39 nerves of the foot and ankle diagram
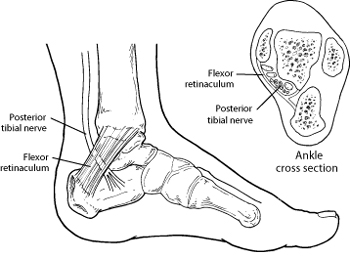
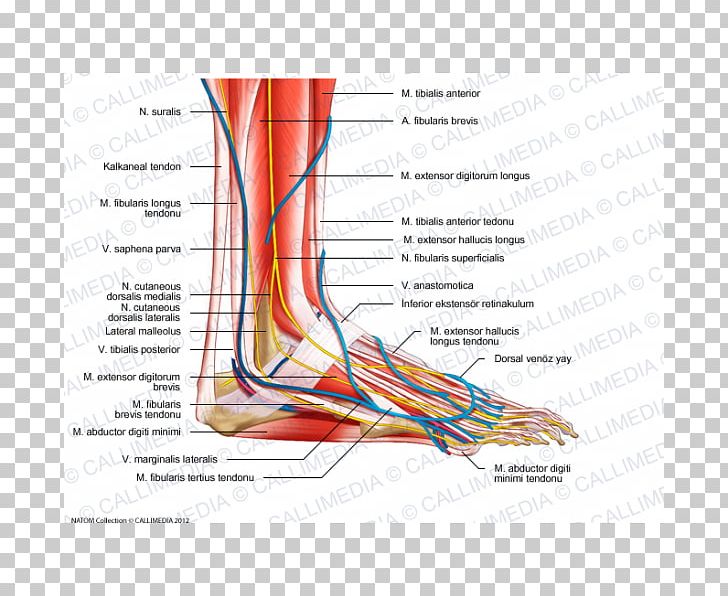
Jul 6, 2020 — Nerves. The main nerve to the foot, the posterior tibial nerve, enters the sole of the foot by running behind the inside bump on the ankle ( ... The anatomy of the nerves of the foot and ankle is complex, and familiarity with the normal anatomy and course of these nerves as well as common anatomic variants is essential for correct identification at imaging. Ultrasonography (US) and magnetic resonance (MR) imaging allow visualization of these nerves and may facilitate diagnosis of ...
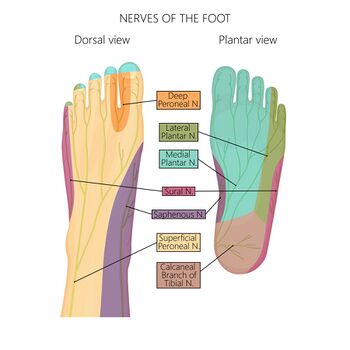
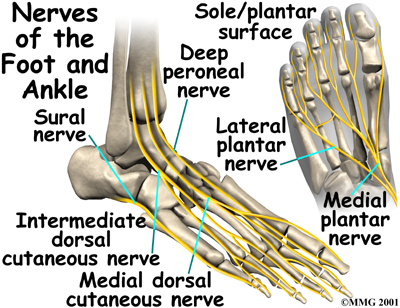
Jan 22, 2022 · Several major nerves serve the human foot. On the top surface of the foot are the dorsal digital nerves and their branches: the deep peroneal nerve, the medial dorsal cutaneous nerve, the intermediate dorsal cutaneous nerve, and the sural nerve. Also on the front surface is the saphenous nerve, which is not included among the dorsal digital nerves because it does not penetrate any of the toes.
Nerves of the foot and ankle diagram
The nerves on the front and outer edge of the ankle control the muscles in this area, and they give sensation to the top and outside edge of the foot. Blood Vessels. The ankle gets blood from nearby arteries that pass by the ankle on their way to the foot. The dorsalis pedis runs in front of the ankle to the top of the foot. (You can feel your ... Problems with nerves in the feet are very common. Many times, an injured nerve will cause intense pain and heat felt within the foot. Nerves act as a network, communicating important information from the foot to the brain. Learn more about the various conditions and problems that can affect the nerves in the foot. Sural Nerve Entrapment 1. Commonly mistaken for Achilles tendinopathy, this entity typically occurs due to trauma. 9 It presents as pain and paresthesias of the lateral ankle, heel and foot. TN. There is a multitude of distinct FAEN of the TN. These have been listed in a proximal to distal fashion.
