44 uniform circular motion free body diagram
4.4 Uniform Circular Motion - General Physics Using Calculus I 5.7 Drawing Free-Body Diagrams. 5 Chapter Review. 6 Applications of Newton's Laws. Introduction. 6.1 Solving Problems with Newton's Laws. 6.2 Friction. 6.3 Centripetal Force. ... Uniform circular motion is a specific type of motion in which an object travels in a circle with a constant speed. For example, any point on a propeller spinning ... 5.7 Drawing Free-Body Diagrams - General Physics Using Calculus I (a) Provide a free-body diagram showing all the forces on the runner. ( Hint: Place all forces at the center of his body, and include his weight.) (b) Give a revised diagram showing the xy -component form. The traffic light hangs from the cables as shown. Draw a free-body diagram on a coordinate plane for this situation. Show Solution
Uniform circular motion - Boston University This acceleration involves a speeding up or slowing down of an object as it moves along a circular path, and is equal to zero for uniform circular motion. The a is in a direction tangent to the circle, so its the tangential acceleration. This is very different from the centripetal acceleration, which acts in the radial direction. Free-body diagrams
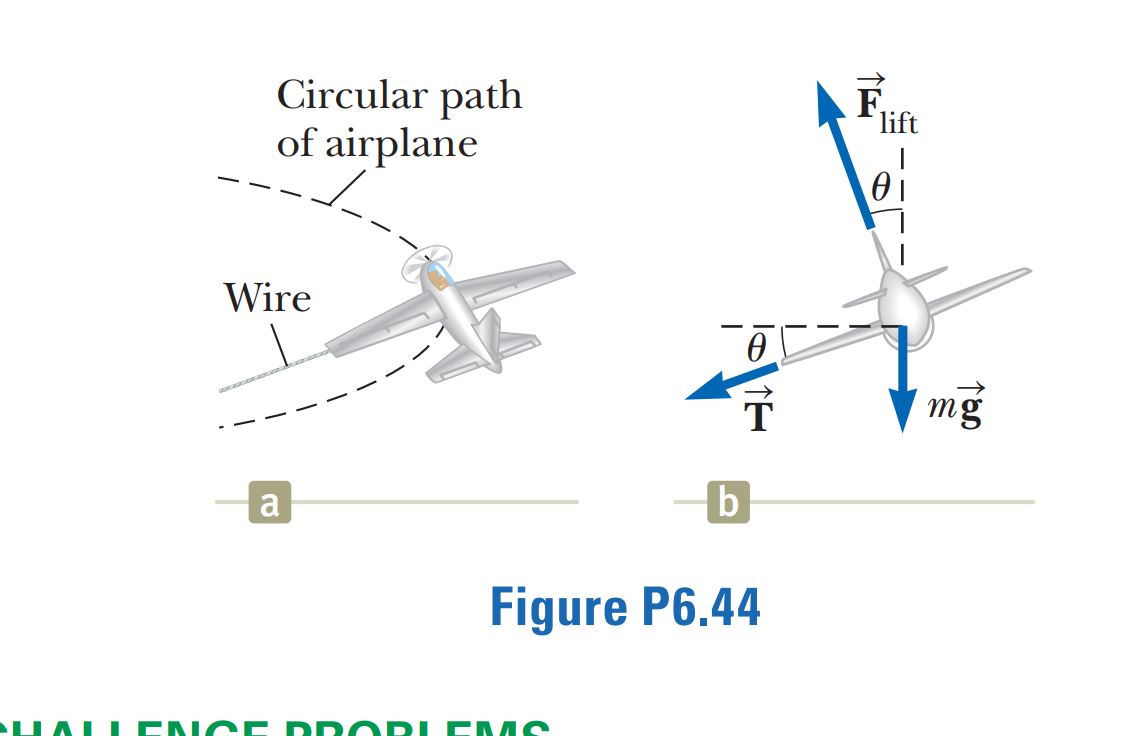
Uniform circular motion free body diagram
Uniform Circular Motion - SMU Uniform Circular Motion Prelab Assignment. Name:_____ 4-digit Code Number:_____ ... Draw a free-body diagram for the mass, labeling and describing all forces indicated. If the mass is 15 cm from the axis of rotation and makes 25 revolutions in 10 seconds, what is its speed in m/s? If m = 0.1 kg and the values in part (b) still hold, what are ... PDF TOPIC 1.5: CIRCULAR MOTION - Province of Manitoba Free-body diagrams are covered in Senior 3 Physics. Notes to the Teacher Students can draw free-body diagrams to illustrate forces acting on a sphere or a coin moving in a uniform circular motion. In each case, they should indicate the force(s) responsible for the centripetal force. The relative length of the vectors corresponding to the forces ... PDF Uniform Circular Motion - Sc Figure 1: The diagram here shows the directions of the velocity and acceleration of an object in ccw uniform circular motion. At all times the velocity is tangent to the circle and the acceleration is directed radially inwards to the axis of rotation.
