heart is called the . epicardium Functions of Muscle Tissue. 1) attached to bone or skin in skeletal muscles. 2) controls voluntary movements (walking, bending) 3) multi nuclei internal to the sarcolemma. 4) Yes Striations are present. Skeletal Muscle: 1) Location 2) Function 3) # and location of nuclei 4) Presence of Striations. 1)wall of the heart.
The above diagram shows the cross-section of the four-chambered mammalian heart. Cardiac Muscle Structure and Cardiac Muscle Function. Let us look at the Cardiac Muscle Function and Cardiac Muscle Structure in detail, here. Gross Anatomy. Cardiac muscle tissue is also called the myocardium, and forms the heart's bulk.
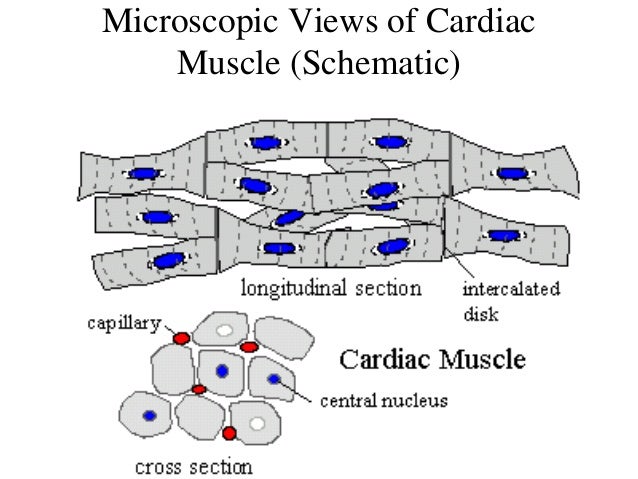
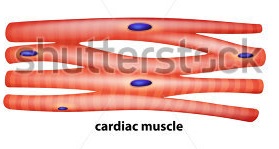
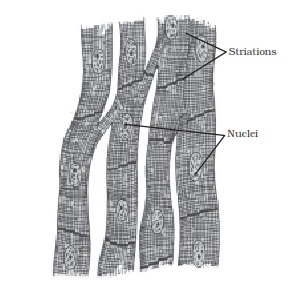
Cardiac muscle tissue is made up of many interlocking cardiac muscle cells, or fibers, that give the tissue its properties. Each cardiac muscle fiber contains a single nucleus and is striated, or striped, because it appears to have light and dark bands when seen through a microscope.
Anyone with Personal experience or studies please?
Cardiac Muscle Definition. Cardiac muscle, also known as heart muscle, is the layer of muscle tissue which lies between the endocardium and epicardium.These inner and outer layers of the heart, respectively, surround the cardiac muscle tissue and separate it from the blood and other organs. Cardiac muscle is made from sheets of cardiac muscle cells.
Cardiac muscle fibers cells also are extensively branched and are connected to one another at their ends by intercalated discs. An intercalated disc allows the cardiac muscle cells to contract in a wave-like pattern so that the heart can work as a pump. Cardiac Muscle Tissue. Cardiac muscle tissue is only found in the heart.
Muscle-related connective tissue: Muscle fibers are within a connective tissue framework that is continuous with tendons.As a result, passive muscles are able to serve as ties that reinforce joints & oppose forces on bones. Muscle associated fascia: 1. epimysium = loose or dense connective tissue surrounding an entire muscle 2.
In this article we will discuss about the structure of junctional tissues of human heart with the help of suitable diagram. Cardiac muscle consists essentially of certain specialised structures which are responsible for initiation and transmission of cardiac impulses at a higher rate than the rest of the muscle.
Source: https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/10.1161/circ.144.suppl_1.10712 Now of course the spin will be that this is also caused by Covid, as both covid and the vaccine introduce the toxic S protein that apparently is causing these issues, but then there's this: https://www.nejm.org/doi/full/10.1056/NEJMcibr2113694 Which is also explained here: https://alexberenson.substack.com/p/a-frightening-new-potential-explanation TL:DR - The vaccines produce significantly more S proteins than natural in...
Heart muscle possesses tone. This tone is independent of nerves and can be adjusted. In this way, it can maintain a fairly constant tension upon its varying contents. It has been observed that the different properties of cardiac muscles (Table 7.1) are not developed in all the tissues of heart in the same order.
Cardiac muscle tissue works to keep your heart pumping through involuntary movements. This is one feature that differentiates it from skeletal muscle tissue, which you can control.