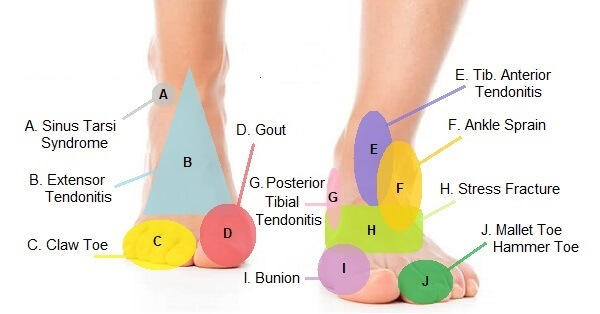
Nerves of the foot and ankle diagram. Dr. Ebraheim's educational animated video describes the nerves of the lower leg in a very easy and simple animation.Lateral cutaneous nerve of the calfSural ... Ankle and foot. The ankle region is innervated by articular branches of the tibial and deep fibular nerves. Regarding the nerves of the foot, we have the following: dorsal digital nerves, proper plantar digital nerves, lateral dorsal cutaneous nerve, and plantar (medial and lateral) nerves. A foot pain diagram is a great tool to help you work out what is causing your ankle and foot pain. There are a whole range of structures e.g. bones, muscles, tendons and nerves which will each give slightly different foot pain symptoms. The foot pain identifier diagrams you find here will help you to identify the possible causes of your foot problem and then help you find out everything you need to know about the causes, symptoms, diagnosis and best treatment options for each. Match the corresponding numbers on the foot diagram below for a list of conditions that may be causing your foot and ankle pain. This is meant for educational purposes only. If you're having a problem with your foot or ankle, visit a podiatrist - a foot and ankle specialist! Top (Dorsal) View of Foot & Ankle Number 1 and 2:
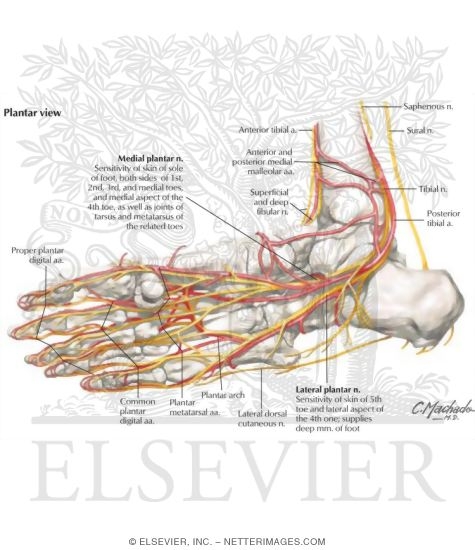
The L5 spinal nerve controls hip, knee, foot, and toe movements. Read more about Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerve Roots. advertisement. The L4 and L5 nerves (along with other sacral nerves) contribute to the formation of the large sciatic nerve that runs down from the rear pelvis into the back of the leg and terminates in the foot. The sural nerve is a purely sensory nerve. Its main function is to provide the sensory supply for the posterolateral aspect of the distal third of the leg, lateral aspect of the foot, heel and ankle. This article will discuss the anatomy and function of the sural nerve. Key facts about the sural nerve. Table quiz. The nerves of the foot assistance move the body and keep balance both while it’s moving and at rest. All these nerves extend as branches of nerves in the leg that travel through the ankle and into the foot. The sural nerve branches from the tibial and common fibular nerves and is responsible for feeling on the outside of the foot and the little toe. The median and lateral plantar nerves are the 2 biggest nerves in the bottom of the foot. The deep fibular nerve is parallel and lateral to the tendon of the extensor hallucis longus muscle and goes inside the dorsal aspect of the foot on the lateral aspect of the dorsalis pedis artery. The nerve produces a lateral branch just distal towards the ankle joint, which stimulates the extensor digitorum brevis from its deep surface. The ...
by A Tang · 2021 · Cited by 1 — The foot receives its nerve supply from the superficial peroneal (fibular) nerve, deep fibular nerve, tibial nerve (and its branches), ... The anterior compartment of the leg acts to dorsiflex and invert the foot through the ankle joint. The extensor hallucis longus and the extensor digitorum longus also extend the toes. The anterior compartment of the leg muscles is innervated by the deep fibular nerve (L4-L5) and supplied blood via the anterior tibial artery. The joints and ligaments of the ankle and foot complex act as stabilizers against these forces and constantly adapt during weight-bearing activities, especially on uneven surfaces. It is estimated that an average 180-lb man absorbs 76.2 tons on each foot while walking 1 mile and that the same man absorbs 121.5 tons per foot while running 1 mile. Jul 03, 2018 · All of these nerves extend as branches of nerves in the leg that pass through the ankle and into the foot. The sural nerve branches from the tibial and common fibular nerves and is responsible for feeling on the outside of the foot and the small toe. The medial and lateral plantar nerves are the two largest nerves in the bottom of the foot.