Uniform circular motion free body diagram. What I need answered (data in image): 1. Make a free - Chegg 1. Make a free body diagram for the bob while it is in uniform circular motion. Discuss the net force, and what if any forces cancel 2. Make a free body diagram for the stationary bob, i.e. when the spring and weight hanger over the pulley are attached. Discuss the net force, and what if any forces cancel. Backround: 1. PDF Lecture 6 Circular Motion - University of Sydney School of Physics uniform circular motion - tangential speed is constant. Is the object accelerating? Velocity is a vector ... the free-body diagram. The centripetal acceleration has to be provided by some other force (tension, friction, normal force) in order for circular motion to occur. 10 Free-Body Diagrams for Objects in Uniform Circular Motion | Fiveable Let's practice with free-body diagrams for uniform circular motion by drawing one for each position of the roller coaster. Remember, in this instance, there is only centripetal acceleration, no tangential acceleration. If there is a centripetal force causing centripetal acceleration, it must point to the center. Uniform Circular Motion (free-body diagram) | Physics Forums Uniform Circular Motion (free-body diagram) Joshuarr May 16, 2012 May 16, 2012 #1 Joshuarr 23 1 Homework Statement Curved portions of highways are always banked (tilted) to prevent cars from sliding off the highway. When a highway is dry, the frictional force between the tires and the road surface may be enough to prevent sliding.
UNIFORM CIRCULAR MOTION - effectuall.github.io UNIFORM CIRCULAR MOTION. Visualize free-body diagram for an object in uniform circular Motion. PAUSE. Uniform circular motion, centripetal acceleration - University of Tennessee Uniform circular motion, F c = mv 2 /r; Reasoning: F c = mv 2 /r. In part (a) the horizontal component of the normal force must provide all the centripetal acceleration and in part (b) the frictional force must provide part of the centripetal acceleration. A free-body diagram of the car on the track is shown below. Details of the calculation: Uniform Circular Motion - Definition, Laws, Formula, Examples, Videos ... So if a particle is moving in a uniform circular motion: 1) Its speed is constant 2) Velocity is changing at every instant 3) There is no tangential acceleration 4) Radial (centripetal) acceleration = ω2r 5) v=ωr Uniform circular motion - Boston University In this case, the free-body diagram has three forces, the force of gravity, the normal force, and a frictional force. The friction here is static friction, because even though the objects are moving, they are not moving relative to the turntable. If there is no relative motion, you have static friction.
Uniform circular motion | CourseNotes 9-29-99. Sections 5.1 - 5.2. Uniform circular motion. When an object is experiencing uniform circular motion, it is traveling in a circular path at a constant speed. If r is the radius of the path, and we define the period, T, as the time it takes to make a complete circle, then the speed is given by the circumference over the period. 6.3: Uniform circular motion - Physics LibreTexts Note that this free-body diagram is only "valid" at a particular instant in time since the acceleration vector continuously changes direction and would not always be lined up with the x axis. Figure 6.3. 2 undergoing uniform circular motion. Writing out the x and y components of Newton's Second Law: ∑ F x = T = m a R ∑ F y = N − F g = 0 Identifying Free-Body Diagrams for Objects in Uniform Circular Motion ... Identifying Free-Body Diagrams for Objects in Uniform Circular Motion AP Physics 1 Skills Practice 1. A jogger is running at a steady pace on the boundary of a flat, circular track. Draw a... Uniform circular motion in vertical plane: Free body diagram confusion The free body diagram at point B shows tension in the rod acting towards the centre of the circle and a weight force (mg) acting downwards. With just these 2 forces, the net force wouldn't be acting towards the centre of the circle, so there has to be some missing force on the free body diagram (that can counteract the weight force of the object).