Muscle Tissue. Click on the button or title to get to the appropriate image: Cardiac Muscle, Intercalated Discs: Sarcomeres, High Magnification: Cardiac Muscle, Transverse Section: Skeletal Muscle Vasculature: Central Nuclei & Striations: Smooth Muscle, Longitudinal Section: Intercalated Discs, Intermediate Magnification:
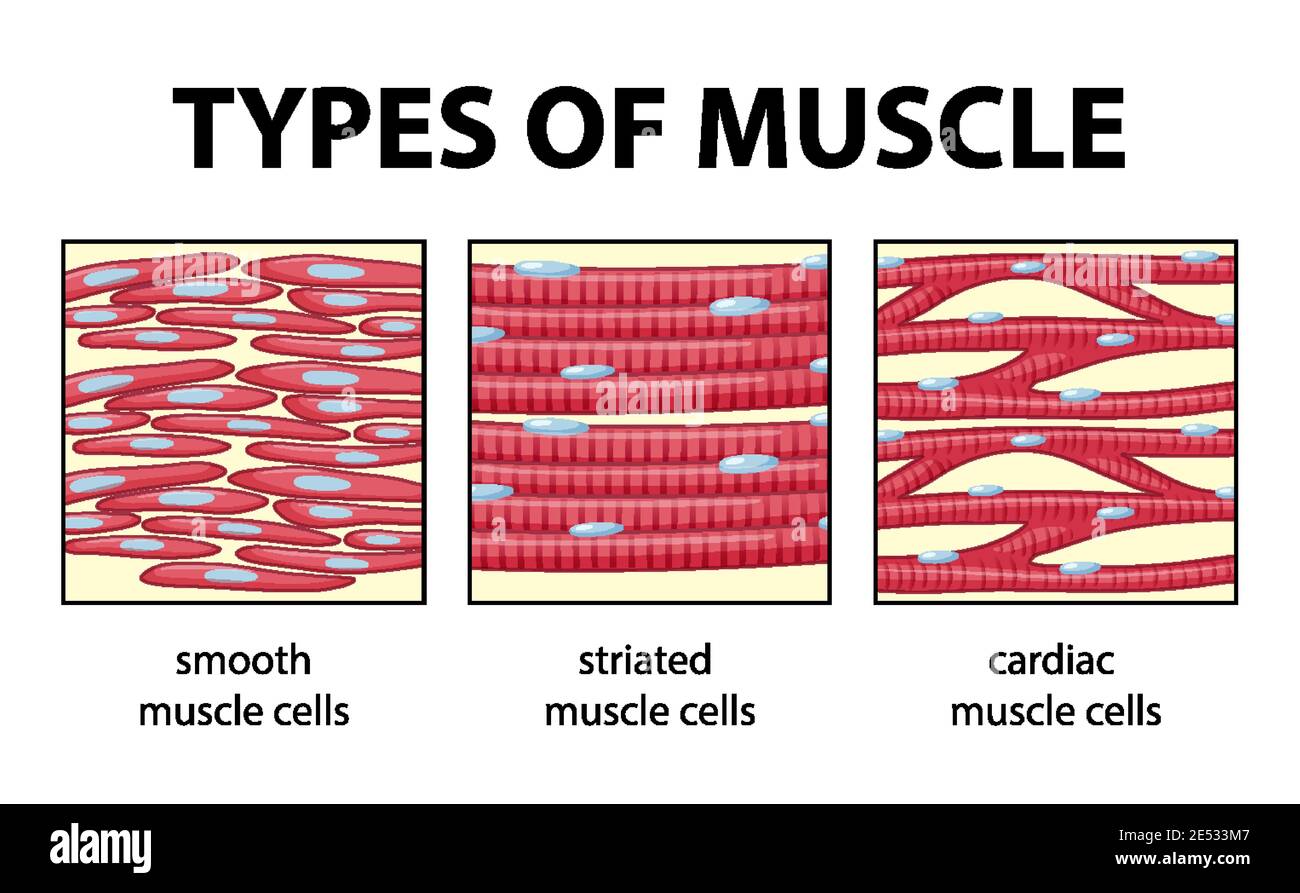
Cardiac muscle tissue is striated like skeletal muscle, containing contractile units called sarcomeres in highly regular arrangements of bundles. While skeletal muscles are arranged in regular, parallel bundles, cardiac muscle connects at branching, irregular angles known as intercalated discs. Smooth muscle tissue is non-striated and involuntary.
Oct 04, 2019 · Cardiac muscle, also known as heart muscle, is the layer of muscle tissue which lies between the endocardium and epicardium. These inner and outer layers of the heart, respectively, surround the cardiac muscle tissue and separate it from the blood and other organs.