Nerves of the Foot. There are five main nerves that run past the ankle into the foot (Figure 17). All five of these are derived from two nerves that originate from the lumbar spine. The sciatic nerve branches into four of the five primary nerves of the foot. Two segments of the sciatic nerve branch before the knee joint: the tibial nerve and peroneal nerve.
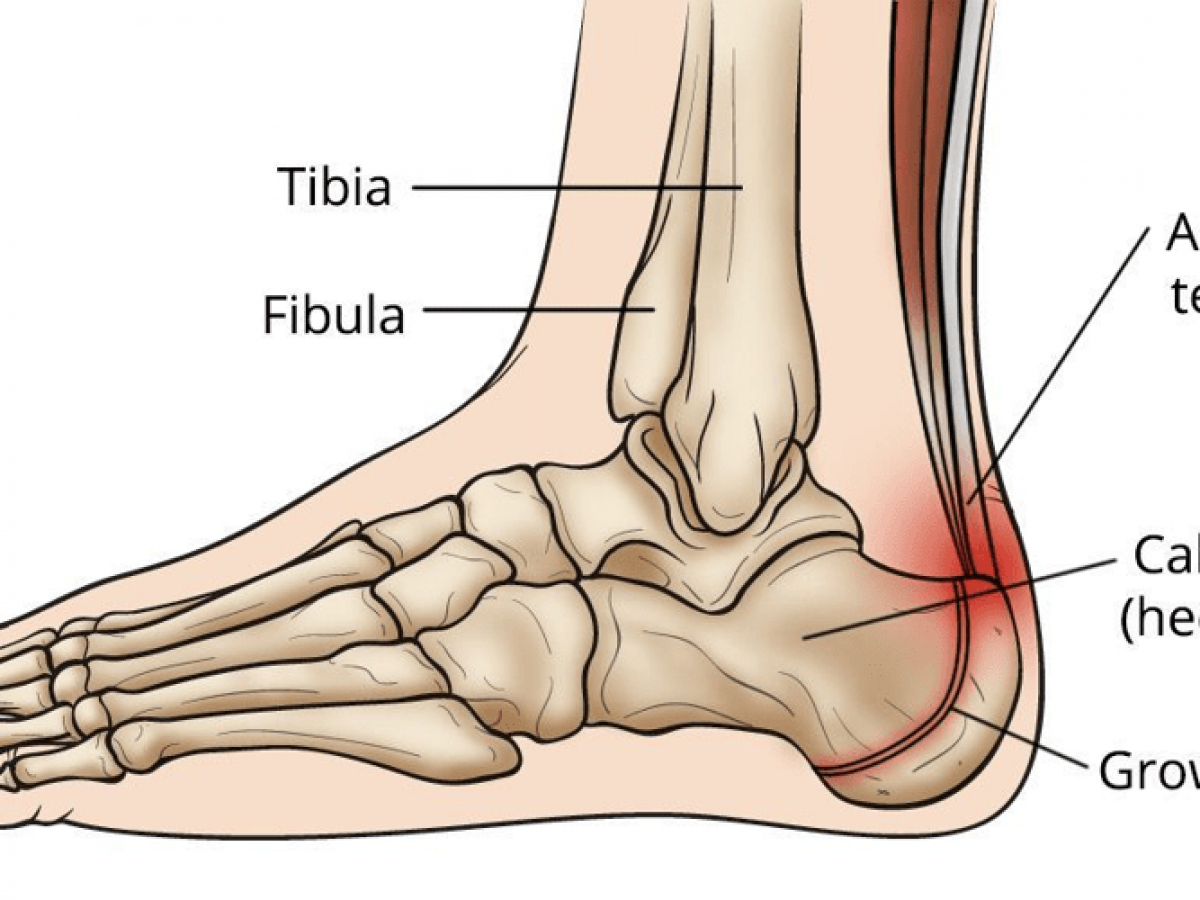
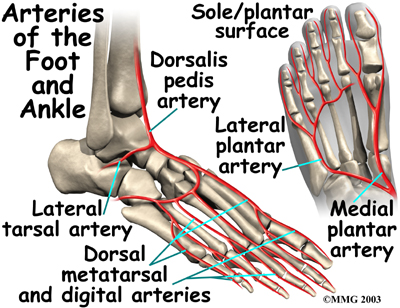
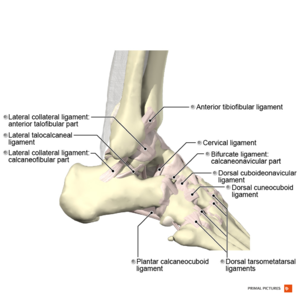
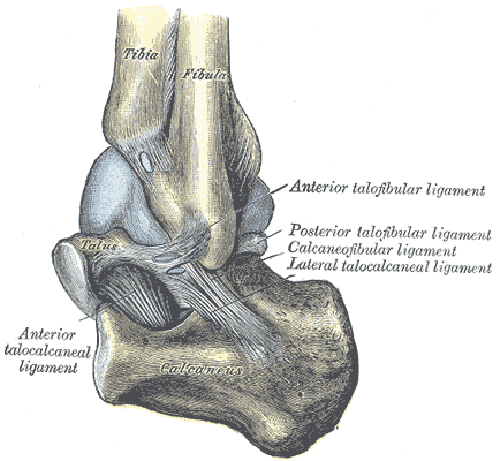
The arteriessupplying the ankle joint are branches of the anterior and posterior tibial arteries as well as the peroneal artery. The nervesof the ankle are derived from the deep and superficial