Uniform Circular Motion Free Body Diagrams | Physics Forums Introductory Physics Homework Help Uniform Circular Motion Free Body Diagrams archelon Feb 8, 2012 Feb 8, 2012 #1 archelon 1 0 Homework Statement A circular-motion addict of mass 82.0 kg rides a Ferris wheel around in a vertical circle of radius 14.0 m at a constant speed of 7.10 m/s. (a) What is the period of the motion?
Identifying Free-Body Diagrams for Objects in Uniform Circular Motion ... The free-body diagram above is of an object orbiting the earth in a uniform circular motion. The force of gravity arrow points towards the center of the orbit. One thing to notice is that the...
Uniform Circular Motion Free Body Diagrams - YouTube About Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy & Safety How YouTube works Test new features Press Copyright Contact us Creators ...
Drawing Free-body Diagrams: Rules | Physics | JoVE 5.11: Drawing Free-body Diagrams: Rules. The first step in describing and analyzing most phenomena in physics involves the careful drawing of a free-body diagram. Free-body diagrams are useful in analyzing forces acting on an object or system, and are employed extensively in the study and application of Newton's laws of motion.
Forces and Free-Body Diagrams for Circular Motion - Teacher Notes The Forces and Free-Body Diagrams in Circular Motion Concept Builder is an adjustable-size file that displays nicely on smart phones, on tablets such as the iPad, on Chromebooks, and on laptops and desktops. The size of the Concept Builder can be scaled to fit the device that it is displayed on.
Uniform Circular Motion - APlusPhysics The motion of an object in a circular path at constant speed is known as uniform circular motion (UCM). An object in UCM is constantly changing direction, and since velocity is a vector and has direction, you could say that an object undergoing UCM has a constantly changing velocity, even if its speed remains constant. ... Our free body diagram ...
Free-body diagrams for uniform circular motion - Khan Academy Check your understanding of free-body diagrams for uniform circular motion in this set of free practice questions aligned to AP Physics I standards.
Solved For a uniform circular motion lab, how would | Chegg.com For a uniform circular motion lab, how would you: Draw a free body diagram showing all the forces acting on the bob when the spring and weight hanger are attached and the bob is not in motion. Question: For a uniform circular motion lab, how would you: Draw a free body diagram showing all the forces acting on the bob when the spring and weight ...
Forces and Free-Body Diagrams for Circular Motion - Physics Classroom Forces and Free-Body Diagrams in Circular Motion The Forces in Circles Concept Builder provides learners with the challenge of identifying the free-body diagrams for situations involving the motion of objects in circles. Learners are presented with a short verbal description of an object's motion.
Circular motion, free-body diagram - Physics Stack Exchange A child flies a toy sphere attached at the end of a light elastic string. The string is level with the horizontal... The actual question is easy to solve using uniform circular motion equations (and has nothing to do with my question). In the free-body diagram below, what is the balancing force in the question mark? centripetal-force Share
Circular Motion and Free-Body Diagrams - StudySmarter US A free-body diagram is a diagram that shows all of the vector forces acting on an object. Free-body diagrams for objects in circular motion have a centripetal force that keeps the object moving in a circle. We can identify which forces contribute to the centripetal force to find the centripetal acceleration.
PDF Uniform Circular Motion - Sc Figure 1: The diagram here shows the directions of the velocity and acceleration of an object in ccw uniform circular motion. At all times the velocity is tangent to the circle and the acceleration is directed radially inwards to the axis of rotation.
PDF TOPIC 1.5: CIRCULAR MOTION - Province of Manitoba Free-body diagrams are covered in Senior 3 Physics. Notes to the Teacher Students can draw free-body diagrams to illustrate forces acting on a sphere or a coin moving in a uniform circular motion. In each case, they should indicate the force(s) responsible for the centripetal force. The relative length of the vectors corresponding to the forces ...
Uniform Circular Motion - SMU Uniform Circular Motion Prelab Assignment. Name:_____ 4-digit Code Number:_____ ... Draw a free-body diagram for the mass, labeling and describing all forces indicated. If the mass is 15 cm from the axis of rotation and makes 25 revolutions in 10 seconds, what is its speed in m/s? If m = 0.1 kg and the values in part (b) still hold, what are ...

0 Response to "44 uniform circular motion free body diagram"
Post a Comment