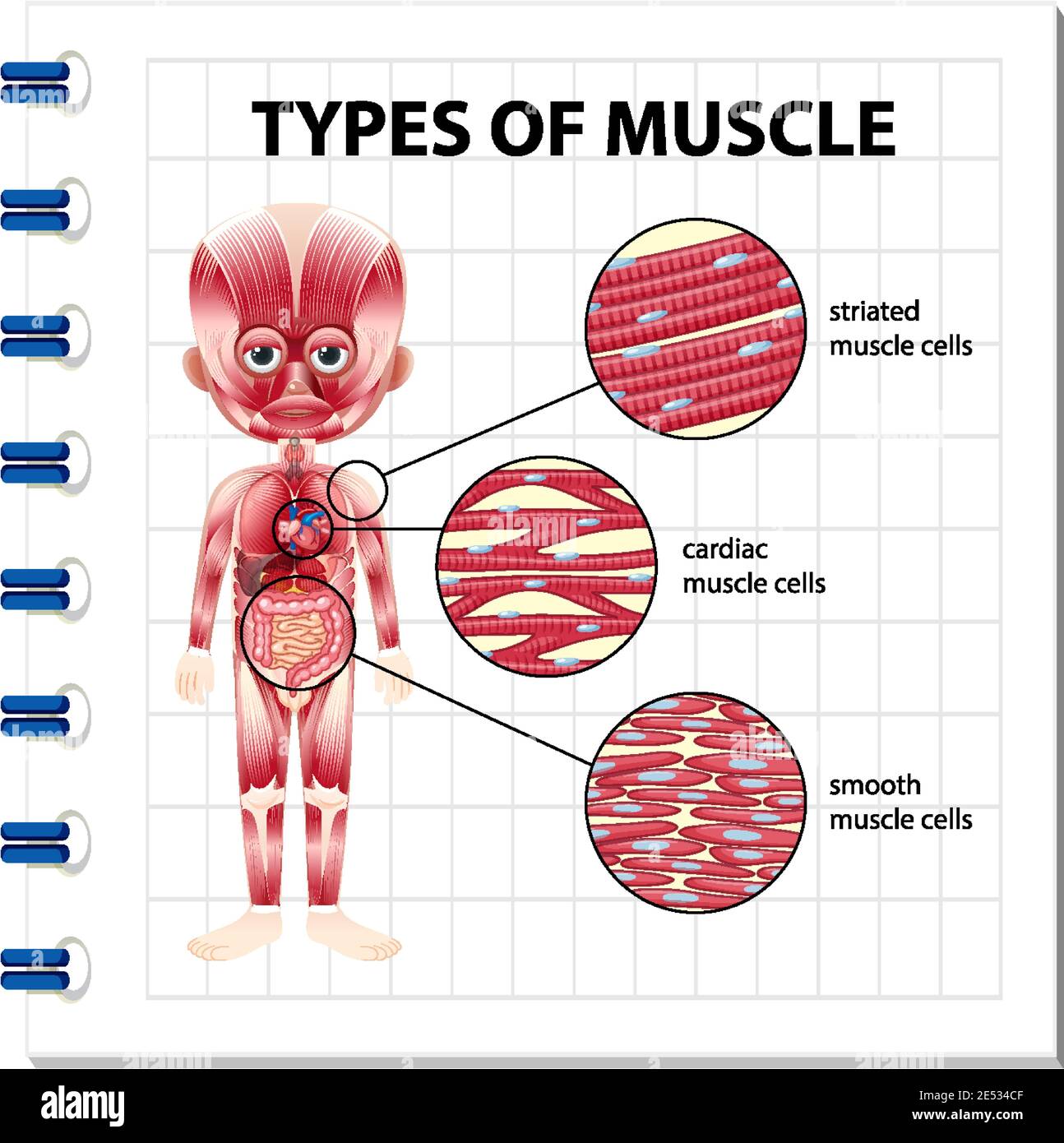
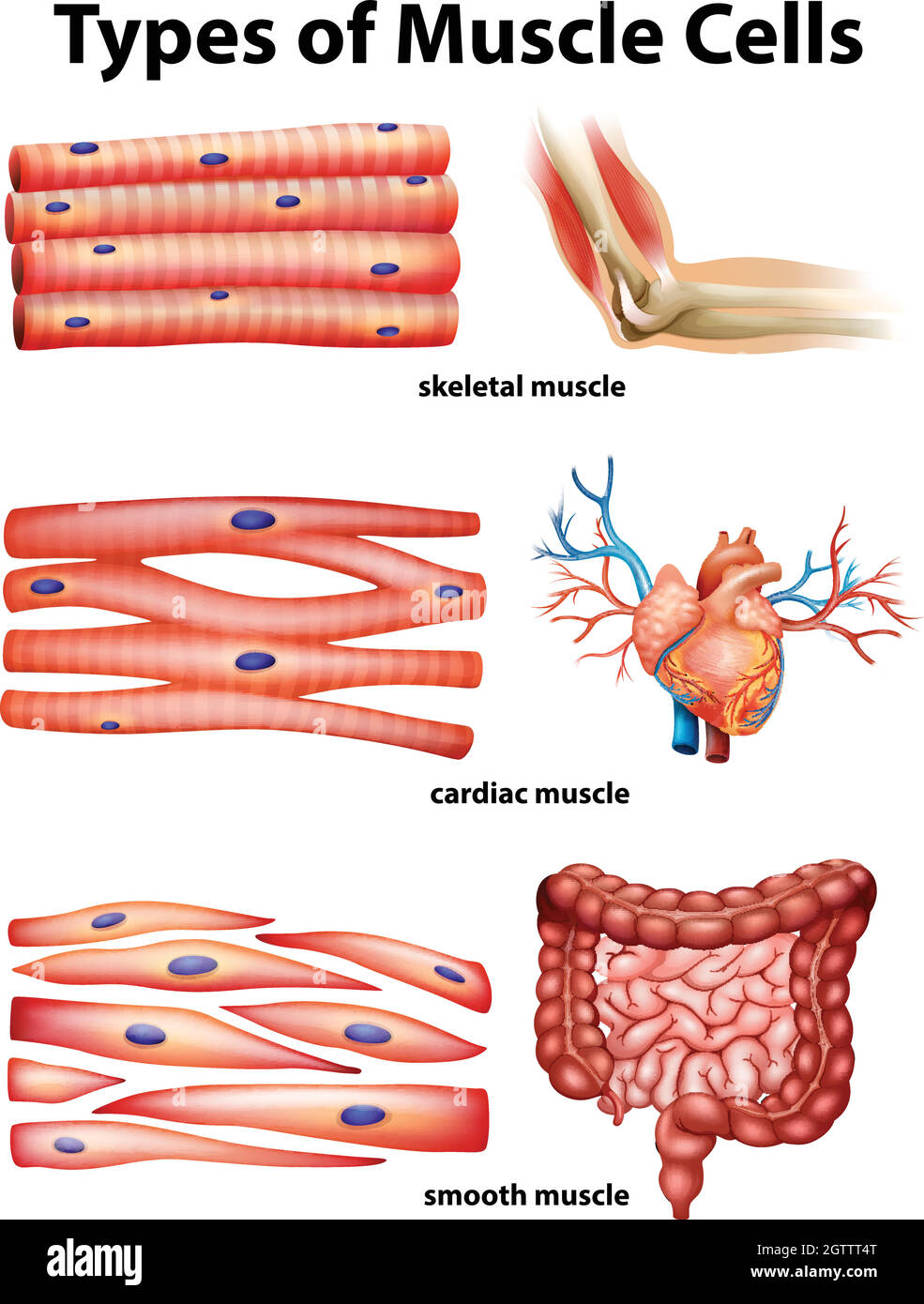
The muscular tissue is of three types: Skeletal Muscle Tissue. Smooth Muscle Tissue. Cardiac Muscle Tissue. Skeletal Muscle Tissue. These muscles are attached to the skeleton and help in its movement. These muscles are also known as striated muscles because of the presence of alternate patterns of light and dark bands.
Cardiac muscle tissue, or myocardium, is a specialized type of muscle tissue that forms the heart. This muscle tissue, which contracts and releases ...Blood pressure: Systolic mmHgNormal: Less than 120Hypertension stage 2: 140 or higherHypertension stage 1: 130–139Cardiac muscle tissue · Cardiomyopathy · Tips for healthy tissue · Summary
In this video I have shown the simplest way of drawing Muscle drawing. It is the pen diagram of Skeletal, Smooth and Cardiac Muscle for class 10, 11 and 12. ...
Cardiac muscle is similar to skeletal muscle in that it is striated and that the sarcomere is the contractile unit, contraction being achieved by the relationship between calcium, troponins and the myofilaments. This article will consider the structure of cardiac muscle as well as relevant clinical conditions.
Has anyone heard of the parasite Trypanosoma cruzi? I was doing some research earlier today and saw that there is an insect that’s called the “kissing bug” that after it bites a human, releases their fecal matter droppings which usually enters the opening of the bite and leads to human transmission of the trypanosoma parasite to humans which causes a disease called “African sleeping sickness”. It has been shown to lead to AIDS like responses(extreme fatigue, suppressed immune system due to death...
Muscle tissue: Contracts to cause movement. Epithelial tissue: Forms boundaries betweendifferent environments, protects, secretes, absorbs,filters. Connective tissue: Supports, protects, bindsother tissues together • Muscles attached to bones (skeletal) • Muscles of heart (cardiac) • Muscles of walls of hollow organs (smooth)















:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/article/en/cardiac-tissue/Dlly3NxuFvJnfdwmsCvVrQ_LNOsY5VQ7ADcaM1g9m5g_Cardiac_Muscle.png)



0 Response to "39 cardiac muscle tissue diagram"
Post a Comment