peroneal nerves, the tibial nerves, and the sural and saphenous nerves. The Foot Bones of the foot as seen from the medial (arch) side.
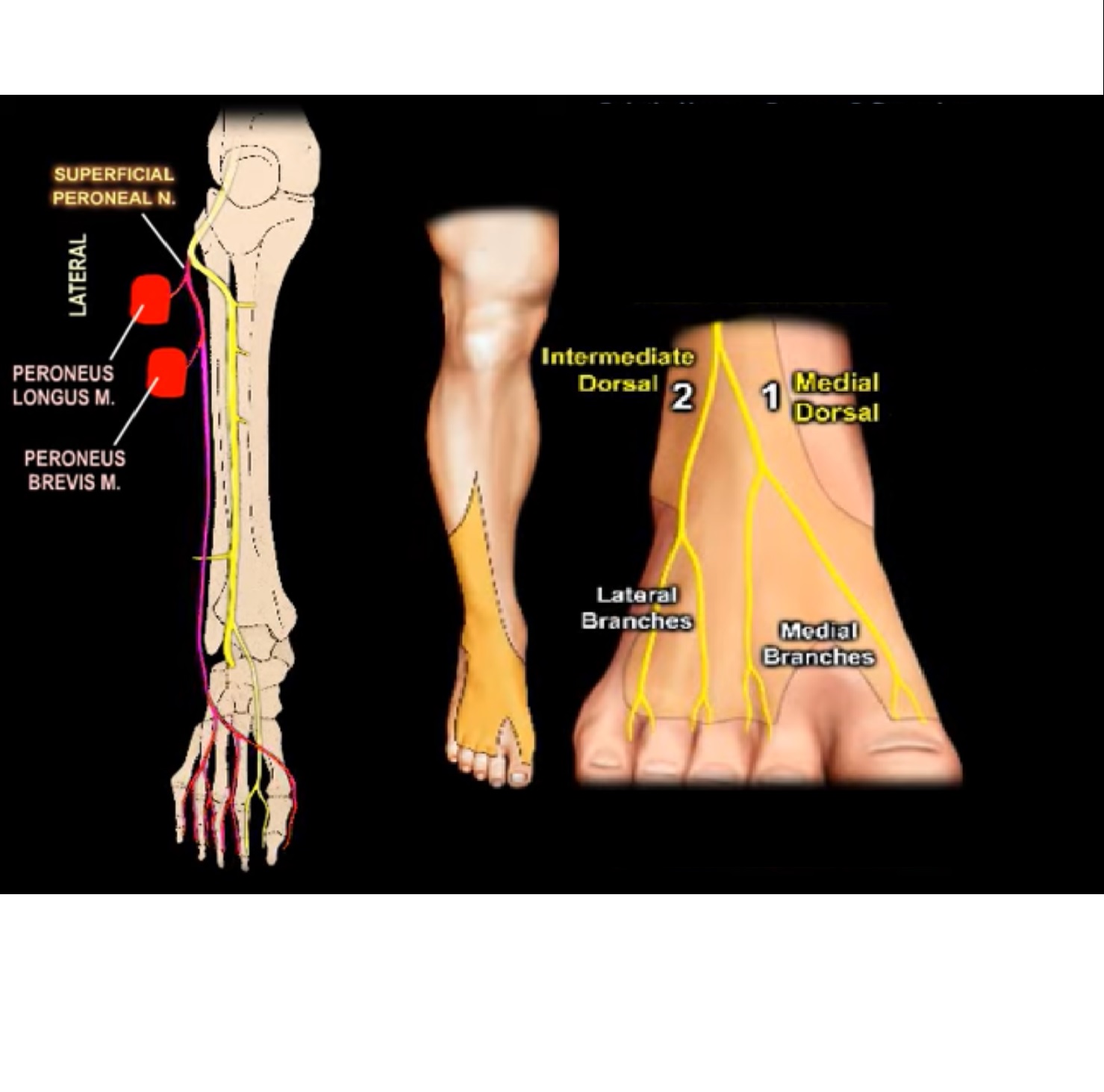
The peroneal tendons run down together behind the outer side of the ankle and then split before attaching to different parts of the foot. Peroneus Longus: Originates from the upper part of the fibula, passes underneath the foot and attaches by the medial foot arch Peroneus Brevis: Originates from the lower part of the fibula and attaches to the outer side of the midfoot
provides blood supply to plantar foot and toes. branches. plantar digital arteries. plantar metatarsal arteries. Arcuate artery. is a vascular arch that runs in the dorsal midfoot deep to the extensor tendons. gives off dorsal metatarsal arteries that run in the 2nd, 3rd and 4th intermetatarsal spaces.
various nerves about the ankle and foot. It is also important to recognize common anatomic vari-ants. In this article, we review the normal anat-TEACHING POINTS During ankle dorsiflexion, excessive traction may occur along the exit point of the superficial peroneal nerve, injuring it and causing secondary neuroma formation at this level. The nerve
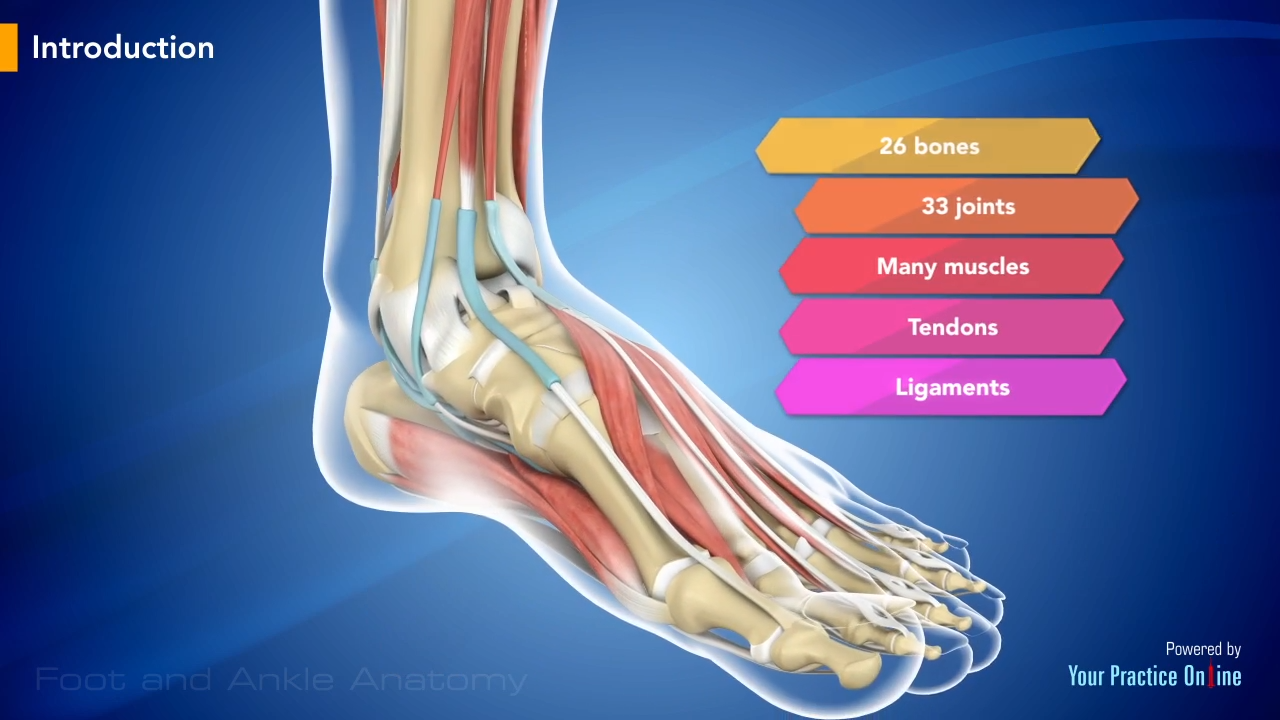
The calcaneus (heel bone) is the largest bone in the foot. Muscles, tendons, and ligaments run along the surfaces of the feet, allowing the complex movements needed for motion and balance.
Jul 11, 2021 · 3%. (70/2732) 3. It is the terminal branch of the superficial peroneal nerve; injury leads to reduced sensation over medial aspect of great toe. 83%. (2260/2732) 4. It is the terminal branch of the deep peroneal nerve; injury leads to first interphylangeal joint flexion weakness. 3%.
There are six nerves associated with the motor and sensory functions of the foot and ankle. They are: Nerve Innervations: Superficial peroneal nerve (L4-S1) Lateral plantar nerve (S2-S3) Medial plantar nerve (L5-S3)
A high arch is the opposite of a flat foot, and somewhat less common. The term pes cavus encompasses a broad spectrum of foot deformities. However, a pain management doctor gave me a diagram of the L5 and S1 nerve, showing they split off. He also said in spinal fusion, this is more often than not the outcome.
Download scientific diagram | Anatomical dissection of the cutaneous nerves of the foot and ankle. 1 Superficial peroneal nerve, 2 Fascial piercing of the superficial peroneal nerve, 3 Superficial ...
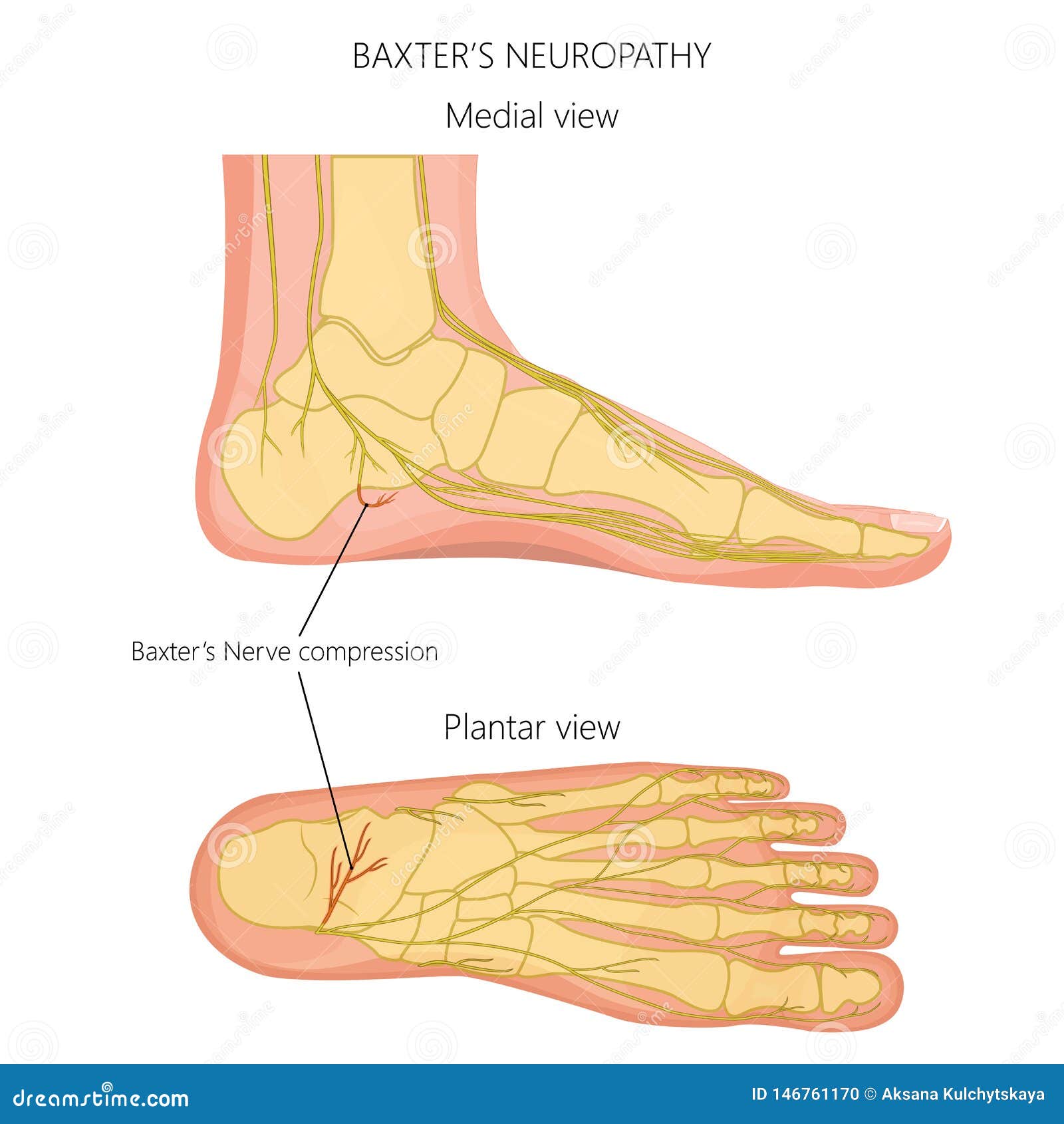
Peripheral nerve entrapments are a relatively rare and heterogeneous group of nerve disorders encompassing a wide variety of etiologies and clinical presentations. These conditions can present significant diagnostic challenges, owing to both the variety of symptoms these patients display, along with …
Description. Required. This colorful anatomical chart illustrates the anatomy of the foot and joints of the foot. The poster also details some common pathologies of the foot and foot joints. The poster is printed on premium glossy (200g) paper. Convenient Poster size 50x67cm (20x26'').
Nerves In Foot Diagram. nerves of the leg and foot along its route through the legs the sciatic nerve splits into the tibial and mon fibular peroneal nerves which in turn split into many smaller nerves in the legs and feet the nerves of the foot help move the body and keep balance both while it’s moving and at rest a plete guide to the nerves in your feet foot vitals tingling feet the ...
Neuritis and Neuromas of the Foot and Ankle. Edited by Eric Malicky MD . Clinical Presentation. Injury or irritation to nerves in the foot and ankle often creates pain and/or numbness. They occur as a result of an injury to a specific nerve. Nerve damage can result from the original injury, casting/wrap, or surgery.
The anatomy of the nerves of the foot and ankle is complex, and familiarity with the normal anatomy and course of these nerves as well as common anatomic variants is essential for correct identification at imaging. Ultrasonography (US) and magnetic resonance (MR) imaging allow visualization of these nerves and may facilitate diagnosis of various compression syndromes, such as "jogger's ...
The femoral nerve contributes one nerve to the ankle: 5) The saphenous nerve (L3-L4) is just anterior to the medial malleolus. Sensory: anteromedial side of the leg, medial side of foot. Technique: see below, blocked with deep peroneal n. and superficial peroneal n. The deep peroneal, superficial, peroneal, and saphenous nerves can be blocked ...
Sural Nerve Entrapment 1. Commonly mistaken for Achilles tendinopathy, this entity typically occurs due to trauma. 9 It presents as pain and paresthesias of the lateral ankle, heel and foot. TN. There is a multitude of distinct FAEN of the TN. These have been listed in a proximal to distal fashion.
Problems with nerves in the feet are very common. Many times, an injured nerve will cause intense pain and heat felt within the foot. Nerves act as a network, communicating important information from the foot to the brain. Learn more about the various conditions and problems that can affect the nerves in the foot.
The nerves on the front and outer edge of the ankle control the muscles in this area, and they give sensation to the top and outside edge of the foot. Blood Vessels. The ankle gets blood from nearby arteries that pass by the ankle on their way to the foot. The dorsalis pedis runs in front of the ankle to the top of the foot. (You can feel your ...























0 Response to "39 nerves of the foot and ankle diagram"
Post a Comment